-
摘要:
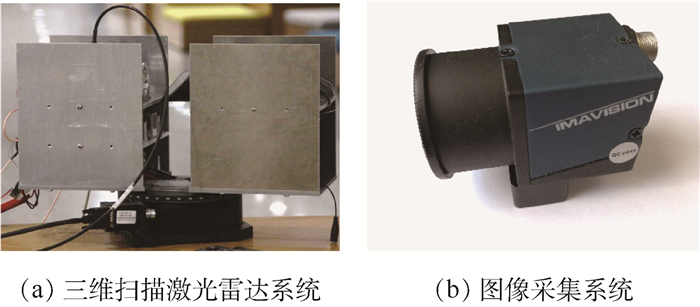
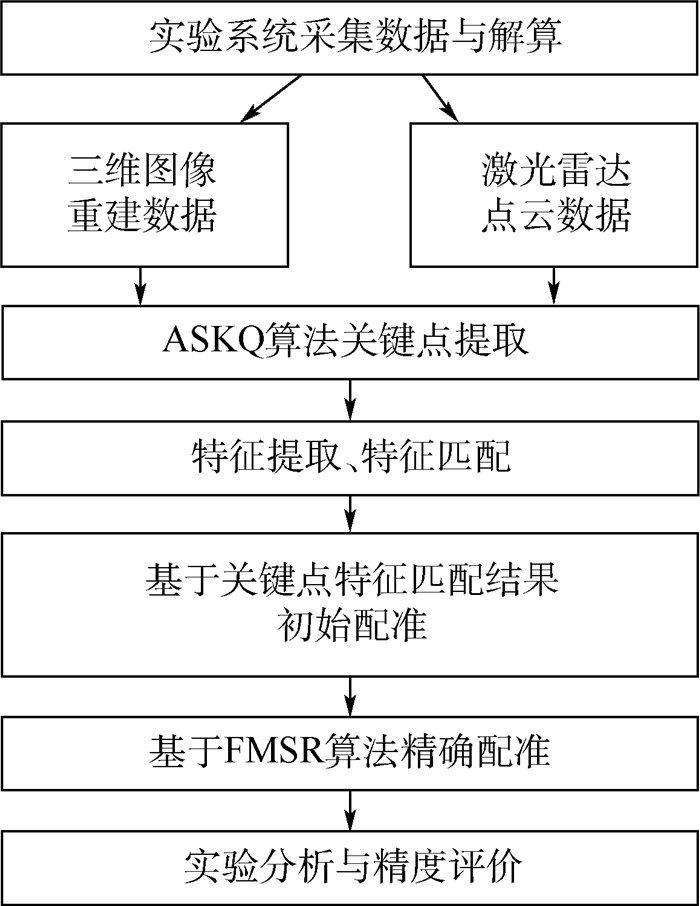
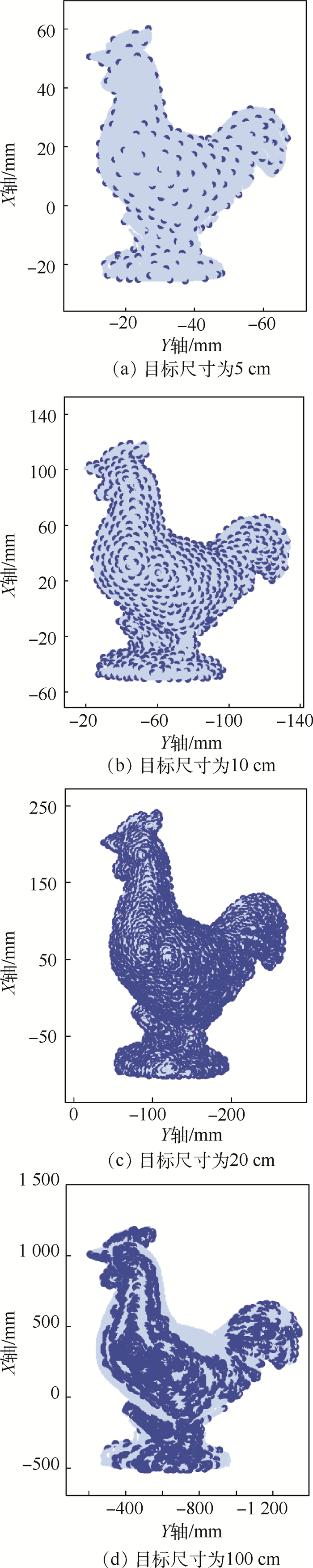
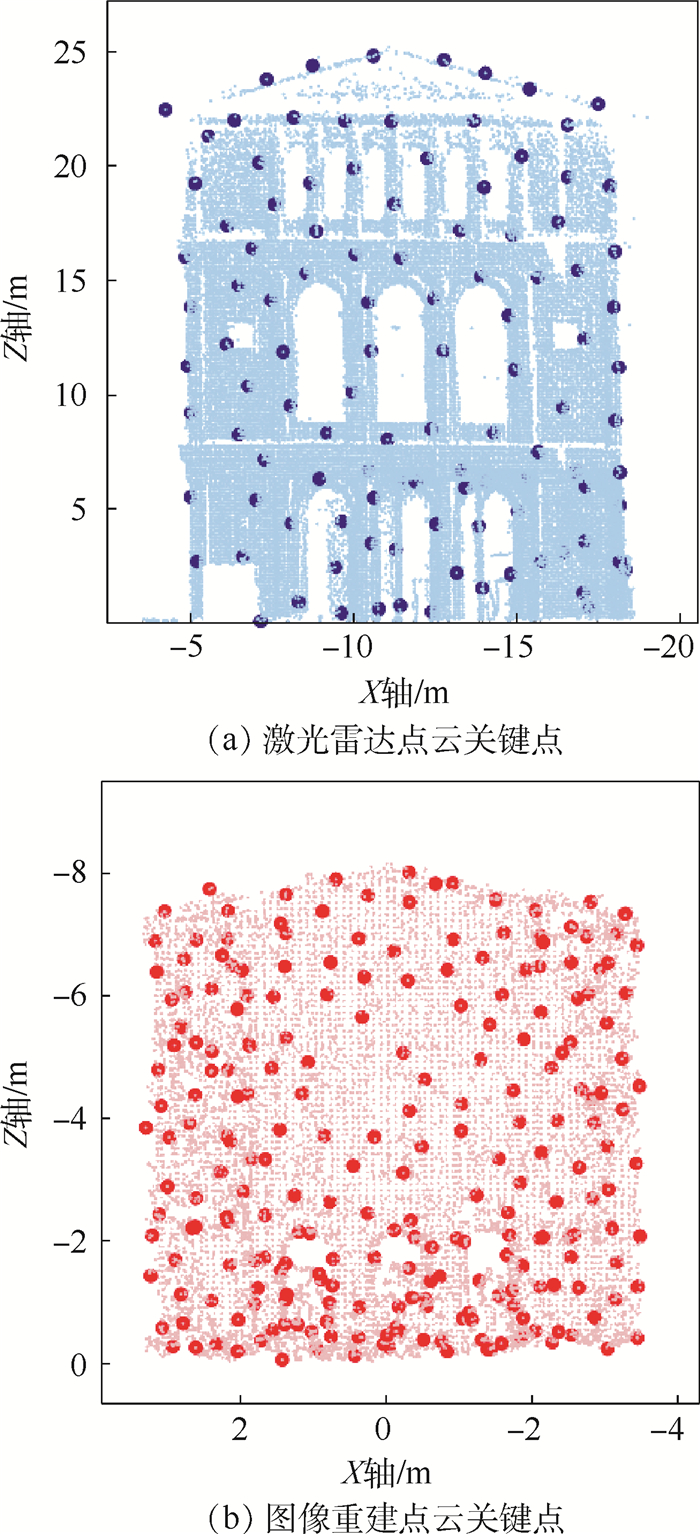
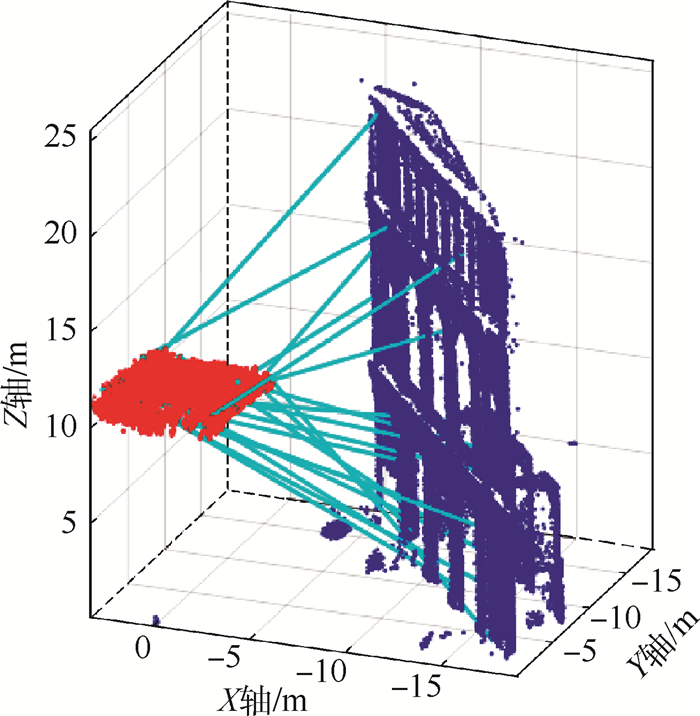
为了实现激光雷达点云与图像重建点云的三维空间配准,基于自研三维扫描激光雷达系统,提出了新型的快速多尺度因子(FMSR)点云配准算法,研究了空间点云配准技术。该算法主要包括初始配准和精确配准2个步骤:初始配准使用基于尺度自适应关键点质量(ASKQ)的点云特征提取算法,提取关键点的特征匹配对,求解点云配准初始参数;精确配准利用K-邻近(KNN)算法全局搜索,提升计算效率,多次迭代得到2组点云之间的最优旋转矩阵、最优平移向量和最优尺度因子。仿真和实验结果表明,所提出的算法对空间目标(尺寸为20.30 m×7.85 m×26.56 m)实现空间点云配准,配准精度达到0.194 m,运行时间为16.207 s;与多尺度迭代最近点(S-ICP)算法相比,配准精度提高了0.131 m,运行时间提高了30%。所提出的空间点云配准技术可为场景重建和纹理匹配提供算法基础。
-
关键词:
- 激光雷达 /
- 图像重建 /
- 空间点云配准 /
- 尺度自适应关键点质量(ASKQ)算法 /
- 快速多尺度因子(FMSR)点云配准算法
Abstract:In order to realize the registration of point cloud data respectively obtained from LiDAR and camera, we used a fast multi-scale registration (FMSR) algorithm to register the point cloud data, based on a self-designed three-dimensional scanning laser radar system in our laboratory. The algorithm includes two steps:coarse registration and fine registration. In the coarse registration, an adaptive scale key point quality (ASKQ) algorithm was used to match key points and determine the initial parameters for fine registration. And in the fine registration, K-nearest neighbors (KNN) algorithm was used to simplify the search process and improve the algorithm efficiency. The optimal rotation matrix, translation vector and scale factor between two sets of point cloud data were obtained through many iterations. The simulation verified the stability of FMSR algorithm for multiscale registration. Simulation and experimental results show that the proposed algorithm successfully registers the point cloud data of the self-made LiDAR system and commercial camera. The root-mean-square error of the registration is 0.194 m and the execution time is 16.207 s, for a building with size of 20.30 m×7.85 m×26.56 m. Compared with an existing scale-iterative closest point (S-ICP) algorithm, the registration accuracy of the proposed algorithm is improved by 0.131 m, and the execution time is reduced by 30%. The proposed point cloud registration method can provide an algorithm basis for scene reconstruction and texture matching.
-
当前通信网络业务呈现多元化的发展趋势,视频会议、远程教学、网络电视等组播业务快速增长。作为构建网络通信重要设施的交换机,其能否有效支持单播、组播混合调度将直接影响着整个网络通信的传输效率和通过量。
就交换结构而言,输出排队(Output Queuing,OQ)结构有N(输入输出端口数目)倍加速比的需求,在构建高速大容量网络中,可扩展性较差。而输入排队(Input Queuing,IQ)结构加速比为1,具有良好的可扩展性[1]。IQ结构研究最多的是虚拟输出排队(Virtual Output Queuing,VOQ)结构,但其输入输出竞争紧密耦合的集中式调度特性使得控制过程较为复杂[2]。而IQ结构中最新研究的联合输入交叉队列(Combined Input and Crossbar Queued,CICQ)结构通过在交换矩阵的每个交叉节点配置一定容量的缓存,很大程度解耦了输入输出竞争的裁决,简化了整个调度过程,使得分布式调度成为可能。
在CICQ结构的研究中,早期主要研究单播业务的调度[3-5],文献[4]提出的SBF-GWF(the Shortest Buffer First and the Greatest Weigh buffer First) 性能较为突出。随着组播应用的需求,研究提出了一系列的组播调度算法[6-9],主要分为基于轮询(Round Robin,RR)的算法[6-7]和以队长或排队时间为权重的最大权重匹配法[8-9],文献[9]中提出的MF-MRSF(Maxfanout First and Maximum Ratio of Service First)是目前性能较好的组播算法。另外,部分研究讨论了单组播混合业务[10-15]的调度,但大部分是通过在交换结构上隔离单组播业务,使单组播业务在调度中仍然按照各自相对独立的算法进行处理[11-13]。
Mhamdi和Vassiliadis首次提出一种CICQ结构中单组播业务统一调度的算法——MURS(Multicast and Unicast Round robin Scheduling)[14],该算法基于轮询策略,虽然复杂度低,但性能较差。文献[15]通过分析单组播业务差别,提出一种最大权重匹配算法——LCMS (Low-Cost Multicast Scheduling)。该算法的性能比MURS算法有所提升,但与OQ结构中先入先出(First In First Out,FIFO)算法相比,仍有巨大的差距。其主要原因是OQ 结构中交换机始终处于工作保持(Work-Conserving)状态,保证了100%的通过率,进而降低了分组时延。另一方面,LCMS算法未充分考虑组播业务在调度过程中的状态及CICQ输入输出调度之间的关系。
因此,本文首次在单组播混合调度中,以使交换机尽量工作于Work-Conserving状态为目标,结合组播业务在调度过程中的状态特征及CICQ结构中输入输出调度之间的相互影响关系,提出一种新的单组播混合调度算法,即单组播交叉缓存均衡(Multicast and Unicast Crossbuffer Balance,MUCB)算法,仿真显示其性能明显优于现有主流算法。
本文结构安排如下:第1节对CICQ结构中单组播混合调度中的主要问题进行了分析;第2节具体给出了MUCB算法;第3节对MUCB算法和当前主流的单组播混合调度算法进行了仿真比较和分析;最后对本文进行了总结并指出今后研究工作的方向。
1. 问题分析
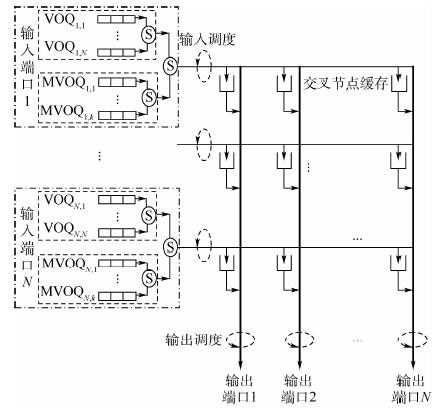
图 1为CICQ交换结构示意图。假定当前时隙输入调度后进入交叉缓存的分组,最早在下个时隙进行输出调度,故一次调度指当前时隙的输入调度和其下一个时隙的输出调度。基于CICQ结构和调度过程,单组播混合业务调度需要考虑到以下问题。
1) 组播队头阻塞问题:克服组播队头阻塞需要在每个输入端口设置2N-1个虚拟组播队列,这在实际应用中难以实现,尤其是对大规模交换机而言。目前研究中普遍采用的方法是设置k(1<k<<2N-1)个虚拟组播队列,这虽然可以缓解组播队头阻塞,但无法彻底解决该问题。
2) 组播分组入队机制问题:k个组播队列无法包含所有组播分组可能的目的端口类型,到达的组播分组要按照一定算法进入虚拟组播队列。
3) 单播、组播竞争裁决问题:每个输入端口分别配置虚拟单播队列和虚拟组播队列,当该输入端口要传输分组到交叉缓存时,需要通过一定的裁决机制选取合适的头分组。
4) 交换机的Work-Conserving逼近问题:CICQ结构中单组播混合调度的Work-Conserving状态是指任意一次调度中,若所有输入端口队列中有分组去往某个输出端口,那么该次调度的输出调度中此输出端口必须有分组被调度离开交换机。
CICQ结构中输出调度与输入调度并非完全解耦,输出调度决定交叉缓存中的分组在当前时隙是否离开交换机,其影响输入调度时分组能否进入该交叉缓存,进而影响组播队头阻塞的程度。所以,降低头分组阻塞的一个有效手段是在输出调度中,尽量使可能出现队头阻塞的组播头分组的目的端口所对应交叉缓存中的分组优先被调度。
Modulo算法通过简单地对到达组播分组的扇出数求模[14],结果为该组播分组要进入的虚拟组播队列的编号。这种算法实现简单,是目前普遍采用的相对有效的组播入队方法。
单播分组若被选中,在一个时隙内就可完成输入调度或输出调度,组播分组若在一个时隙内其所有目的端口不能完全被匹配,则无法在该时隙内完全完成输入调度或输出调度。同时,组播队列机制没有克服头分组阻塞问题。因此在单组播混合调度中,组播业务的性能容易下降,对整体性能影响较大。但若在调度中完全优先组播调度,将导致单播、组播之间公平性下降,也会使单播性能严重下降进而影响总体性能。故而单播、组播竞争裁决时,需考虑单播、组播共有的参数及组播相较于单播特有的参数来权衡二者优先级进而提升调度总体性能。
由CICQ结构中Work-Conserving状态的定义可知,当输入端口中有去往每个输出端口的分组时,若输入调度后每列交叉缓存不为空,则在输出调度中,每个输出端口都有分组可被调度离开交换机,交换机便工作于Work-Conserving状态。在输入调度中,通过使得每列交叉缓存中分组的数目尽量相同,是一种有效的使交换机的工作状态逼近于Work-Conserving的方式。

(1) 式中:矩阵D表示输入端头分组中去往输出端口的数目,如D(1,1)=2表示输入端口1所有单组播队列的头分组中,有2个去往输出端口1;矩阵X表示交叉缓存状态,如X(1,1)=0表示交叉缓存(1,1)为空。
输入调度中,要使矩阵X所有列方向上1的数目相同,可优先让X矩阵中1的数目最少的列向量(矩阵D中与该列向量列坐标相同的列向量的模不为0)对应交叉缓存有分组进入。分析式(1)情形,当先选中第1列交叉缓存后,应选择目的端口数较少的输入端口2传输分组,则第2列交叉缓存仍可有输入端口1的分组进入,根据前述Work-Conserving定义,交换机达到Work-Conserving状态。若选择输入端口1,其在本时隙将传输去往第1列交叉缓存的分组,使第2列交叉缓存在本时隙无分组进入,交换机不能达到Work-Conserving状态。
2. MUCB算法
为使CICQ结构每列交叉缓存中分组数目均衡,输入调度中需优先考虑分组数目最少的列交叉缓存对应的输出端口调度。选择输出端口后,根据对式(1)的分析,在可去往该输出端口的所有输入端口中,选择目的端口数最少的输入端口传输分组,以尽量使交换机达到Work-Conserving状态。
选择输入输出端口后,对于单组播队列间裁决问题,考虑组播到达时扇出数,通过设置权重来同时顾及到组播与单播、组播之间竞争。对于到达扇出数相同的组播之间的竞争,可在组播权重设置中加入其当前扇出数因素。最后,在单组播分组权重中加入各自等待时间来均衡二者竞争时的公平性。
输出调度中,交叉缓存权重考虑其对应输入端口头分组的状态可减弱组播队头阻塞带来的影响。与输入调度类似,可根据单组播头分组等待时间、组播到达扇出数及组播当前扇出数来设置对应交叉缓存分组的权重。
为叙述的方便,下面给出相关符号含义:O为输出端口的集合,且按端口号升序排列;I为输入端口的集合,且按端口号升序排列;Vij为输入端口i中去往输出端口j的队列;Mik为输入端口i的第k个组播队列;Xij为输入端口i和输出端口j对应交叉节点缓存;Bj为输出端口j的列方向交叉缓存中分组数目;Mi为输入端口i的所有虚拟组播队列;Uj为对于输出端口j满足以下条件的所有输入端口的集合:Xij 为空,同时Vij 不为空或Mi中所有非空头分组中有去往输出端口j;Tj为Uj与I的交集,且按端口号升序排列;Di为输入端口i所有非空头分组目的端口种类数;WijV为Vij头分组的等待时间;w为组播权重因子;Aik为Mik头分组到达时扇出;Cik为Mik头分组当前扇出;DikM为Mik头分组的等待时间;WikM=w×Aik×Aik/Cik×DikM,考虑组播最小扇出为2,为使等待时间相同的单播分组与组播扇出为2的组播分组在刚成为头分组时权重相同,设w=0.5;WijX=WijV+WikM,其中Mik目的端口包含j;Xj为输出端口j对应的列方向交叉缓存的集合。
下面给出MUCB算法的具体步骤。
第1步 Modulo
对于输入端口i,假设有k个虚拟组播队列。当组播分组到达时,该组播分组扇出数为Φ,则该组播分组进入组播队列Mij ,其中j=Φmod k。
第2步 输入调度
1) 令O包含全部输出端口,I包含全部输入端口。
2) 若O为空,该时隙结束输入调度。
3) 从O集合的第1个元素开始,选择Bj最小的输出端口j。
4) 若Tj为空,从O中剔除端口j,回到第2)步。
5) 从Tj集合的第1个元素开始,选择Di最小的输入端口i。
6) 在Vij与Mi中选择WijV或WikM中最大的队列,其中Mik的头分组目的端口包含j。传输选中队列的头分组到交叉缓存,其中组播分组按照其目的端口与输入端口i对应交叉缓存状态的最大匹配传输。
7) 从I中剔除端口i,更新U、T、Bj状态,回到第3)步。
以上每步抉择,若在比较中遇到相同的情形,则奇数时隙时,不再变更被选中的目标(如端口号);偶数时隙时,选择新的目标。
第3步 输出调度
对于每个输出端口j,在Xj中选择Xij非空且WijX最大分组调度离开交换机,遇到权重相同的情形时,按照与输入调度相同方式进行选择。
3. 仿真结果
单组播混合调度中,输入输出负载间的关系为

(2) 式中:μ为输出负载;λ为输入负载;fu为单播业务比例;|Φ|为组播平均扇出;fm为组播业务比例,仿真结果中的负载均为输出负载。
MF-MRSF算法和SBF算法分别是目前性能较好的组播和单播调度算法。MF-MRSF算法以可匹配端口数和全部目的端口数的比率为权重来裁决组播之间竞争,同时输出调度算法考虑了输入调度需求。仿照MURS算法思路,将MF-MRSF算法和SBF算法结合得到一种单组播混合调度算法,仍称为MF-MRSF算法。
LCMS算法为单组播分组设置了统一的权重,其中组播权重设置时考虑了其到达时扇出数大于单播的因素,并依此提升组播优先级。同时以单组播分组各自等待时间来均衡二者权重关系。
MF-MRSF算法与LCMS算法在不同业务条件下性能互有优势,但均优于MURS算法。本节将以OQ结构中的FIFO算法性能数据作参照,给出MUCB算法与这2种算法之间性能仿真对比数据。
现有研究中对单组播混合非均匀业务的仿真很少,对组播非均匀业务尚未有比较统一的说明和分析,故本节给出的数据都以均匀业务为对象。
仿真时间为100万个时隙,交换机端口数为16×16,每个输入端口设有4个虚拟组播队列,各算法组播入队均采用Modulo算法。ON-OFF业务的平均突发长度(mean burst length)等于16。
3.1 均匀Bernoulli业务
均匀Bernoulli业务下,在低负载时各算法通过率、时延性能良好且几乎相同,以下将给出负载较高时各算法之间的性能差异。
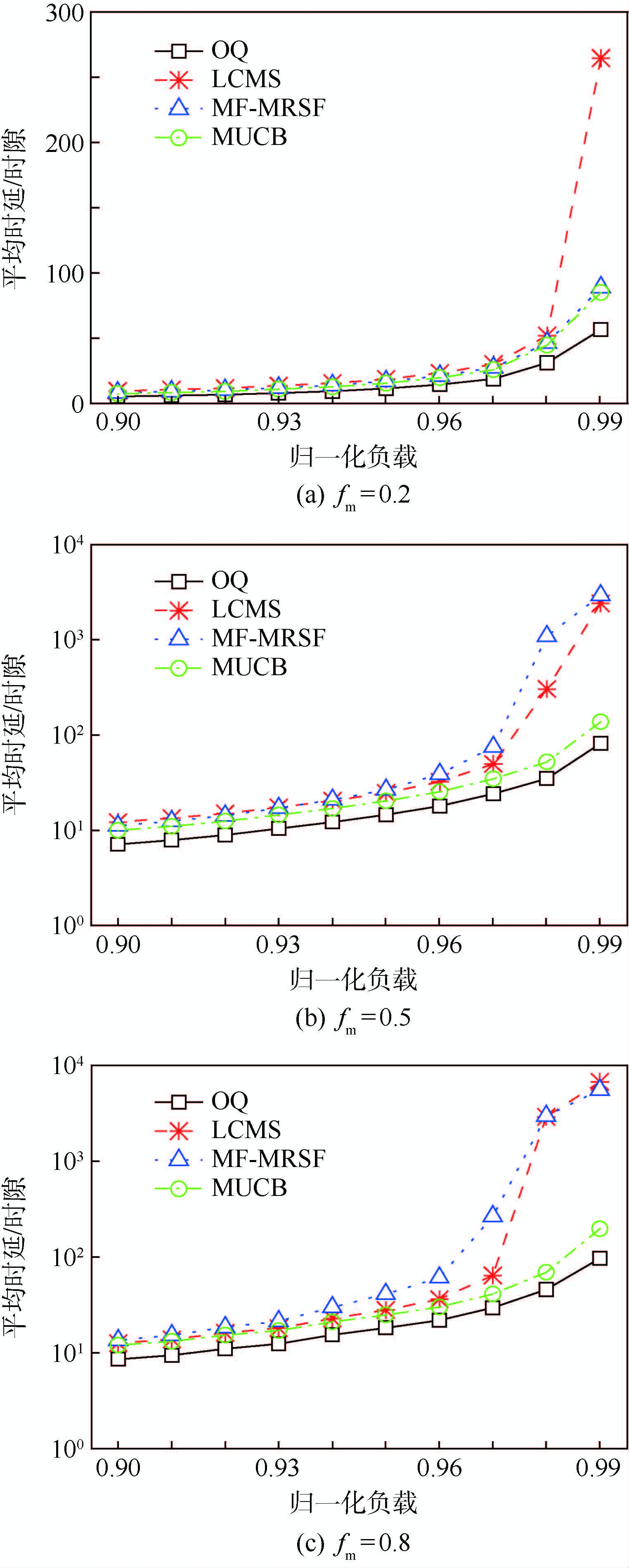
表 1给出了不同组播业务比例下通过率,图 2(a)~图 2(c)分别给出不同组播业务比例下时延性能对比。可以看出在均匀Bernoulli业务下,组播业务比例为0.2时,MUCB算法时延性能略优于MF-MRSF算法,但明显优于LCMS算法。但当组播业务比例为0.5和0.8时,相较于MF-MRSF、LCMS算法,MUCB算法时延性能有极大地提升。
表 1 均匀Bernoulli业务通过率Table 1. Throughput under uniform Bernoulli traffic算法 归一化负载(fm=0.2) 归一化负载(fm=0.5) 归一化负载(fm=0.8) 0.90 0.95 0.99 0.90 0.95 0.99 0.90 0.95 0.99 MF-MRSF 0.999 993 0.999 988 0.999 935 0.999 974 0.999 968 0.992 779 0.999 976 0.999 971 0.986 823 LCMS 0.999 991 0.999 985 0.999 586 0.999 973 0.999 977 0.995 416 0.999 977 0.999 977 0.986 048 MUCB 0.999 994 0.999 989 0.999 945 0.999 977 0.999 989 0.999 902 0.999 972 0.999 980 0.999 917 OQ 0.999 995 0.999 991 0.999 957 0.999 984 0.999 993 0.999 939 0.999 983 0.999 985 0.999 937 3.2 均匀ON-OFF业务
均匀ON-OFF业务下,各算法在负载较高时通过率、时延性能恶化严重,没有比较意义,以下将给出负载较低时各算法之间的性能差异。
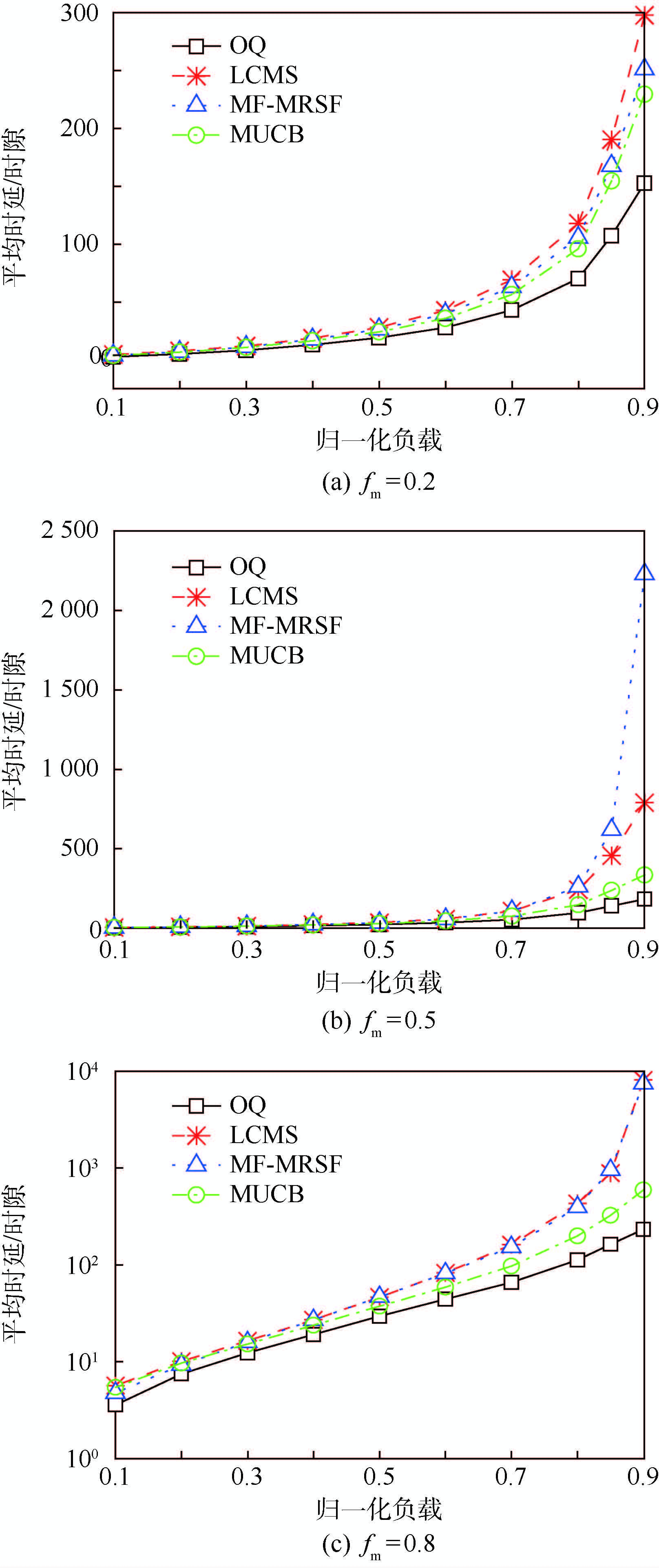
表 2给出了不同组播业务比例下通过率数据对比,图 3(a)~图 3(c)分别给出不同业务组播比例下平均时延性能对比。可以看出在均匀ON-OFF业务下,MUCB算法相较于MF-MRSF与LCMS算法的时延性能优势的变化趋势与均匀Bernoulli业务相似,都随着组播业务比例增加而增大。
表 2 均匀ON-OFF业务通过率Table 2. Throughput under uniform ON-OFF traffic算法 归一化负载(fm=0.2) 归一化负载(fm=0.5) 归一化负载(fm=0.8) 0.30 0.60 0.90 0.30 0.60 0.90 0.30 0.60 0.90 MF-MRSF 0.999 999 0.999 997 0.999 758 1 0.999 956 0.995 684 0.999 994 0.999 952 0.985 620 LCMS 0.999 998 0.999 992 0.999 696 1 0.999 969 0.998 816 0.999 992 0.999 968 0.985 124 MUCB 0.999 999 0.999 997 0.999 701 1 0.999 973 0.999 674 0.999 993 0.999 983 0.999 583 OQ 1 0.999 999 0.999 762 1 0.999 977 0.999 878 0.999 997 0.999 989 0.999 859 通过仿真结果对比可以看出,在均匀Bernoulli和均匀ON-OFF业务下,与LCMS、MF-MRSF算法相比,MUCB算法均表现出更好的性能,且在组播业务比例较高时,这种优势更加明显。总体而言,MUCB算法的性能更加接近于OQ结构中的FIFO调度。
4. 结 论
1) 分析了CICQ结构中单播、组播混合调度面临的组播头分组阻塞、单组播间竞争裁决、使交换机尽量工作于Work-Conserving状态3个问题及三者之间关系。
2) 以上述分析为基础,提出一种单组播混合调度算法——MUCB算法。仿真显示,与现有研究中性能相对较好的LCMS算法及MF-MRSF算法相比,在均匀ON-OFF业务和均匀Bernoulli业务下,MUCB算法的性能均表现最好。
研究中并未考虑组播分组的入队算法问题,而Modulo算法虽然简单,但也有很大缺陷。未来研究中,可考虑结合输入、输出调度需求设计性能更加优良的组播分组入队算法。
-
表 1 FMSR算法精确配准结果
Table 1. Fine registration results of FMSR algorithm
理论值μ 最优尺度因子S 最优旋转矩阵R 最优平移向量T 均方根误差Qrms/m 时间/s 0.5 0.487 (-0.483, 0.010, -0.049) (2.659, -145.708, -25.783) 0.002 4.043 1 0.977 (-0.483, 0.010, -0.049) (5.338, -291.396, -51.402) 0.002 2.601 2 1.954 (-0.483, 0.010, -0.049) (10.679, -582.779, -102.807) 0.002 2.509 10 9.768 (-0.483, 0.010, -0.049) (53.439, -2 913.906, -513.807) 0.002 2.489 表 2 S-ICP算法与FMSR算法对比
Table 2. Comparison of S-ICP and FMSR algorithms
参数 S-ICP算法 FMSR算法 最优尺度因子S 3.000 3.300 最优旋转矩阵R (1.683, -0.035, 0.935) (1.561, -0.044, -2.214) 最优平移向量T (-39.233, -29.415, 2.564) (17.394, 12.485, -0.957) 均方根误差Qrms/m 0.325 0.194 时间/s 23.212 16.207 -
[1] 骆社周, 习晓环, 王成.激光雷达遥感在文化遗产保护中的应用[J].遥感技术与应用, 2014, 29(6):1054-1059.LUO S Z, XI X H, WANG C.The application of LiDAR remote sensing of cultural heritage preservation[J].Remote Sensing Technology and Application, 2014, 29(6):1054-1059(in Chinese). [2] 赵一鸣, 李艳华, 商雅楠, 等.激光雷达的应用及发展趋势[J].遥测遥控, 2014, 35(5):4-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1000.2014.05.002ZHAO Y M, LI Y H, SHANG Y N, et al.Application and development direction of LiDAR[J].Journal of Telemetry, Tracking and Command, 2014, 35(5):4-22(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-1000.2014.05.002 [3] 曾齐红.机载激光雷达点云数据处理与建筑物三维重建[D].上海: 上海大学, 2009.ZENG Q H.Airborne LiDAR point cloud data processing and 3D building reconstruction[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai University, 2009(in Chinese). [4] YANG M D, CHAO C F, HUANG K S, et al.Image-based 3D scene reconstruction and exploration in augmented reality[J]. Automation in Construction, 2013, 33:48-60. doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2012.09.017 [5] WANG R.3D building modeling using images and LiDAR:A review[J].International Journal of Image and Data Fusion, 2013, 4(4):273-292. doi: 10.1080/19479832.2013.811124 [6] ABAYOWA B O, YILMAZ A, HARDIE R C.Automatic registration of optical aerial imagery to a LiDAR point cloud for generation of city models[J].ISPRS Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 2015, 106:68-81. doi: 10.1016/j.isprsjprs.2015.05.006 [7] 王欣, 张明明, 于晓, 等.应用改进迭代最近点方法的点云数据配准[J].光学精密工程, 2012, 20(9):2068-2077.WANG X, ZHANG M M, YU X, et al.Point cloud registration based on improved iterative closest point method[J].Optics and Precision Engineering, 2012, 20(9):2068-2077(in Chinese). [8] BESL P J, MCKAY N D.A method for registration of 3-D shapes[J].Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering, 1992, 14(3):239-256. [9] YING S, PENG J, DU S, et al.A scale stretch method based on ICP for 3D data registration[J].IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2009, 6(3):559-565. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2009.2021337 [10] CHEN Y, MEDIONI G.Object modelling by registration of multiple range images[J].Image and Vision Computing, 1992, 10(3):145-155. doi: 10.1016/0262-8856(92)90066-C [11] RUSINKIEWICZ S, LEVOY M.Efficient variants of the ICP algorithm[C]//Proceedings 3rd International Conference on 3-D Digital Imaging and Modeling.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2001: 145-152. [12] 戴静兰, 陈志杨, 叶修梓.ICP算法在点云配准中的应用[J].中国图象图形学报, 2007, 12(3):517-521. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2007.03.023DAI J L, CHEN Z Y, YE X Z.The application of ICP algorithm in point cloud alignment[J].Journal of Image and Graphics, 2007, 12(3):517-521(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-8961.2007.03.023 [13] 邹际祥.基于KD-tree加速的点云数据配准技术研究[D].合肥: 安徽大学, 2013.ZOU J X.The research of point cloud data registration technique based on KD-tree acceleration[D].Hefei: Anhui University, 2013(in Chinese). [14] MIAN A, BENNAMOUN M, OWENS R.On the repeatability and quality of keypoints for local feature-based 3D object retrieval from cluttered scenes[J].International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 89(2-3):348-361. doi: 10.1007/s11263-009-0296-z [15] LI X L, LI Y Y, XU L J.Terrestrial laser scanner autonomous self-calibration with no prior knowledge of point-clouds[J].IEEE Sensors Journal, 2018, 18(22):9277-9285. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2018.2869559 [16] LI X L, LI Y Y, XIE X H, et al.Lab-built terrestrial laser scanner self-calibration using mounting angle error correction[J].Optics Express, 2018, 26(11):14444-14460. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.014444 [17] LI X L, YANG B W, XIE X H, et al.Influence of waveform characteristics on LiDAR ranging accuracy and precision[J]. Sensors, 2018, 18(4):1156-1172. doi: 10.3390/s18041156 [18] LI X L, WANG H M, YANG B W, et al.Influence of time-pickoff circuit parameters on LiDAR range precision[J]. Sensors, 2017, 17(10):2369-2389. doi: 10.3390/s17102369 [19] XU L J, FENG J, LI X L, et al.Automatic registration method for TLS LiDAR data and image-based reconstructed data[J].IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2018, 16(3):482-486. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 袁龙,熊庆旭,萧翰. 基于缓解HoL堵塞的单组播混合调度算法. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2019(02): 405-412 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 梁佳诚,熊庆旭,萧翰. 一种星载CICQ交换机单组播分组调度算法. 无线电通信技术. 2018(01): 48-54 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-








 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:




 百度学术
百度学术