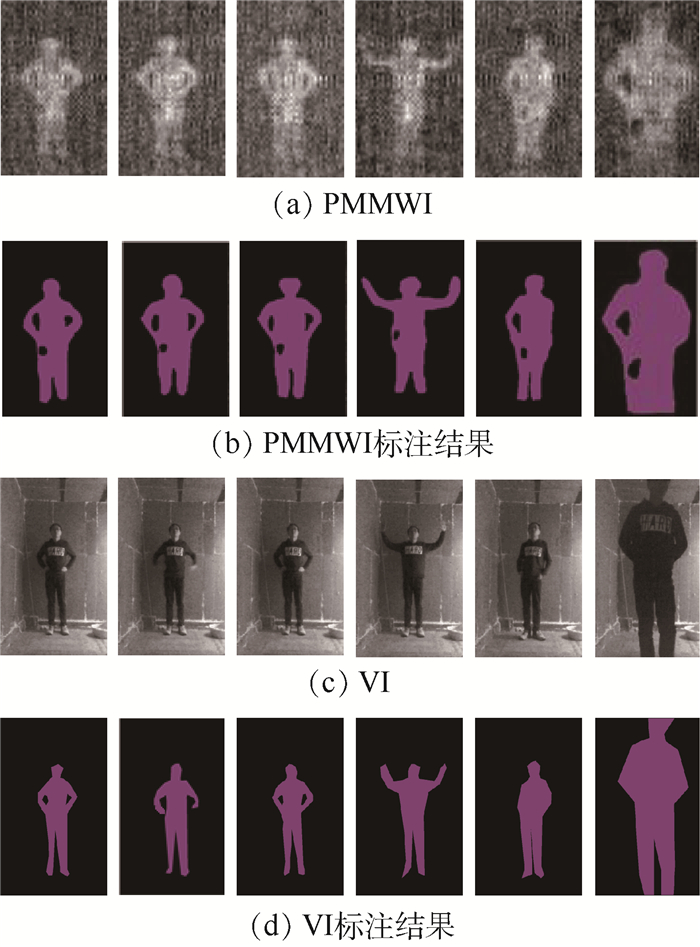
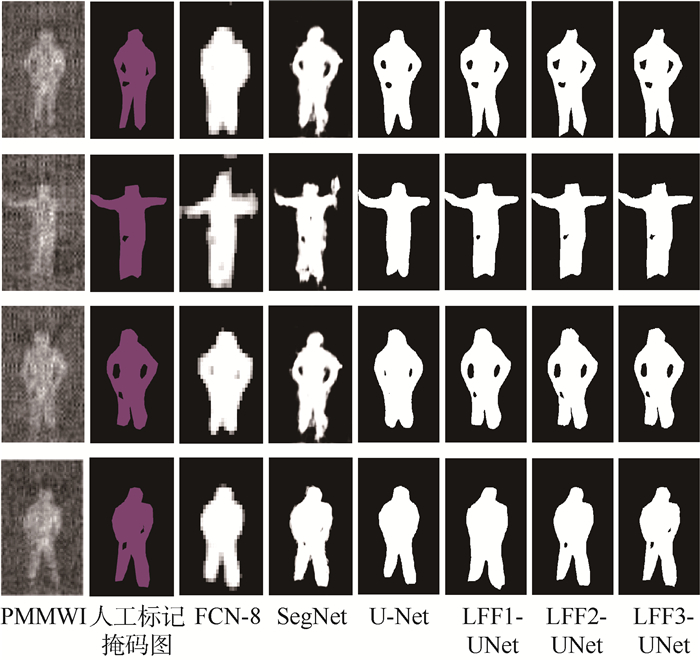
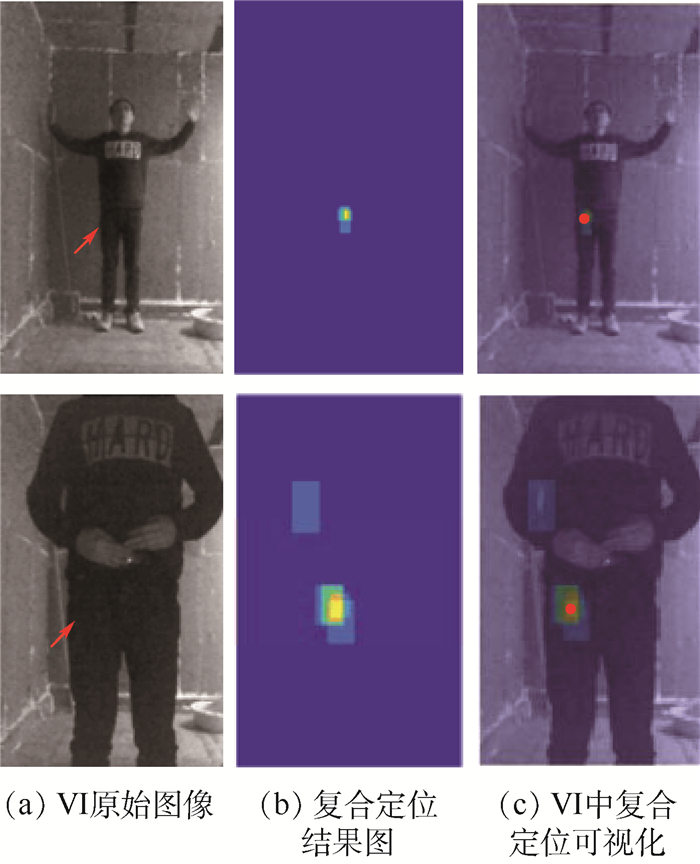
Detection and localization of concealed forbidden objects on human body based on complementary advantages of PMMWI and Ⅵ
-
摘要:
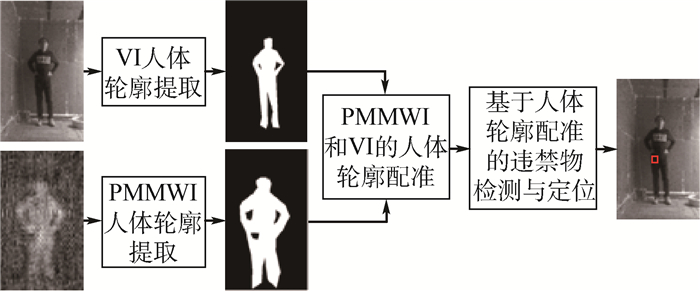
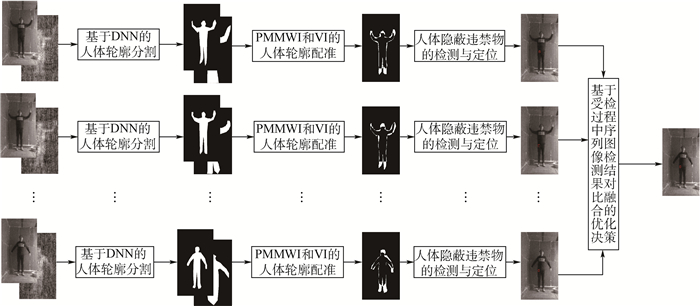
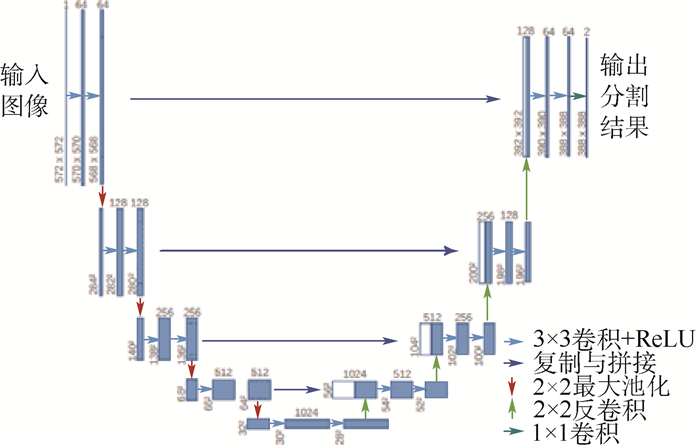
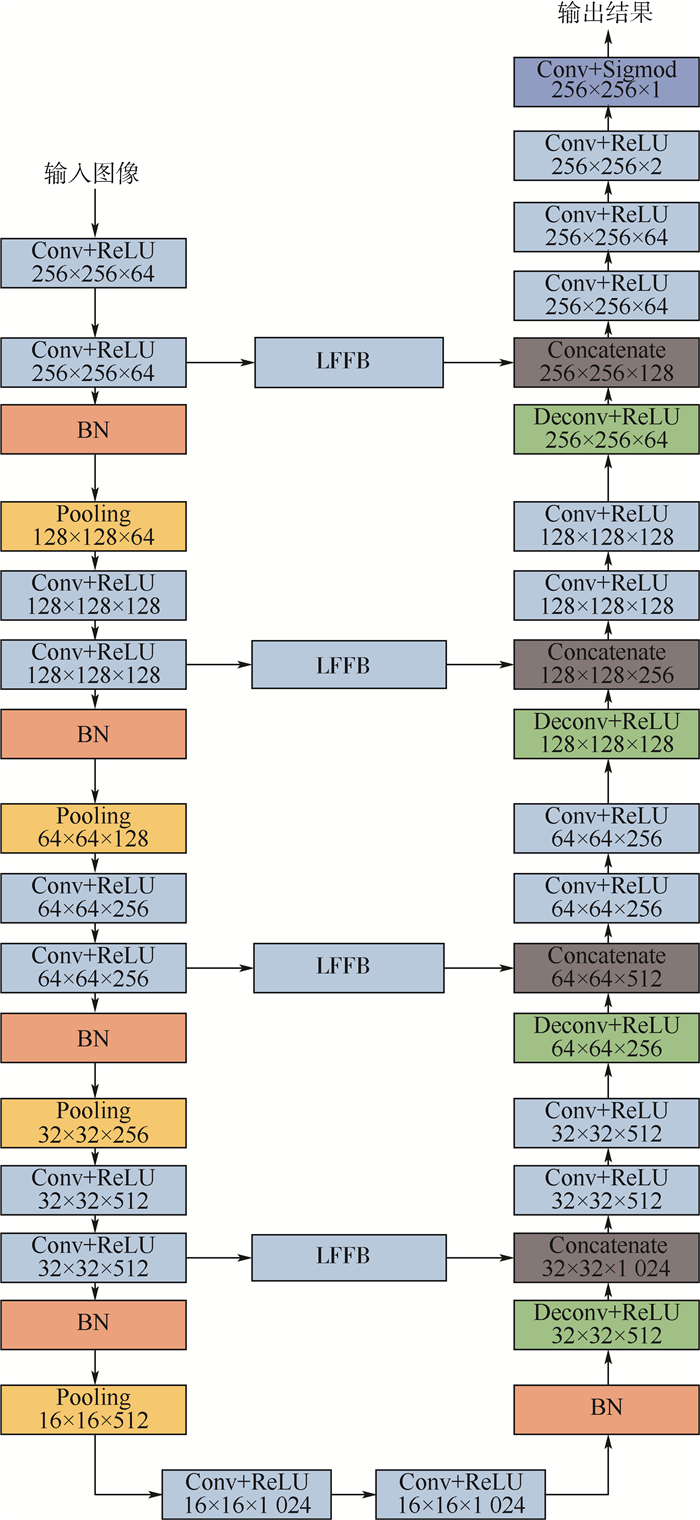
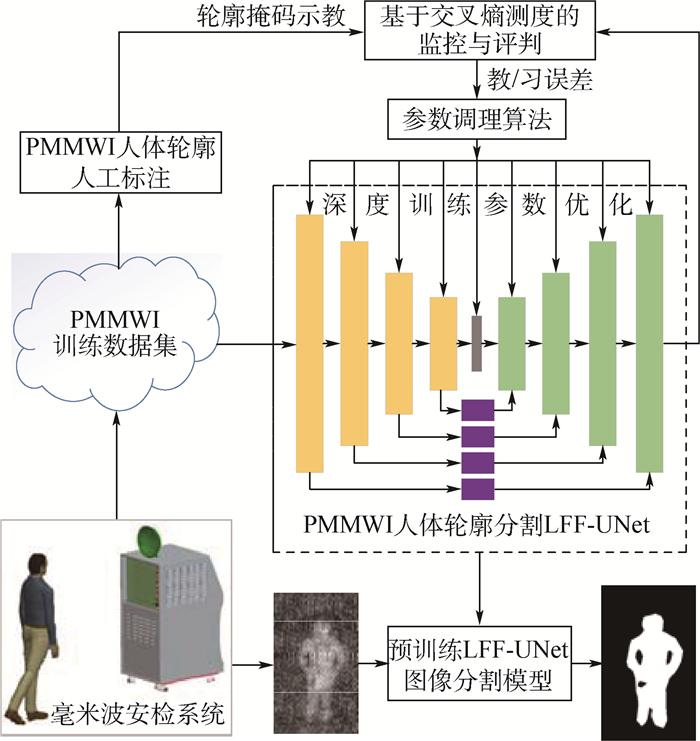
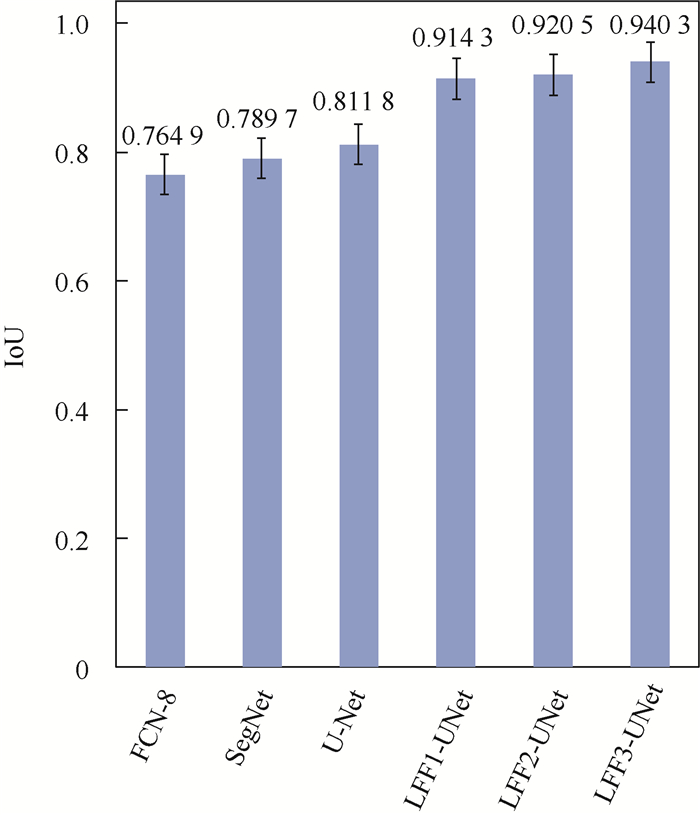
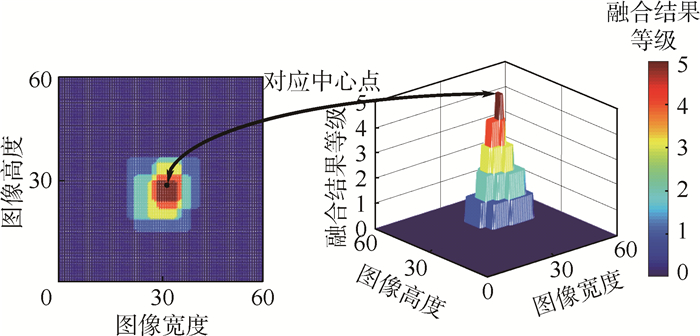
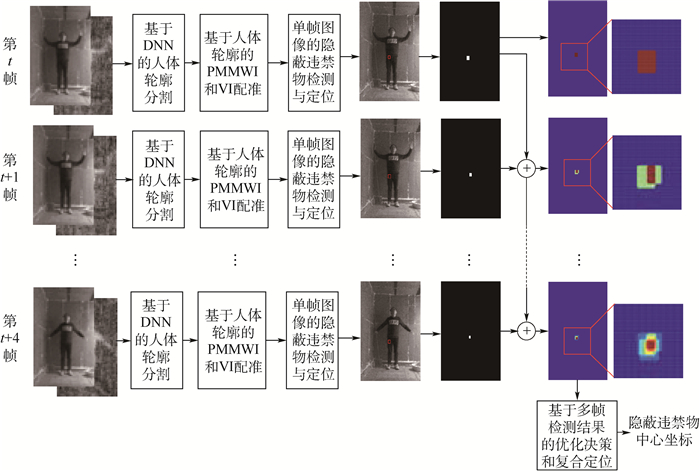
根据公共场所人体安检的性能要求和技术需求,将被动毫米波成像(PMMWI)的可透视成像性能优势与可见光成像(Ⅵ)的细节高分辨性能优势相结合,提出一种基于PMMWI与Ⅵ优势互补的人体隐蔽违禁物检测与定位算法。首先,提出一种基于低层特征融合的改进U-Net以增强深度神经网络(DNN)对PMMWI中弱小目标轮廓的敏感度,提高PMMWI中人体轮廓和隐蔽违禁物的分割精度,并同时实现Ⅵ中人体轮廓的像素级分割;然后,在PMMWI和Ⅵ中的人体轮廓分割基础上,通过基于人体轮廓的尺度变换与滑动适配实现PMMWI人体轮廓和Ⅵ人体轮廓的良好配准,根据配准结果实现单帧图像中人体隐蔽违禁物的高效检测;最后,通过序列图像检测结果的对比融合与优化决策给出隐蔽违禁物的定位结果。一系列综合实验与对比分析结果,验证了提出的人体隐蔽违禁物检测与定位算法的性能优势。
-
关键词:
- 毫米波安检 /
- 被动毫米波成像(PMMWI) /
- 人体轮廓分割 /
- 深度学习 /
- 深度神经网络(DNN) /
- 隐蔽违禁物检测与定位
Abstract:According to the performance requirements and technology demands of human security check in public place, combining the performance advantages of perspective imaging of passive millimeter wave imaging (PMMWI) and high discriminability in image details of visible imaging (Ⅵ), an approach for detection and localization of concealed forbidden objects on human body is presented in this paper based on the complementary advantages of PMMWI and Ⅵ. Firstly, an improved U-Net based on feature fusion in low layers is presented to enhance the sensitivity of deep neural networks (DNN) to the contour of dim small targets, and improve the accuracy of segmentation of human contours and concealed forbidden objects. Meanwhile, the pixel-level segmentation of human contours in Ⅵ is also implemented. Then, the contours of human body in PMMWI are registered with some corresponding ones in Ⅵ by scale transform and sliding fit, so the concealed forbidden objects on human body can be detected from a single frame with a high precision. Finally, the concealed forbidden objects are localized by contrasting fusion and optimizing decision according to detection results with sequence images. A series of comprehensive experiments and comparative analysis results validate the good performance of the proposed detection and localization algorithm of concealed forbidden objects on human body towards security check of public places.
-
伴随着机载设备、光电子元器件高集成化、小型化发展趋势,各类元件功耗与发热量的同步增加,由此而产生的百瓦/平方厘米级高热流密度散热需求愈加迫切[1-3],行之有效的散热措施成为了保证电子设备正常、可靠运行的核心技术之一[4-7]。针对不同散热需求差异,常见散热技术其散热能力由小到大分别为:外加翅片自然对流散热、强迫风冷散热、微通道热沉水冷散热[3]、喷雾冷却散热[6]和射流冷却散热[2-3]等,以上技术均利用了流体的自然/强迫对流换热的换热系数较高的特点。
根据文献[8]中提出的“场协同”原理可知,通过改变速度方向与热流方向的夹角,可以控制对流换热的强度,且两者夹角越小换热强度越大。对于射流冲击冷却,在孔口下方滞止点附近,速度梯度与温度梯度夹角较小,此处的换热系数高于贴壁射流处[9]。基于以上特点,射流冷却散热技术可用于高热流密度热源散热,并达到较高换热系数。现阶段, 针对射流冷却技术的研究主要集中于不同冷却工质种类[10]、射流孔板结构[11-12]、射流距离、射流表面形貌[13-14]及系统参数控制等对热沉性能的影响情况[15-18]。
Chang等[10]使用3M公司的PF5060介电液体作为工质,对不同雷诺数 (Re=2 000,3 000,5 000)下,采用不同射流高度、孔径比的单孔受限射流冷却装置的性能进行了可视化实验测试,结果表明沸腾的起始点(Onset Nuclear Boiling, ONB)与Re成正比,与射流高度、孔径比成反比。Sung和Mudawar[11-12]对采用矩形狭缝、等截面/渐变截面圆形阵列射流孔对阵列射流复合微通道冷却模组在单相、两相工况下的性能进行了相关数值模拟及实验研究。以HFE 7100电子氟化液为工质,当入口温度Tin=20℃(过冷度约80℃)时可实现CHF(Critical Heat Flux)最高可达1 127 W/cm2(热源尺寸为1 cm×2 cm)。在射流速度较低时,CHF主要由微通道流特性决定,当速度较高时,其主要由射流特性决定。Ruander和Viond[17]使用FC-72为工质,对单孔冲击光滑表面的浸没射流冷却性能进行了研究,其可视化实验结果表明,整个表面均实现充分沸腾所需的时间与初始壁面过热度大小成反比。
上述研究表明,合理的射流孔板结构、强化射流表面形貌设计可以在一定程度上提升射流热沉的冷却能力。同时,笔者考虑到由于工质汽化时相变潜热的存在,能够在较小的壁面温升下增加散热能力。因此,在前人研究基础上,设计了2种复合不同肋化表面的可视化阵列射流热沉:光滑切割针肋、外覆多孔烧结层的粗糙针肋。同时结合高速摄像机,以无水乙醇为工质,对其在固定入口温度、固定背压下的换热能力进行了性能测试及可视化实验,对2种肋化表面结构相较光滑射流表面对于强化沸腾换热的有效性进行验证。
1. 复合阵列射流热沉设计
本文设计了2种不同可视化复合阵列射流热沉,热沉整体结构示意图如图 1所示。热沉整体呈左右轴对称结构,工质由上部入口(蓝色箭头处)进入热沉后首先流经整流段(填充不锈钢丝网),实现均匀分配通过各射流孔的工质流量;然后经射流孔板入射至无氧铜基板表面,此时冷流体与热壁面完成能量交换;最后再由两侧出口(红色箭头处)分别流出。其中,盖板和支撑板层间使用硅橡胶垫片,结合螺栓连接实现机械密封。
1.1 整流腔设计
整流腔用于实现通过各射流孔的工质流量的均匀分配,采用了填充不同目数丝网的方案,将整流腔内分成阻力损失不同的三等份。中间部分填充150目不锈钢丝网,增大流动阻力;两侧选择孔隙率更大、流动阻力更小的100目不锈钢丝网,引导中心位置工质向两侧阻力较小区流动。使用FLUENT对整流腔流体流动情况进行了仿真分析,结果显示上述整流腔设计可以有效避免入口正下方区域工质流速过大。
1.2 受冲击表面肋化结构设计
可视化复合阵列射流热沉采用1×5的阵列射流孔板,底部有效肋化区域的投影面尺寸为6 mm×30 mm,形成5个射流单元,如图 2所示。每个射流单元对应基板表面4×4的阵列针肋。在2种肋化结构方案中,针肋尺寸均为0.6 mm×0.6 mm×1.0 mm(长×宽×高),粗糙肋化表面采用在机械加工针肋表面再烧结一层多孔铜粉颗粒层。其中,铜粉粒径为75~53 μm,多孔层总厚度约为2倍的粒径。射流结构参数见表 1。
表 1 阵列射流结构参数Table 1. Array jet structure parametersmm 参数 射流孔径 孔间距 孔板厚度 射流距离 数值 0.5 6 3 3 注:射流距离为射流孔板下表面至基板上表面(肋底部)。 针肋结构可以通过破坏层流底层,在较低雷诺数下增加扰动促进湍流的发生;烧结铜粉多孔介质层表面可以形成多个汽化核心,进而促进相变的发生。因此,2种肋化表面可以同时实现对单相、两相工况的性能提升。粗糙肋化表面实物图及扫描电子显微镜(SEM)照片见图 3。
2. 实验系统
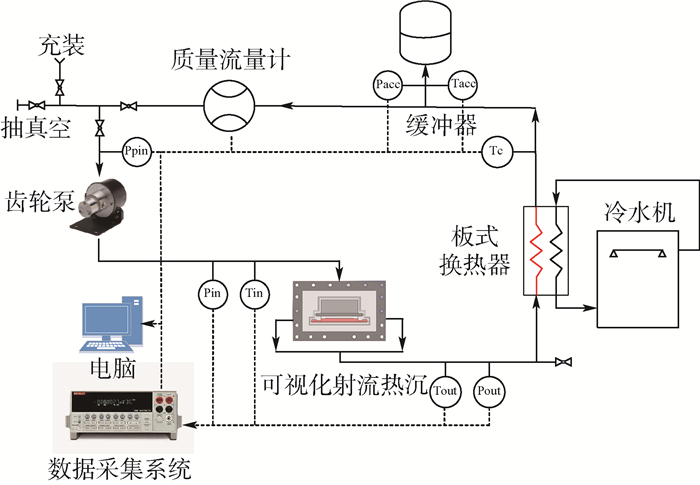
实验系统可分为性能测试及可视化拍摄两部分。其中,性能测试系统示意图如图 4所示,采用闭式泵流体回路作为测试系统。
2.1 性能测试系统
性能测试系统中主要部件包括:可视化射流热沉、板式换热器、质量流量计、齿轮泵、缓冲器和数据采集系统。系统工质使用机械泵驱动循环,经过滤器进入测试段,工质受热后进入板式换热器进行冷凝冷却,最终流回泵输入端完成整个循环。热沉使用陶瓷加热片作为模拟热源,实验时贴于基板下表面。系统使用二次冷却回路,板式换热器热侧为循环工质,冷侧连接恒温冷水机,通过控制循环水温度对测试系统温度进行控制。
实验时,保持射流结构和系统输入条件不变,即热沉孔径、孔数、孔间距、射流距离、射流速度(系统工质流量)、射流温度指标保持不变。观测在使用不同表面强化方式时,射流区域内液相工质随着加热热流密度的变化的流动、传热特性。
2.2 可视化拍摄系统
可视化实验的核心观测是与常规光滑表面基板相比较,2种复合不同肋化表面的阵列射流冷却热沉内工质的流动状态及流型转化特点。
拍摄系统采用KYENCE公司VW-600C彩色高速显微摄像机主机、VW-Z2长距离高清显微变焦镜头(60x)、主体部分内置专用金卤灯光源。
3. 数据处理与误差分析
3.1 数据处理
施加于基板的有效加热热流密度Φ通过陶瓷加热片供电功率UI(电压U与电流I的乘积)经校核后折算得到。在相同的环境条件下,热沉向环境的漏热量仅与装置外表面的温度有关,与热沉内部工质状态无关。使用单相稳态热平衡关系式,计算工质实际吸收的加热功率Q与陶瓷加热片供电功率UI的比值作为折算系数ξ。

(1) 式中:A为热源面积。
将基板上表面与射流工质间的换热温差记为ΔTm,壁面温度Tw由傅里叶导热定律[9]计算得到:

(2) 
(3) 式中:Tin为工质入口温度;T为正对中部射流下方,基板内布置的热电偶探头实测得到的固体温度;Δx为测温点所在位置距基板表面的距离, Δx=2 mm;λ为基板无氧铜材料的热导率,取λ=381 W/(m·K)。
使用壁面温度Tw与工质入口温度Tin的差值ΔTm计算对流换热系数h,作为衡量热沉综合传热性能的指标:

(4) 此外,为了考核不同射流速度Ujet或工质流量qv对热沉内部流动及传热特性的影响,采用无量纲雷诺数Re综合考虑二者的影响。

(5) 
(6) 
(7) 式中:Djet为射流孔直径;Ajet为所有射流孔面积和;射流孔数N=5;ρ为工质密度;qm为工质质量流量;ν为运动黏度。以工质入口温度Tin为上述物性参数的定性温度。
使用进、出口工质压力损失ΔP作为衡量热沉流动阻力特性的指标。

(8) 式中:Pin和Pout分别为测量得到的热沉进、出口工质压力。
3.2 误差分析
假设不存在粗大误差与系统误差的前提下,根据系统中各测量仪表的精度得到直接误差σxi,基于误差分析理论采用误差传递函数公式(9),对各间接误差σy进行分析计算:

(9) 式中:xi为直接测量参数;f(x)为间接测量参数。
系统中温度测量分别使用了:2种K型热电偶(底面温度、工质温度),精度分别为±2%、±0.75%;压阻式压力传感器,精度±5%;科里奥利力质量流量计,液体流量测量精度±0.2%,密度测量误差 < ±5 kg/m3。根据各参数可能出现的最大值,最终计算得各参数误差如表 2所示。
表 2 实验不确定度Table 2. Uncertainties of experiment% 误差 参数 数值 直接相对误差 T ±2 Tin、Tout ±0.75 x、Djet ±2 qm、qv ±0.2 ρ ±0.6 P ±0.25 间接相对误差 Φ ±0.13 Tw ±1 ΔTm ±0.96 h ±2.26 Ujet ±0.2 Re ±2.2 ΔP ±0.25 4. 结果与讨论
实验使用无水乙醇为工质,各工况下均控制工质入口温度Tin=(20±1)℃不变。根据性能测试系统采集到的入口温度/压力、出口温度/压力、底板温度等系统测量数据,可以得到相关热沉换热特性(如:换热系数、壁面过热度、压力损失等)。包含对照组在内,光滑表面、光滑肋化表面和粗糙肋化表面3个不同可视化热沉分别命名为KS0、KS1和KS2。
各实验工况分为两大类:第1类基于常规沸腾曲线测试方法,测试段入口工质流量保持不变,逐渐增加加热热流密度;第2类选定加热热流密度不变,逐步减小入口工质流量。
实验的过程中,当系统各温度、压力指标趋于稳定,则认为达到热平衡状态,此时进行针对热沉射流腔的高速拍摄,用以观测各工况下工质的流型转化特性。
4.1 固定工质流量
首先,对3种可视化热沉在保持相同的入口条件(入口温度Tin=(20±1)℃、体积流量qv=(7.5±0.5) mL/s)下,热沉性能随加热热流密度Φ增加(Φ=5~100 W/cm2)时的变化情况进行了实验研究。
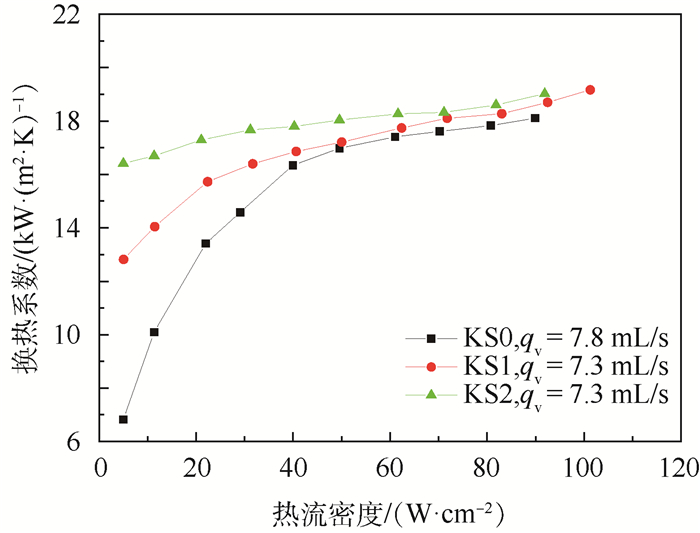
图 5为壁面过热度随热流密度的变化。实验结果显示:在qv保持固定,只增加Φ时,ΔTm随Φ增加而逐渐增大。大部分工况下KS1、KS2性能均优于光滑射流表面结构KS0,在相同热流密度下换热温差更小(见图 5)、换热系数更大(见图 6)。当Φ < 70 W/cm2时,ΔTm值KS0>KS1>KS2;当Φ进一步增加时,三者性能趋于一致,壁面温度趋近于对应压力下的饱和温度。
图 6为换热系数随热流密度的变化。由图中可知:① h-Φ曲线在初始工况下,2种肋化表面KS1、KS2均大于对照组KS0的h,且h值KS2>KS1>KS0;②各热沉h均随着热流密度Φ增加而增大,其中KS0换热系数近似抛物线增大,增长率逐渐放缓,而肋化表面KS1、KS2的换热系数h从起始小热流密度工况始终能保持较高值,且随Φ增大后续小幅度波动增加,增长率小幅度增加。
可视化实验结果显示,在上述各工况下,对照组KS0内部均为液相,未出现明显相变。而对于2种肋化表面的热沉KS1、KS2,随着加热热流密度Φ的增加,可以观察到射流腔体内部由于工质温度梯度的存在,导致了冷、热流体分层流动及相互掺混形成湍流。但由于此时工质流量相对于总发热功率Q较大,在测试工况内,射流腔体内部未见明显的沸腾现象发生。与常规沸腾曲线单相段传热系数(Heat Transfer Coefficient, HTC)随热流密度几无变化现象相悖,结果表明在热流密度小于60 W/cm2时,换热系数随着热流密度的增加而增大。分析认为,上述现象产生的原因主要是本文采用的射流速度(射流雷诺数)较小,当加热热流密度较小时,腔体内工质主要保持层流状态,此时换热强度和换热系数均较小,对于无表面强化结构的KS0,其换热系数最小;随着加热热流密度的增加,距离加热壁面距离不同位置处工质温度不同,对应的黏度、密度等均发生变化,此时流体掺混增加,工质与壁面间由单相层流换热转换为单相湍流换热,因此出现了换热系数上升。但单相湍流换热能力不会无限制增长,因此传热系数值最终趋于常数。
4.2 固定加热热流密度
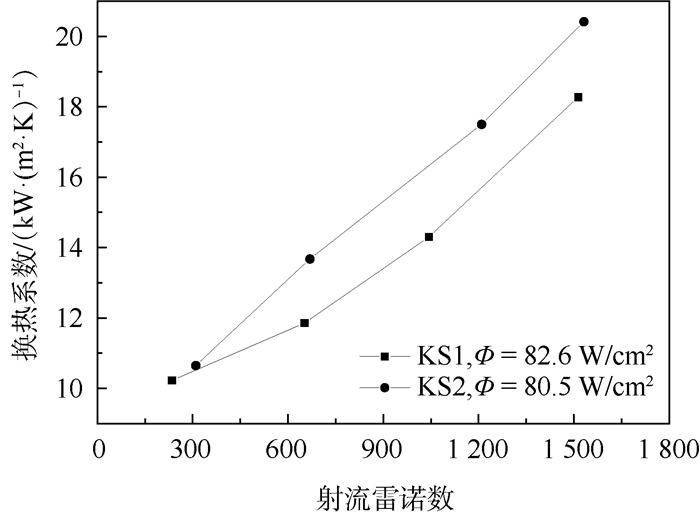
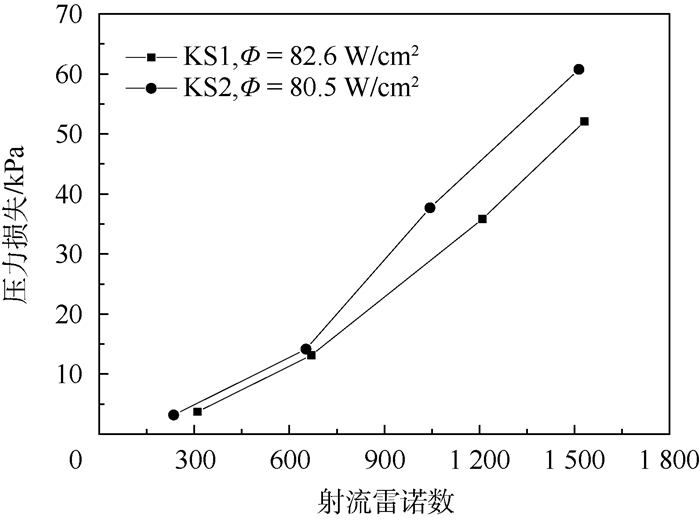
实验测试了2种不同肋化表面的热沉KS1、KS2在固定热流密度Φ时的传热性能及压力损失随入口工质流量qv变化的情况。其中工质入口温度Tin=(20±1)℃保持不变,Φ=82.6 W/cm2(KS1), Φ=80.5 W/cm2(KS2),qv=1.0~7.5 mL/s,其他系统参数保持不变。换热系数h随射流雷诺数Re的变化情况见图 7。
使用射流雷诺数对应不同的工质流量,对比不同肋化表面结构受工质流量影响的情况。根据定热流密度变工质流量的实验结果可知,热沉整体压力损失ΔP与射流雷诺数Re成正比,减小系统流量可以显著降低热沉压力损失,即可降低对泵驱动能力的要求,如图 8所示。综合图 7及图 8实验结果可以看出,虽然降低工质流量,热沉换热系数会出现一定程度下降,但在一定范围内,可以在满足需求的前提下降低热沉压力损失。
可视化实验观测结果分为稳态分析和瞬态分析两部分。稳态分析侧重于比较不同工况间的流动状态差异,瞬态分析侧重于展示某一工况时腔体内气泡生成随时间的变化情况。
4.2.1 KS1可视化结果
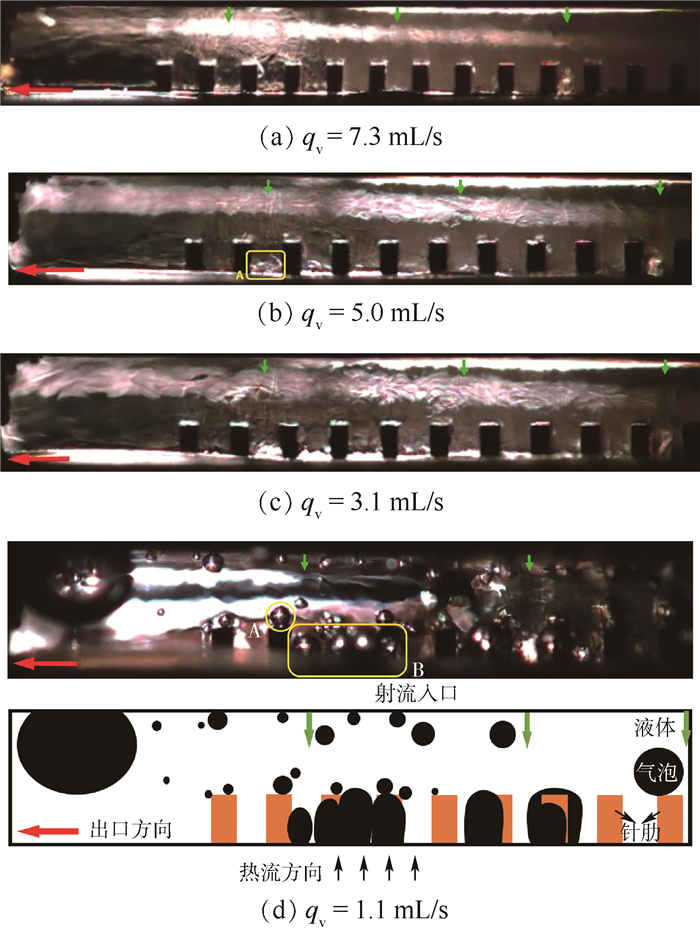
对于KS1,固定热流密度Φ=82.6 W/cm2不变,观察在4种不同流量:qv=7.3,5.0,3.1,1.1 mL/s时左半边射流腔体内部工质流动情况,结果如图 9所示。由图中可知:①随着qv的降低,射流腔体上部及出口处均处于单相状态,仅在肋间通道底部出现一定的气体薄层,如图 9(b)中A处所示;②在发生相变之前,由于工质在垂直基板表面方向出现明显的温度梯度,射流腔体内可观察到明显的分层流动产生,从图 9(c)可以观测到,在针肋上方,工质流动的混乱程度远大于下游靠近出口处。上述现象表明在底部针肋结构的作用下,一方面可以强化液态工质与固体基板间的热交换,另一方面也强化了各层流体工质的掺混。③进一步降低工质流量至qv=1.1mL/s,结果如图 9(d)所示,当系统达到热平衡后,观察可见在针肋的顶部、侧面(A处)及肋间底部(B处)均会周期性的生成气泡,即为泡状流。其中,肋顶及肋侧气泡尺寸较小且发生速率较大,肋间底部气泡尺寸较大且生成速率较小。
详细分析了KS1在qv=1.1 mL/s工况下针肋顶部、侧部、肋间底部不同位置工质流型处随时间t变化的情况如图 10所示,并综合分析了气泡的形态、生成周期等差异。A处为针肋顶部、侧部气泡生长随时间变化的规律,可以观察到:①当小气泡在肋顶部生成后会持续长大,如图 10(a)和(b)所示;②由于液态工质的扰动,气泡的位置会发生一定移动但始终未脱离固体壁面如图 10(c)所示;③随着相邻位置气泡持续生长,当两气泡相遇,会“融合”成为一个更大的气泡,如图 10(d)和(e)所示;④“融合”后的大气泡会受到更大的浮力作用,最终脱离固体壁面溢出。B处为针肋底部,气泡呈竖直柱状生长,单个气泡生成至溢出周期更长。
4.2.2 KS2可视化结果
对于KS2,固定热流密度Φ=80.5 W/cm2,在4种不同流量:qv=7.4,5.8,3.2,1.5 mL/s时,射流腔体内部工质流动情况如图 11所示。可视化观测结果显示:①与KS1相同,在qv较小时,如图 11(a)所示,射流腔内工质保持液相,仅出现了由于密度不同而导致的分层流动现象;②随着qv的减小,当在qv=5.8 mL/s时,如图 11(b)所示,可观察到明显的相变发生,远离射流孔的针肋顶部(A处)和侧部(B处)分别出现孤立小气泡,肋间通道(C处)有更大尺寸的气泡生成,此时已达到沸腾起始点,流动状态以泡状流为主;③当qv=3.2 mL/s时,如图 11(c)所示,由于qv的减小,射流速度及滞止压力均下降,相变产生的气泡无法及时脱离壁面,相邻小气泡“融合”成为更大的气柱,由于此时热沉入口压力有一定波动,气柱会周期性的被排出并重新产生,此时整个射流腔体内部形成与通道内弹状流流动状态类似的气柱;④当qv进一步减小至qv=1.5 mL/s时,如图 11(d)所示,此时冷流体射流已无法直接接触底部壁面,冷流体无法及时补充,靠近左右对称轴线A处的工质继续保持核态沸腾状态,随着饱和工质在下游持续吸热,上游孤立气泡逐渐合并形成连续“气塞”,在水平方向生成更大的气柱(B、C区),下游处工质的流动以环状流为主。
对比KS1和KS2定热流密度Φ变工质流量qv工况的可视化观测结果可知,在降低工质流量的过程中,KS2可以更早地观测到持续的气泡生成,即相较KS1其更快进入两相工况,由此证明,多孔层的存在可以更有效的强化换热,促进两相工况的发生。同时,对比2种不同强化热沉可知,沸腾产生气泡的尺寸只与相变发生的位置有关,与有无多孔层无关。
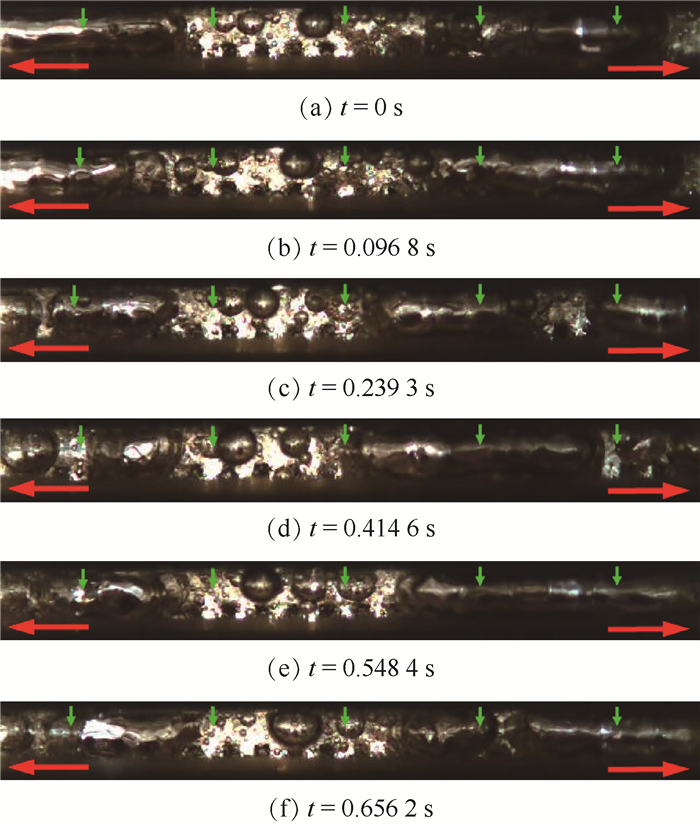
图 12展示了KS2在Φ=80.5 W/cm2、qv=5.8 mL/s工况下的气泡生长规律。A处为针肋顶部,可以观察到:①气泡会周期性的生成并逐步增大(图 12(a)~(c));②同一时刻,不同位置会有多个处于不同生长阶段的小气泡(图 12(b)、(c));③各个气泡持续生长的过程中,相邻两小气泡接触会相互“融合”变成一个大气泡(图 12(d)、(e)), 随着时间推进大气泡继续与旁边小气泡“融合”成为一个更大的气泡。B处为针肋间柱状气泡,由于拍摄时间较短,其形态尺寸并未出现明显变化。
图 13展示了KS2在相同热流密度,流量更小时的流动特性,此时Φ=80.5 W/cm2、qv=1.5 mL/s。由于该工况下流量更小,射流腔内“气塞”的生长和移动规律与图 12差异较大。可以观察到:①热沉中部约四分之一区域始终处于核态沸腾状态为泡状流;②热沉靠近下游两侧“气塞”形成后向下游逐渐生长,生长至一定尺寸后内部气态工质从出口排出,热沉中部重新生成新的“气塞”,继续重复上述过程,此时流动状态主要为环状流。
结合前述性能测试结果综合分析可视化观测结果,对于定流量qv工况:①当热流密度较小时,3种热沉内均处于强迫对流换热,无工质相变发生;②KS0由于基板上表面光滑无促进扰动发生的结构,工质基本保持层流状态,而KS1、KS2针肋结构可以有效地促进湍流的发生,强化单相对流换热系数;③当热流密度足够大时,由于KS2表面形貌更加不规则,随着热流密度Φ的进一步增大,针肋上表面更易形成汽化核心促进局部相变的发生。对于固定热流密度Φ工况:随着流量的降低,KS1、KS2两种强化热沉均能促进相变的发生,但KS2进入两相工况的时间更早,气泡的生成速率更快。
5. 结论
本文结合高速显微摄像手段,研究了不同肋化表面(光滑肋化表面/粗糙肋化表面)结构形态对受限式阵列射流冷却的流动、传热特性的影响。为了对其展开研究,设计了一种可用于高热流密度散热的可视化复合阵列射流冷却热沉,其中针肋尺寸均为0.6 mm×0.6 mm×1.0 mm的矩形针肋;粗糙肋化表面的针肋外覆多孔介质层颗粒尺寸73~53 μm,厚度约为2倍的颗粒直径。
实验测试的结果表明,2种肋化射流表面相较对照组光滑射流表面,均可以同时提升射流冷却热沉的单相强迫对流换热性能,并促进两相工况沸腾相变的发生。
在使用无水乙醇为工质,保持入口温度恒定Tin=(20±1)℃时,分别对加热热流密度逐渐增加、固定入口工质流量qv=(7.5±0.5) mL/s;及固定加热热流密度、入口工质流量持续变化两种工况下对射流腔内流动与传热情况展开了性能测试及可视化观测研究。结果表明:
1) 在固定工质流量不变的工况中,由于工质流量相对较大,各热沉内均未观察到射流腔内有显著的相变发生。
2) 在固定加热热流密度的工况中,随着工质流量的减小,可以在两种肋化表面射流热沉的射流腔内观察到泡状流、弹状流、环状流的发生。
3) 粗糙肋化表面相较光滑肋化表面传热性能更优,且其射流腔内可以更早地观察到沸腾现象的出现,即烧结多孔层可以有效地促进相变的发生,并优化整体性能。
-
表 1 人体隐蔽违禁物检测IoU对比
Table 1. Comparison of IoU for detection of concealed forbidden objects on human body
检测方式 a b c d e 远距离检测 0.642 0.859 0.782 0.490 0.648 近距离检测 0.786 0.810 0.362 0.584 0.853 -
[1] 王任肩, 王宇光, 陈志福, 等.大型活动中的安检排爆工作及技术保障研究[J].警察技术, 2018(5):19-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9875.2018.05.004WANG R J, WANG Y G, CHEN Z F, et al.Research on exploder clearing work and technical support in security inspection of large activities[J].Police Technology, 2018(5):19-22(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9875.2018.05.004 [2] 费鹏, 方维海, 温鑫, 等.用于人员安检的主动毫米波成像技术现状与展望[J].微波学报, 2015, 31(2):91-96.FEI P, FANG W H, WEN X, et al.State of the art and future prospect of the active millimeter wave imaging technique for personnel screening[J].Journal of Microwaves, 2015, 31(2):91-96(in Chinese). [3] GROSSMAN E N, MILLER A J.Active millimeter-wave imaging for concealed weapons detection[C]//Proceedings of Conference on Passive Millimeter-Wave Imaging Technology Ⅵ and Radar International Society for Optics and Photonics.Bellingham: SPIE, 2003, 5077: 62-70. [4] ANDREWS D A, HARMER S W, BOWRING N J, et al.Active millimeter wave sensor for standoff concealed threat detection[J].IEEE Sensors Journal, 2013, 13(12):4948-4954. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2013.2273487 [5] DU K, ZHANG L, CHEN W, et al.Concealed objects detection based on FWT in active millimeter-wave images[C]//Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Electronics and Information Engineering.Bellingham: SPIE, 2017, 10322: 103221O. [6] REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R, et al.Faster R-CNN:Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J].IEEE Transaction on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6):1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [7] 骆尚, 吴晓峰, 杨明辉, 等.基于卷积神经网络的毫米波图像人体隐匿物检测[J].复旦学报(自然科学版), 2018, 57(4):442-452.LUO S, WU X F, YANG M H, et al.Convolutional-neural-network-based human concealed object detection for millimeter wave images[J].Journal of Fudan University(Natural Science), 2018, 57(4):442-452(in Chinese). [8] SINCLAIR G N, ANDERTON R N, APPLEBY R.Passive millimeter-wave concealed weapon detection[C]//Proceedings of Enabling Technologies for Law Enforcement and Security.Bellingham: SPIE, 2001, 4232: 142-152. [9] YEOM S, LEE D, SON J, et al.Real-time outdoor concealed-object detection with passive millimeter wave imaging[J].Optics Express, 2011, 19(3):2530-2536. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.002530 [10] YEOM S, LEE D, JANG Y, et al.Real-time concealed-object detection and recognition with passive millimeter wave imaging[J].Optics Express, 2012, 20(9):9371-9381. doi: 10.1364/OE.20.009371 [11] 周健, 叶金晶, 孙谦晨, 等.主动毫米波成像性别识别算法研究[J].红外, 2018, 39(9):34-40. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8785.2018.09.006ZHOU J, YE J J, SUN Q C, et al.Study of a gender identification algorithm for active millimeter-wave imaging[J].Infrared, 2018, 39(9):34-40(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8785.2018.09.006 [12] SHELHAMER E, LONG J, DARRELL T.Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4):640-651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [13] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R.SegNet:A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12):2481-2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [14] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T.U-Net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. [15] 桑伟, 岳胜利.毫米波成像技术在人体安全检查领域的应用[J].中国安防, 2013(4):83-87. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7873.2013.04.018SANG W, YUE S L.Application of millimeter wave imaging technology on the area of human body security inspection[J].China Security & Protection, 2013(4):83-87(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-7873.2013.04.018 [16] IGLOVIKOV V, SHVETS A.TernausNet: U-Net with VGG11 encoder pre-trained on ImageNet for image segmentation[D].(2018-01-17)[2018-12-20]. [17] LIN M, CHEN Q, YAN S C.Network in network[D].(2014-03-04)[2018-12-20]. [18] SZEGEDY C, LIU W, JIA Y, et al.Going deeper with convolutions[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-9. [19] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al.Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[D].(2015-12-11)[2018-12-20]. [20] HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al.Deep residual learning for image recognition[D].(2015-12-10)[2018-12-20]. [21] XIE S, GIRSHICK R, DOLLÁR P, et al.Aggregated residual transformations for deep neural networks[D].(2017-04-11)[2018-12-20]. [22] KINGMA D P, BA J L.Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[D].(2017-01-30)[2018-12-20]. [23] ZEILER M D, FERGUS R.Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]//Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2014: 818-833. -








 下载:
下载:












 下载:
下载: