-
摘要:
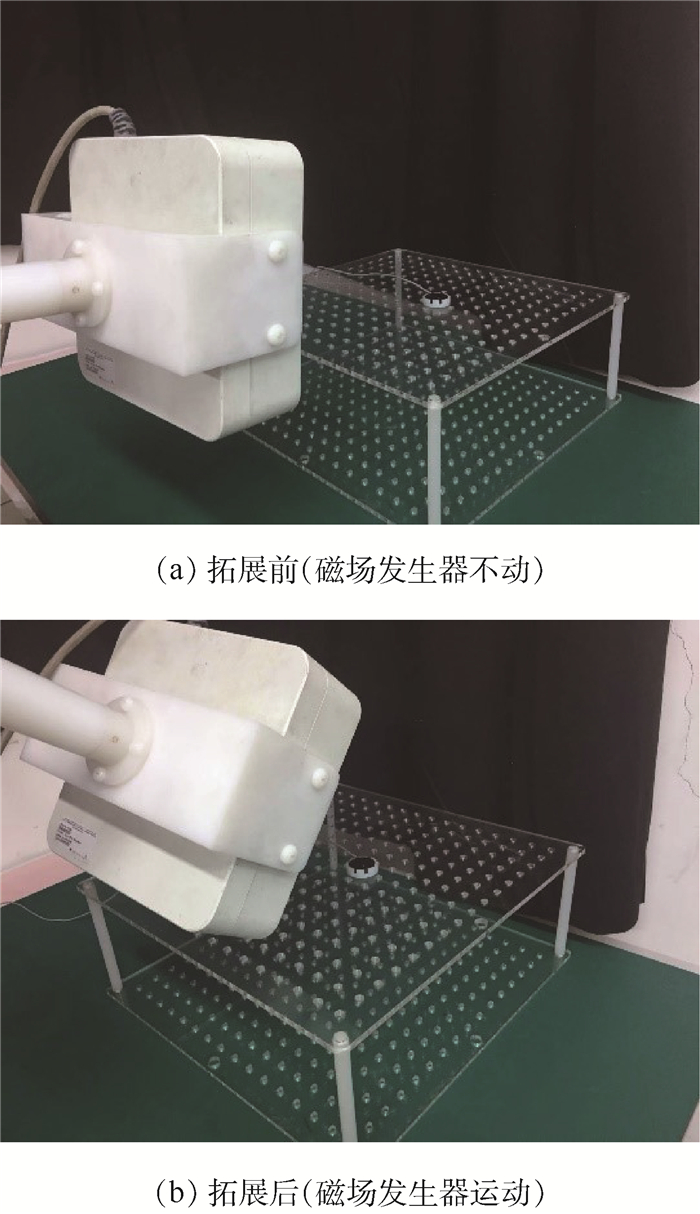
针对NDI电磁定位跟踪设备工作空间有限且在工作空间内定位精度不一致的问题,提出了一种利用机械臂移动磁场发生器从而拓展电磁定位系统工作空间且保证定位精度的方法。利用NDI系统返回的误差指示值衡量定位精度,当误差指示值超出设定的阈值时,利用机械臂移动磁场发生器使传感器重新位于NDI系统的最佳测量工作区,并将电磁定位系统测量的位姿通过空间变换方式统一到机械臂基座坐标系,从而在保证定位精度的同时也起到扩展工作空间的作用。为验证所提方法的有效性,通过实验验证定位误差与误差指标值及传感器到磁场发生器中心的距离成正相关关系;通过拓展前后的误差分析表明,所提方法能有效降低定位误差,平均位置误差从2.61 mm降低到1.34 mm,平均姿态误差从2.42°降低到1.37°。所提方法可应用于类似血管介入手术导管在大范围移动的器械定位与跟踪。
Abstract:Aimed at the problem of limited workspace and inconsistent measurement accuracy of NDI electromagnetic tracking equipment, a method for expanding the workspace of electromagnetic tracking system and guaranteeing measurement accuracy by moving magnetic field generator is proposed. This method uses the indicator value returned by NDI system as the measurement of accuracy. When the indicator value exceeds the set threshold, the magnetic field generator connected with the manipulator is moved to relocate the sensor in the optimum working area, and the position and attitude measured by the system are unified into the coordinate system of the manipulator base through spatial transformation. In order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, experiments are conducted to verify that the measurement error is positively correlated with the indicator value and the distance between the sensor and the center of the magnetic field generator. Then, by comparing the errors before and after the expansion, it is shown that the mean position error can be reduced from 2.61 mm to 1.34 mm, and the mean orientation error can be reduced from 2.42° to 1.37°. This method can be used to locate and track large-scale moving instruments such as vascular interventional catheters.
-
由于圆柱绕流不仅是研究分离流、涡流及有关涡脱落机理的重要基础,而且在航天工程、水利工程等领域都有着重要的工程应用价值,因此关于圆柱绕流的研究受到越来越多的重视。
圆柱绕流问题在早期的研究过程中局限性大,研究成果也都比较简单。1985年,伊杰里奇克[1]通过实验得出在均匀来流条件下,圆柱体的阻力系数Cd大小与来流雷诺数(Re) 有很大关系,并给出了相应的关系曲线。中国科学院力学研究所凌国灿[2]在1985年对圆柱绕流旋涡运动及离散涡方法进行了研究。1992年,清华大学苑明顺[3]用大涡模拟方法对亚临界条件下二维圆柱绕流问题进行了数值模拟,在二维模型中引入了涡量耗散项来模拟涡街的三维涡量耗散效应,对比分析了有关流动特性,结果表明,采用大涡模拟能够得到比较合理的主要流动参数。王亚玲等[4]利用计算流体力学软件CFX-4,对黏性不可压缩流体的圆柱绕流在定常情况下进行了三维数值模拟。国内外学者通过大量的实验和数值方法研究了圆柱绕流的气动力特性及变化规律[5-7],但是关于高雷诺数下圆柱绕流近壁区的流动特征及流动机理等方面的分析还不够深入,对圆柱绕流过程中边界层转捩的影响更是很少关注。
在圆柱绕流过程中,转捩是其中一个重要的影响因素。转捩现象是流体力学中的经典难题,是流体从层流状态到湍流状态的过渡过程。而且在实际的工程应用中,转捩现象是很多飞行器外绕流的一个重要过程,如果能够准确地预测转捩点的位置并且控制转捩的发生,就能够大幅度提高飞行器的空气动力性能。同样对于圆柱绕流问题,如果能够很好地预测并控制转捩过程,模拟出圆柱尾迹的复杂流动状况,对圆柱绕流问题的研究具有非常重要的意义。
基于工程需要,国内外研究人员根据实验结果及经验提出了一些模拟转捩过程的模型,随时间的发展主要是早期提出的低雷诺数湍流模型及其修正形式,其中以Schmidt和Pantankar[8]的工作较有代表性;之后提出的考虑间歇性的转捩模型,其中以Vancoillie和Dick[9]以及Steelant和Dick[10]的工作较有代表性;以及目前提出的基于局部变量的转捩模型,其中有代表性的是Walters和Leylek[11]的工作,以及Langtry和Menter等[12-14]提出的完全基于当地变量的γ-



Transition SST模型的优点为:①避免了一般情况下对平均场进行积分的过程,计算周期短,计算要求较低;②对自由来流湍流度、分离和压力梯度等影响转捩的因素敏感;③与SST k-ω湍流模型相容,便于与现有的CFD程序结合。
本文采用Transition SST模型对亚临界区(Re=1.4×105)、临界区(Re=5.0×105和Re=8.5×105)、超临界区(Re=1×106) 和过临界区(Re=3×106) 的圆柱绕流问题进行了数值模拟,实现了对圆柱绕流的转捩预测。在亚临界区(Re=1.4×105) 和临界区(Re=8.5×105) 的条件下,将其结果与实验结果及采用SST k-ω两方程湍流模型得到的结果进行了对比分析。结果表明,通过Transition SST模型较为准确地预测出了圆柱绕流边界层的转捩过程和圆柱绕流近壁区的流动特征,验证了Transition SST模型在模拟圆柱绕流方面的优越性及该模型预测转捩位置的能力。在此基础上,应用Transition SST模型通过流场结构及摩擦力系数等曲线分析了不同雷诺数下圆柱绕流边界层转捩位置和圆柱绕流近壁区流动特征的变化规律。
1. 数值计算方法
1.1 基本控制方程
对于不可压缩黏性流体,其流动控制方程可表示为

(1) 
(2) 式中:ui为流体沿xi方向的速度分量,在二维情况下i=1,2,u1=u和u2=v分别为水平和垂直方向的速度分量;t为时间;p为压力;Re=ρ∞U∞D/μ为雷诺数,ρ∞为来流密度,U∞为来流速度,D为圆柱直径,μ为黏性系数。
1.2 湍流模型
本文采用的SST k-ω湍流模型中关于湍动能k以及比耗散率ω的输运方程[15]为

(3) 和

(4) 式中:Gk为湍动能的速度梯度;Gω为比耗散率的速度梯度;Γk和Γω分别为k和ω的有效扩散系数;Yk和Yω分别为关于k和ω的湍流耗散项;Dω为交叉扩散项;ρ为来流密度。
SST k-ω湍流模型定义的有效扩散系数[15]Γk和Γω分别为

(5) 
(6) 式中:σk和σω分别为关于k和ω的湍流普朗特数;μt为湍流黏性系数[15],可以通过下式得到:

(7) 其中:S为应变率;a1为模型参数,a1=0.31。
σk和σω[15]分别被定义为

(8) 
(9) 式中:F1和F2为混合函数。
湍流黏性系数μt中a*的定义[15]如下:

(10) 式中:Ret=ρk/μω;Rk=6;a0*=βi/3,βi=0.072;一般对于高雷诺数的SST k-ω两方程湍流模型,a*=a∞*=1。
1.3 转捩模型
将关于间歇因子γ和当地边界层动量厚度雷诺数


(11) 式中:转捩源项[12]定义如下:

(12) 
(13) 
(14) 
(15) 其中:Flength为控制转捩区长度的参数;Ω为旋涡强度;Fonset为涡量雷诺数ReV的函数[12]:

(16) 
(17) 
(18) 
(19) 
(20) 
(21) 
(22) 式中:y为沿外法线方向与壁面之间的距离;Fonset用来启动Pγ,ReV/(2.193Reθc)为当地转捩的判据,当该比值超过1时,Pγ启动,即γ开始增长,Reθc为临界雷诺数,转捩雷诺数

基于动量厚度雷诺数


(23) 式中:

(24) 
(25) 
(26) 
(27) 
(28) 
(29) 
(30) 
(31) 式中:θBL为边界层动量厚度;Reθt为当地转捩雷诺数;Fθt为开关函数,从边界层内到边界层外由1逐渐变为0;Fwake的作用是确保Fθt在圆柱下游的尾流区域中为0;cθt和σθt分别为常数[12]:cθt=0.03,σθt=2.0。
2. 数值模拟条件及网格
2.1 数值计算条件及物理模型
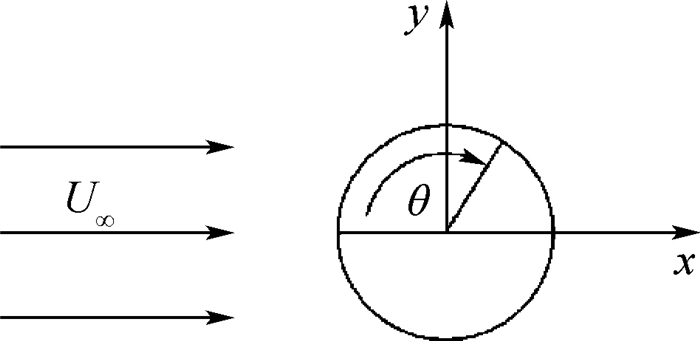
本文研究的是来流速度U∞沿x轴正方向流向直径为D的二维圆柱绕流问题,如图 1所示。图中:θ为圆柱表面的方位角。分别取来流雷诺数Re=1.4×105(亚临界区)、Re=5.0×105、8.5×105(临界区)、Re=1×106(超临界区) 和Re=3×106(过临界区),根据实验条件选择来流的湍流强度为0.8%。
本文时均阻力系数Cd、斯特劳哈尔数St、时均摩擦力系数Cf分别由下列各式确定:

(32) 
(33) 
(34) 式中:Fd为圆柱所受到的时均阻力;f为涡脱落的频率;τ0为壁面剪切应力。
2.2 计算网格及边界条件
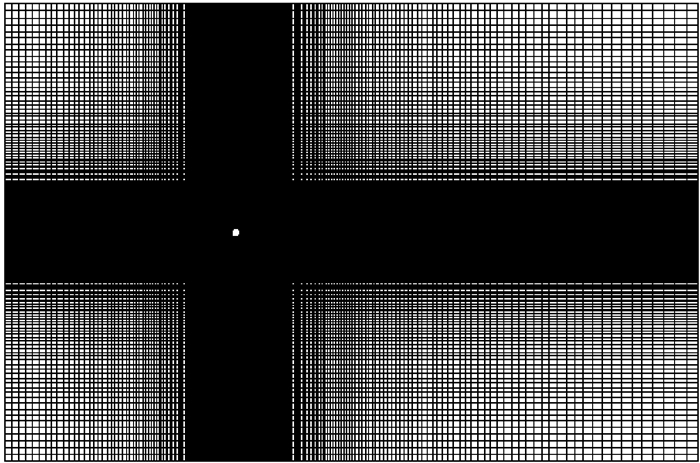
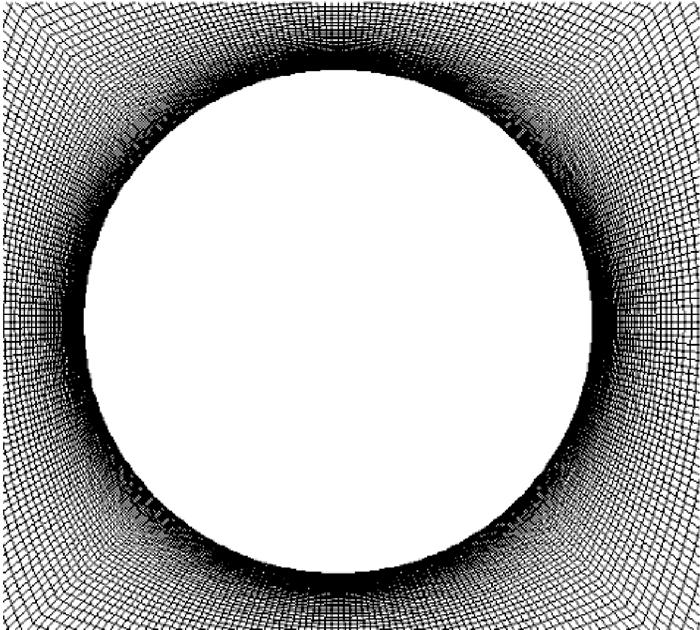
计算域取40D×55D的矩形域,其中计算域左边界和计算域上下边界与圆柱中心的距离均为20D,计算域右边界与圆柱中心的距离为35D。物面法向第1层网格高度由y+~1确定。图 2和图 3分别为整个计算域网格和圆柱表面附近网格的示意图。
计算域的左边界采用速度入口边界条件,在此边界上沿x、y方向速度分量分别为u=U∞,v=0;圆柱表面采用无滑移壁面边界条件,即u=v=0;计算域的上下边界采用对称边界条件;计算域的右边界采用流动出口边界条件。
3. 数值模拟结果
3.1 亚临界区数值模拟结果分析
表 1给出了亚临界区(Re=1.4×105) 时数值模拟计算得到的二维圆柱时均阻力系数Cd和斯特劳哈尔数St的值,其中也给出了Cantwell[16]和Schewe[17]通过实验测得的结果及苑明顺[3]通过数值模拟计算得到的结果。通过表 1中Cd和St的对比可以看出,在亚临界区采用Transition SST模型和SST k-ω模型都能够很好地模拟圆柱绕流问题,但与采用SST k-ω模型模拟所得到的结果相比,采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的结果与实验结果符合得更好。
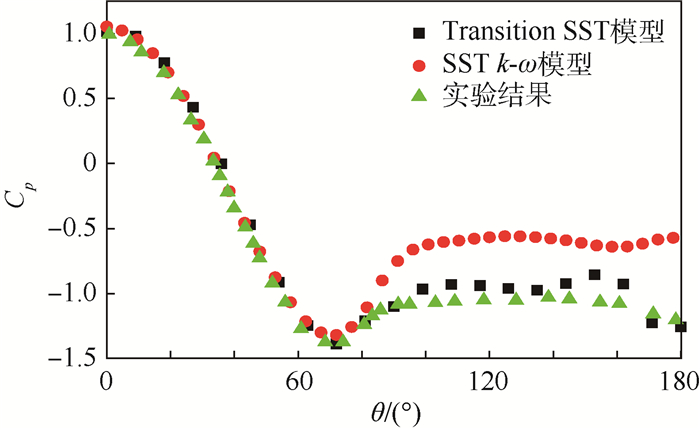
表 1 在亚临界区时二维圆柱时均阻力系数Cd和St数值模拟计算结果Table 1. Numerical predicted results of time average drag coefficient Cd and St of 2D cylinder in subcritical region图 4给出了亚临界区(Re=1.4×105) 时通过数值模拟得到的圆柱表面时均压力系数Cp分布曲线,同时也给出了Cantwell[16]实验测得的结果。
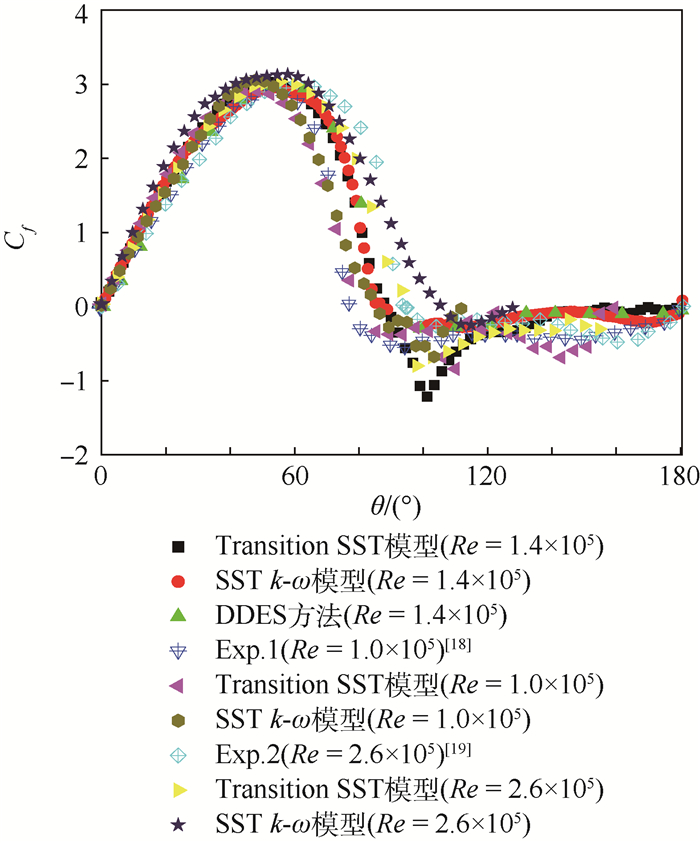
图 5给出了亚临界区(Re=1.0×105、1.4×105和2.6×105) 时通过数值模拟得到的圆柱表面时均摩擦力系数Cf分布曲线,还给出了Krish-nan等[18]通过DDES方法得到的结果以及Achenbach[19]通过实验测得的结果Exp.1(Re=1.0×105) 和Exp.2(Re=2.6×105)。
由图 4和图 5可知,由于Transition SST模型对分离和压力梯度等因素比SST k-ω模型更为敏感,所以采用Transition SST模型更为准确地模拟出了圆柱绕流背风面压力和摩擦力的变化情况,使得采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的压力和摩擦力系数与实验结果更为相符。
从图 5可以进一步看出,采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的结果(Re=1.4×105) 在圆柱上表面θ≈0°~50°范围内Cf随θ增大逐渐增大,并在θ≈50°处达到最大值;在θ≈50°~88°范围内Cf随θ增大而逐渐减小,并在圆柱上表面θ≈88°处Cf的正负符号发生变化,这表明流动在这个位置发生了分离,即分离点的位置为θ≈88°。同样从图 5可以看出,采用SST k-ω模型和Krishnan等[18]通过DDES方法得到分离点的位置分别为θ≈85°和θ≈87°,采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的结果与Krishnan等[18]通过DDES方法得到的结果更加相符。通过3种模型模拟得到的分离点位置介于Re=1.0×105和Re=2.6×105时通过实验方法得到的分离点位置θ≈78°和θ≈94°之间,符合在亚临界区分离点位置随雷诺数增大逐渐后移的变化规律。而在圆柱上表面θ≈88°~120°范围内采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的结果与SST k-ω模型及DDES方法得到不同变化的原因,可能是因为Re=1.4×105时处在亚临界区向临界区的过渡阶段,流动分离后有一个再附的趋势,即有一个形成分离泡的趋势。
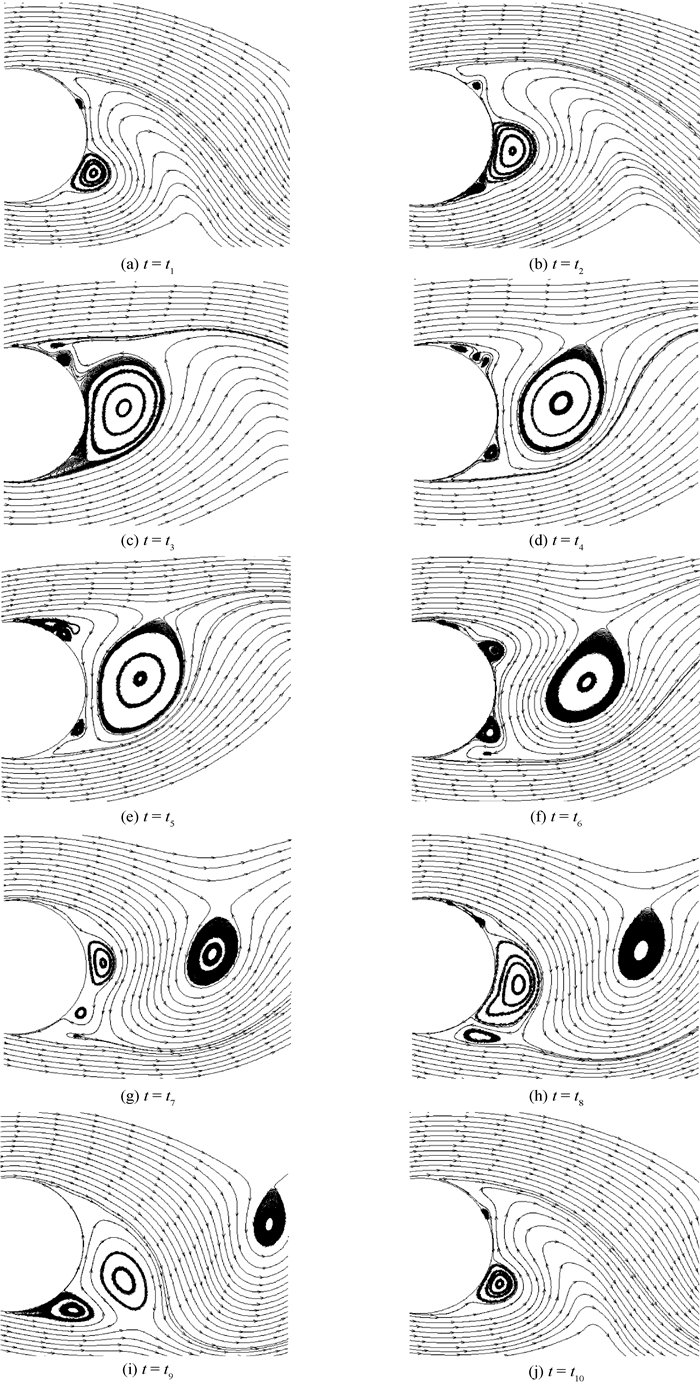
由于Transition SST模型对分离和压力梯度等因素的敏感性,采用Transition SST模型可以较为准确地模拟出亚临界区(Re=1.4×105) 时圆柱绕流尾迹区在一个周期内的流动特征,如图 6所示。对于圆柱绕流问题来说,其尾迹区域的近壁区流动特征主要是分离与局部二次分离产生的不同尺度旋涡的合并、成对、分叉等强烈的相互作用,旋涡脱落的过程实际上是多个涡间以及与剪切层相互作用的结果[17]。在大雷诺数下,只要旋涡强度足够大或者距离壁面足够近,二维或三维旋涡均可在近壁区诱导产生局部分离,形成新的旋涡[20-21]。
从图 6可以看出圆柱背风面尾迹区流动在一个周期内的变化过程。由于t1时刻尾迹区圆柱下表面附近的旋涡距离壁面足够近,在其诱导作用下t2时刻在尾迹区圆柱下表面附近发生了局部流动分离,产生了一个新的旋涡;尾迹区圆柱下表面附近的旋涡随时间沿流向向后发展逐渐变大,与尾迹区圆柱上表面附近的剪切层相互作用,在t3时刻尾迹区圆柱上表面附近产生了2个正向旋转的小涡,且此2个小涡与之前尾迹区圆柱上表面附近产生的反向旋转的小涡由于旋向以及来流的影响逐渐开始合并,在t6时刻完成合并,成为一个正向旋转的旋涡。同样由于涡间以及来流的影响,在t6时刻发展的正向旋涡和在t2时刻由诱导作用发生局部分离产生的旋涡开始逐渐合并,在t8时刻完成合并发展为一个大的分离涡,之后发生旋涡脱落。这就是尾迹区圆柱上表面附近旋涡产生及发展脱落的过程,同样可以看到尾迹区圆柱下表面附近旋涡产生及发展脱落的过程。
综上所述,由于Transition SST模型对流动分离和压力梯度等因素较为敏感,能够很好地模拟圆柱表面的压力、摩擦力变化及圆柱绕流尾迹近壁区的分离等流动特征,从而使得Transition SST模型更加适用于模拟亚临界区的圆柱绕流问题。
3.2 临界区数值模拟结果分析
表 2给出了临界区(Re=8.5×105) 时对二维圆柱绕流数值模拟得到的时均阻力系数Cd和斯特劳哈数St的值,表中还给出了Achenbach[19]和Jones等[22]的实验结果。可以看出,与采用SST k-ω模型模拟得到的结果相比,采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的Cd和St与实验结果符合得更好。
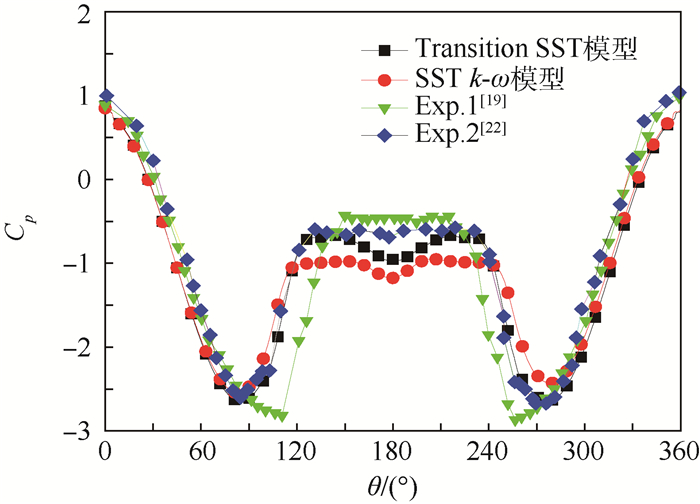
图 7为在临界区(Re=8.5×105) 时数值模拟计算所得圆柱表面时均压力系数Cp分布曲线,还分别给出了Achenbach[19] (Exp.1) 和Jones等[22] (Exp.2) 实验测得的结果。
从图 7可以看出,相比于采用SST k-ω模型模拟得到的圆柱表面压力系数Cp,采用Transition SST模型模拟计算得到的圆柱表面压力系数Cp与Jones等[22]得到的实验结果(Exp.2) 更加相符。而采用SST k-ω模型和Transition SST模型模拟得到的圆柱表面压力系数Cp与Achenbach[19]得到的实验结果(Exp.1) 在圆柱迎风面都符合得很好,但是在圆柱背风面与实验结果差异都比较大。Achenbach[19]提到由于受到实验条件和方法的局限性,在实验过程中没能够很好地模拟圆柱背风面的压力分布,这是在背风面与2种模型模拟的结果和Jones等[22]实验得到的结果产生较大差异的原因。
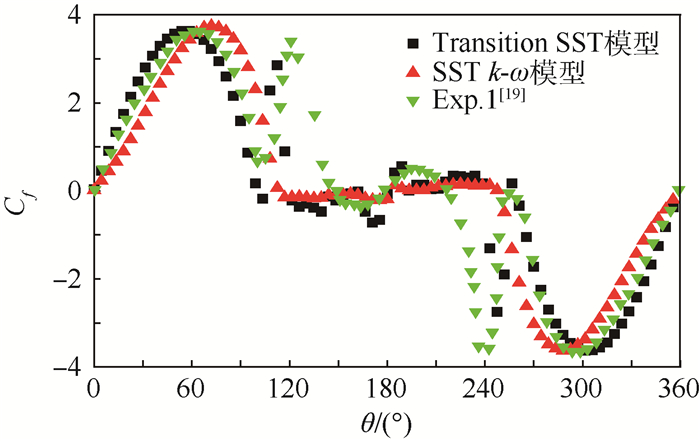
图 8为临界区(Re=8.5×105) 时数值模拟计算所得圆柱表面时均摩擦力系数Cf分布曲线,还
给出了Achenbach[19]实验测得的结果(Exp.1)。可以看出,相比于采用SST k-ω模型,采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的圆柱表面时均摩擦力系数Cf曲线与实验结果更加相符,而且模拟出了与实验结果一致的摩擦力系数Cf突然增大又回落减小的过程,也就是圆柱边界层的转捩过程。
同样,由于Transition SST模型对流动分离和压力梯度等因素的敏感性,使得图 7和图 8中采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的结果与实验结果更为相符。
而且从图 8可以看出,采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的圆柱表面时均摩擦力系数Cf在圆柱上表面θ≈99°处时符号由正变负,之后在θ≈103°处Cf的符号又由负变正,表明在θ≈99°~103°这段位置上边界层流动发生了分离和再附的过程,即产生了分离泡;并且时均摩擦力系数Cf在θ≈103°处变为正值后突然开始变大,之后又回落减小,这说明边界层内流动在这里发生了从层流到湍流的转捩过程;在θ≈120°处Cf的符号再次由正变负,说明流动在这里发生了湍流分离。而实验得到的Cf值在θ≈105°处突然变大,之后又回落减小,在θ≈147°处Cf的符号由正变负发生了流动分离。实验结果中并没有捕捉到边界层分离再附产生的分离泡现象,Achenbach[19]提出理论上应该会产生分离泡,没有产生的原因可能是因为实验条件等问题的影响。
图 8中采用SST k-ω模型与实验结果符合程度最差,且采用SST k-ω模型模拟得到的Cf在θ≈113°处由正变负,圆柱表面在此处流动发生了分离,但并没有模拟出边界层分离再附产生的分离泡现象和边界层转捩现象,不能很好地模拟二维圆柱绕流问题。
从图 8还可以看出,采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的圆柱边界层转捩区是在圆柱上表面θ≈103°~120°的位置,而实验得到的转捩区则是在圆柱上表面θ≈105°~147°的位置。采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的圆柱边界层转捩区长度明显要比实验得到的转捩区长度短。而且可以看出,采用Transition SST模型和SST k-ω模型模拟得到的圆柱边界层分离点位置分别在θ≈120°和θ≈113°处,但是实验得到的分离点位置是在θ≈147°处,采用2种模型模拟得到的分离点位置与实验结果都有一定差异,但采用Transition SST模型得到的模拟结果与实验结果更加接近。
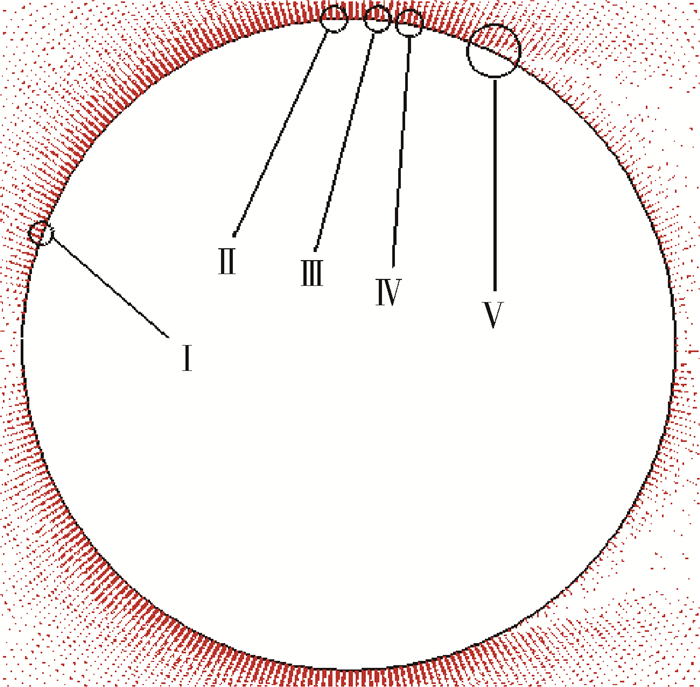
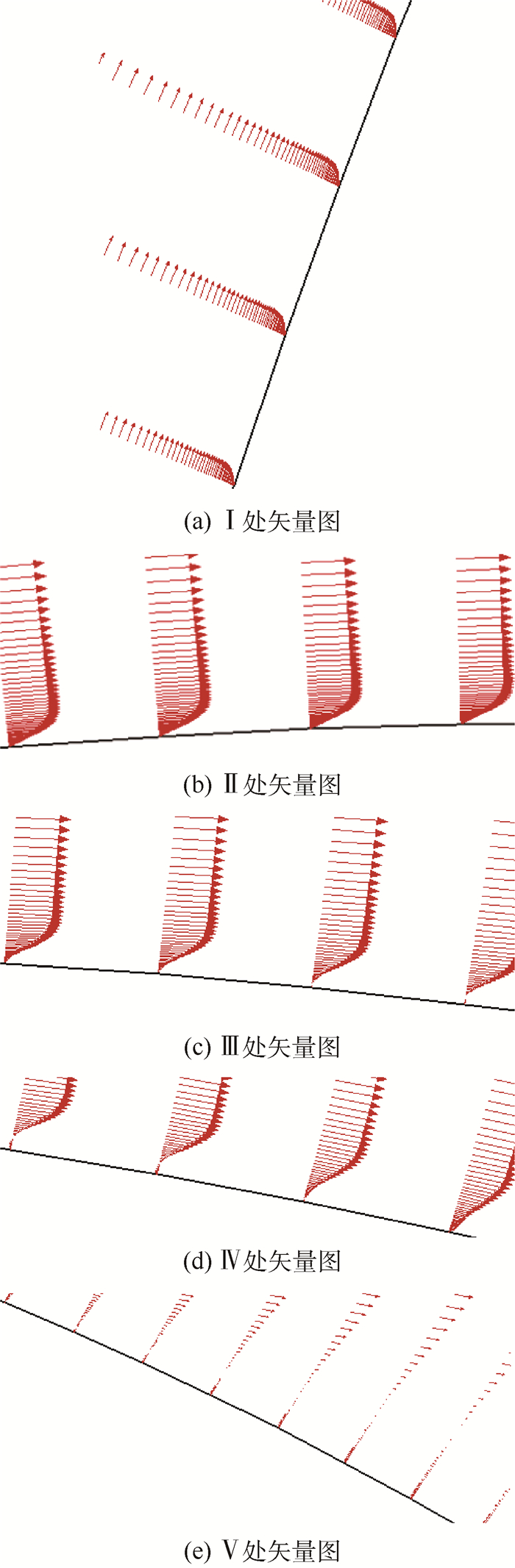
图 9为临界区(Re=8.5×105) 条件下采用Transition SST模型模拟得到的二维圆柱表面附近流场区域的速度矢量图。图 10为图 9中Ⅰ~Ⅴ处的局部放大矢量图。
从图 10(a)可以看到,在此区域内沿流向圆柱上表面外法线方向的速度梯度在逐渐增大,这使得沿流向圆柱上表面剪切应力逐渐变大,从而导致沿流向圆柱上表面时均摩擦力系数Cf逐渐变大,这也是图 8中θ从0°增大到60°时沿流向圆柱上表面时均摩擦力系数Cf逐渐增大的原因。
从图 10(b)可以看到,在此区域内沿流向圆柱上表面外法线方向的速度梯度在逐渐变小,这使得沿流向圆柱上表面剪切应力逐渐减小,从而导致沿流向圆柱上表面时均摩擦力系数Cf是逐渐减小的,这也是图 8中θ从60°增大到99°时沿流向圆柱上表面时均摩擦力系数Cf逐渐减小的原因。
从图 10(c)和图 10(d)可以看到,此区域圆柱上表面附近气流的速度矢量方向先是与主流方向相同,在θ≈99°时圆柱表面附近气流的速度矢量方向变为零,之后速度矢量与主流方向相反,在θ≈103°之后又从与主流方向相反变为与主流方向相同。这说明在θ≈99°~103°范围内流动发生了分离和再附的过程,即形成了一个分离泡。这也是图 8中在圆柱上表面θ≈99°~103°范围内时均摩擦力系数Cf为负值的原因,即Cf的正负符号2次发生变化的原因。
从图 10(e)可以看到,在θ≈120°之后圆柱表面附近流动方向与主流方向相反,说明在此处之后流动发生了分离。同样这也是图 8中在圆柱上表面θ≈120°~180°范围内Cf变为负值的原因。
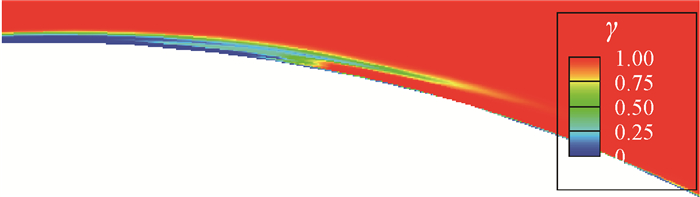
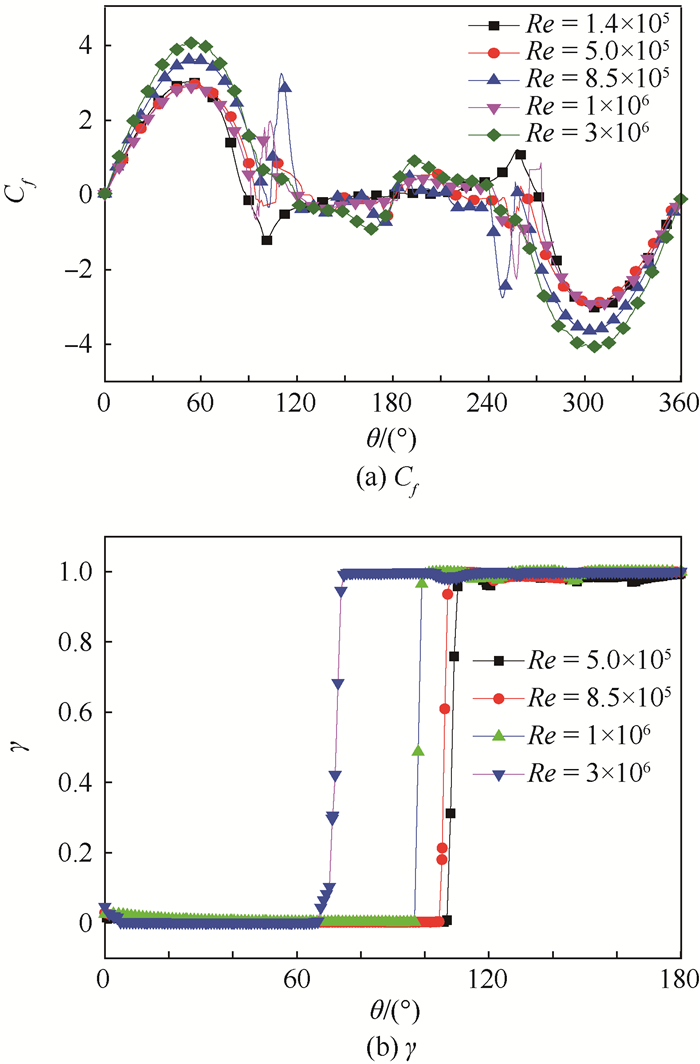
图 11为圆柱上表面附近流场间歇因子γ分布云图。图中:γ=0代表层流流动,γ=1代表完全湍流,γ从0到1的变化过程即发生了转捩。通过图 11可以看出,在圆柱上表面θ≈103°处边界层发生了转捩,边界层的流动从层流流动变成了湍流流动,导致圆柱表面摩擦力突然增大。这即是图 8中在θ≈103°处圆柱上表面时均摩擦力系数Cf突然急剧增大,并在增大到最大值后回落的原因。
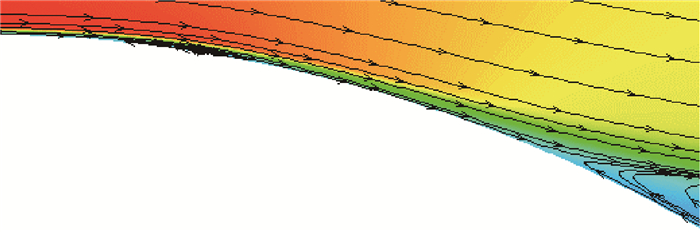
图 12为圆柱上表面过顶点后局部速度云图和流线图,为了展示圆柱壁面附近的流动规律,对壁面附近的流线进行了加密处理。从图 12也可以看出,过圆柱上表面顶点之后在θ≈99°~103°的区域内边界层出现了流动分离并再附的过程,即产生了一个分离泡,与图 10(c)和图 10(d)的结果对应一致。分离再附之后,沿圆柱表面向后流动,在θ≈120°处流动最终发生湍流分离,形成尾迹流。
与亚临界区圆柱绕流问题的情况相同,由于Transition SST模型对分离和压力梯度等影响转捩的因素较为敏感,使得采用Transition SST模型能够很好地捕捉到圆柱绕流边界层内的转捩过程以及圆柱绕流尾迹近壁区的流动特征,从而可以更好地模拟临界区的圆柱绕流问题。
3.3 不同雷诺数下的模拟结果对比分析
图 13为采用Transition SST模型在不同雷诺数下对二维圆柱绕流模拟计算得到的圆柱表面时均摩擦力系数Cf和圆柱边界层的间歇因子γ分布曲线。图 14为模拟所得到的不同雷诺数条件下圆柱上表面附近局部流场的速度分布云图和流线图,为了展示圆柱壁面附近的流动变化,对圆柱壁面附近的流线进行了加密处理。
由图 13(a)可以看出,当雷诺数Re=1.4×105时(亚临界区),在θ≈85°处圆柱表面时均摩擦力系数Cf直接从正值变为负值。从图 14(a)的流场结构可以看到,这是因为流体在绕圆柱流动过程中,在θ≈85°处边界层分离后直接形成了背风面底部分离涡流动区。
从图 13(a)可以看到,对应Re=5.0×105、8.5×105(临界区) 和Re=1×106(超临界区),圆柱表面时均摩擦力系数Cf的符号分别在θ≈94°、99°和90°处从正值变成负值,之后分别在θ≈107°、103°和97°处Cf的符号又由负值变成正值,从图 14(b)、图 14(c)和图 12的流场结构中可以看出这是因为流体在绕圆柱流动过程中发生了一个分离到再附的过程,即形成了一个分离泡。
从图 13(a)可以看到,当Re=5.0×105时,在θ≈107°处圆柱上表面的时均摩擦力系数Cf发生了突然增大之后回落减小的过程,而且由图 13(b)可见,在此处边界层间歇因子γ发生了从0到1的变化过程,说明流动在θ≈107°处发生转捩;同样可以看出,当Re=8.5×105和1×106时,圆柱表面边界层内的流动发生了从层流到湍流的转捩过程,且转捩点分别在θ≈103°和θ≈97°附近。从以上结果可知,对于二维圆柱绕流问题,当雷诺数在临界区和超临界区时,随着雷诺数的增大,圆柱边界层转捩点的位置逐渐向来流方向移动。
从图 13(a)还可以看到,当雷诺数Re=3×106(过临界区) 时,在圆柱上表面(或下表面) 时均摩擦力系数Cf仅在θ≈120°时发生了一次从正变为负过程,结合图 14(d)的流场结构可知,在此雷诺数条件下,圆柱绕流直接发生了底部流动分离,在底部流动分离之前没有出现分离泡。从图 13(b)可以看出,当Re=3×106时,在圆柱上表面θ≈63°处边界层间歇因子γ发生了从0到1的变化过程,说明在θ≈63°时边界层流动发生了从层流到湍流的转捩,但图 13(a)中在Re=3×106时圆柱表面时均摩擦力系数Cf的值并未出现突增的现象,这是因为转捩前Cf的值就很大,而转捩引起的Cf的变化较小,导致转捩时Cf的变化不明显。
4. 结论
本文采用SST k-ω两方程湍流模型与γ-

1) 采用Transition SST模型能够很好地模拟圆柱绕流问题。这是由于Transition SST模型对流动分离和压力梯度等因素较为敏感,所以可以很好地捕捉到不同雷诺数下圆柱绕流尾迹近壁区的流动特征,并且能够较为准确地预测边界层转捩位置及转捩过程。
2) 当自由来流雷诺数处于临界区、超临界区和过临界区时,圆柱绕流边界层会出现从层流到湍流的转捩过程,且圆柱绕流边界层转捩位置随雷诺数增大逐渐靠近圆柱前驻点(即θ=0°)。
3) 当自由来流雷诺数处于亚临界区时,圆柱绕流边界层发生层流分离,无分离泡及转捩现象发生;当自由来流雷诺数处于临界区和超临界区时,圆柱绕流边界层产生分离泡后发生转捩现象,并在转捩后圆柱绕流边界层发生湍流分离;当自由来流雷诺数处于过临界区时,圆柱绕流边界层无分离泡现象发生,且在转捩之后发生湍流分离。
-
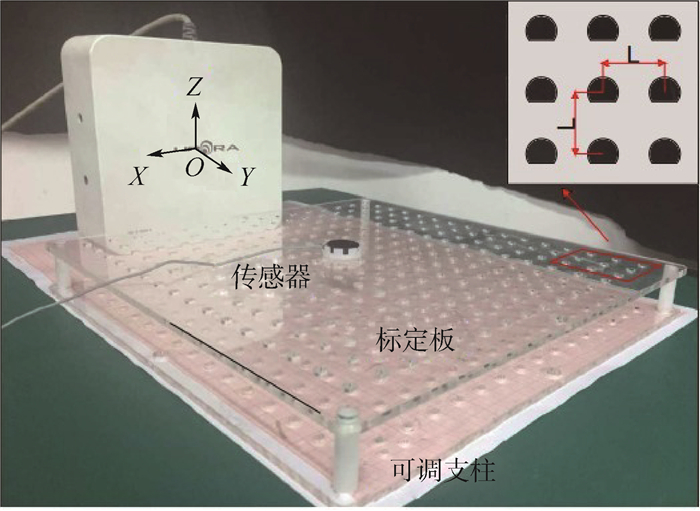
表 1 几种电磁定位产品主要性能指标
Table 1. Main performance indicators of several electromagnetic tracing products
产品 测量距离/mm 位置精度/mm 方位精度/(°) Aurora 500 1.6 1.1 Fastrak 762 0.762 0.15 Isotrak 762 2.54 0.75 表 2 不同平面拓展前后位置误差与姿态误差
Table 2. Position error and orientation error of different planes before and after expansion
Z/mm 拓展前位置误差/mm 拓展后位置误差/mm 拓展前姿态误差/(°) 拓展后姿态误差/(°) Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD 0 2.74 0.71 1.34 0.28 2.36 1.13 1.41 0.41 90 2.42 0.64 1.28 0.19 2.29 1.25 1.32 0.28 150 2.68 0.65 1.39 0.22 2.62 1.38 1.37 0.32 平均值 2.61 0.67 1.34 0.23 2.42 1.25 1.37 0.34 -
[1] FRANZ A M, HAIDEGGER T, BIRKFELLNER W, et al.Electromagnetic tracking in medicine—A review of technology, validation, and applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2014, 33(8):1702-1725. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2014.2321777 [2] BIRKFELLNER W.Calibration of tracking systems in surgical environment[J].IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 1998, 17(5):737-742. [3] PÉRIÉ D, TATE A J, CHENG P L, et al.Evaluation and calibration of an electromagnetic tracking device for biomechanical analysis of lifting tasks[J].Journal of Biomechanics, 2002, 35(2):293-297. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9290(01)00188-9 [4] FEUERSTEIN M, REICHL T, VOGEL J, et al.Magneto-optical tracking of flexible laparoscopic ultrasound:Model-based online detection and correction of magnetic tracking errors[J].IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2009, 28(6):951-967. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2008.2008954 [5] WALLACE M J, GUPTA S, HICKS M E.Out-of-plane computed-tomography-guided biopsy using a magnetic-field-based navigation system[J].Cardio Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 2006, 29(1):108-113. doi: 10.1007/s00270-005-0041-0 [6] KRVCKER J, XU S, GLOSSOP N, et al.Electromagnetic tracking for thermal ablation and biopsy guidance:Clinical evaluation of spatial accuracy[J].Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 2007, 18(9):1141-1150. doi: 10.1016/j.jvir.2007.06.014 [7] WOOD B J, ZHANG H, DURRANI A, et al.Navigation with electromagnetic tracking for interventional radiology procedures:A feasibility study[J].Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 2005, 16(4):493-505. doi: 10.1097/01.RVI.0000148827.62296.B4 [8] GERGEL I, GAA J, MVLLER M, et al.A novel fully automatic system for the evaluation of electromagnetic tracker[C]//Conference on Medical Imaging-Image-Guided Procedures, Robotic Interventions and Modeling.Bellingham: SPIE, 2012, 8316: 831608. [9] BOUTALEB S, RACINE E, FILLION O, et al.Performance and suitability assessment of a real-time 3D electromagnetic needle tracking system for interstitial brachytherapy[J].Journal of Contemporary Brachytherapy, 2015, 7(4):280-289. [10] KWARTOWITZ D M, RETTMANN M E, HOLMES D R, et al.A novel technique for analysis of accuracy of magnetic tracking systems used in image guided surgery[C]//Conference on Medical Imaging 2010-Visualization, Image-Guided Procedures, and Modeling.Bellingham: SPIE, 2010, 7625: 76251L. [11] 关少亚, 孟偲, 万元宇, 等.基于薄板样条函数的电磁定位系统位姿校正方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(11):2350-2355. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract14640.shtmlGUAN S Y, MENG C, WAN Y Y, et al.A thin plate spline based method for correction of position and posture of electromagnetic tracking system[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(11):2350-2355(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract14640.shtml [12] REICHL T, GARDIAZABAL J, NAVAB N.Electromagnetic servoing—A new tracking paradigm[J].IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging, 2013, 32(8):1526-1535. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2013.2259636 [13] LUND K.Electromagnetic navigation vs fluoroscopy in aortic endovascular procedures—A phantom study[J].International Journal of Computer Assisted Radiology & Surgery, 2016, 12(1):1-7. [14] VILLAGRAN C R T, IKEDA S, FUKUDA T, et al.Catheter insertion path reconstruction with autonomous system for endovascular surgery[C]//International Symposium on Computational Intelligence in Robotics & Automation.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 47. [15] 秦成.电磁跟踪系统的研究[D].武汉: 华中科技大学, 2013.QIN C.The research of electromagnetic tracking system[D].Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [16] 罗伟, 张庆, 李珊珊, 等.新一代Aurora电磁跟踪系统在医学手术导航中的应用[J].中国医疗器械杂志, 2013, 37(2):126-128.LUO W, ZHANG Q, LI S S, et al.New generation Aurora electromagnetic tracking system in the medical surgical navigation[J].Chinese Journal Medical instrumentation, 2013, 37(2):126-128(in Chinese). [17] RAAB F, BLOOD E, STEINER T, et al.Magnetic position and orientation tracking system[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1979, 15(5):709-718. [18] PARK F C, MARTIN B J.Robot sensor calibration:Solving AX=XB on the Euclidean group[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1994, 10(5):717-721. doi: 10.1109/70.326576 [19] Northern Digital Inc.Aurora user guide[Z].Revision 4.Waterloo: Northern Digital Inc., 2008: 38. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王宝元. 基于传播路径特性分析的电磁信号局放源定位方法研究. 宁夏师范学院学报. 2020(04): 24-29 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 毕津滔,张永德,孙波涛. 基于电磁跟踪与超声图像的介入机器人穿刺导航方法及实验研究. 仪器仪表学报. 2019(07): 253-262 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(5)
-








 下载:
下载:














 下载:
下载:




 百度学术
百度学术