-
摘要:
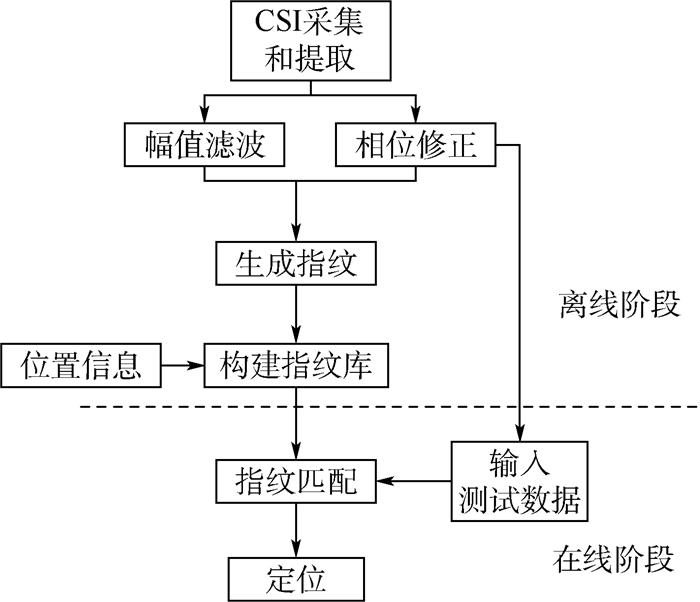
考虑到室内环境的复杂性和多径效应对WiFi指纹定位性能的影响从Intel 5300无线网卡中提取信道状态信息(CSI),利用修正后的CSI幅值和相位信息作为指纹特征,使用极限梯度提升(XGBoost)算法构建高精度指纹库,实现分米级的高精度室内定位。进一步通过实测数据分析了采样间隔、室内视距(LOS)和非视距(NLOS)环境、缺失值和数据维度等因素对所提算法定位性能的影响。实际室内环境下的实验结果表明,本文算法受NLOS影响较小,对室内复杂环境有很强的鲁棒性;此外,该算法能够很好地处理高维稀疏数据,解决CSI指纹特征的"误匹配"问题,且对缺失数据不敏感,定位准确度优于90%。
-
关键词:
- 室内定位 /
- 信道状态信息(CSI) /
- 指纹匹配 /
- 极限梯度提升(XGBoost) /
- 相位延拓
Abstract:Considering the influence of complex indoor environment and multi-path effects on the WiFi fingerprint positioning performance, this paper extracts channel state information (CSI) from the Intel 5300 wireless network card and utilizes the modified CSI amplitude and phase information as fingerprint features. A high-precision fingerprint database was built using the extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) algorithm to achieve indoor positioning at a decimeter level. Experiments in the actual indoor environment have been conducted to evaluate the effects of sampling interval, line of sight (LOS) and non line of sight (NLOS), missing values, and data dimensions on the localization performance of the proposed method. The results of real indoor experiment show that the proposed CSI-XGBoost method is less affected by NLOS and robust to complex indoor environments. In addition, this method can handle high-dimensional sparse data well and solve the mismatching problem of CSI fingerprinting. Moreover, this method is insensitive to missing data, with localization accuracy of better than 90%.
-
表 1 不同采样间隔的定位性能比较
Table 1. Comparison of positioning performance at different sampling intervals
定位性能 采样间隔/m 1.2 0.8 0.4 定位准确度/% 97.7 97.5 97.4 平均定位误差/m 0.054 0.060 0.066 训练时间/s 1.69 14.29 322.99 表 2 NLOS和LOS环境下的定位性能比较
Table 2. Comparison of positioning performance in NLOS and LOS environments
算法 定位性能 NLOS LOS CSI-XGBoost 定位准确度/% 99.01 98.84 平均定位误差/m 0.029 0.038 CSI-SVM 定位准确度/% 98.97 98.27 平均定位误差/m 0.030 0.054 CSI-KNN 平均定位误差/m 3.392 3.191 CSI-MKNN 平均定位误差/m 0.652 1.248 表 3 缺失值对不同算法定位性能的影响
Table 3. Effect of missing values on positioning performance of different algorithms
算法 定位性能 无缺失值 有缺失值 CSI-XGBoost 定位准确度/% 98.8 95.9 平均定位误差/m 0.038 0.147 CSI-SVM 定位准确度/% 98.3 93.7 平均定位误差/m 0.054 0.225 CSI-KNN 平均定位误差/m 1.004 4.875 CSI-MKNN 平均定位误差/m 0.658 5.273 表 4 数据维度对不同算法定位性能的影响
Table 4. Effect of data dimensions on positioning performance of different algorithms
算法 平均定位误差/m RSSI-KNN 1.331 RSSI-MKNN 0.249 CSI-KNN 1.773 CSI-MKNN 0.746 CSI-PCA-KNN 1.772 CSI-PCA-MKNN 0.150 CSI-SVM 0.038 CSI-XGBoost 0.054 -
[1] BAHL P, PADMANABHAN V N. RADAR: An in-building RF-based user location and tracking system[C]//Proceedings of IEEE INFOCOM.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2000: 775-784. [2] YOUSSEF M, AGRAWALA A.The Horus WLAN location determination system[C]//International Conference on Mobile Systems.New York: ACM, 2005: 205-218. [3] HALPERIN D, HU W J, SHETH A, et al.802.11 with multiple antenna for dummies[J].ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2010, 40(1):19-25. doi: 10.1145/1672308 [4] HALPERIN D, HU W J, SHETH A, et al.Predictable 802.11 packet delivery from wireless channel measurements[J] ACM SIGCOMM Computer Communication Review, 2010, 40(10):159-170. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/NSTLQK/NSTL_QKJJ0220057194/ [5] YANG Z, ZHOU Z M, LIU Y H.From RSSI to CSI:Indoor localization via channel response[J].ACM Computing Surveys, 2013, 46(2):1-32. http://dl.acm.org/citation.cfm?id=2543592 [6] WANG X Y, GAO L J, MAO S W, et al.DeepFi: Deep learning for indoor fingerprinting using channel state information[C]//2015 IEEE Wireless Communications & Networking Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 1666-1671. [7] WANG X Y, GAO L J, MAO S W.PhaseFi: Phase fingerprinting for indoor[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Global Communication Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-6. [8] WU K S, XIAO J, YI Y W, et al.CSI-based indoor localization[J].IEEE Transactions on Parallel and Distributed System, 2013, 24(7):1300-1309. doi: 10.1109/TPDS.2012.214 [9] XIAO J, WU K S, YI Y W, et al.FIFS: Fine-grained indoor fingerprinting system[C]//Proceedings of IEEE ICCCN.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 1-7. [10] CHAPRE Y, IGNJATOVIC A, SENEVIRATNE A, et al.CSI-MIMO:An effcient WiFi fingerprinting using channel state information with MIMO[J].Pervasive Mobile Computing, 2015, 23:89-103. doi: 10.1016/j.pmcj.2015.07.002 [11] CHEN T Q, GUESTRIN C.XGBoost: A scale tree boosting system[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.New York: ACM, 2016: 13-17. [12] LAN/MAN Standards Committee.IEEE Standard for Information technology-Telecommunications and information exchange between systems-Local and metropolitan area networks-Specific requirements: Part 11.Wireless LAN medium access control (MAC) and physical layer (PHY) specifications: IEEE 802.11n[S].Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2009: 312-335. [13] SEN S, RADUNOVIC B, CHOUDHURY R R, et al.You are facing the Mona Lisa: Spot localization using PHY layer information[C]//Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Mobile Systems, Applications, and Services.New York: ACM, 2012: 183-196. [14] WANG X Y, GAO L J, MAO S W.CSI phase fingerprinting for indoor localization with a deep learning approach[J].IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2016, 3(6):1113-1123. doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2016.2558659 [15] 杨萌, 修春娣, 杨东凯.基于感知概率的室内定位系统[J].全球定位系统, 2013, 38(6):238-241. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHWZ201404011.htmYANG M, XIU C D, YANG D K.Indoor positioning system using perceptual probability[J].Global Positioning System, 2013, 38(6):238-241(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-CHWZ201404011.htm -







 下载:
下载: