Method for calculating firing data of guided rocket launcher based on surrogate model
-
摘要:
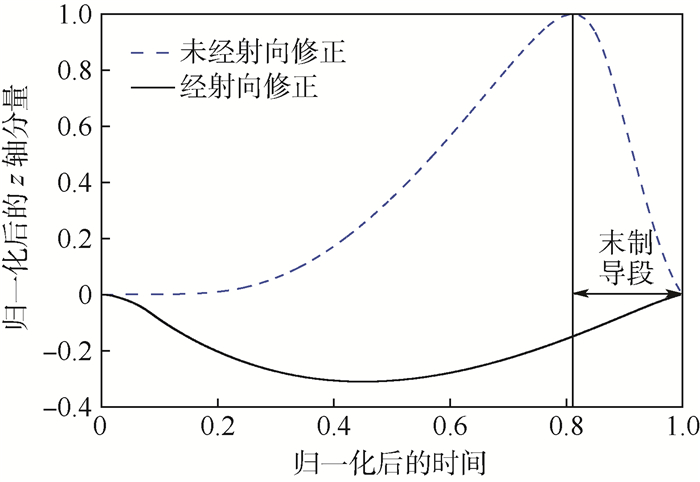
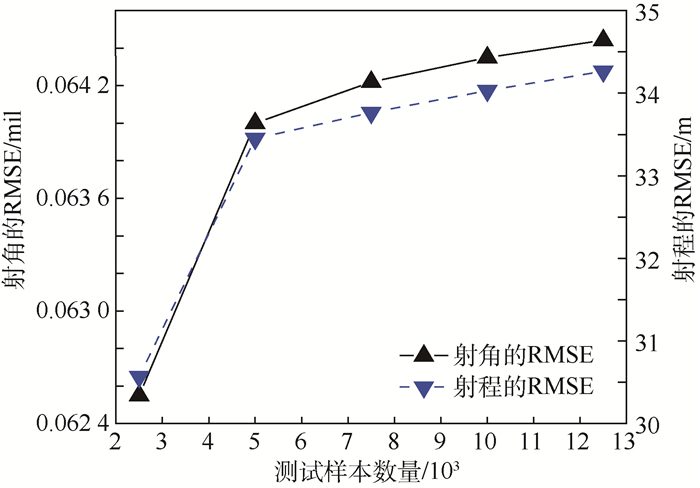
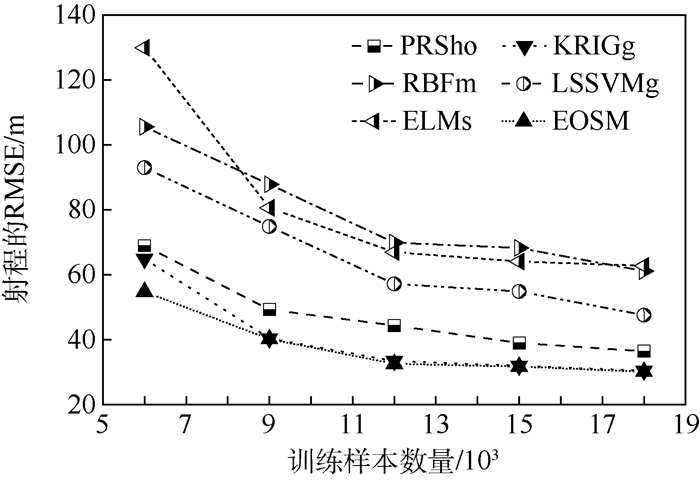
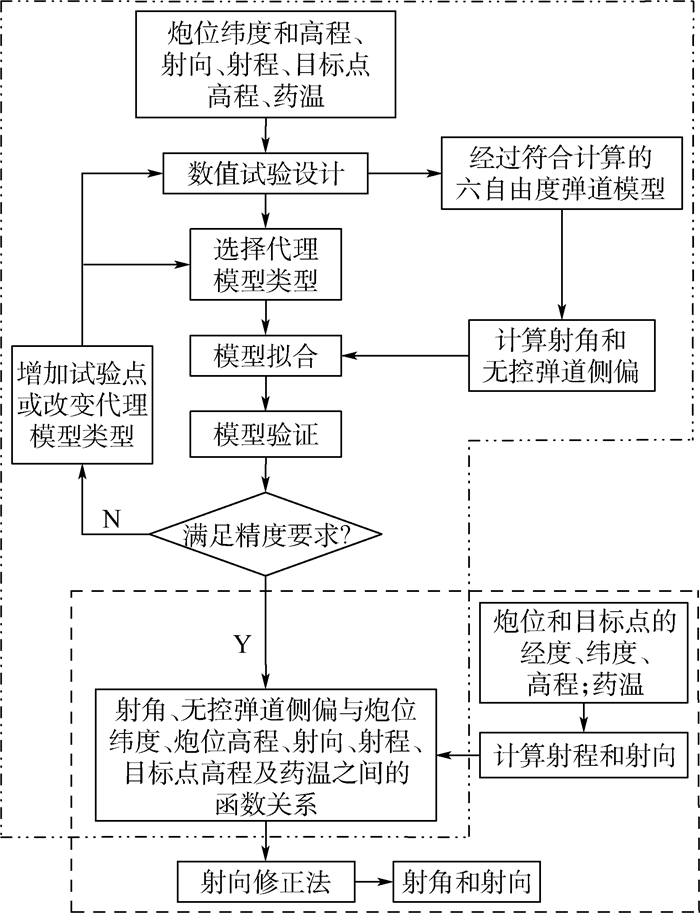
针对制导火箭炮发射诸元的快速计算问题,提出了一种结合大样本数据和代理模型计算发射诸元的新方法。运用代理模型建立射角、无控弹道侧偏与炮位纬度、炮位高程、射向、射程、目标点高程及药温之间的函数关系,并根据射程和无控弹道侧偏的预测值对射向进行修正。仿真结果表明,高阶多项式响应面、相关函数为高斯函数的Kriging、高阶单项式径向基函数、核函数为高斯函数的最小二乘支持向量机、激活函数为正弦函数的超限学习机以及由上述单一代理模型构建的组合代理模型均具有较高的预测精度,各种单一代理模型对射角和无控弹道侧偏的预测时间均小于1 ms,证明了基于代理模型的射角和无控弹道侧偏预测方法切实可行,且通过对射向进行修正有效减小了由于地球自转引起的无控弹道侧偏。
Abstract:Aimed at the problem of rapid calculation of firing data of guided rocket launcher, a new method for calculating firing data based on large sample data and surrogate model is proposed. The surrogate models are used to establish the functional relations between the firing angle, uncontrolled lateral range and six influencing factors, including latitude of artillery location, elevation of artillery location, target azimuth, range between artillery location and target location, elevation of target location and propellant temperature, and the target azimuth is corrected according to the range and predicted value of the uncontrolled lateral range. The simulation results show that the high-order polynomial response surface, the Kriging with Gaussian correlation function, the radial basis function with high-order monomial, the least squares support vector machine with Gaussian kernel function, the extreme learning machine with sine activation function and an ensemble of the above individual surrogate models have higher prediction accuracy, and the execution time of each individual surrogate model for a prediction of firing angle or uncontrolled lateral range is less than 1 ms, which verifies the effectiveness and feasibility of the proposed method. Moreover, the uncontrolled lateral range due to the earth's rotation is effectively reduced after the target azimuth correction.
-
Key words:
- guided rocket launcher /
- firing data /
- large sample data /
- surrogate model /
- target azimuth correction
-
表 1 各影响因素的变化范围
Table 1. Variation range of various influencing factors
因素 范围 B0/(°) [0, 60.00] H0/m [0, 5 000.00] AT/mil [0, 6 000.00) XG/km [80.00,300.00] HT/m [0, 5 000.00] TS/℃ [-40.00, 50.00] 表 2 阶数对PRS预测精度的影响
Table 2. Effect of order on prediction accuracy of PRS
阶数 射角 无控弹道侧偏 射程 MAE/mil MRE/% RMSE/mil MAE/m RMSE/m MAE/m MRE/% RMSE/m 1 50.867 5.023 11.813 2455.38 606.87 17422.75 11.57 6658.22 2 24.550 3.211 7.545 1485.90 347.41 11483.88 8.50 4 490.55 3 9.817 1.236 2.385 914.41 185.51 4331.12 2.97 1368.86 4 6.167 0.652 1.245 509.76 94.03 2830.85 1.25 706.48 5 3.737 0.384 0.590 234.81 37.76 1298.65 0.77 320.38 6 2.333 0.240 0.323 99.02 16.15 768.27 0.47 172.21 7 1.476 0.151 0.186 49.15 7.01 519.29 0.23 95.82 8 1.085 0.111 0.120 25.06 3.46 343.80 0.15 61.56 9 0.667 0.068 0.084 13.76 1.41 208.69 0.13 44.40 10 0.792 0.078 0.088 18.10 1.93 245.16 0.14 46.51 表 3 相关函数对Kriging预测精度的影响
Table 3. Effect of correlation function on prediction accuracy of Kriging
相关函数 射角 无控弹道侧偏 射程 MAE/mil MRE/% RMSE/mil MAE/m RMSE/m MAE/m MRE/% RMSE/m Cubic 0.550 0.068 0.079 14.26 1.50 217.88 0.11 45.18 Exp 1.667 0.176 0.168 64.60 6.52 583.94 0.23 69.05 Gauss 0.483 0.051 0.064 6.64 0.65 182.31 0.09 33.45 Lin 1.567 0.164 0.174 65.82 5.84 564.56 0.22 76.00 Matern32 1.433 0.151 0.117 34.79 2.44 542.97 0.21 51.70 Matern52 1.183 0.124 0.099 16.82 1.25 449.70 0.17 48.59 Spherical 1.583 0.167 0.165 58.83 5.55 602.85 0.24 67.90 Spline 0.533 0.056 0.070 10.68 1.08 201.42 0.10 40.79 表 4 基函数对RBF预测精度的影响
Table 4. Effect of basis function on prediction accuracy of RBF
基函数 射角 无控弹道侧偏 射程 MAE/mil MRE/% RMSE/mil MAE/m RMSE/m MAE/m MRE/% RMSE/m Gauss 1.783 0.189 0.240 26.05 2.88 852.03 0.51 131.14 IMQ 1.350 0.165 0.182 23.69 2.64 680.56 0.53 101.25 MN 1.033 0.105 0.133 23.22 2.59 414.72 0.25 69.86 MQ 1.317 0.158 0.179 24.30 2.67 657.65 0.50 98.90 TPS 1.103 0.117 0.139 23.44 2.66 443.64 0.34 74.68 表 5 核函数对LSSVM预测精度的影响
Table 5. Effect of kernel function on prediction accuracy of LSSVM
核函数 射角 无控弹道侧偏 射程 MAE/mil MRE/% RMSE/mil MAE/m RMSE/m MAE/m MRE/% RMSE/m Lin 50.850 5.020 11.813 2455.39 606.87 17422.75 11.56 6658.22 Polynomial 1.017 0.106 0.120 24.49 3.50 365.25 0.17 61.98 Gauss 0.983 0.102 0.114 13.85 1.77 335.83 0.16 57.17 表 6 激活函数对ELM预测精度的影响
Table 6. Effect of activation function on prediction accuracy of ELM
激活函数 射角 无控弹道侧偏 射程 MAE/mil MRE/% RMSE/mil MAE/m RMSE/m MAE/m MRE/% RMSE/m Radbas 11.850 1.932 1.202 190.80 17.04 6 131.68 4.78 762.77 Sigmoid 1.167 0.135 0.157 33.68 3.15 640.92 0.44 85.99 Sine 1.117 0.115 0.130 24.18 2.65 337.00 0.22 66.95 Tanh 8.350 1.412 0.920 160.13 15.40 5692.56 3.86 581.62 Tribas 59.217 8.505 9.667 2 468.48 519.41 41920.08 31.48 6278.87 表 7 单一代理模型和组合代理模型的预测精度
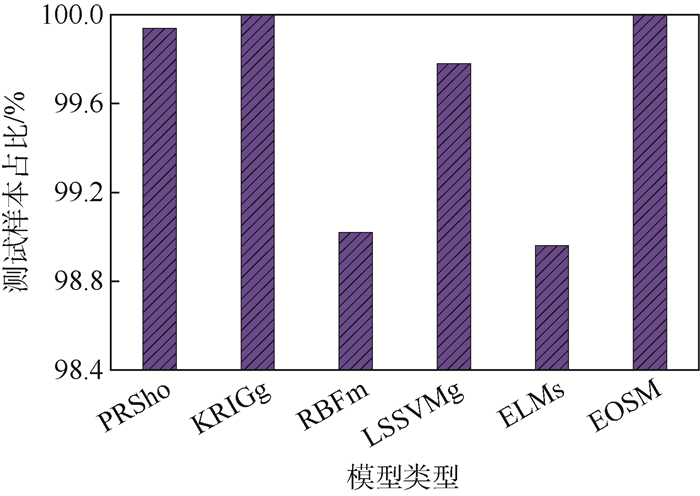
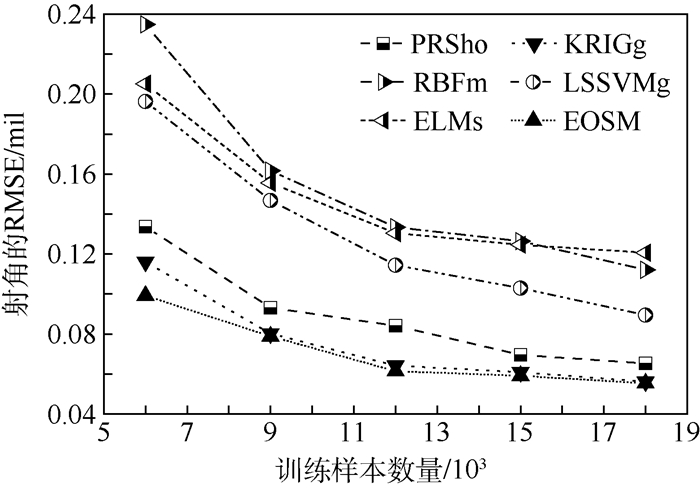
Table 7. Prediction accuracy of individual surrogate models and ensemble of surrogate models
模型类型 射角 无控弹道侧偏 射程 MAE/mil MRE/% RMSE/mil MAE/m RMSE/m MAE/m MRE/% RMSE/m PRSho 0.667 0.068 0.084 13.76 1.41 208.69 0.13 44.40 KRIGg 0.483 0.051 0.064 6.64 0.65 182.31 0.09 33.45 RBFm 1.033 0.105 0.133 23.22 2.59 414.72 0.25 69.86 LSSVMg 0.983 0.102 0.114 13.85 1.77 335.83 0.16 57.17 ELMs 1.117 0.115 0.130 24.18 2.65 337.00 0.22 66.95 EOSM 0.467 0.049 0.061 5.93 0.60 177.69 0.08 32.60 表 8 射向修正法的修正效果
Table 8. Correction effect of target azimuth correction method
m 模型类型 (Δ z)Max (Δ z)Rmse (Δ x)Max PRSho 24.19 4.62 0.42 KRIGg 23.75 4.49 0.42 RBFm 28.72 5.05 0.50 LSSVMg 25.82 4.71 0.43 ELMs 33.13 5.18 0.48 EOSM 23.51 4.46 0.41 -
[1] 杨明, 高宏伟, 汤祁忠.制导火箭弹射表编拟研究[J].火力与指挥控制, 2013, 38(12):156-159. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2013.12.041YANG M, GAO H W, TANG Q Z.Research on compilation of firing tables of guided rocket[J].Fire Control & Command Control, 2013, 38(12):156-159(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2013.12.041 [2] 徐劲祥, 祁载康, 林德福, 等.火箭炮射表编拟及发射诸元快速装定研究[J].南京理工大学学报, 2004, 28(3):333-336. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9830.2004.03.026XU J X, QI Z K, LIN D F, et al.Study on the compilation of firing tables and rapid firing elements binding of rocket gun system[J].Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2004, 28(3):333-336(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9830.2004.03.026 [3] 韩子鹏.弹箭外弹道学[M].北京:北京理工大学出版社, 2014:467-472.HAN Z P.Exterior ballistics of projectiles and rockets[M]. Beijing:Beijing Institute of Technology Press, 2014:467-472(in Chinese). [4] CHUSILP P, CHARUBHUN W, RIDLUAN A.Developing firing table software for artillery projectiles using iterative search and 6-DOF trajectory model[C]//Proceedings of the Second TSME International Conference on Mechanical Engineering.Krabi: The Thai Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2011: AME04. [5] 周珞晶, 张为华, 苏明照, 等.火箭弹计算机射表的发射角快速确定方法[J].弹箭与制导学报, 1998(4):48-52.ZHOU L J, ZHANG W H, SU M Z, et al.Rapid determining method for launching angle of computer's firing table of rocket projectiles[J].Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 1998(4):48-52(in Chinese). [6] 赵东华, 张怀智, 郭胜强, 等.基于二分法的弹道解算决定火炮射击诸元[J].火力与指挥控制, 2012, 37(12):182-183. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2012.12.048ZHAO D H, ZHANG H Z, GUO S Q, et al.Researched on determining firing data of gun based on solving ballistic equations with binary search[J].Fire Control & Command Control, 2012, 37(12):182-183(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2012.12.048 [7] CHUSILP P, CHARUBHUN W, NUTKUMHANG N.Investigating an iterative method to compute firing angles for artillery projectiles[C]//Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 940-945. [8] CHARUBHUN W, CHUSILP P.Development of automatic firing angle calculation for ground to ground MLRS[C]//Proceedings of the 2015 Asian Conference on Defence Technology. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 17-26. [9] VIANA F A C, SIMPSON T W, BALABANOV V, et al.Metamodeling in multidisciplinary design optimization:How far have we really come [J].AIAA Journal, 2014, 52(4):670-690. doi: 10.2514/1.J052375 [10] KOZIEL S, LEIFSSON L.Surrogate-based modeling and optimization[M].Berlin:Springer, 2013:285-391. [11] VIANA F A C.Surrogates toolbox user's guide version 3.0[EB/OL].[2018-06-06]. [12] FORRESTER A I J, SOBESTER A, KEANE A J.Engineering design via surrogate modelling: A practical guide[M].West Sussex: John Wiley & Sons Ltd., 2008: 49-63. [13] 陈文, 傅卓佳, 魏星.科学与工程计算中的径向基函数方法[M].北京:科学出版社, 2014:28-33.CHEN W, FU Z J, WEI X. Radial basis function methods in science and engineering calculation[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2014:28-33(in Chinese). [14] SUYKENS J A K, GESTEL T V, BRABANTER J D, et al.Least squares support vector machines[M].Hackensack, NJ:World Scientific, 2002:71-116. [15] HUANG G B, ZHU Q Y, SIEW C K. Extreme learning machine: A new learning scheme of feedforward neural networks[C]//Proceedings of the 2004 IEEE International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2004: 985-990. [16] RASMUSSEN C E, WILLIAMS C K I. Gaussian process for machine learning[M].Cambridge:Massachusetts Institute of Technology Press, 2006:85. [17] CRISTIANINI N, SHAWE-TAYLOR J.An introduction to support vector machines and other kernel-based learning methods[M]. Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2000:112. [18] 马洋, 罗文彩.组合代理模型研究及在飞行器气动性能预测中的应用[C]//第17届中国系统仿真技术及其应用学术年会论文集.北京: 中国自动化学会系统仿真专业委员会, 2016: 26-31.MA Y, LUO W C. Study on ensemble of surrogate models and application in prediction of aerodynamic characteristics of space vehicle[C]//Proceedings of 17th Chinese Conference on System Simulation Technology & Application. Beijing: System Simulation Committee of Chinese Association of Automation, 2016: 26-31(in Chinese). [19] 龚纯, 王正林.精通MATLAB最优化计算[M]. 3版.北京:电子工业出版社, 2014:337-341.GONG C, WANG Z L.Proficient in MATLAB optimization calculation[M].3rd ed. Beijing:Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2014:337-341(in Chinese). [20] 张志勇, 陈志华, 黄振贵, 等.远程火箭弹精度影响分析及其修正[C]//中国力学大会-2015论文摘要集.北京: 中国力学学会办公室, 2015: 239.ZHANG Z Y, CHEN Z H, HUANG Z G, et al. Precision influence analysis and modification of long-range rockets[C]//Collection of Extent Abstracts of the Chinese Congress of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics 2015.Beijing: Chinese Society of Theoretical and Applied Mechanics Office, 2015: 239(in Chinese). [21] International Organization for Standardization (ISO). Standard atmosphere: ISO 2533: 1975[S].Geneva: ISO, 1975. -







 下载:
下载: