Constant-force curved-surface-tracking with robotic manipulator based on adaptive iterative algorithm
-
摘要:
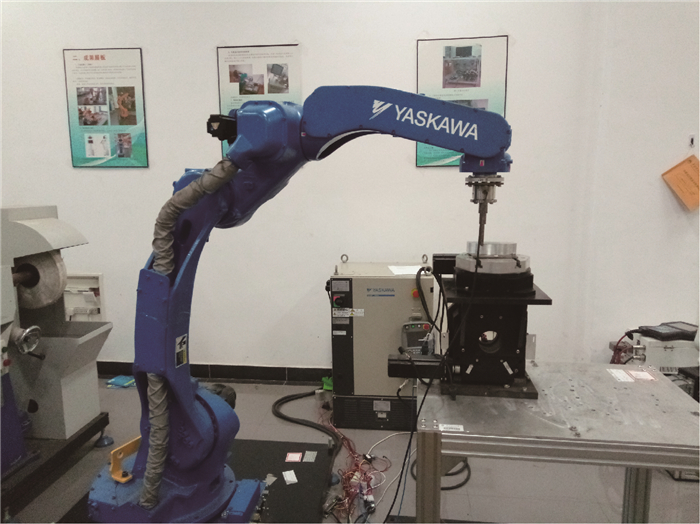
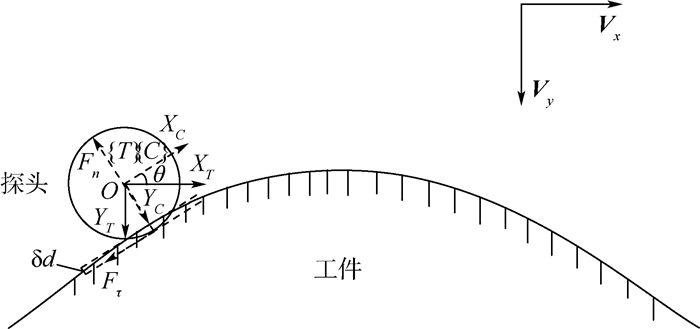
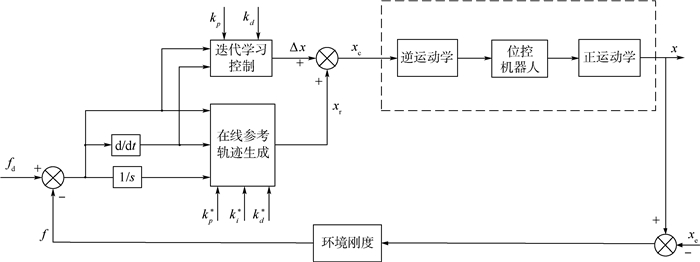
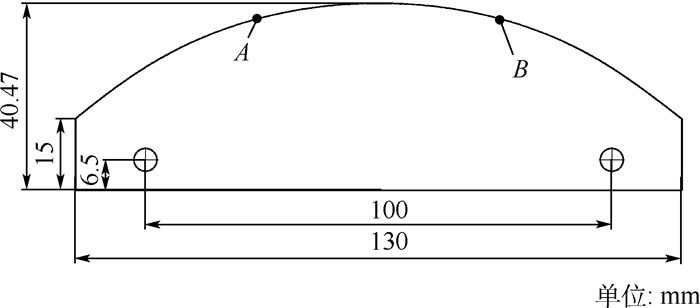
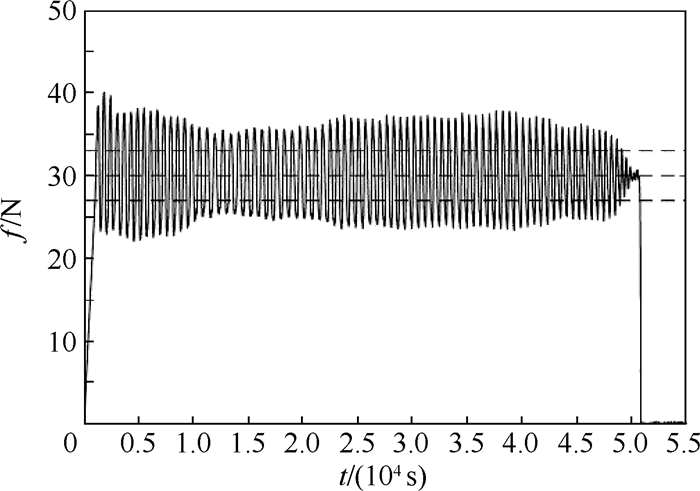
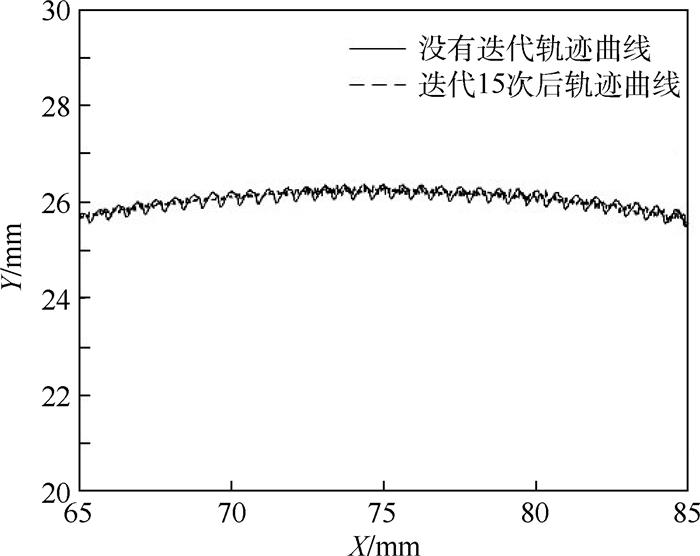
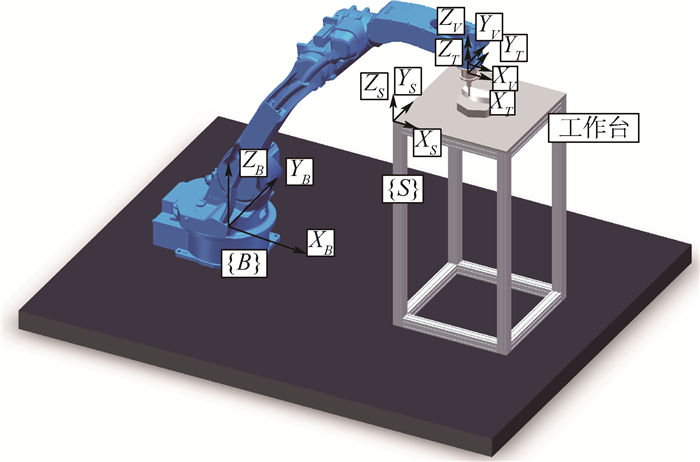
针对利用机器人进行打磨、抛光、去毛刺等场合时末端执行器对曲面工件轮廓跟踪时难以得到恒定接触力的问题,对机器人末端执行器和工件轮廓接触时的接触力进行研究,建立了实际跟踪过程中机器人末端执行器的接触力和已知传感器坐标系的映射关系,提出了一种基于自适应迭代学习算法的机器人力/位混合曲面恒力跟踪控制方法。该方法由两部分组成:基于机器人和环境接触时的阻抗模型设计了迭代学习控制律,在PD反馈控制的基础上通过迭代项克服机器人的未知参数和不确定性,并构建Lyapunov能量函数证明所提控制律的收敛性;将迭代学习控制律和力/位混合曲面恒力跟踪控制方法结合起来设计了用于曲面工件轮廓跟踪的控制方法。实验结果显示,经过15次迭代,接触力的波动范围逐渐变小并稳定在±3 N之内,验证了所提方法的有效性。
Abstract:This paper dealt with the fluctuation and instability of contact force that isgenerated between robot end-effector and environment during the process of robotic grinding, polishing and deburring. In order to obtain constant tracking force, the contact force is generated by robot end-effector onto the workpiece surface is analyzed and the mapping relationship between the contact force of robot end-effector in real contact conditions and the known sensor coordinate system was built. Meanwhile, a hybrid force/position control scheme based on adaptive iterative learning algorithm was proposed to compensate the robot end-effector trajectory offset. The control method is composed with two steps. An iterative learning control law was designed based on the impe-dance model of robot-environment in dynamic interaction task. This control law coped with the unknown parameters and disturbances by adding the iterative term to the PD feedback structure. Meanwhile, a Lyapunov energy function was designed to prove the convergence of the control law. The adaptive iterative learning control law was then combined with the force/position hybrid control method to design the constant-force curved-surface-tracking control scheme with robotic manipulator. The experimental results show that after 15 times iteration, the fluctuating range of contact force becomes small gradually and is within ±3 N, which illustrates the effectiveness of the designed control scheme.
-
表 1 误差分析
Table 1. Error analysis
迭代次数 接触力/N 误差绝对值平均值 误差标准差 误差方差 0 4.179 8 2.423 4 5.872 6 1 3.609 1 1.983 2 3.932 9 2 3.063 5 2.218 6 4.922 1 3 2.860 2 2.440 7 5.957 0 4 2.522 3 2.079 6 4.324 8 5 2.260 9 1.661 3 2.759 8 6 1.997 8 2.002 7 2.010 8 7 1.700 3 1.368 5 1.872 7 8 1.613 2 1.283 5 1.647 4 9 1.686 4 1.344 6 1.808 0 10 1.475 7 1.224 4 1.499 1 11 1.352 7 1.147 7 1.317 1 12 1.326 1 1.144 1 1.384 4 13 1.260 4 0.996 0 1.006 3 14 1.021 7 0.976 3 0.953 1 15 0.886 1 0.870 5 0.757 7 -
[1] TIAN F, LI Z, LV C, et al.Polishing pressure investigations of robot automatic polishing on curved surfaces[J].The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2016, 87(1-4):639-646. doi: 10.1007/s00170-016-8527-2 [2] NAGATA F, KUSUMOTO Y, FUJIMOTO Y, et al.Robotic sanding system for new designed furniture with free-formed surface[J].Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2007, 23(4):371-379. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2006.04.004 [3] ZILIANI G, VISIOLI A, LEGNANI G.A mechatronic approach for robotic deburring[J].Mechatronics, 2007, 17(8):431-441. doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2007.04.012 [4] PLIEGO-JIMÉNEZ J, ARTEAGA-PÉREZ M A.Adaptive position/force control for robot manipulators in contact with a rigid surface with uncertain parameters[J].European Journal of Control, 2015, 22:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ejcon.2015.01.003 [5] ROSWELL A, XI F J, LIU G.Modelling and analysis of contact stress for automated polishing[J].International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2006, 46(3-4):424-435. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.05.006 [6] QIAO B, LU R J.Impedance force control for position controlled robotic manipulators under the constraint of unknown environments[J].Journal of Southeast University(English Edition), 2003, 19(4):359-363. [7] 李正义, 唐小琦, 熊烁, 等.沿任意倾斜面的机器人力/位置控制方法研究[J].中国机械工程, 2012, 23(3):304-309. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2012.03.012LI Z Y, TANG X Q, XIONG S, et al.Study on robot force position control method for arbitrarily inclined plane tracking[J].China Mechanical Engineering, 2012, 23(3):304-309(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-132X.2012.03.012 [8] DUAN J, GAN Y, CHEN M, et al.Adaptive variable impedance control for dynamic contact force tracking in uncertain environment[J].Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2018, 102:54-65. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2018.01.009 [9] 李二超, 李战明, 李炜.基于视觉的机器人模糊自适应阻抗控制[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2011, 42(2):409-413.LI E C, LI Z M, LI W.Fuzzy adaptive impedance control of robot based on vision[J].Journal of Central South University(Science and Technology), 2011, 42(2):409-413(in Chinese). [10] BAETEN J, DE SCHUTTER J.Hybrid vision/force control at corners in planar robotic-contour following[J].ASME Transactions on Mechatronics, 2002, 7(2):143-151. [11] JEON S W, AHN D S, BAE H J, et al.Object contour following task based on integrated information of vision and force sensor[C]//International Conference on Control, Automation and Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 1040-1045. [12] LANGE F, HIRZINGER G.Iterative self-improvement of force feedback control in contour tracking[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1992: 1399-1404. [13] VISIOLI A, ZILIANI G, LEGNANI G.Iterative-learning hybrid force/velocity control for contour tracking[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2010, 26(2):388-393. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2010.2041265 [14] ROVEDA L, PALLUCCA G, PEDROCCHI N, et al.Iterative learning procedure with reinforcement for high-accuracy force tracking in robotized tasks[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2018, 14(4):1753-1763. doi: 10.1109/TII.2017.2748236 [15] WINKLER A, SUCHÝ J.Force controlled contour following on unknown objects with an industrial robot[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Robotic and Sensors Environments.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 208-213. [16] KUMAR N, PANWAR V, SUKAVANAM N, et al.Neural network based hybrid force/position control for robot manipulators[J].International Journal of Precision Engineering and Manufacturing, 2011, 12(3):419-426. doi: 10.1007/s12541-011-0054-3 [17] JUNG S, HSIA T C.Robust neural force control scheme under uncertainties in robot dynamics and unknown environment[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2002, 47(2):403-412. [18] KARAYIANNIDIS Y, ROVITHAKIS G, DOULGERI Z.Force/position tracking for a robotic manipulator in compliant contact with a surface using neuro-adaptive control[J].Automatica, 2007, 43(7):1281-1288. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2006.12.019 [19] HE W, DONG Y, SUN C.Adaptive neural impedance control of a robotic manipulator with input saturation[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics:Systems, 2016, 46(3):334-344. doi: 10.1109/TSMC.2015.2429555 [20] 丁希仑, 周乐来, 周军.机器人的空间位姿误差分析方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2009, 35(2):241-245.DING X L, ZHOU L L, ZHOU J.Pose error analysis of robot in three dimension[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2009, 35(2):241-245(in Chinese). [21] 张铁, 胡广.曲面轮廓恒力跟踪的非线性双闭环控制[J].电机与控制学报, 2017, 21(7):99-106.ZHANG T, HU G.Nonlinear dual-loop force controller of contour following[J].Electric Machines and Control, 2017, 21(7):99-106(in Chinese). [22] TAYEBI A.Adaptive iterative learning control for robot manipulators[J].Automatica, 2004, 40(7):1195-1203. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2004.01.026 [23] GRAIG J J.Introduction to robotics mechanics and control[M].London:Pearson, 2004. [24] 乔兵, 吴洪涛, 朱剑英, 等.面向位控机器人的力/位混合控制[J].机器人, 1999, 21(3):217-222. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-0446.1999.03.010QIAO B, WU H T, ZHU J Y, et al.Hybrid force position control for position-controlled robotic manipulators[J].Robot, 1999, 21(3):217-222(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-0446.1999.03.010 [25] SERAJI H, COLBAUGH R.Force tracking in impedance control[C]//IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1993: 409-506. [26] 李二超, 李战明.基于力/力矩信息的面向位控机器人的阻抗控制[J].控制与决策, 2016, 31(5):957-960.LI E C, LI Z M.Impedance control for positional-controlled robotic manipulators based on force/torque information[J].Control and Decision, 2016, 31(5):957-960(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: