-
摘要:
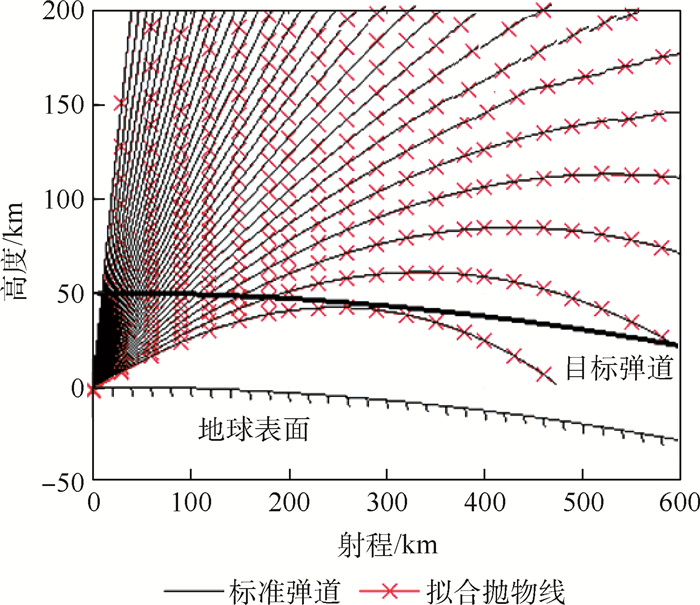
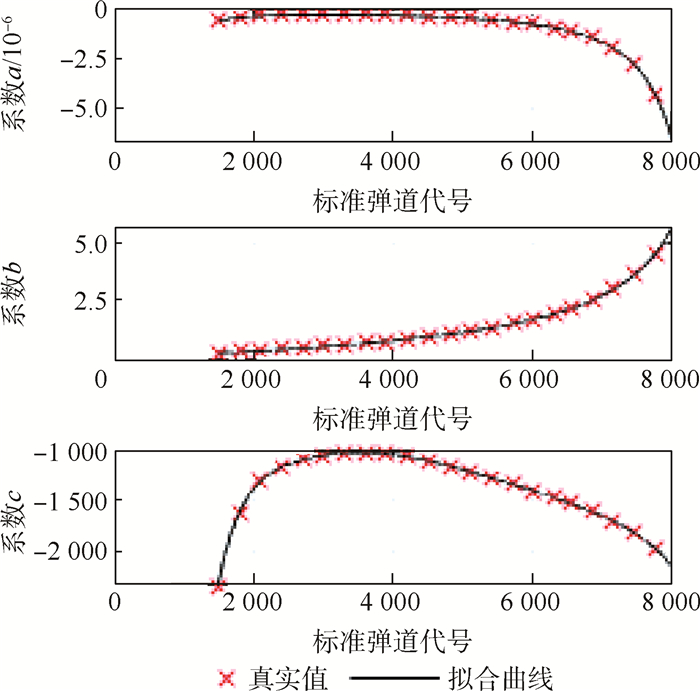
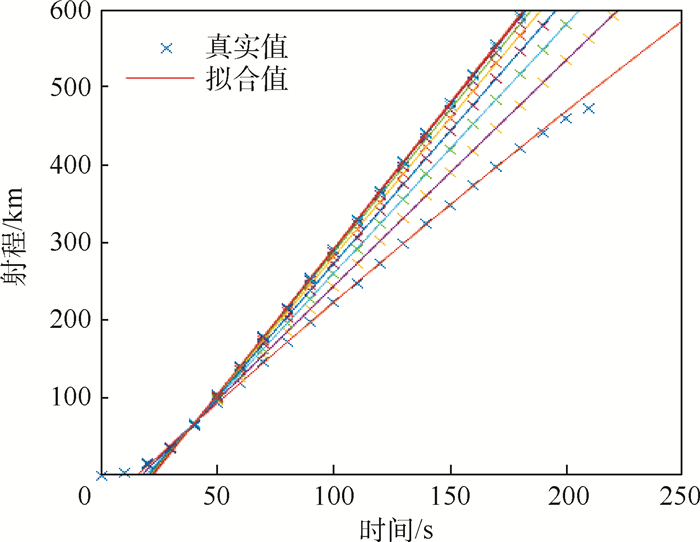
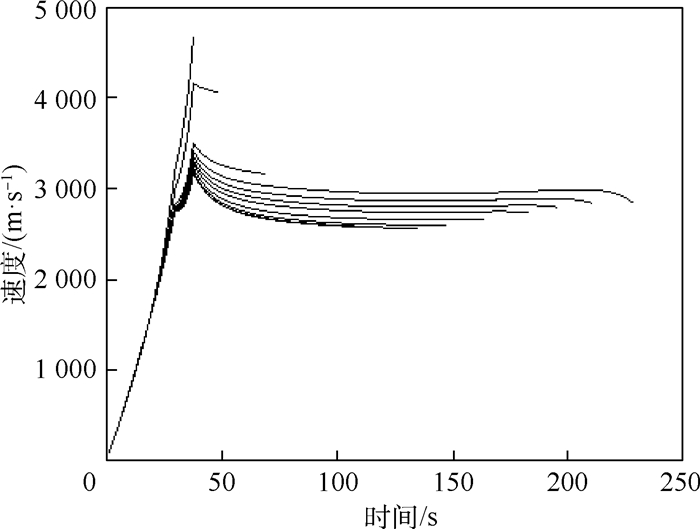
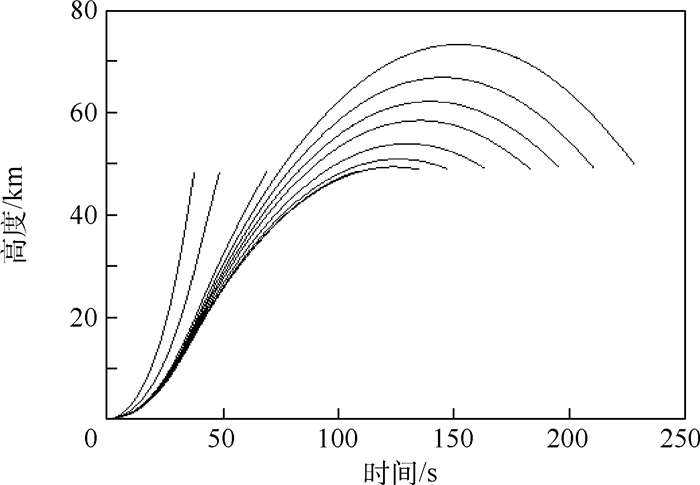
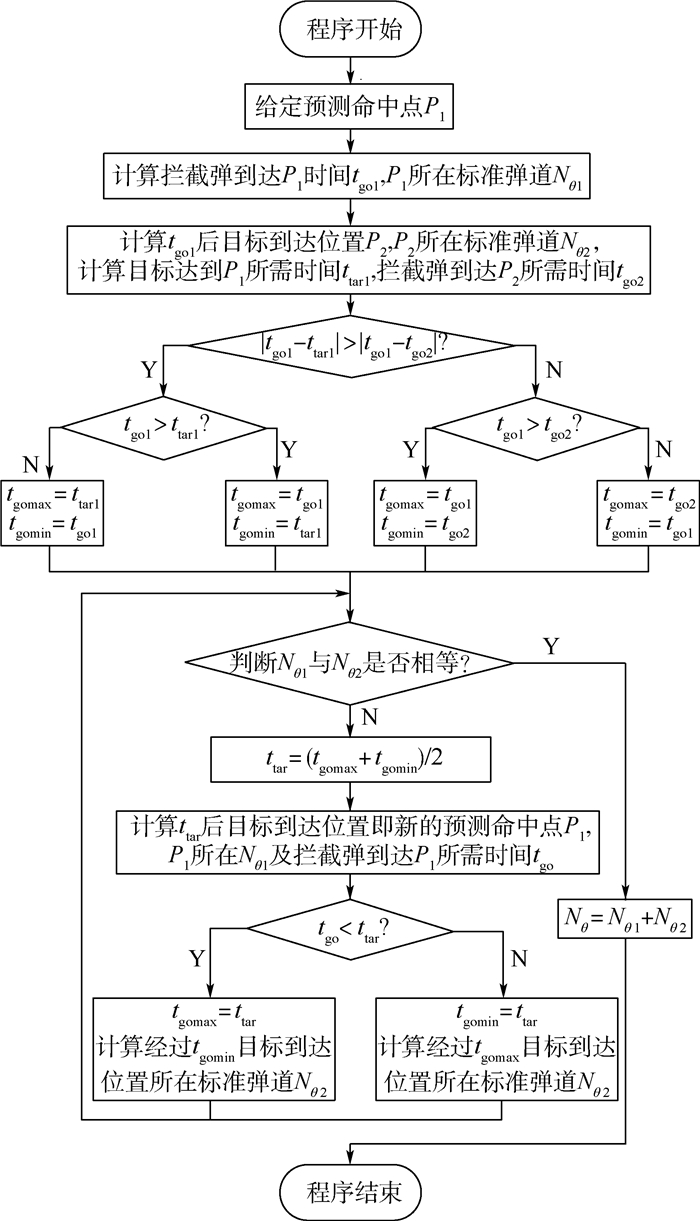
根据公开资料对THAAD增程型拦截弹建模,针对大射程的特点规划了高抛弹道,生成标准弹道族。提出了迭代预测命中点法,利用解析方法计算剩余飞行时间,基于多项式拟合法寻找标准弹道,确定预测命中点,完成预测制导任务。将迭代预测命中点法与迭代飞行时间法进行对比,迭代预测命中点法初值选取容易,程序运行时间减少20%,制导过程中无需调用标准弹道文件,节省了计算机存储空间。通过改变射程、航路捷径对预测制导方法进行仿真验证,结果表明,拦截弹拦截射程可覆盖到600 km,并且能完成存在航路捷径时的拦截任务,平均脱靶量在200 m以内,应对气动不确定性的效果良好。
-
关键词:
- THAAD增程型拦截弹 /
- 预测制导 /
- 标准弹道族 /
- 预测命中点 /
- 剩余飞行时间
Abstract:Based on public information, the model of THAAD-ER interceptor was established. Aimed at longer range, the high throw trajectory was planned, and a bunch of standard trajectories were produced. Predicted impact point iterated method is proposed, which contains solving time-to-go with analytic solution, seeking out the expected standard trajectory with polynomial fitting, and ascertaining the predictive impact point, and finally predictive guidance completes. Comparison is taken between predicted impact point iterated method and flight time iterated method, and it is easy to choose initial value with predicted impact point iterated method, and the program runtime decreases by 20%; standard trajectory files are not necessary during guidance process, which can save storage space of the computer on the interceptor. Large amount of simulations were carried out with different range and course shortcut, and the results show that interception range of THAAD-ER interceptor can reach 600 km, and the interception task can be completed with average miss distance less than 200 m when course shortcut remains. It has a good response to aerodynamic uncertainty.
-
表 1 助推器参数
Table 1. Parameters of boosters
级数 质量/kg 推力/kN 燃烧时间/s 1 860 80 30 2 170 30 8 表 2 程序运行时间对比
Table 2. Program run time comparison
仿真次数 设定迭代飞行时间法运行时间/s 设定迭代飞行时间法脱靶量/m 设定预测命中点法运行时间/s 设定预测命中点法脱靶量/m 运行时间节省比例/% 脱靶量减少比例/% 1 28.72 96.89 23.21 16.21 19.19 83.27 2 29.17 293.83 23.29 83.85 20.16 71.46 3 29.22 79.10 23.39 79.10 19.95 0 4 29.14 296.38 22.90 174.68 21.41 41.06 5 29.32 99.86 22.45 79.49 23.43 20.40 6 29.03 178.72 23.26 199.82 19.88 -11.81 7 28.88 251.91 23.12 311.36 19.94 -23.60 表 3 不同射程拦截仿真结果
Table 3. Simulation results of interception with different ranges
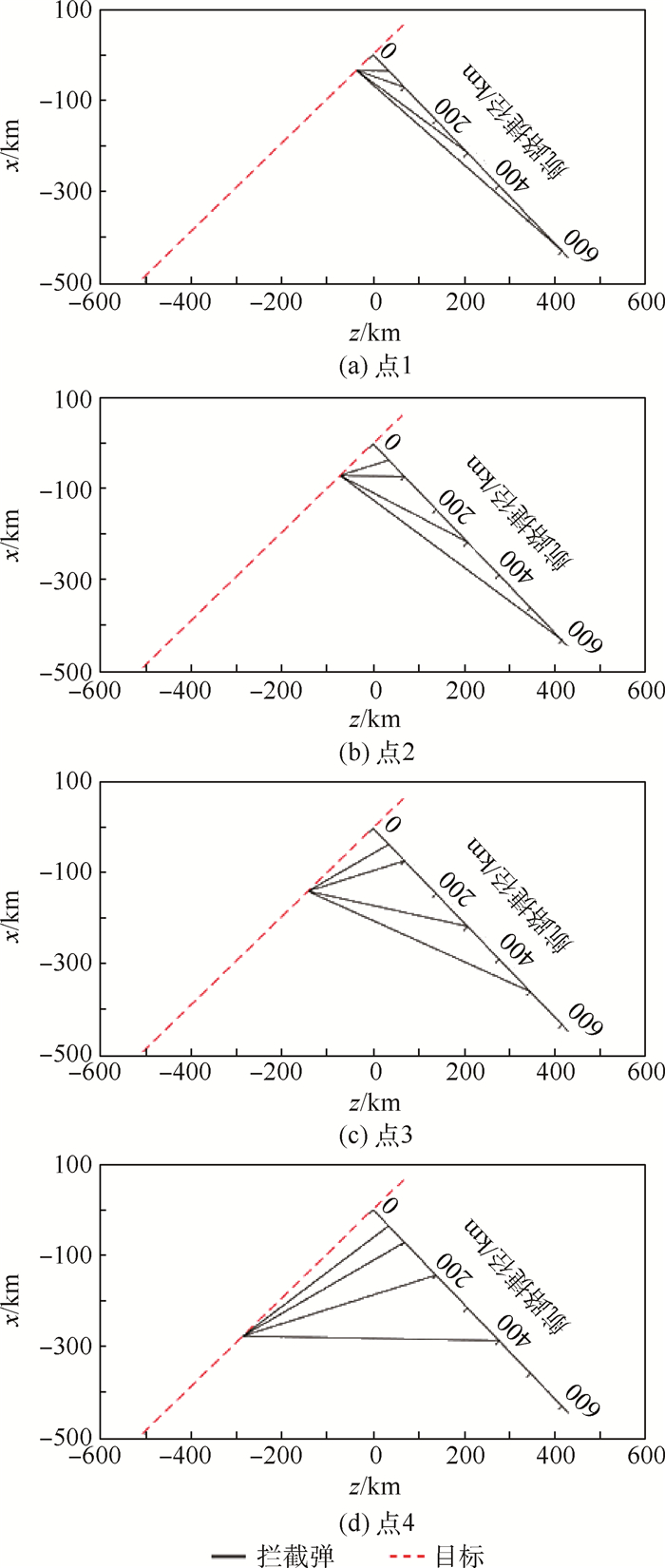
设定的预测命中点 射程/km 脱靶量/m 终点 拦截点偏移/m 末速度/ (m·s-1) x坐标/m y坐标/m z坐标/m x坐标/m y坐标/m z坐标/m -34 862 48 202 -35 956 50.09 15.79 -34 870 48 188 -35 965 19 4 686.31 -69 770 47 692 -71 961 100.02 19.06 -69 626 47 677 -71 812 208 4 066.02 -110 274 46 608 -113 736 158.42 28.24 -110 274 46 636 -113 736 29 3 164.37 -138 417 45 542 -142 763 198.54 36.85 -138 200 45 514 -142 540 312 2 781.90 -173 091 43 878 -178 526 248.31 81.13 -172 846 43 810 -178 273 359 2 587.59 -218 956 41 080 -225 831 314.38 23.63 -218 838 41 112 -225 709 173 2 566.10 -243 346 39 316 -250 987 349.59 63.27 -243 350 39 379 -250 991 63 2 598.21 -277 268 36 542 -285 973 398.33 86.28 -277 275 36 628 -285 981 86 2 660.54 -320 014 32 516 -330 062 460.45 194.60 -320 514 32 270 -330 577 759 2 740.87 -349 067 29 441 -360 027 502.05 199.82 -349 473 29 596 -360 446 604 2 796.76 -386 483 25 077 -398 618 554.99 1.57 -386 325 25 095 -398 455 228 2 838.07 -432 395 19 101 -445 971 620.12 385.45 -431 661 19 588 -445 214 1 161 2 834.60 表 4 设定的预测命中点坐标
Table 4. Expected predicted impact point coordinate
序号 x/m y/m z/m 1 -34 862 48 202 -35 956 2 -69 770 47 692 -71 961 3 -138 417 45 542 -142 763 4 -277 268 36 542 -285 973 表 5 存在航路捷径时的脱靶量
Table 5. Miss distance with course shortcut
航路捷径/km 脱靶量/m 点1 点2 点3 点4 0 3.64 19.06 36.85 86.28 50 6.05 4.85 33.76 118.10 100 36.12 82.94 24.95 134.39 150 178.31 75.37 33.20 258.81 200 87.18 124.92 71.07 449.50 250 55.86 42.33 127.59 415.55 300 37.56 52.74 153.13 326.55 350 95.33 104.96 217.85 135.17 400 180.90 191.41 353.20 128.68 450 260.17 230.11 225.70 500 260.78 168.21 109.11 550 125.82 103.70 167.82 600 319.18 377.57 表 6 不确定性仿真结果
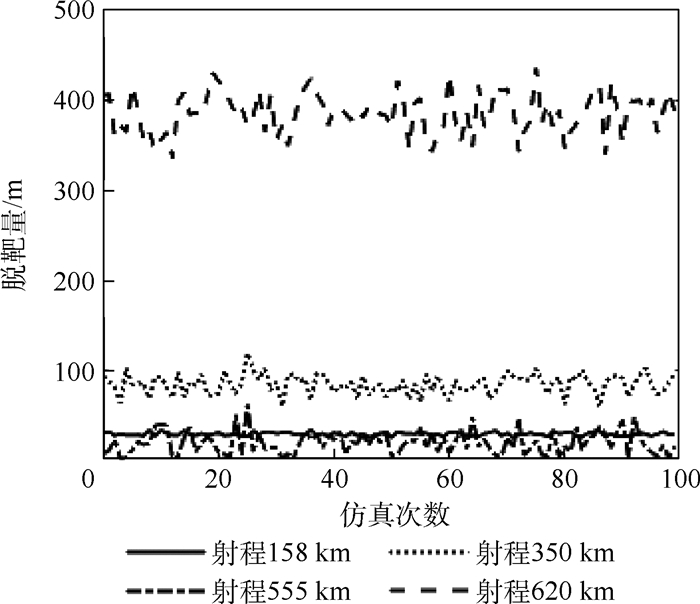
Table 6. Uncertainty simulation results
射程/km 无噪声脱靶量/m 有噪声平均脱靶量/m 有噪声脱靶量标准差/m 平均飞行时间/s 有噪声脱靶量最大值/m 158.42 28.24 27.94 2.08 69.73 32.66 349.59 63.27 83.21 11.25 147.65 118.10 554.99 1.57 18.04 13.02 210.51 60.86 620.12 385.45 384.89 23.31 228.39 435.42 -
[1] ZARCHAN P.Tactical and strategic missile guidance[M]. 6th ed. Reston: AIAA, 2012. [2] KUMAR P, DWIVEDI P N, BHATTACHARYA A, et al. Variable gain predictive PN guidance for interception of high speed re-entry targets[J]. IFAC-PapersOnLine, 2018, 51(1): 64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ifacol.2018.05.012 [3] 李辕, 赵继广, 白国玉, 等. 基于预测碰撞点的剩余飞行时间估计方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(8): 1667-1674. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0509LI Y, ZHAO J G, BAI G Y, et al. Method of time-to-go estimation based on predicted crack point[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(8): 1667-1674(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0509 [4] 李辕, 闫梁, 赵继广, 等. 顺轨拦截模式剩余飞行时间估计方法[J]. 航空学报, 2015, 36(9): 3082-3091.LI Y, YAN L, ZHAO J G, et al. The method of time-to-go estimation for head-pursuit engagement[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2015, 36(9): 3082-3091(in Chinese). [5] DHANANJAY N, GHOSE D.Accurate time-to-go estimation for proportional navigation guidance[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2014, 37(4): 1378-1383. doi: 10.2514/1.G000082 [6] GHOSH S, GHOSE D, RAHA S.Unified time-to-go algorithms for proportional navigation class of guidance[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2016, 39(6): 1-18. [7] GRUBIN C, SHULTZ P, SOUFL R.A boost guidance scheme for following a trajectory profile and satisfying injection constraints[C]//Astrodynamics Guidance and Control Conference, 1964: 639. [8] SALAMA M, HANCOCK G, SHOUMAN A.The predicted interception guidance method[C]//25th AIAA Aerospace Sciences Meeting.Reston: AIAA, 1987: 126. [9] 张华伟, 董茜, 王文灿, 等. 基于预测命中点的反弹道导弹拦截方法研究[J]. 弹箭与制导学报, 2007, 27(2): 196-199. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2007.02.062ZHANG H W, DONG Q, WANG W C, et al. Rearch way of intercepting ballistic missile based on the forecasting hitting position[J]. Journal of Projectiles Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2007, 27(2): 196-199(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2007.02.062 [10] ZHANG X, LEI H M, LI J, et al.Ballistic missile trajectory prediction and the solution algorithms for impact point prediction[C]//Proceedings of 2014 IEEE Chinese Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 879-883. [11] ZHAO Y T, HU Y A, ZHANG Y A.Design and simulation of an optimal guidance law for ship-air missile based on interception point prediction[C]//2011 Chinese Control and Decision Conference (CCDC).Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 3647-3652. [12] HAHN P V, FREDERICK R A, SLEGERS N.Predictive guidance of a projectile for hit-to-kill interception[J]. IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2009, 17(4): 745-755. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2008.2004440 [13] DWIVEDI P N, BHALE P G, BHATTACHARYYA A, et al. Generalized state estimation and model predictive guidance for spiraling and ballistic targets[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2014, 37(1): 243-264. doi: 10.2514/1.60075 [14] SONG E J, TAHK M J.Real-time midcourse guidance with intercept point prediction[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 1998, 6(8): 957-967. doi: 10.1016/S0967-0661(98)00041-0 [15] ZHANG J, YOU L Q, CHEN W C.Boost-phase guidance with neural network for interception of ballistic missile[C]//International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 426-431. [16] 陈万春. 一种基于多项式拟合法的拦截弹预测制导方法:CN107766967A[P].2018-03-06.CHEN W C.A predictive guidance law of interceptor based on polynomial fitting method: CN107766967A[P].2018-03-06(in Chinese). [17] 尤刘球. 动能拦截弹目标信息估计与预测制导方法研究[D]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2017: 1-2.YOU L Q.Research on target information estimation and predictive guidance[D].Beijing: Beihang University, 2017: 1-2(in Chinese). [18] 韩英宏, 雷延花, 梁卓, 等. 带侧窗动能杀伤器直接力姿态控制[J]. 航天控制, 2015, 33(4): 51-55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2015.04.009HAN Y H, LEI Y H, LIANG Z, et al. Direct force attitude control of kinetic kill vehicle with side window[J]. Aerospace Control, 2015, 33(4): 51-55(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3242.2015.04.009 [19] 谢经纬, 陈万春. 大气层外拦截弹建模与攻防效能分析[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(9): 1826-1838. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0095XIE J W, CHEN W C.Modeling of exo-atmospheric interceptor and effectiveness analysis for penetration and defense[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(9): 1826-1838(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0095 [20] 盛永智, 陈万春, 孟璇. 反导预测拦截及防御问题研究[C]//2005中国飞行力学学术年会, 2005: 110-115.SHENG Y Z, CHEN W C, MENG X.Research on predictive interception and defense of antimissile[C]//2005 Proceedings of China Annual Conference on Flight Mechanics, 2005: 110-115(in Chinese). [21] 李静琳, 陈万春, 闵昌万. 高超末段机动突防/精确打击弹道建模与优化[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(3): 555-567. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0308LI J L, CHEN W C, MIN C W.Terminal hypersonic trajectory modeling and optimization for maneuvering penetration and precision strike[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(3): 555-567(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0308 [22] 周慧钟, 李忠应, 王瑾枚. 有翼导弹飞行动力学[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 1983: 46-47.ZHOU H Z, LI Z Y, WANG J M.Flight dynamics of winged missiles[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 1983: 46-47(in Chinese). [23] 陈桂秀. 用程序求解最小二乘拟合多项式的系数[J]. 青海师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 26(3): 14-17. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7542.2010.03.004CHEN G X.Solve the least square curve fitting polynomial coefficient with program[J]. Journal of Qinghai Normal University(Natural Science Edition), 2010, 26(3): 14-17(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7542.2010.03.004 [24] 刘瑶, 张占月, 黄梓辰, 等. 基于拦截纵深的中段反导武器部署研究[J]. 指挥与控制学报, 2017, 3(2): 119-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2017.02.0119LIU Y, ZHANG Z Y, HUANG Z C, et al. Deployment of midcourse anti-missile weapon based on intercepting depth[J]. Journal of Command and Control, 2017, 3(2): 119-126(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2096-0204.2017.02.0119 [25] 刘芳, 陈万春. PAC-3拦截弹六自由度反导建模与拦截仿真分析[J]. 飞行力学, 2012, 30(5): 440-443.LIU F, CHEN W C.PAC-3 interceptor 6DOF antimissile modeling and intercept simulation analysis[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2012, 30(5): 440-443(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(7)
1. 陈万春,陈中原,龚晓鹏. 智能机动突防策略研究进展. 飞行力学. 2024(05): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 郑佳,陈万春,于琦. 导弹通用模型架构数字配装及参数灵敏度分析. 飞行力学. 2024(05): 83-88 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 李加申,王晓芳,林海. 引入虚拟目标的高超声速巡航导弹智能机动突防策略. 兵工学报. 2024(11): 3856-3867 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 王鹏,赵石磊,陈万春. 基于可达区在线预测的GPI中制导协同拦截策略. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2024(11): 3463-3476 .  本站查看
本站查看5. 宫志华,刘洋,段鹏伟,陈春江. 基于两种基函数表征的外弹道数据融合方法比较分析. 弹道学报. 2024(04): 97-103 .  百度学术
百度学术6. 李雅轩,王研,刘新福. 面向弹道导弹防御的快速最优拦截弹道规划. 宇航学报. 2024(12): 1931-1943 .  百度学术
百度学术7. 周聪,闫晓东,唐硕,吕石. 大气层内模型预测静态规划拦截中制导. 航空学报. 2021(11): 246-261 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-







 下载:
下载:











 百度学术
百度学术

