Non-cooperative UAV target recognition in low-altitude airspace based on motion model
-
摘要:
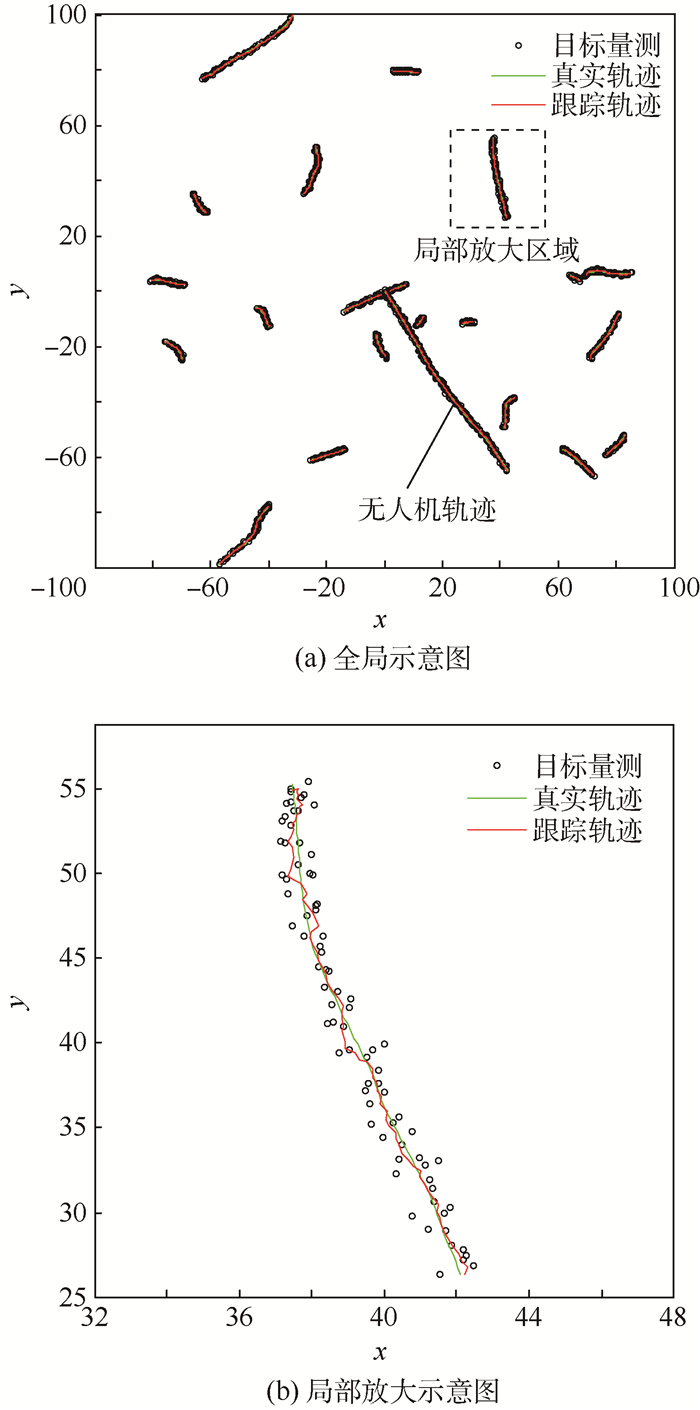
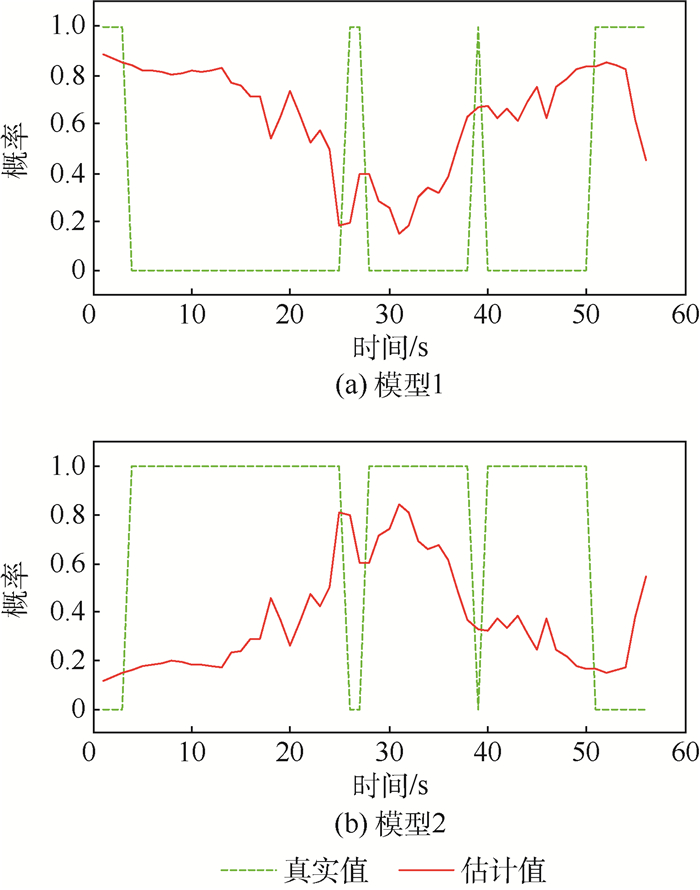
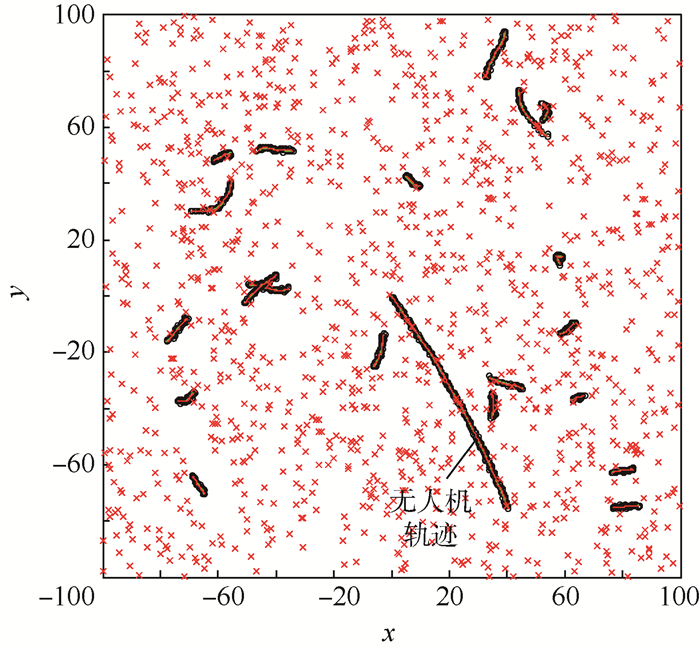
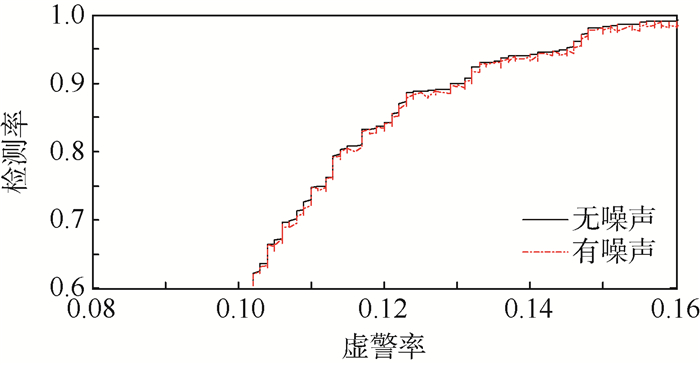
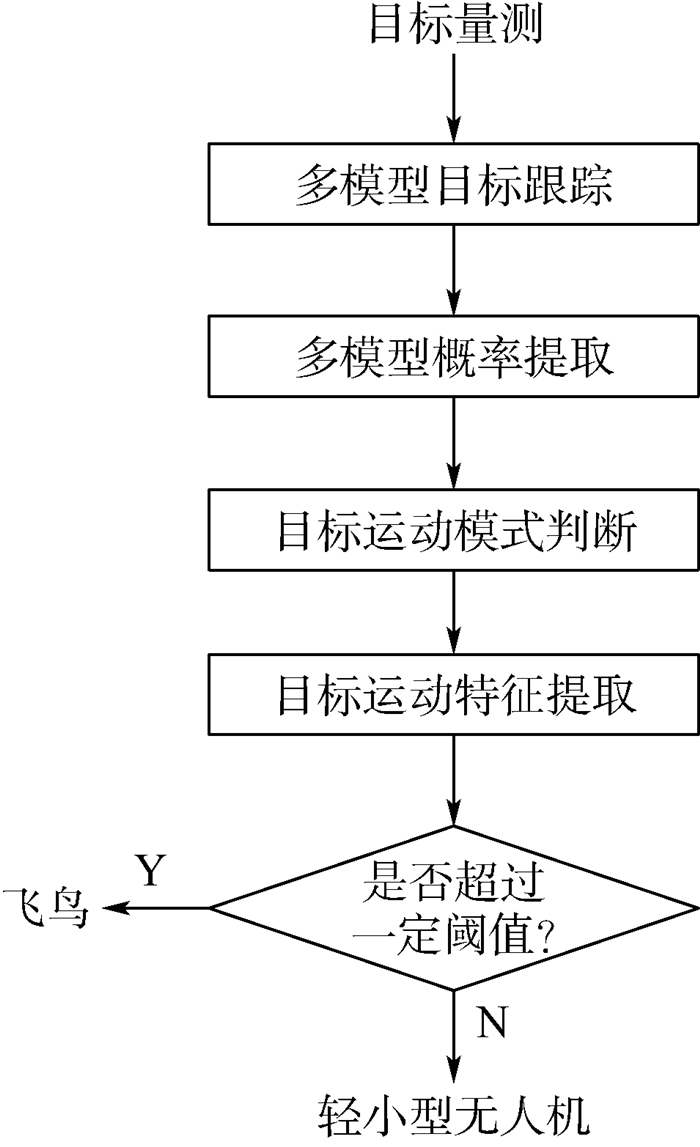
为保障低空安全,在利用雷达数据探测无人机目标的同时剔除飞鸟等虚警信息,提出了一种基于运动模型的低空非合作无人机目标识别方法,作为已有目标跟踪方法应用的拓展。首先,建立多种运动模型模拟无人机和飞鸟目标运动;然后,基于多种运动模型进行目标跟踪,并估计各种运动模型的出现概率;最后,以各种运动模型在连续时间内出现概率的方差均值来度量目标运动模型的转换频率。通过对仿真数据和机场低空监视雷达实测数据的处理,所提方法能够在杂波环境中跟踪无人机目标并剔除飞鸟目标,进一步验证了其有效性和实用性。
Abstract:To guarantee the safety of low-altitude airspace, a target recognition method based on motion model was proposed for the non-cooperative UAV target in low-altitude airspace, as an extension of the application of the existing target tracking algorithm, which could detect the UAV and reject the false alarms such as flying birds with radar data. Firstly, multiple motion models were established to simulate the movement of UAV and flying bird targets. Secondly, the targets were tracked with multiple motion models and the appearance probabilities of these models were estimated. Thirdly, the transformation frequency between target motion models was measured by the mean variance of the appearance probabilities of multiple models in continuous time domain. By processing the simulation data and the measured data of the airport low-altitude surveillance radar, the method can track the UAV target in cluttered environment and eliminate the flying bird target, further verifying its effectiveness and practicability.
-
Key words:
- motion model /
- UAV /
- target /
- recognition /
- radar
-
表 1 无人机与飞鸟目标的F均值
Table 1. Mean value of F of UAV and flying bird targets
无人机 飞鸟 p=0.2 p=0.3 p=0.4 p=0.5 0.005 9 0.044 7 0.051 1 0.059 4 0.062 5 表 2 无人机目标识别结果
Table 2. UAV target recognition results
S 无人机目标 其他低空目标 0.005 1 0 0.01 1 2 0.02 1 2 0.03 1 5 0.04 1 6 0.05 1 7 0.06 1 10 0.07 1 11 0.08 1 12 0.09 1 14 -
[1] 陈唯实.轻小型无人机监管、探测与干扰技术[J].中国民用航空, 2017, 253(7):33-34.CHEN W S.The supervision, detection and jamming technologies for light and small UAV[J].China Civil Aviation, 2017, 253(7):33-34(in Chinese). [2] 吕信明.军用无人机的发展及对策[J].国防科技, 2013, 34(1):5-7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4547.2013.01.002LV X M.Military UAV development and countermeasures[J].National Defense Science & Technology, 2013, 34(1):5-7(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-4547.2013.01.002 [3] 陈超帅, 王世勇.大疆无人机目标红外辐射特性测量及温度反演[J].光电工程, 2017, 44(4):427-434. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.007CHEN C S, WANG S Y.Infrared radiation characteristics mea-surement and temperature retrieval based on DJI unmanned aerial vehicle[J].Opto-Electronic Engineering, 2017, 44(4):427-434(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-501X.2017.04.007 [4] 罗德与施瓦茨(中国)科技有限公司.无人机自动识别、定位和压制系统(一)[J].中国无线电, 2016(8):72-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.08.047Rohde & Schwarz.Automatic identification, positioning and suppression system of UAV (Ⅰ)[J].China Radio, 2016(8):72-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.08.047 [5] 罗德与施瓦茨(中国)科技有限公司.无人机自动识别、定位和压制系统(二)[J].中国无线电, 2016(9):71-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.09.045Rohde & Schwarz.Automatic identification, positioning and suppression system of UAV (Ⅱ)[J].China Radio, 2016(9):71-72(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.09.045 [6] 罗德与施瓦茨(中国)科技有限公司.无人机自动识别、定位和压制系统(三)[J].中国无线电, 2016(10):72-73. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.10.044Rohde & Schwarz.Automatic identification, positioning and suppression system of UAV (Ⅲ)[J].China Radio, 2016(10):72-73(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2016.10.044 [7] 吕冰, 王爱举, 马妍, 等.无线电技术在民用无人机管控中的应用[J].中国无线电, 2017(8):24-26. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2017.08.022LV B, WANG A J, MA Y, et al.Radio technology application in civil UAV control[J].China Radio, 2017(8):24-26(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7797.2017.08.022 [8] 陈唯实, 闫军, 李敬.基于Rao-Blackwellized蒙特卡罗数据关联的检测跟踪联合优化[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(4):700-708.CHEN W S, YAN J, LI J.Joint optimization of detection and tracking with Rao-Blackwellized Monte Carlo data association[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(4):700-708(in Chinese). [9] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等.雷达低可观测目标探测技术[J].科技导报, 2017, 35(11):30-38.CHEN X L, GUAN J, HUANG Y, et al.Radar low-observable target detection[J].Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(11):30-38(in Chinese). [10] 陈小龙, 关键, 黄勇, 等.雷达低可观测动目标精细化处理及应用[J].科技导报, 2017, 35(20):19-27.CHEN X L, GUAN J, HUANG Y, et al.Radar refined processing and its applications for low-observable moving target[J].Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(20):19-27(in Chinese). [11] ZHANG J, XU Q Y, CAO X B, et al.Hierarchical incorporation of shape and shape dynamics for flying bird detection[J].Neurocomputing, 2014, 131(5):179-190. [12] BAI X R, XING M D, ZHOU F, et al.Imaging micromotion targets with rotating parts based on empirical-mode decomposition[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(11):3514-3523. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2008.2002322 [13] STANKOVIC L, THAYAPARAN T, DAKOVIC M, et al.Micro-Doppler removal in the radar imaging analysis[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2013, 49(2):1234-1250. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2013.6494410 [14] ZHANG Q, YEO T S, TAN H S, et al.Imaging of a moving target with rotating parts based on the Hough transform[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2008, 46(1):291-299. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.907105 [15] 张群, 何其芳, 罗迎.基于贝塞尔函数基信号分解的微动群目标特征提取方法[J].电子与信息学报, 2016, 38(12):3056-3062.ZHANG Q, HE Q F, LUO Y.Micro-Doppler feature extraction of group targets using signal decomposition based on Bessel function basis[J].Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38(12):3056-3062(in Chinese). [16] 张群, 罗迎.雷达目标微多普勒效应[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2013:22-30.ZHANG Q, LUO Y.Micro-Doppler effect of radar targets[M].Beijing:National Defense Industry Press, 2013:22-30(in Chinese). [17] 陈唯实, 李敬.基于空域特性的低空空域雷达目标检测[J].航空学报, 2015, 36(9):3060-3068.CHEN W S, LI J.Radar target detection in low-altitude airspace with spatial features[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(9):3060-3068(in Chinese). [18] 陈唯实.基于时域特性的非相参雷达目标检测与跟踪[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2016, 38(8):1800-1807.CHEN W S.Incoherent radar target detection and tracking with temporal features[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(8):1800-1807(in Chinese). [19] CHEN W S.Spatial and temporal features selection for low-altitude target detection[J].Aerospace Science and Technology, 2015, 40(1):171-180. [20] 陈唯实, 李敬.雷达探鸟技术发展与应用综述[J].现代雷达, 2017, 39(2):7-17.CHEN W S, LI J.Review on developments and applications of avian radar technology[J].Modern Radar, 2017, 39(2):7-17(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: