-
摘要:
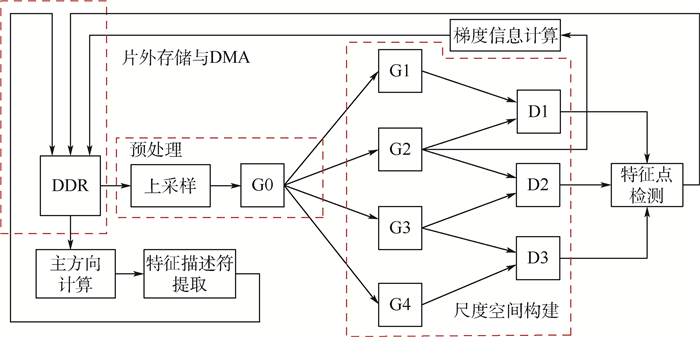
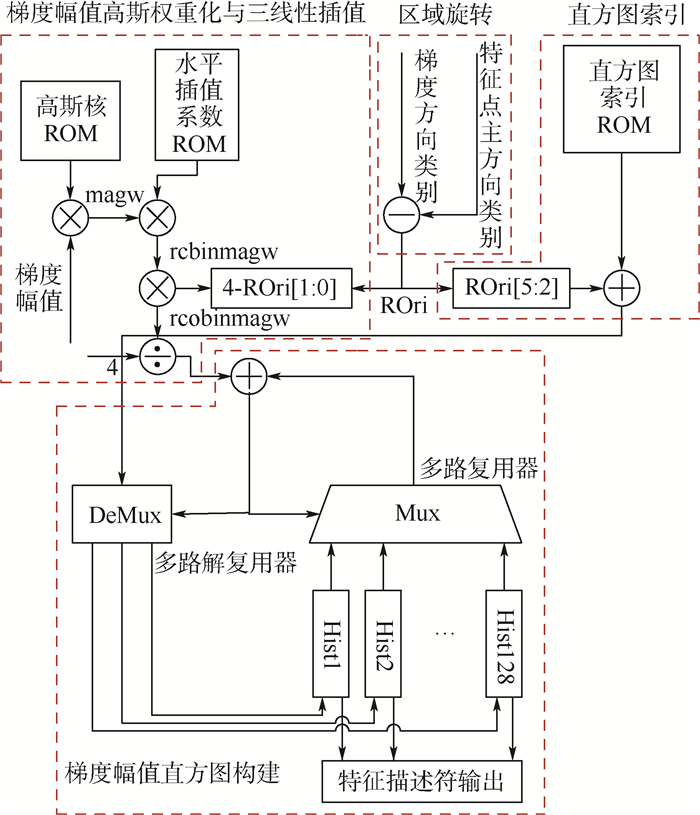
尺度不变特征变换(SIFT)算法具有优良的鲁棒性,在计算机视觉领域得到广泛应用。针对SIFT算法高计算复杂度而导致其在CPU上运行实时性低的问题,基于现场可编程门阵列(FPGA)设计了一种低复杂度的快速SIFT硬件架构,主要对算法的特征描述符提取部分进行优化。通过降低梯度信息(包括梯度幅值和梯度方向)的位宽、优化高斯权重系数的产生、简化三线性插值系数的计算和简化梯度幅值直方图索引的求解等方法,避免了指数、三角函数和乘法等复杂计算,降低了硬件设计复杂度和硬件资源消耗。实验结果显示,提出的低复杂度快速SIFT硬件架构,与软件相比,可以获得约200倍的加速;与相关研究相比,速度提高了3倍,特征描述符稳定性提高了18%以上。
-
关键词:
- 现场可编程门阵列(FPGA) /
- 尺度不变特征变换(SIFT) /
- 硬件设计 /
- 梯度信息 /
- 特征描述符提取
Abstract:Scale invariant feature transform (SIFT) algorithm is widely used in the field of computer vision because of its excellent robustness. In order to solve the problem of low real-time performance of computation-intensive SIFT algorithm on CPU, a fast SIFT hardware architecture is proposed based on field programmable gate array (FPGA), with reduced complexity by optimizing the feature descriptor extraction part of the algorithm. By reducing the bit width of gradient information (including gradient amplitude and gradient direction), optimizing the generation of the Gauss weight coefficients, simplifying the calculation of the three linear interpolation coefficients and simplifying the computation process of the histogram index of the gradient amplitude, the proposed design avoids complex computations such as exponent, trigonometric function and multiplication, and reduces the complexity of hardware architecture and hardware resource consumption. The experimental results show that the proposed low-complexity fast SIFT hardware architecture can speed up by about 200 times compared to the software implementation. Compared with the related research, the speed is improved by 3 times and the stability of the feature descriptor is increased by more than 18%.
-
表 1 相对梯度方向分类方式
Table 1. Classification method of relative gradient direction
前后类别说明 类别 分类前类别 0~7 8~11 12~15 16~19 20~23 24~27 28~31 32~35 分类后类别 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 表 2 旋转变化特征描述符稳定性检测
Table 2. Stability detection of feature descriptors for rotation change
旋转程度/(°) 匹配率 5 0.80 10 0.85 15 0.75 20 0.5 25 0.45 30 0.35 注:旋转变化平均匹配率为0.62。 表 3 特征描述符稳定性对比
Table 3. Stability comparison of feature descriptors
表 4 硬件资源消耗对比
Table 4. Comparison of hardware resource consumption
表 5 梯度方向优化前后硬件资源消耗对比
Table 5. Comparison of hardware resource consumption before and after gradient direction optimization
模块 LUT/个 Register/个 梯度阵列(m=14,g=16) 0 7 680×2 梯度阵列(m=14,g=6) 0 5 120×2 梯度方向分类模块 102 6 -
[1] 王亭亭, 蔡志浩, 王英勋.无人机室内视觉/惯导组合导航方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(1):176-186.WANG T T, CAI Z H, WANG Y X.Integrated vision/inertial navigation method of UAVs in indoor environment[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(1):176-186(in Chinese). [2] LOWE D G.Distinctive image features from scale-invariant keypoints[J].International Journal of Computer Vision, 2004, 60(2):91-110. [3] JIANG J, LI X, ZHANG G.SIFT hardware implementation for real-time image feature extraction[J].IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems for Video Technology, 2014, 24(7):1209-1220. doi: 10.1109/TCSVT.2014.2302535 [4] MA W, WEN Z, WU Y, et al.Remote sensing image registration with modified SIFT and enhanced feature matching[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2017, 14(1):3-7. doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2016.2600858 [5] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T.Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 3431-3440. [6] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al.Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [7] VIJAY K B G, CARNEIRO G, REID I.Learning local image descriptors with deep siamese and triplet convolutional networks by minimizing global loss functions[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 5385-5394. [8] 王琳, 刘强.基于局部特征的多目标图像分割算法[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(6):061002.WANG L, LIU Q.A multi-object image segmentation algorithm based on local features[J].Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(6):061002(in Chinese). [9] HEYMANN S, MVLLER K, SMOLIC A, et al.SIFT implementation and optimization for general-purpose GPU[J].Media Culture & Society, 2007, 67(1):7-13. [10] ZHANG Q, CHEN Y, ZHANG Y, et al.SIFT implementation and optimization for multi-core systems[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Parallel and Distributed Processing.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 1-8. [11] LIU Q, LIU J, SANG R, et al.Fast neural network training on fpga using quasi-Newton optimization method[J].IEEE Transactions on Very Large Scale Integration Systems, 2018, 26(8):1575-1579. doi: 10.1109/TVLSI.2018.2820016 [12] VOURVOULAKIS J, KALOMIROS J, LYGOURAS J.FPGA accelerator for real-time SIFT matching with RANSAC support[J].Microprocessors and Microsystems, 2017, 49:105-116. doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2016.11.011 [13] QASAIMEH M, SAGAHYROON A, SHANABLEH T.FPGA-based parallel hardware architecture for real-time image classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2015, 1(1):56-70. [14] VOURVOULAKIS J, KALOMIROS J, LYGOURAS J.Fully pipelined FPGA-based architecture for real-time SIFT extraction[J].Microprocessors and Microsystems, 2016, 40:53-73. doi: 10.1016/j.micpro.2015.11.013 [15] CHIU L C, CHANG T S, CHEN J Y, et al.Fast SIFT design for real-time visual feature extraction[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(8):3158-3167. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2259841 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(14)
-








 下载:
下载: