-
摘要:
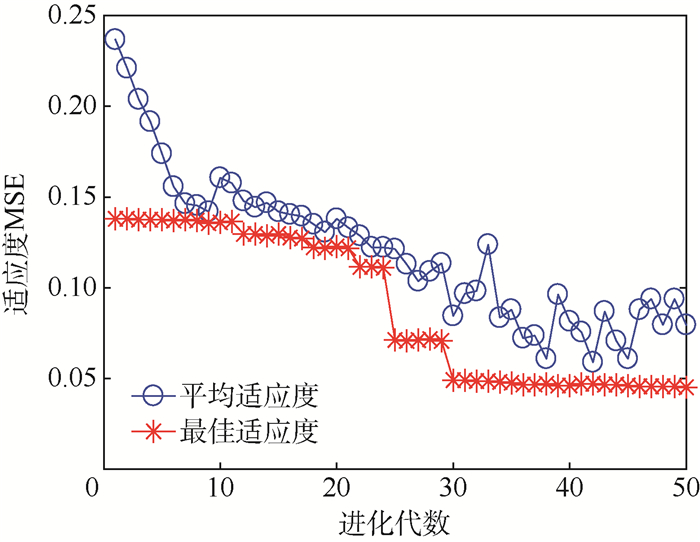
针对提高大范围土壤湿度测量精度的问题,研究了土壤湿度的全球卫星导航系统干涉测量法(GNSS-IR),提出了一种基于支持向量机(SVM)的土壤湿度反演模型,利用遗传算法(GA)的自动寻优功能寻找SVM的最佳参数。结果表明,GA-SVM模型在测试集上得到的土壤湿度反演值与实测值的平均绝对百分比误差(MAPE)仅为0.69%,最大相对误差(MRE)为1.22%,线性回归方程决定系数达到了0.956 9。进一步与统计回归、粒子群优化的SVM模型(PSO-SVM)及反向传播(BP)神经网络方法进行对比,结果说明:在样本数目有限的情况下,GA-SVM方法更适用于土壤湿度的GNSS-IR技术反演,且反演精度较高,泛化性能良好。
-
关键词:
- 土壤湿度 /
- 全球卫星导航系统(GNSS) /
- 干涉测量法(IR) /
- 支持向量机(SVM) /
- 遗传算法(GA)
Abstract:In order to improve the precision of soil moisture measurement in a wide range, in this paper, the global navigation satellite system interferometry and reflectometry (GNSS-IR) for soil moisture was studied and a soil moisture inversion model based on support vector machine (SVM) was proposed. In this model, the automatic optimizing function of genetic algorithm (GA) was applied to optimize the parameters of SVM. The results show that the mean absolute percentage error (MAPE), the maximum relative error (MRE) and the coefficient of determination for equation of linear regression are 0.69%, 1.22% and 0.9569 respectively between the soil moisture inverted by the proposed GA-SVM model and the ground measured values. In addition, the performance of GA-SVM model was also compared with the statistical regression, particle swarm optimization SVM model (PSO-SVM) and back propagation (BP) neural network. The comparison results show that the GA-SVM method is more suitable for the GNSS-IR soil moisture inversion than other machine learning algorithms in small training set scenario, and it has higher inversion precision and better generalization performance.
-
表 1 不同土壤湿度反演模型结果比较
Table 1. Result comparison of different soil moisture inversion models
日期 实测值/(cm3·cm-3) GA-SVM PSO-SVM BP神经网络 反演值/(cm3·cm-3) 绝对误差/(cm3·cm-3) 相对误差/% 反演值/(cm3·cm-3) 绝对误差/(cm3·cm-3) 相对误差/% 反演值/(cm3·cm-3) 绝对误差/(cm3·cm-3) 相对误差/% 2014-03-10 25.83 25.76 -0.07 0.27 26.14 0.31 1.20 26.52 0.69 2.67 2014-03-11 25.55 25.41 -0.14 0.55 26.18 0.63 2.47 26.95 1.40 5.48 2014-03-12 25.21 25.10 -0.11 0.44 25.30 0.09 0.36 27.09 1.88 7.46 2014-03-13 24.55 24.85 0.30 1.22 25.72 1.17 4.77 24.95 0.40 1.63 2014-03-14 24.45 24.64 0.19 0.78 25.38 0.93 3.80 24.99 0.54 2.21 2014-03-15 24.27 24.48 0.21 0.87 24.87 0.60 2.47 24.44 0.17 0.70 2014-03-16 24.07 24.24 0.17 0.71 24.24 0.17 0.71 25.23 1.16 4.82 2014-03-17 23.97 24.18 0.21 0.88 23.99 0.02 0.08 25.47 1.50 6.26 2014-03-18 23.83 23.99 0.16 0.67 23.94 0.11 0.46 24.10 0.27 1.13 2014-03-19 23.88 23.71 -0.17 0.71 24.62 0.74 3.10 24.66 0.78 3.27 2014-03-20 23.62 23.58 -0.04 0.17 24.06 0.44 1.86 25.55 1.93 8.17 2014-03-21 23.24 23.49 0.25 1.08 23.62 0.38 1.64 24.36 1.12 4.82 表 2 土壤湿度反演结果评价比较
Table 2. Comparison of soil moisture inversion result evaluation
评价指标 计算方法 GA-SVM PSO-SVM BP神经网络 平均绝对误差/(cm3·cm-3) 
0.168 0.466 0.987 最大相对误差/% 
1.22 4.77 8.18 均方根误差/(cm3·cm-3) 
0.182 0.579 1.144 平均绝对百分比误差/% 
0.69 1.91 4.05 -
[1] JACKSON T J, SCHMUGGE J, ENGMAN E T.Remote sensing applications to hydrology:Soil moisture[J].Hydrological Sciences Journal, 1996, 41(4):517-530. doi: 10.1080/02626669609491523 [2] 严颂华, 龚健雅, 张训械, 等.GNSS-R测量地表土壤湿度的地基实验[J].地球物理学报, 2011, 54(11):2735-2744. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.11.003YAN S H, GONG J Y, ZHANG X X, et al.Ground based GNSS-R observations for soil moisture[J].Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 2011, 54(11):2735-2744(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0001-5733.2011.11.003 [3] MARTIN-NEIRA M.A pasive reflectometry and interferometry system (PARIS) application to ocean altimetry[J].ESA Journal, 1993, 17(4):331-355. [4] RODRIGUEZ-ALVAREZ N, BOSCH-LLUIS X, CAMPS A, et al.Soil moisture retrieval using GNSS-R techniques:Experimental results over a bare soil field[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2009, 47(11):3616-3624. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2009.2030672 [5] LARSON K M, SMALL E E, GUTMANN E, et al.Using GPS multipath to measure soil moisture fluctuations:Initial results[J].GPS Solutions, 2008, 12(3):173-177. doi: 10.1007/s10291-007-0076-6 [6] CHEW C C, SMALL E E, LARSON K M, et al.Vegetation sen-sing using GPS-interferometric reflectometry:Theoretical effects of canopy parameters on signal-to-noise ratio data[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2015, 53(5):2755-2764. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2014.2364513 [7] LI F, PENG X, CHEN X, et al.Analysis of key issues on GNSS-R soil moisture retrieval based on different antenna patterns[J].Sensors, 2018, 18(8):2498-2513. doi: 10.3390/s18082498 [8] YAN S H, ZHANG N, CHEN N C, et al.Feasibility of using signal strength indicator data to estimate soil moisture based on GNSS interference signal analysis[J].Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 9(1):61-70. doi: 10.1080/2150704X.2017.1384587 [9] ZHANG S B, ROUSSEL N, BONIFACE K, et al.Use of reflected GNSS SNR data to retrieve either soil moisture or vegetation height from a wheat crop[J].Hydrology & Earth System Sciences Discussions, 2017, 21(9):1-26. [10] LARSON K M, BRAUN J J, SMALL E E, et al.GPS multipath and its relation to near-surface soil moisture content[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2010, 3(1):91-99. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2009.2033612 [11] 敖敏思, 朱建军, 胡友健, 等.利用SNR观测值进行GPS土壤湿度监测[J].武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2015, 40(1):117-120.AO M S, ZHU J J, HU Y J, et al.Comparative experiments on soil moisture monitoring with GPS SNR observations[J].Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2015, 40(1):117-120(in Chinese). [12] CHEW C C, SMALL E E, LARSON K M, et al.Effects of near-surface soil moisture on GPS SNR data:Development of a retrieval algorithm for soil moisture[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2014, 52(1):537-543. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2013.2242332 [13] 杨磊, 吴秋兰, 张波, 等.SVRM辅助的北斗GEO卫星反射信号土壤湿度反演方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(6):1134-1141.YANG L, WU Q L, ZHANG B, et al.SVRM-assisted soil moisture retrieval method using reflected signal from BeiDou GEO satellites[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(6):1134-1141(in Chinese). [14] ARROYO A A, CAMPS A, AGUASCA A, et al.Dual-polarization GNSS-R interference pattern technique for soil moisture mapping[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2014, 7(5):1533-1544. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2014.2320792 [15] BILICH A, LARSON K M.Correction published 29 March 2008:Mapping the GPS multipath environment using the signal-to-noise ratio(SNR)[J].Radio Science, 2016, 42(6):1-16. doi: 10.1029/2008RS003839 [16] CHEW C C, SMALL E E, LARSON K M.An algorithm for soil moisture estimation using GPS-interferometric reflectometry for bare and vegetated soil[J].GPS Solutions, 2016, 20(3):1-13. [17] VAPNIK V.The nature of statistical learning theory[C]//Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Berlin: Springer, 1995: 988-999. [18] 李晓宇, 张新峰, 沈兰荪.一种确定径向基核函数参数的方法[J].电子学报, 2005, 33(12):2459-2463.LI X Y, ZHANG X F, SHEN L S.A selection means on the parameter of radius basis function[J].Acta Electronica Sinica, 2005, 33(12):2459-2463(in Chinese). [19] HOLLAND J H. Genetic algorithms[J].Scientific American, 1992,267(1):66-72. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0792-66 -








 下载:
下载: