A robust coordinated control method for hovering of electromagnetic spacecraft formation
-
摘要:
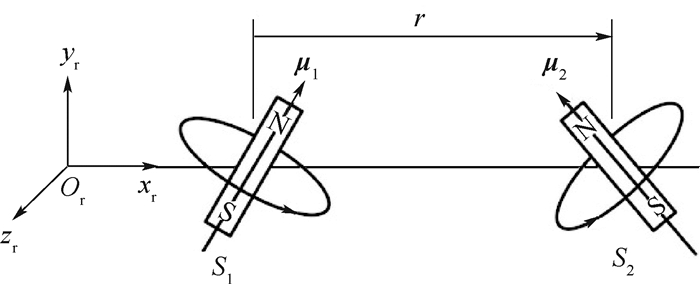
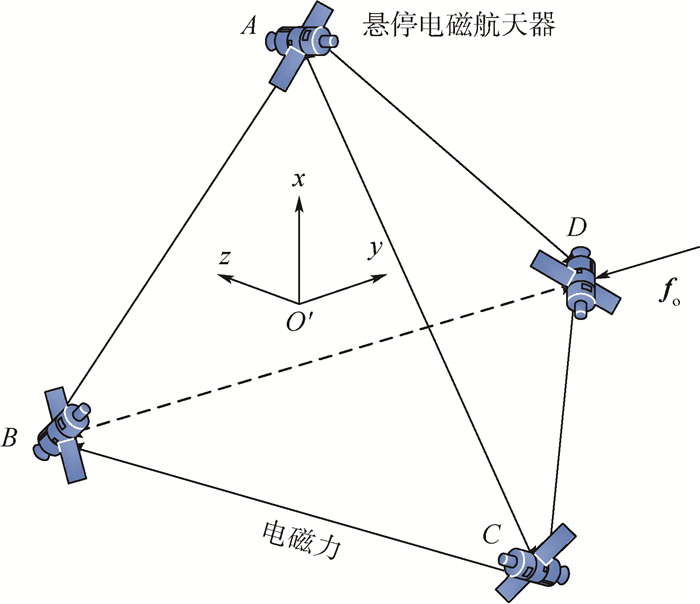
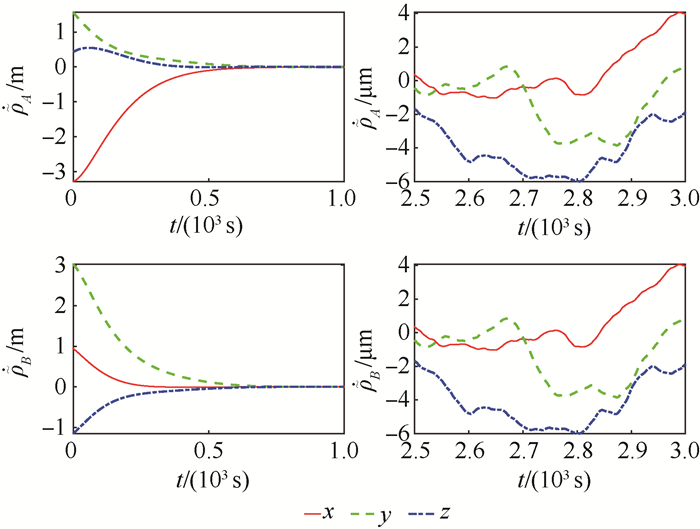
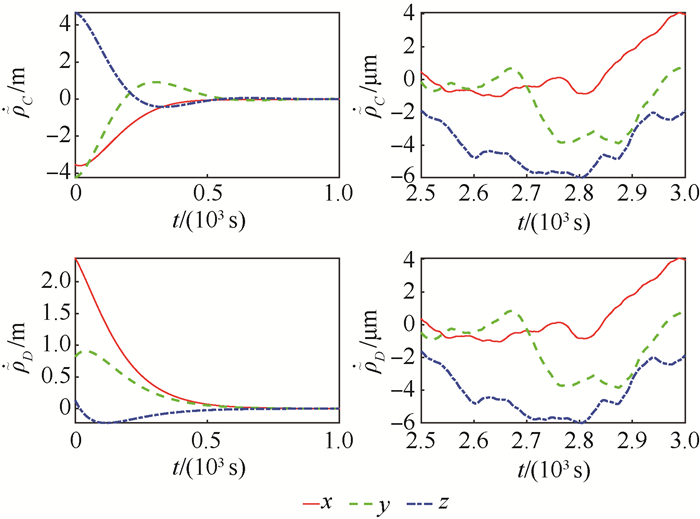
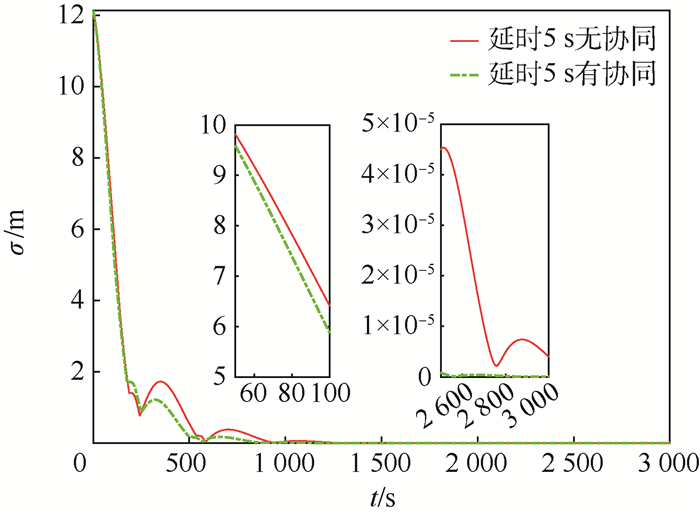
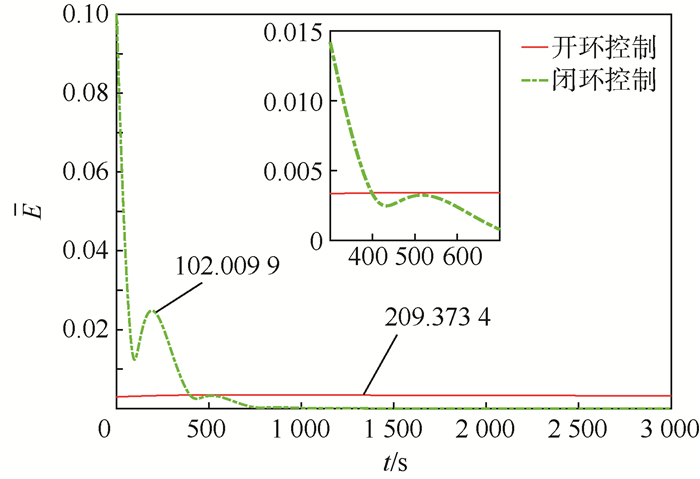
针对电磁航天器编队近地轨道悬停问题,提出一种在缺少参考轨道准确信息时的协同控制方法。用TH方程描述航天器间的相对运动,选择与参考轨道同周期的圆轨道为标称轨道。将参考轨道相对于标称圆轨道的偏差、地球非球形引力、大气阻力及其他天体引力等参数单独归类,视其为不确定量,构成不确定系统。通过引入一致性理论,在电磁作用模型和动力学方程均存在不确定性的条件下,针对航天器编队悬停的目标设计了鲁棒协同控制律。考虑能量消耗最优和均衡以及轨道姿态解耦,给出了通过优化进行磁矩配置的方案。仿真结果表明,所设计的鲁棒协同控制律能够实现编队电磁航天器高精度悬停,所给出的磁矩配置方案能够实现磁矩的合理分配。
Abstract:Aimed at the problem of near-Earth orbit hovering of electromagnetic spacecraft formation, a coordinated control method is proposed in the absence of accurate information of reference orbit. The relative motion between spacecraft is described by the TH equation, and the circular orbit of the same cycle as the reference orbit is selected as the nominal orbit. The deviation of the reference orbit from the nominal circular orbit, the Earth's non-spherical gravity, the atmospheric resistance and the other celestial gravitation are classified separately, and they are considered as uncertain and constitute an uncertain system. By introducing the consistency theory, the robust coordinated control law is designed for the target of spacecraft formation hovering under the condition that the electromagnetic action model and the dynamic equation are all uncertain. Considering the optimal and balanced energy consumption and the decoupling of orbital attitude, a scheme of magnetic moment distribution through optimization is given. The simulation results show that the designed robust coordinated control law can achieve high-precision hovering of electromagnetic spacecraft formation. The proposed magnetic moment configuration scheme can realize the rational distribution of magnetic moments.
-
Key words:
- electromagnetic spacecraft /
- formation flying /
- consistency protocol /
- robust control /
- hovering
-
表 1 参考轨道参数
Table 1. Reference orbital parameters
轨道参数 数值 a/km 7 371 e 0.01 i/(°) 45 Ω/(°) 45 ω/(°) 30 θ/(°) 0 表 2 状态初值信息
Table 2. Initial value information of state
参数 期望值X 初始摄动值δx 位置/m 
5×rand(-1, 1), rand(-1, 1)表示(-1, 1)区间的随机数 速度/
(m·s-1)[0 0 0] 0.01×rand(-1, 1) -
[1] 林来兴, 黎康.卫星对空间目标悬停的轨道动力学与控制方法研究[J].中国空间科学技术, 2008, 28(1):9-12. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-758X.2008.01.002LIN L X, LI K.Orbit dynamics and control of satellites hovering over space target[J].Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2008, 28(1):9-12(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-758X.2008.01.002 [2] 朱亚文, 闫野.椭圆轨道卫星空间任意位置悬停的方法[J].中国空间科学技术, 2010, 30(6):17-23.ZHU Y W, YAN Y.Hovering method at any selected position over space target on elliptical orbit[J].Chinese Space Science and Technology, 2010, 30(6):17-23(in Chinese). [3] 林来兴, 张小琳.纳型卫星编队飞行技术现状及发展趋势[J].航天器工程, 2017, 26(5):65-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2017.05.011LIN L X, ZHANG X L.Current status and developing trends of nanosatellites formation flying[J].Spacecraft Engineering, 2017, 26(5):65-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8748.2017.05.011 [4] 张皓, 师鹏, 李保军, 等.利用库仑力实现悬停轨道的新方法研究[J].宇航学报, 2012, 33(1):68-75. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2012.01.010ZHANG H, SHI P, LI B J, et al.Hover orbit using inter-spacecraft coulomb forces[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2012, 33(1):68-75(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2012.01.010 [5] 李俊峰, 龚胜平.非开普勒轨道动力学与控制[J].宇航学报, 2009, 30(1):47-53. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2009.00.009LI J F, GONG S P.Dynamics and control of the non-Keplerian orbits[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2009, 30(1):47-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2009.00.009 [6] HUANG J, LI C, MA G, et al.Coulomb control of a triangular three-body satellite formation using nonlinear model predictive method[C]//Proceedings of the 33rd Chinese Control Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 7685-7690. [7] POLLOCK G E, GANGESTAD J W, LONGUSKI J M.Inclination change in low-earth orbit via the geomagnetic Lorentz force[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2010, 33(5):1387-1395. doi: 10.2514/1.48610 [8] KWON D W.Propellantless formation flight applications using electromagnetic satellite formations[J].Acta Astronautica, 2010, 67(9-10):1189-1201. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2010.06.042 [9] KONG E M C, KWON D W, SCHWEIGHART S A, et al.Electromagnetic formation flight for multi-satellite arrays[J].Journal of Spacecraft & Rockets, 2004, 41(4):659-666. [10] 魏伟, 左敏, 苏婷立, 等.航天器对接的全局渐近稳定控制[J].清华大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 56(1):106-110. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXB201601016.htmWEI W, ZUO M, SU T L, et al.Global asymptotically stable control for spacecraft docking[J] Journal of Tsinghua University(Science and Technology), 2016, 56(1):106-110(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-QHXB201601016.htm [11] ELIAS L M, KWON D W, SEDWICK R J, et al.Electromagnetic formation flight dynamics including reaction wheel gyroscopic stiffening effects[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and & Dynamics, 2007, 30(2):499-511. [12] 黄涣, 杨乐平, 朱彦伟, 等.双星电磁编队的动力学平衡态稳定性与控制[J].国防科技大学学报, 2013, 35(3):12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.03.003HUANG H, YANG L P, ZHU Y W, et al.Stability and control of dynamics equilibrium for two-spacecraft electromagnetic formation[J].Journal of National University of Defense Technology, 2013, 35(3):12-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2486.2013.03.003 [13] 徐增文, 师鹏, 赵育善.双电磁航天器编队构型保持自适应控制[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 41(12):2302-2308.XU Z W, SHI P, ZHAO Y S.Adaptive control for two-spacecraft electromagnetic formation keeping[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(12):2302-2308(in Chinese). [14] 邵龙飞, 师鹏, 赵育善.电磁航天器编队动力学建模与运动规划方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 41(4):737-743.SHAO L F, SHI P, ZHAO Y S.Dynamics modeling and motion programming for electromagnetic formation flight[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(4):737-743(in Chinese). [15] KWON D W, SEDWICK R J, LEE S I, et al.Electromagnetic formation flight testbed using superconducting coils[J].Journal of Spacecraft & Rockets, 2011, 48(1):124-134. [16] AHSUN U, MILLER D W.Dynamics and control of electromagnetic satellite formations[C]//American Control Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 1730-1735. [17] MILLER D W, AHSUN U, RAMIREZRIBEROS J L.Control of electromagnetic satellite formations in near-earth orbits[J].Journal of Guidance, Control and Dynamics, 2010, 33(6):1883-1891. doi: 10.2514/1.47637 [18] 胡敏, 曾国强, 党朝辉.近地轨道集群航天器电磁编队飞行非线性反馈控制方法[J].空间科学学报, 2012, 32(3):417-423.HU M, ZENG G Q, DANG Z H.Nonlinear feedback control of fractionated spacecraft electromagnetic formation flying in low-earth obrit[J].Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2012, 32(3):417-423(in Chinese). [19] ZENG G, HU M.Finite-time control for electromagnetic satellite formations[J].Acta Astronautica, 2012, 74(3):120-130. [20] ZHANG J, YUAN C, JIANG D, et al.Adaptive terminal sliding mode control of electromagnetic spacecraft formation flying in near-earth orbits[J].Advances in Mechanical Engineering, 2014, 2014(1):512583. [21] 齐彧.电磁航天器编队飞行关键技术研究[D].北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2017.QI Y.Research on key technology of electromagnetic satellites formation flight[D].Beijing: Beihang University, 2017(in Chinese). [22] ZHANG B Q, SONG S M.Decentralized coordinated control for multiple spacecraft formation maneuvers[J].Acta Astronautica, 2012, 74:79-97. doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2011.12.017 -








 下载:
下载: