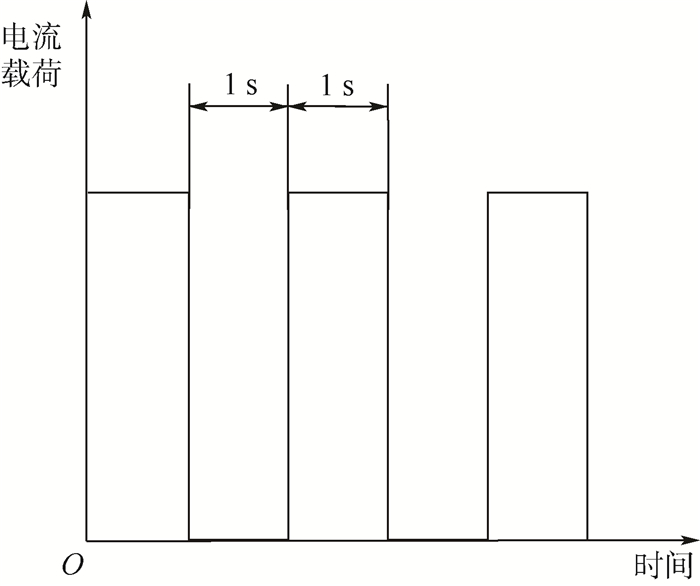
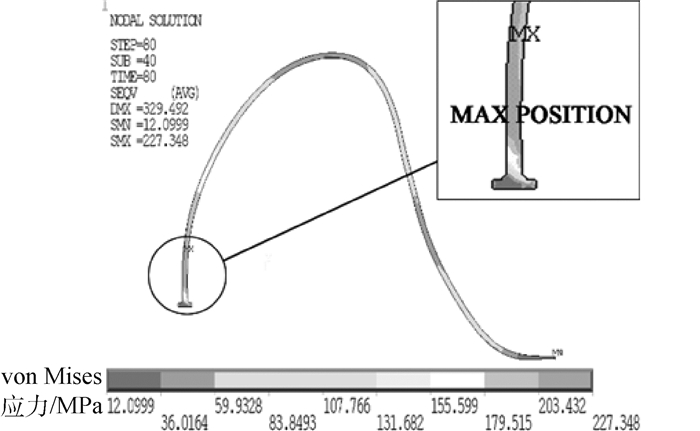
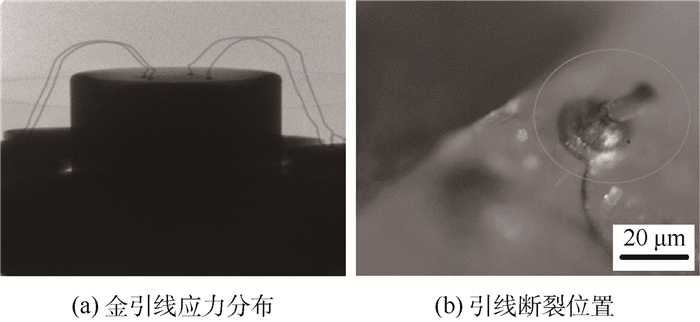
Fatigue fracture lifetime prediction for gold bonding wires of high-power LED under cyclically electrical loading
-
摘要:
随着大功率发光二极管(LED)在照明领域的普及与广泛应用,可靠性逐渐成为研究的重点。大功率LED封装器件中金引线疲劳断裂失效一直是制约其可靠性的重要因素。通过针对大功率LED封装器件中的金引线力学仿真与功率循环试验相结合的方法,首先确定循环电载荷条件下该型LED的主要失效原因为金引线疲劳断裂,其次提出基于电流加速模型的加速因子提取方法和基于应变幅值的Coffin-Manson解析寿命预测方法,最终完成对LED金引线疲劳断裂寿命的预测和试验验证。研究结果表明:所提方法具有较高的寿命预测精度,可以满足大功率LED封装器件可靠性快速、准确评估的要求。
-
关键词:
- 大功率发光二极管(LED) /
- 金引线 /
- 疲劳断裂 /
- 寿命预测 /
- 可靠性
Abstract:With the popularity and widespread application of high-power light-emitting diode (LED) in lighting industry, its reliability has gradually become one of research focuses.The failure of gold bonding wires in the traditional LED package has been a critical bottleneck that restricts its reliability. In this paper, the failure mechanism of LED under cyclically electrical loading is firstly identified through both gold bonding wire mechanical simulation and power cycling test experiment, which is the fatigue fracture of gold bonding wire. Then, two lifetime prediction methods, the acceleration factor extraction method based on current acceleration model and the strain-based Coffin-Manson analytical method, are established and verified with experimental results. The results show that the lifetime prediction accuracy of the proposed methods is high and they can achieve a fast and accurate reliability assessment for high-power LEDs with wire-bonding packaging technology.
-
表 1 三种正向电流条件下的测试结果
Table 1. Test results under conditions of three forward currents
正向电流I/mA 器件内阻RS/Ω 压力反向饱和电流Is1/(10-9A) 参考反向饱和电流Is0/(10-10A) 理想因子n 800 4.78 1.4 2 2.67 900 4.37 2.3 2 2.67 1000 4.04 2.9 2 2.67 表 2 加速寿命测量结果和预测结果对比
Table 2. Comparison of accelerated lifetime testing results and prediction results
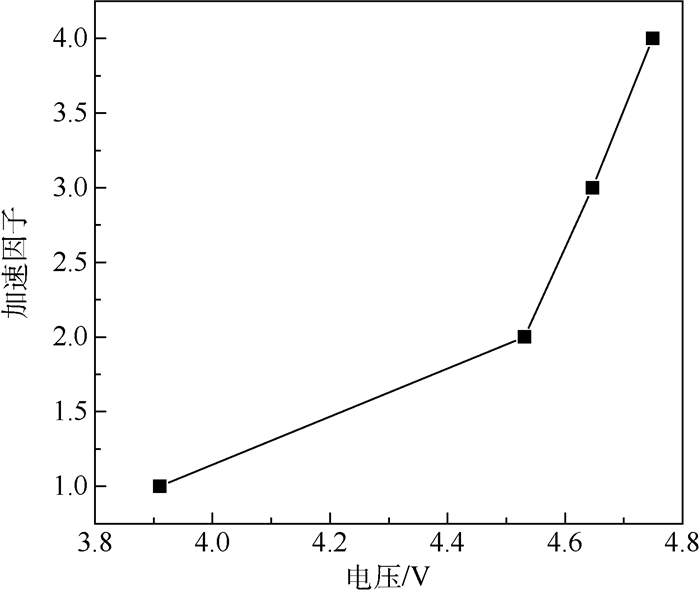
正向电流/mA 63%平均失效时间/h 加速因子 预测寿命/h 700mA试验寿命/h 绝对误差/% 800 400 4.65 1860 1765 5.38 900 82 21.24 1742 1765 1.30 1000 26 68.31 1776 1765 0.62 表 3 基于仿真的金引线疲劳寿命预测结果
Table 3. Gold bonding wire fatigue lifetime prediction results based on simulations
电流/mA 应变幅 实测寿命/h 预测寿命/h 误差/% 700 0.000590 1765 1887 6.912 800 0.000667 400 900 0.000757 82 1000 0.000840 26 -
[1] VAN DRIEL W D, FAN X J.Solidstate lighting reliability:Components to systems[M].Berlin:Springer, 2012. [2] CHANG M H, DAS D, VARDE P V, et al.Light emitting diodes reliability review[J].Microelectronics Reliability, 2012, 52(5):762-782. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2011.07.063 [3] 鲁光祝.IGBT功率模块寿命预测技术研究[D].重庆: 重庆大学, 2012.LU G Z.Lifetime prediction for IGBT power module[D].Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2012(in Chinese). [4] MERKLE L, KADEN T, SONNER M, et al.Mechanical fatigue properties of heavy aluminium wire bonds for power applications[C]//Electronics System-Integration Technology Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 1363-1368. [5] HU J M, PECHT M, DASGUPTA A.A probabilistic approach for predicting thermal fatigue life of wire bonding in microelectronics[J].Journal of Electronic Packaging, 1991,113(3):275-285. doi: 10.1115/1.2905407 [6] HUA Y, LIN M, BASARAN C.Failure modes and FEM analysis of power electronic packaging[J].Finite Elements in Analysis & Design, 2002, 38(7):601-612. [7] SPENCER M L, LORENZ R D.Analysis and in-situ measurement of thermal-mechanical strain in active silicon power semiconductors[C]//Industry Applications Society Meeting.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 1465-1471. [8] 李志星, 张鑫宇, 平恩顺.基于PFA的IGBT键合线失效机理及寿命预测[J].半导体技术, 2013, 38(9):63-66.LI Z X, ZHANG X Y, PING E S.Failure mechanism and lifetime forecasting based on PFA for bonding wire in IGBT[J].Semiconductor Technology, 2013, 38(9):63-66(in Chinese). [9] 姚二现, 庄伟东, 常海萍.IGBT模块功率循环疲劳寿命预测[J].电子产品可靠性与环境试验, 2013, 31(2):12-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5468.2013.02.004YAO E X, ZHUANG W D, CHANG H P.Power cycle fatigue lifetime prediction of IGBT module[J].Electronic Product Reliability & Environmental Testing, 2013, 31(2):12-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5468.2013.02.004 [10] YANG L, AGYAKWA P A, JOHNSON C M.A time-domain physics-of-failure model for the lifetime prediction of wire bond interconnects[J].Microelectronics Reliability, 2011, 51(9-11):1882-1886. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2011.07.052 [11] BIELEN J, GOMMANS J J, THEUNIS F.Prediction of high cycle fatigue in aluminum bond wires: A physics of failure approach combining experiments and multi-physics simulations[C]//International Conference on Thermal, Mechanical and Multiphysics Simulation and Experiments in Micro-Electronics and Micro-Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2006: 1-7. [12] MATSUNAGA T, UEGAI Y.Thermal fatigue life evaluation of aluminum wire bonds[C]//Electronics Systemintegration Technology Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2006: 726-731. [13] HAGER C, STUCK A, TRONEL Y, et al.Comparison between finite-element and analytical calculations for the lifetime estimation of bond wires in IGBT modules[C]//12th International Symposium on Power Semiconductor Devices and ICs.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2000: 291-294. [14] CIAPPA M, FICHTNER W.Lifetime prediction of IGBT modules for traction applications[C]//IEEE International Proceedings on Reliability Physics.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2000: 210-216. [15] ZHANG S U, BANG W L.Fatigue life evaluation of wire bonds in LED packages using numerical analysis[J].Microelectronics Reliability, 2014, 54(12):2853-2859. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2014.07.142 [16] AGYAKWA P A, CORFIELD M R, YANG L, et al.Microstructural evolution of ultrasonically bonded high purity Al wire during extended range thermal cycling[J].Microelectronics Reliability, 2011, 51(2):406-415. doi: 10.1016/j.microrel.2010.08.018 [17] YANG L, AGYAKWA P A, JOHNSON C M.Physics-of-failure lifetime prediction models for wire bond interconnects in power electronic modules[J].IEEE Transactions on Device & Materials Reliability, 2013, 13(1):9-17. [18] 林亮, 陈志忠, 童玉珍, 等.GaN基大功率倒装焊蓝光LED的I-V特性研究[J].半导体光电, 2007, 28(6):766-768. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5868.2007.06.004LIN L, CHEN Z Z, TONG Y Z, et al.Research on current-voltage characteristics of GaN-based high power flip-chip blue LED[J].Semiconductor Optoelectronics, 2007, 28(6):766-768(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5868.2007.06.004 [19] 李炳乾, 布良基, 甘雄文, 等.LED正向压降随温度的变化关系研究[J].光子学报, 2003, 32(11):1349-1351.LI B Q, BU L J, GAN X W, et al.Research on the relationship of the change in forward voltage with temperature of light emitting diode[J].Acta Photonica Sinica, 2003, 32(11):1349-1351(in Chinese). [20] 唐红雨, 杨道国, 张国旗, 等.硅胶粘弹性对大功率LED可靠性的影响[J].电子元件与材料, 2013, 32(9):51-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2028.2013.09.015TANG H Y, YANG D G, ZHANG G Q, et al.Influences of viscoelasticity of silicone on the reliability of high power light emitted diode[J].Electronic Components & Materials, 2013, 32(9):51-55(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-2028.2013.09.015 [21] 董月香.疲劳寿命预测方法综述[J].大型铸锻件, 2006(3):39-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5635.2006.03.014DONG Y X.General description of the fatigue life prediction method[J].Heavy Casting and Forging, 2006(3):39-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-5635.2006.03.014 [22] 郑战光, 蔡敢为, 李兆军, 等.基于损伤力学阐释Manson-Coffin低周疲劳模型[J].中国机械工程, 2011, 22(7):812-814. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJX201107014.htmZHENG Z G, CAI G W, LI Z J, et al.Interpretation of Manson-Coffin model of low cycle fatigue based on damage mechanics[J].China Mechanical Engineering, 2011, 22(7):812-814(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZGJX201107014.htm [23] ZHANG B, TAO G.An improved Coffin-Manson model for mid-power LED wire-bonding reliability[C]//IEEE International Symposium on the Physical and Failure Analysis of Integrated Circuits.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 78-82. -







 下载:
下载: