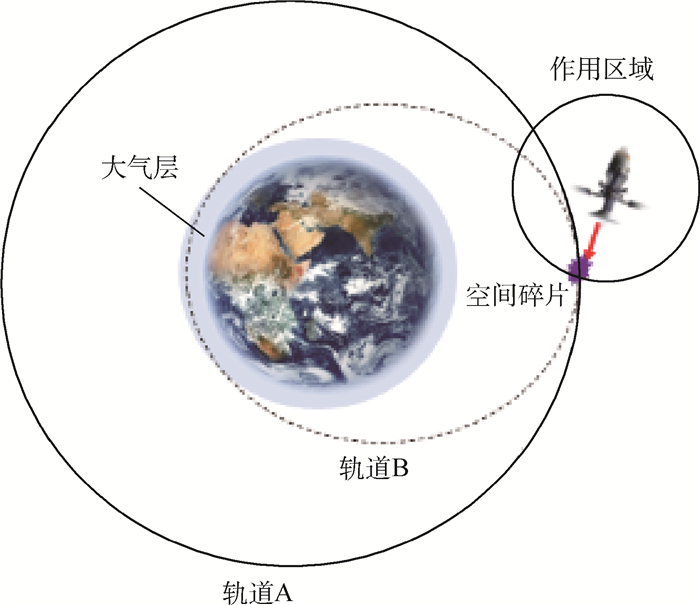
-
摘要:
针对日益增长的空间碎片污染太空环境问题,建立了天基激光能量清除空间碎片的降轨模型。重点讨论了速度增量与空间碎片速度的夹角对近地点高度降低的影响,并考虑到天基平台与空间碎片作用距离的影响,从能量利用率的角度出发,提出了能量分配系数(CEA)的概念。基于CEA,设计出关于脉冲激光能量分配的策略,并与脉冲激光能量平均方式清除空间碎片的方式进行对比分析,说明了脉冲激光能量分配策略的有效性,提高了天基激光能量利用能力,达到了高效清除空间碎片的目的。
Abstract:In view of the growing space debris pollution of space environment, the deorbit model of space-based laser removal of space debris is established. In this model, the effect of the angle between the speed increment and the space debris velocity on the height reduction of perigee is emphatically analyzed, and taking into account the influence of the distance between them, the concept of coefficient of energy assignment (CEA) is proposed from the perspective of energy utilization. According to the CEA, a pulsed laser energy assignment strategy is designed, and it can improve the energy utilization ability to remove space debris more efficiently compared with the way of average energy laser pulse cleaning space debris, illustrating the effectiveness of our removal strategy.
-
Key words:
- space-based laser /
- space debris /
- deorbit model /
- multi-pulse /
- removal scheme
-
表 1 不同位置下的最佳冲量作用角和近地点最终高度
Table 1. Optimal impulse angle and final perigee height at different positions
偏近点角/(°) 最佳冲量作用角/(°) 近地点最终高度/km 0 117.1或242.1 899.6 90 165.3 894.5 180 180.0 892.1 270 194.7 894.507 3 表 2 天基激光和空间碎片的轨道参数
Table 2. Orbital parameters of space-based laser and space debris
轨道参数 天基激光 空间碎片 近地点高度/km 900 800 远地点高度/km 900 810 轨道倾角/(°) 30 30 近地点辐角/(°) 0 0 升交点赤经/(°) 80 80 表 3 基于CEA的脉冲激光能量分配
Table 3. Pulse laser energy assignment based on CEA
CEA值 脉冲激光能量 lmax处速度增量/(m·s-1) 0.9~1.0 2Esingle 0.4 0.5~0.9 Esingle 0.2 0~0.5 0.5Esingle 0.1 -
[1] 李春来, 欧阳自远, 都亨.空间碎片与空间环境[J].第四纪研究, 2002, 22(6):540-551. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2002.06.008LI C L, OUYANG Z Y, DU H.Space debris and space environment[J].Quaternary Sciences, 2002, 22(6):540-551(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-7410.2002.06.008 [2] 徐浩东, 李小将, 李怡勇, 等.地基激光空间碎片清除技术研究[J].装备学院学报, 2011, 22(3):71-75. doi: 10.3783/j.issn.1673-0127.2011.03.016XU H D, LI X J, LI Y Y, et al.Research on technology of space debris removal using ground-based laser[J].Journal of the Academy of Equipment Command & Technology, 2011, 22(3):71-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.3783/j.issn.1673-0127.2011.03.016 [3] BORJA J A, TUN D.Deorbit process using solar radiation force[J].Journal of Spacecraft & Rockets, 2015, 43(3):685-687. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ029966746/ [4] ASLANOV V, YUDINTSEV V.Dynamics of large space debris removal using tethered space tug[J].Acta Astronautica, 2013, 91(10):149-156. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=0180e9b0acf15cee2da4c983700338bc [5] IKI K, KAWAMOTO S, MORINO Y.Experiments and numerical simulations of an electrodynamic tether deployment from a spool-type reel using thrusters[J].Acta Astronautica, 2014, 94(1):318-327. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2013.03.024 [6] FORWARD R L, HOYT R P, UPHOFF C W.Terminator tether (TM):A spacecraft deorbit device[J].Journal of Spacecraft & Rockets, 2000, 37(2):187-196. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ028885242/ [7] NISHIDA S I, KAWAMOTO S, OKAWA Y, et al.Space debris removal system using a small satellite[J].Acta Astronautica, 2009, 65(1):95-102. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0094576509000320 [8] 陈小前.航天器在轨服务技术[M].北京:中国宇航出版社, 2009:200-212.CHEN X Q.Spacecraft on-orbit service technology[M].Beijing:China Astronautic Publishing House, 2009:200-212(in Chinese). [9] 王成林, 张艳, 王鲲鹏.地基激光清除空间碎片的策略[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 41(11):2137-2143. http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13576.shtmlWANG C L, ZHANG Y, WANG K P.Strategy of removing space debris using ground-based lasers[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(11):2137-2143(in Chinese). http://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract13576.shtml [10] 张玉军, 冯书兴.主动式空间碎片清理研究[J].装备学院学报, 2010, 21(6):78-82. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhjsxy201006018ZHANG Y J, FENG S X.Research on active space debris removal[J].Journal of the Academy of Equipment Command & Technology, 2010, 21(6):78-82(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhjsxy201006018 [11] MONROE A D K.Space debris removal using high-power ground-based laser[C]//International Society for Optics and Photonics.Bellingham: SPIE, 1994: 30264. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/234486278_Space_debris_removal_using_high-power_ground-based_laser [12] CHO M.Removal of orbital debris from low earth orbit by laser-generated drag[J].Journal of Spacecraft & Rockets, 1994, 31(5):920-922. doi: 10.2514/3.26537 [13] PHIPPS C R, ALBRECHT G, FRIEDMAN H, et al.ORION:Clearing near-earth space debris using a 20-kW, 530-nm, earth-based, repetitively pulsed laser[J].Laser & Particle Beams, 1996, 14(1):1-44. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zhlxbx201402024 [14] SCHALL W O.Removal of small space debris with orbiting lasers[C]//High-Power Laser Ablation.International Society for Optics and Photonics.Bellingham: SPIE, 1998: 564-574. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/224802161_Removal_of_Small_Space_Debris_with_Orbiting_Lasers [15] BOHN W L.Pulsed COIL for space debris removal[J].Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 1999, 3612(6):79-84. http://www.wanfangdata.com.cn/details/detail.do?_type=perio&id=CC025692951 [16] CAMPBELL J W.Project ORION: Orbital debris removal using ground-based sensors and lasers: NASA-TM-108522[R].Hampton, VA: NASA Technical Memorandum, 1996. [17] 康博琨, 金星, 常浩.空间碎片天基激光辐照下的轨道特性仿真分析[J].红外与激光工程, 2017, 46(3):36-45. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201703006KANG B K, X JIN X, CHANG H.Simulation analysis of orbit characteristics of space debris irradiated by space-based laser system[J].Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(3):36-45(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201703006 [18] 张阔, 陆君, 杨贵龙, 等.大功率TEA CO2激光远场发散角评估方法[J].红外与激光工程, 2015, 44(8):2286-2291. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.08.009ZHANG K, LU J, YANG G L, et al.Estimation of far-field divergence of high power TEA CO2 laser[J].Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2015, 44(8):2286-2291(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2276.2015.08.009 [19] 王成林, 张艳, 王鲲鹏.冲量耦合系数对激光辐照空间碎片冲量矢量的影响[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2016, 53(12):165-173. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGDJ201612023.htmWANG C L, ZHANG Y, WANG K P.Effect of impulse coupling coefficient on impulse vector of laser irradiating space debris[J].Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2016, 53(12):165-173(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-JGDJ201612023.htm [20] WANG C, ZHANG Y, WANG K.Impulse calculation and characteristic analysis of space debris by pulsed laser ablation[J].Advances in Space Research, 2016, 58(9):1854-1863. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2016.07.018 [21] 温泉, 杨丽薇, 赵尚弘, 等.天基激光清除小尺度空间碎片变轨模型研究[J].红外与激光工程, 2017, 46(3):28-35. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201703005WEN Q, YANG L W, ZHAO S H, et al.Research on de-orbiting model of small scale space debris removal using space-based laser[J].Infrared and Laser Engineering, 2017, 46(3):28-35(in Chinese). http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/hwyjggc201703005 [22] PHIPPS C, BIRKAN M, BOHN W, et al.Review:Laser-ablation propulsion[J].Journal of Propulsion & Power, 2010, 26(4):609-637. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/zgyxllx201711029 [23] 杨武霖, 牟永强, 曹燕, 等.天基激光清除空间碎片方案与可行性研究[J].航天器环境工程, 2015, 32(4):361-365. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2015.04.004YANG W L, MOU Y Q, CAO Y, et al.Active removal of space debris by space-based laser system and its feasibility analysis[J].Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2015, 32(4):361-365(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2015.04.004 -







 下载:
下载: