-
摘要:
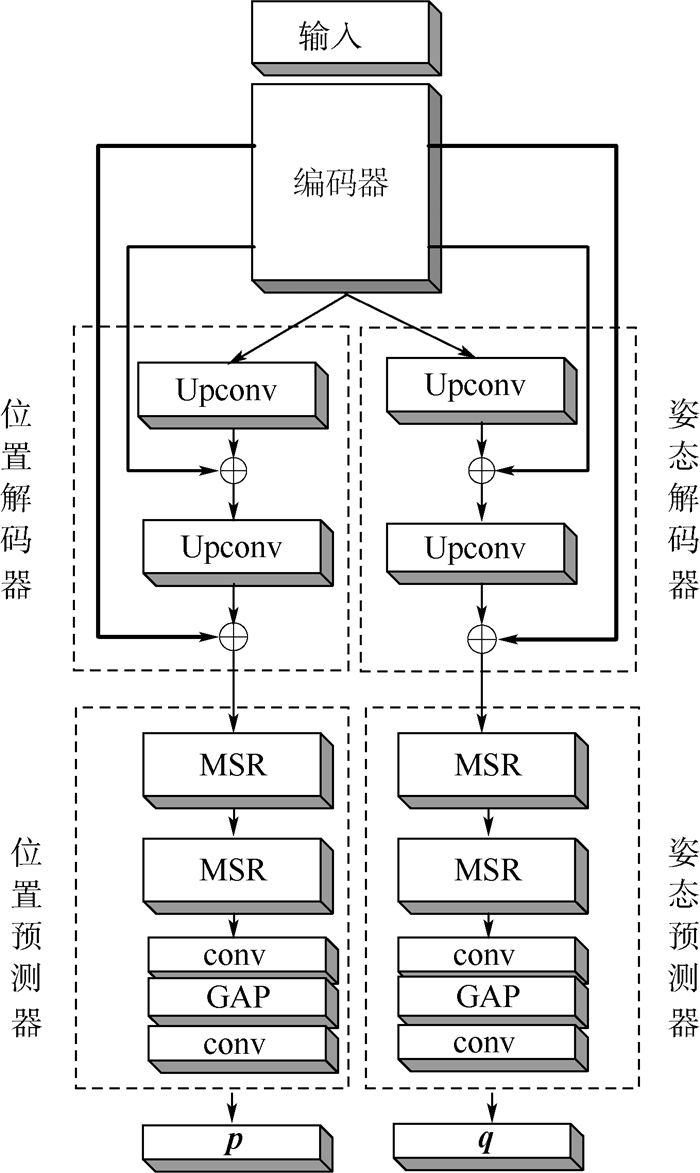
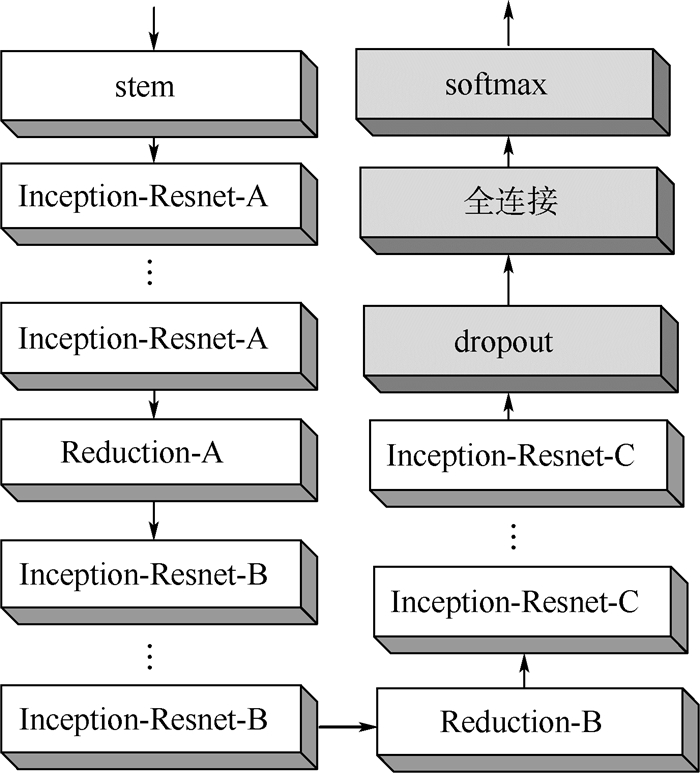
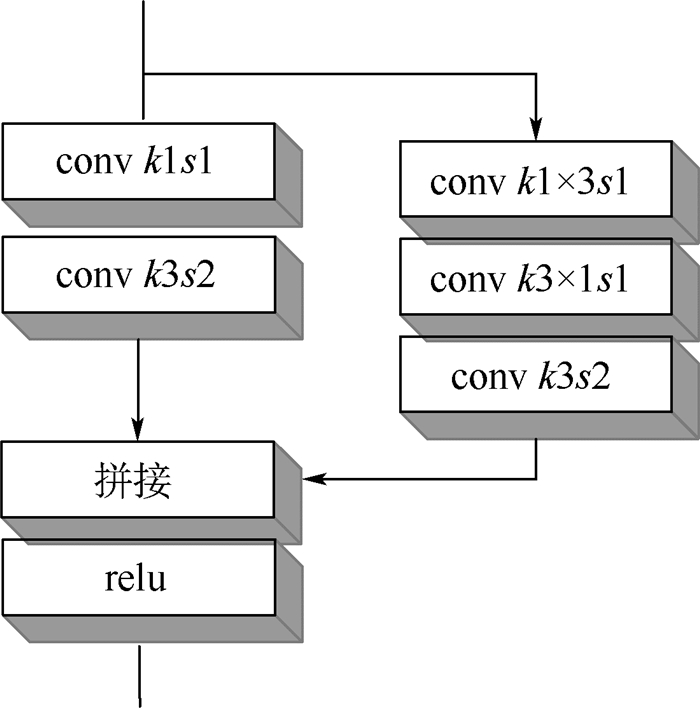
为了从单张RGB图像估计出相机的位姿信息,提出了一种深度编解码双路卷积神经网络(CNN),提升了视觉自定位的精度。首先,使用编码器从输入图像中提取高维特征;然后,使用解码器提升特征的空间分辨率;最后,通过多尺度位姿预测器输出位姿参数。由于位置和姿态的特性不同,网络从解码器开始采用双路结构,对位置和姿态分别进行处理,并且在编解码之间增加跳跃连接以保持空间信息。实验结果表明:所提网络的精度与目前同类型算法相比有明显提升,其中相机姿态角度精度有较大提升。
-
关键词:
- 视觉自定位 /
- 编解码结构 /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 跳跃连接 /
- 双路网络
Abstract:In order to calculate the camera pose from a single RGB image, a deep encoder-decoder dual-stream convolutional neural network (CNN) is proposed, which can improve the accuracy of visual localization. The network first uses an encoder to extract advanced features from input images. Second, the spacialresolution is enhancedby a pose decoder.Finally, a multi-scale estimator is used to output pose parameters. Becauseof the differentperformance of position and orientation, the network adopts a dual-stream structure from the decoder to process the position and orientationseparately. To restore the spatial information, several skip connections are added to encoder-decoder architecture. The experimental results show that the accuracy of the network is obviously improved compared with the congener state-of-the-art algorithms, and the orientation accuracy of camera pose is improved dramatically.
-
电磁定位系统(Electromagnetic Tracking System,EM)利用电磁感应原理进行位姿测量,具有实时定位、精度高、不惧遮挡的优点[1-2],因而被广泛应用于医学手术中器械的跟踪定位[3-4]。如Wallace等[5]将EM应用于肾上腺、肝脏、肺等位置病变活检手术中的穿刺针导航;Krücker等[6]将EM应用于消融手术引导;Wood等[7]将EM应用于血管介入手术。
EM应用于手术导航的缺点之一是定位精度易受环境磁场及导磁手术器械的影响。为了测定环境磁场对定位的影响,Gergel等[8]将一个三脚架并行机械臂作为标定机器人,将EM的传感器固定在机械臂末端,并设计程序分别采集机械臂及EM测量的位姿,通过比较二者的差异来测定EM的定位精度。为了提高EM在干扰环境下的定位精度,Boutaleb等[9]设计出一种60 mm×60 mm×15 mm的可移动标定块,对器械在工作空间中的位置和姿态误差进行定量分析,进而提高器械的定位精度。Kwartowitz等[10]设计出一种用于测量定位系统空间定位误差的平面模型,并用该模型改进EM的定位精度。文献[9-10]的方法仅适用于磁场干扰固定的情形,针对移动导磁器械对测量磁场的干扰,笔者在前期工作中,提出一种基于薄板样条函数的方法来动态矫正传感器受到干扰后的误差[11]。Reichl等[12]为了提高电磁定位精度,提出利用电磁伺服跟踪,通过移动磁场发生器,使传感器一直处于系统工作磁场的中心,在提高定位精度的同时拓展了EM的定位空间。
EM应用于手术导航的另外一个缺点是工作空间有限,且定位精度与传感器的距离相关。对于特定脏器的穿刺手术,因脏器尺寸有限,影响不大。但对于血管介入等手术,由于器械的运动范围较大,超出了EM的工作空间,因而只能用于局部区域的导管跟踪,且难以保证定位精度的可靠性。受Reichl等[12]研究的启发,本文提出了一种利用机械臂移动EM中磁场发生器的位置来扩展其工作空间,并通过使传感器位于最佳工作区域的方法来保证定位的精确度。与Reichl等[12]方法不同,本文方法并不试图使传感器始终位于磁场中心周围区域,而是通过置信度确定最佳工作区域,允许根据不同的应用环境设置不同的置信度阈值,更适合临床应用。
1. EM工作原理及局限
1.1 EM工作原理
EM是一种基于法拉第电磁感应定律的空间位姿测量装置,可实现目标的位姿测量及动态跟踪。图 1为NDI公司的交流磁场三轴正交式电磁定位系统Aurora,主要包括磁场发生器、系统控制器、工具联结器及传感线圈。工作时,磁场发生器生成磁场,待测目标上的传感线圈在磁场内接收磁场信号,传感器联结器利用电磁感应将磁场信号转换为电信号,由系统控制器根据信号强度计算得到待测目标的6自由度坐标值,实现对目标的定位跟踪[13-14]。
1.2 EM的局限性
EM是基于电磁感应定律工作的,在应用中,当磁场周围存在铁磁性物质时,EM将会受到电磁涡流产生的磁场干扰而出现定位误差,所以应用EM需要考虑不同环境对定位精度的影响。此外,EM的工作空间有限,当传感器超出其磁场范围时,便无法进行定位跟踪。表 1为几种比较成熟的电磁定位产品指标[15]。可以看出,产品的测量范围有限,应用到较大的介入范围的手术(如结肠镜检查、神经内窥镜检查、支气管镜检查和血管介入导管导航等)无法满足工作空间的要求。
表 1 几种电磁定位产品主要性能指标Table 1. Main performance indicators of several electromagnetic tracing products产品 测量距离/mm 位置精度/mm 方位精度/(°) Aurora 500 1.6 1.1 Fastrak 762 0.762 0.15 Isotrak 762 2.54 0.75 另外,EM在其工作空间范围内跟踪精度并不一致。一般来说,越远离磁场发生器、靠近磁场范围外侧时,定位精度越低[16]。如果忽略这种定位精度的不均匀性,就会导致应用中整个工作空间内的平均定位精度较低,定位效果较差。所以,在实际手术过程中,为了保证较高的定位精度,需要找出定位范围内定位精度较高的区域,在此区域内对手术器械进行跟踪。
2. EM工作空间拓展
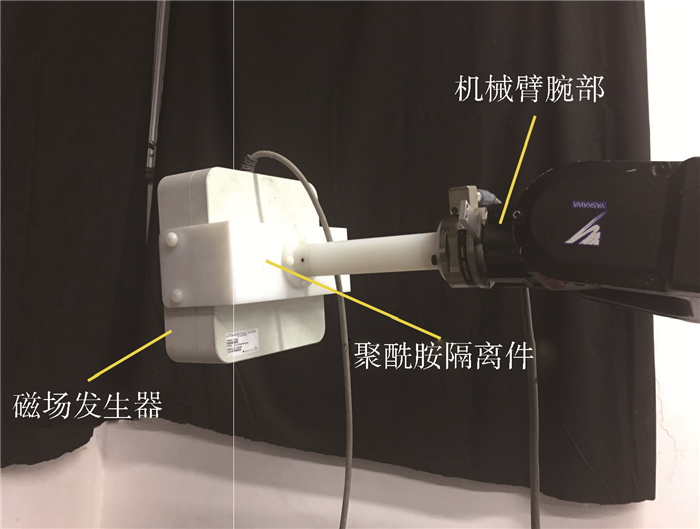
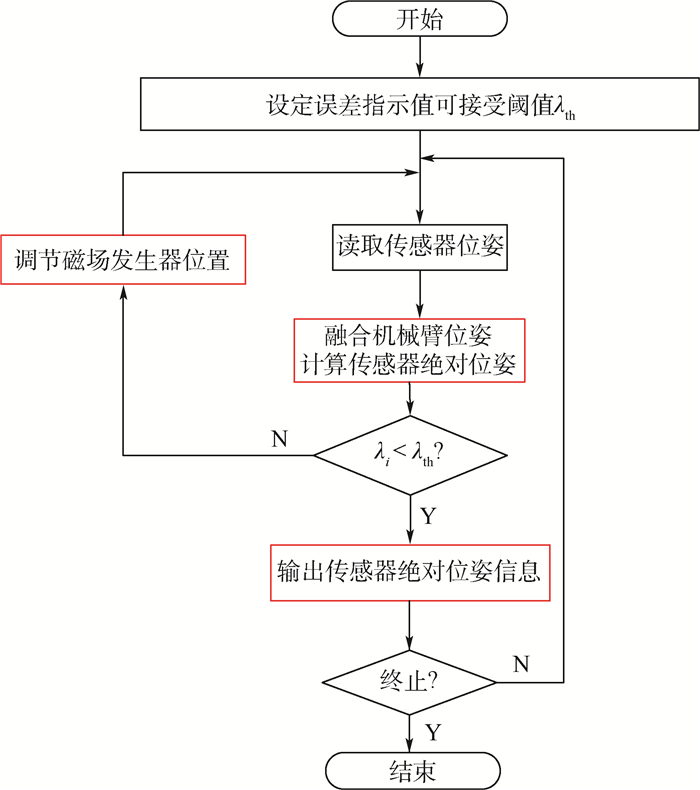
本文提出了一种基于机械臂移动的拓展EM工作空间的方法,使得术中应用EM跟踪大范围运动的手术器械不再受原系统生成磁场范围的限制。如图 2所示,采用通用机械臂(SG-MOTOMAN NX100-HP3,该机械臂有6个自由度,重复定位精度可达±0.03 mm)及电磁定位系统Aurora(定位精度为0.6 mm,可测量6自由度位姿坐标)进行EM工作空间拓展。将Aurora的磁场发生器与机械臂腕部刚性连接,由机械臂带动磁场发生器移动,并融合机械臂位姿将传感器位姿参数统一到机械臂基座坐标系上。如图 3所示,手术过程中系统不断地检测反映测量置信度的误差指示值(indicator value),当判断误差指示值超过预设阈值时,调整磁场发生器的位置,使得传感器线圈一直处在最佳工作区域内。可以由理论推导出,当金属材料到磁场发生器的距离大于磁场发生器到被测传感器的距离的2倍时,由金属材料引起的二次磁场对被测磁场强度的影响不足1%[17]。由于最佳工作区域靠近磁场发生器,传感器距离磁场发生器大致在50~120 mm之间,采用长度为250 mm的聚酰胺材料对磁场发生器与机械臂隔离连接,以忽略机械臂上的金属物质对EM磁场的干扰。此外,拓展要保持传感器在非金属桌子上进行,隔离其他电子设备(如电脑、手机、电灯等),尽可能减少环境对EM定位进行干扰。
2.1 EM工作空间拓展原理
2.1.1 传感器绝对位姿的计算
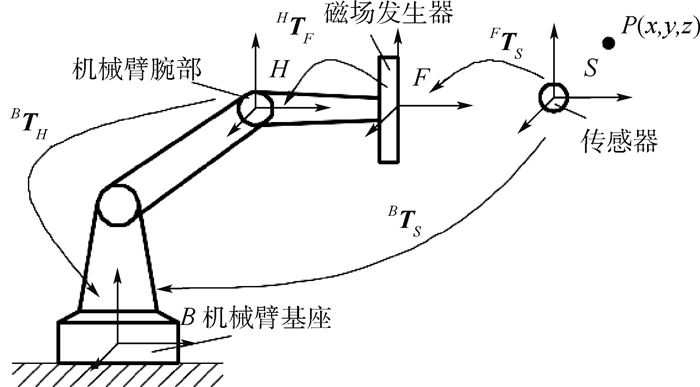
EM测得的位姿为磁场发生器坐标系中传感器线圈的位姿。通过机械臂移动磁场发生器后,由于磁场发生器的位置发生变化,不能用来描述传感器线圈的绝对位姿,需要将移动后用磁场发生器坐标系描述的传感器线圈的位姿统一转化为相对于世界坐标系的绝对位姿。在整个EM拓展流程中,机械臂基座一直处于静止状态,将机械臂基座坐标系视为世界坐标系。对于2个不同的坐标系,其关系可以用6个参数来描述,分别为3个姿态参数(Rx, Ry, Rz)及3个位置参(x, y, z)。对于空间中任意一点P,其在磁场发生器坐标系下的坐标为Ps=[xs, ys, zs]T,在机械臂基座坐标系下的坐标为Pb=[xb, yb, zb]T,二者的转换由式(1)确定:

(1) 式中:R为3×3旋转矩阵,由3个姿态参数决定;T为3×1平移向量,由3个位置参数决定。
根据式(1),可以将磁场发生器测得点的坐标统一到机械臂基座坐标系下。对于求解旋转矩阵R和平移向量T,一般将式(1)改写为

(2) 式中:

图 4为EM工作空间拓展坐标系,从中可以得出

(3) 式中:BTH为4×4机械臂腕部到机械臂基座的转换矩阵;HTF为4×4磁场发生器到机械臂腕部的转换矩阵;FTS为4×4传感器线圈到磁场发生器的转换矩阵。
2.1.2 矩阵标定
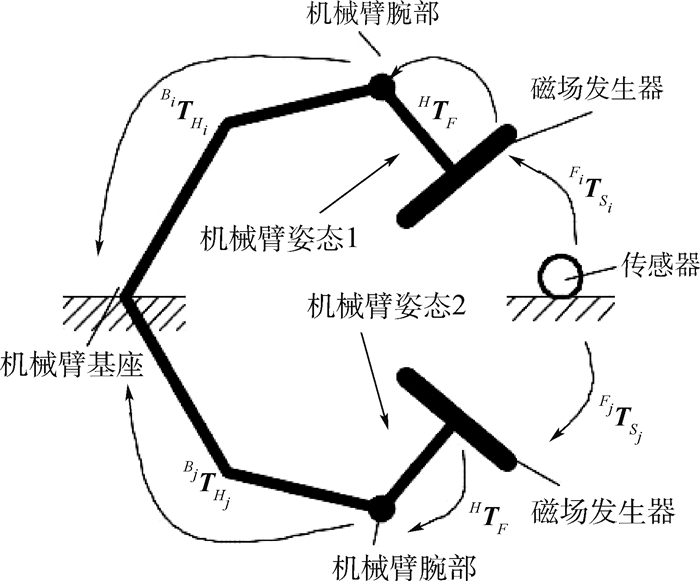
根据式(1)~式(3),可以将传感器线圈坐标系下点的坐标转换到机械臂基座坐标系下,完成点从传感器线圈坐标系到世界坐标系的转换。其中,BTH、FTS可以在实际定位过程中获得,HTF是未知的。在实际应用中,磁场发生器与机械臂腕部刚性连接,HTF保持不变,可以通过标定获得。如图 5所示,为了获得HTF,固定传感器线圈及机械臂基座的位置,使得机械臂基座到传感器线圈的BTS不变,通过机械臂腕部运动带动磁场发生器,改变BTH、FTS来计算得出HTF:

(4) 式中:BTHi为当前机械臂腕部到机械臂基座的转换矩阵;FiTSi为当前传感器线圈到磁场发生器的转换矩阵。

(5) 通过式(5),将式(4)转化为AX=XB形式,利用Park和Martin[18]的求解方法即可标定出磁场发生器与机器人末端的坐标变换关系。标定过程可在手术前一次性完成,简单迅速。
2.2 基于误差指示值调整磁场发生器
由于EM在其工作空间内的定位精度并不一致,应用过程中需要在具有较高精度的定位区域跟踪传感器。不同的EM会有不同的评估测量置信度的方法,如Aurora在每次完成对传感器位姿的计算后,都会返回一个无单位误差指示值(范围为0~9.9),可以利用误差指示值反映定位精度。6自由度传感器内含2个相对位置已知且正交放置的传感器线圈,Aurora系统控制器得到传感器中传感器线圈1的测量值后,通过传感器预定义文件的信息计算得出传感器线圈2的位姿,将传感器线圈2位姿的计算值与测量值进行比较计算得出误差指示值。因此,磁场受到外界的干扰越大,测量值越不准确,误差指示值也越大[19]。
为保证EM定位传感器能保持在最佳工作区域内,通过设定一个误差指示值的阈值λth作为传感器线圈是否处于最佳工作区域的评判标准,当误差指示值超出此阈值时视为定位精度不满足手术要求。在手术中,系统随时检测传感器的位姿,对与系统返回的误差指示值进行判断,一旦误差指示值超出设定的阈值,机器人就会对磁场发生器的位置进行调整:

(6) 式中:HiTFi为磁场发生器到机械臂腕部的转换矩阵;FiTFi+1为磁场发生器当前位姿到磁场发生器下一次位姿的转换矩阵。
3. 实验分析
3.1 误差指示值验证实验
为了验证Aurora的误差指示值能否反映EM的定位误差的变化趋势,设计了实验进行验证。
3.1.1 实验模型
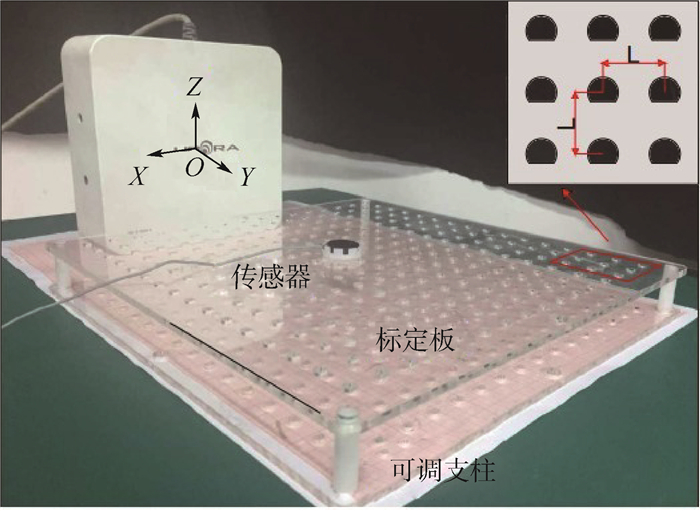
如图 6所示,实验用磁场发生器为Aurora方盒型磁场发生器,传感器为直径25 mm的6自由度盘状传感器。标定板为激光切割的亚克力板,标定板上均布间隔距离一致的D型定位孔。传感器与带有定位销的放置架固定可以插入标定板上的定位孔中。标定板上的D型定位孔朝向一致,当保持磁场发生器与标定板的相对位置不变时,可以保证放置架插入任一定位孔时传感器相对于磁场发生器姿态不变。可以通过可调支柱来调节标定板相对磁场发生器在Z方向上的高度。
3.1.2 实验过程与评价指标
保证磁场发生器与标定板位置固定,可调支柱高度固定,在标定板上选择8×8个定位孔进行采样,记录传感器在每个采样点的6自由度位姿(x,y,z,Rx, Ry, Rz)和误差指示值,进行位置误差和姿态误差的计算。
对于位置误差,设标定板上一点i的位置坐标为(xi, yi, zi),其相邻点j的位置坐标为(xj, yj, zj),则点i与相邻点j的距离为

设标定板平面内相邻两点的距离为LGT, 则点i与相邻点j的距离误差为ΔLi,j=|LGT-Li, j|。对与点i相邻的四邻域点分别计算距离误差,定义点i位置误差为

对于姿态误差,选择距离磁场发生器最近的3×3个点的姿态参数的平均值(Rx,Ry,Rz)作为整个标定板上所有采样的姿态真值。测得任意一点i的姿态为(Rxi,Ryi,Rzi),则点i的姿态误差为

3.1.3 实验结果与分析
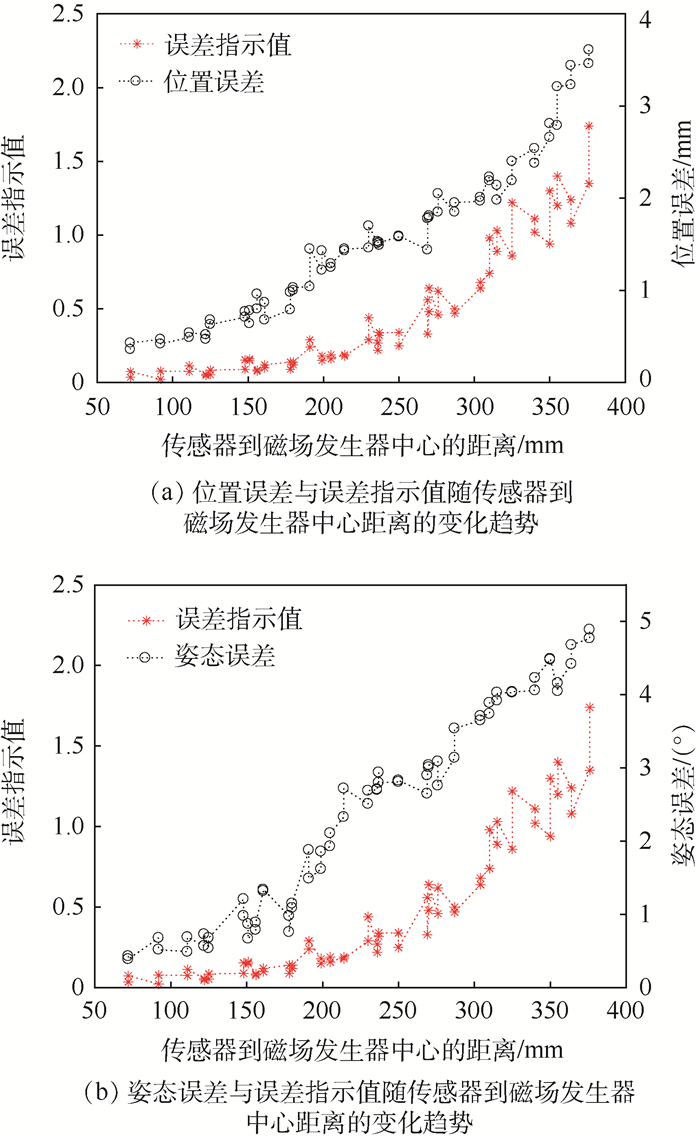
采集8×8个采样点,记录每个采样点的6自由度位姿和误差指示值后,计算每个采样点的位置误差及姿态误差,并以传感器到磁场发生器中心的距离为横坐标,以误差指示值及位置误差或姿态误差为纵坐标绘制图 7。
随着传感器与磁场发生器中心距离的增大,误差指示值呈现增大的趋势,同时位置误差和姿态误差也同样呈现增大的趋势,说明误差指示值可以反映定位误差的变化趋势。从图 7也可以看出,距离磁场发生器中心较近的区域,如距离区间为70~120 mm内,传感器在此区间内逐渐远离磁场发生器中心,虽然位置误差、姿态误差和误差指示值都在增加,但是增加的幅度相对较慢。在进行EM工作空间拓展时,可以在此区间内选定误差指示值阈值来移动磁场发生器保证定位精度。
3.2 EM工作空间拓展验证实验
为了验证本文提出的根据误差指示值阈值调整磁场发生器的方法对于提升EM的定位精度是否有效,设计了EM工作空间拓展验证实验进行验证。
3.2.1 实验模型
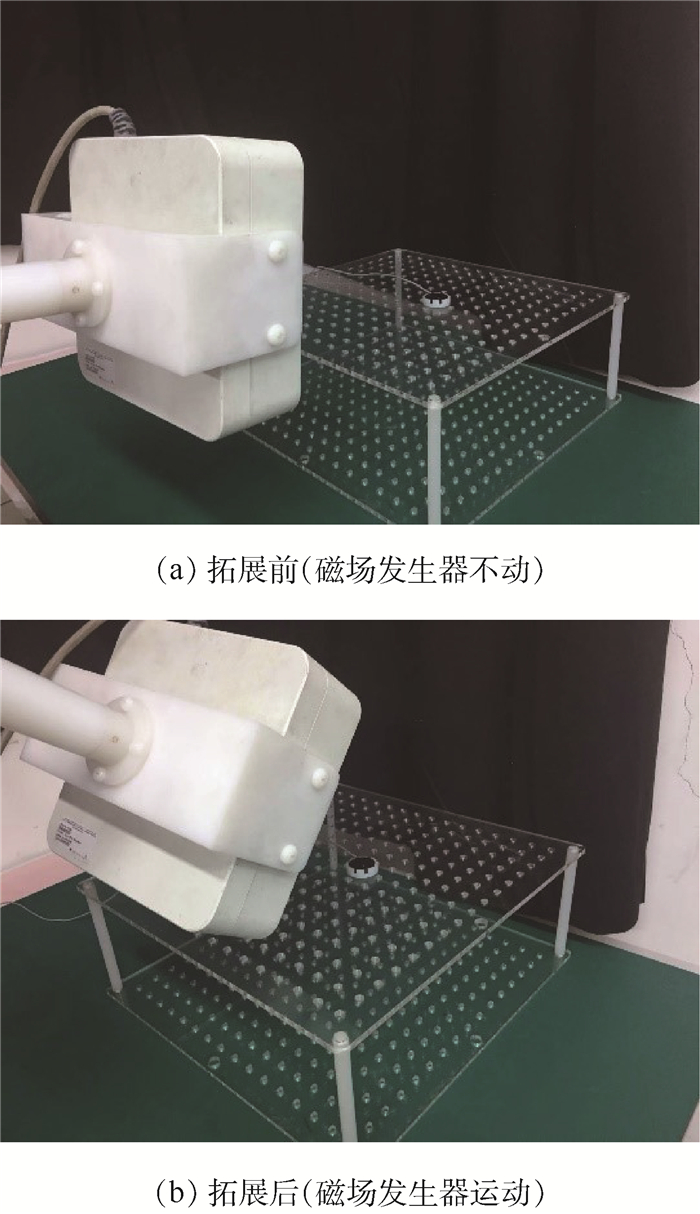
如图 8所示,采用机械臂通过聚酰胺连接件夹持Aurora磁场发生器,对比EM工作空间拓展前后的位置误差及姿态误差。
3.2.2 实验过程与评价指标
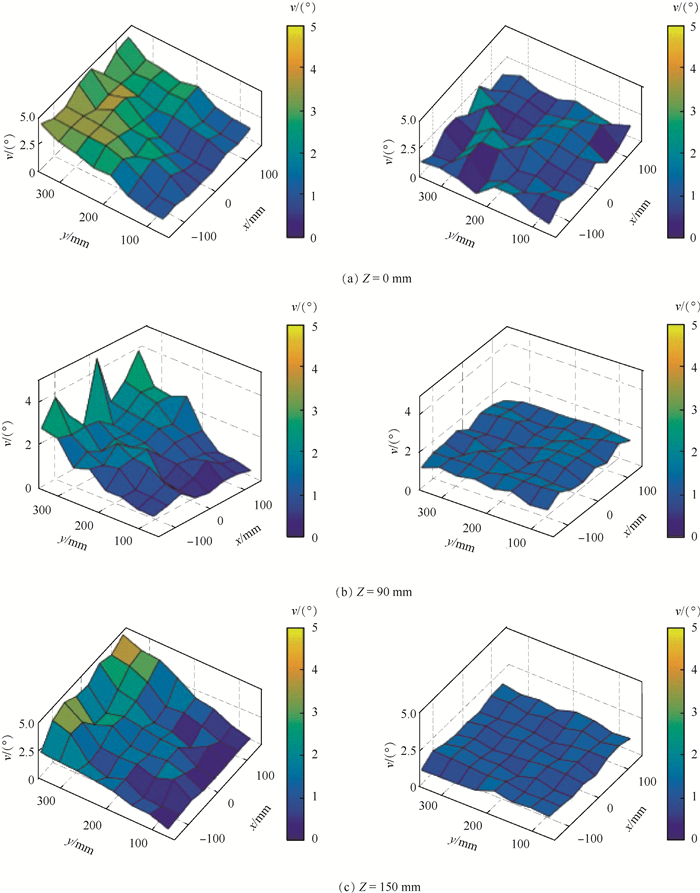
如图 8(a)所示,固定标定板在非金属实验台上不动,在未进行EM空间拓展前,保持机械臂不动,磁场发生器与标定板的相对位姿不变,以实验台平面为Z=0高度平面,通过调节可调支柱,分别测量了靠近磁场发生器底部(Z=0)、靠近磁场发生器中心(Z=90 mm)、靠近磁场发生器顶部(Z=150 mm)3个平面上8×8个点的位置与姿态,计算位置误差及姿态误差。
如图 8(b)所示,同样保持标定板位置不变,根据本文的EM工作空间拓展方法分别测量Z=0, 90, 150 mm 3个平面上8×8个点的位置与姿态,误差指示值阈值λth设置为0.3,一旦EM在定位传感器时误差指示值超过0.3, 则利用机械臂调整磁场发生器的位置,并重新计算传感器的位姿。通过3.1.2节的评价方法计算位置误差及姿态误差。
3.2.3 实验结果与分析
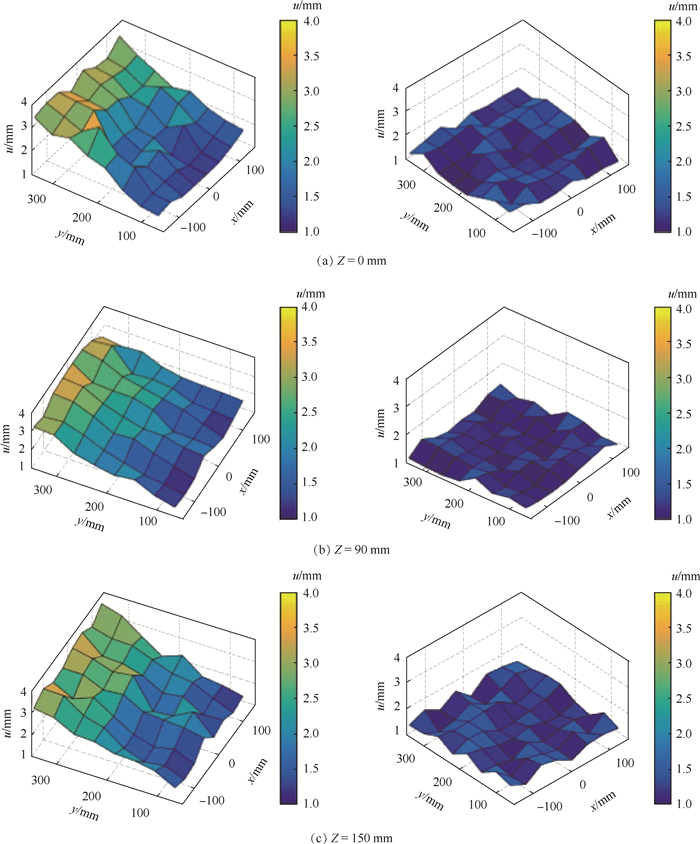
对于Z=0, 90, 150 mm上的8×8个采样点, 采集其位置参数和姿态参数,计算位置误差和姿态误差,将位置误差和姿态误差反映在Z轴上,X轴和Y轴如图 6中的布置反映8×8个采样点的分布,对比拓展前后的位置误差与姿态误差,如图 9和图 10所示。图中:左列为拓展前位置误差或姿态误差,右列为拓展后位置误差或姿态误差。
通过图 9、图 10可以看出,当保持磁场发生器固定不动时,测得的位姿误差依旧随着传感器到磁场发生器中心的距离增大而增大,同样符合误差指示值的变化趋势。表 2统计了不同平面拓展前后的位置误差与姿态误差的平均值(Mean)与均方差(SD), 可以看出,当磁场发生器固定不动时,不同平面采样点的位置误差和姿态误差也不同,磁场发生器中心平面上的采样点误差较小,其余2个平面采样点的误差相对较大。拓展后3个平面采样点的平均位置误差从2.61 mm降低到1.34 mm,平均姿态误差由2.42°降低到1.37°,且SD较拓展前也有显著减小,即拓展后同一平面的误差分布更为均匀,验证了根据误差指示值移动磁场发生器在拓展EM工作空间的同时可以有效提升电磁定位的精度。
表 2 不同平面拓展前后位置误差与姿态误差Table 2. Position error and orientation error of different planes before and after expansionZ/mm 拓展前位置误差/mm 拓展后位置误差/mm 拓展前姿态误差/(°) 拓展后姿态误差/(°) Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD Mean SD 0 2.74 0.71 1.34 0.28 2.36 1.13 1.41 0.41 90 2.42 0.64 1.28 0.19 2.29 1.25 1.32 0.28 150 2.68 0.65 1.39 0.22 2.62 1.38 1.37 0.32 平均值 2.61 0.67 1.34 0.23 2.42 1.25 1.37 0.34 4. 结论
本文针对血管介入等大范围手术中应用EM跟踪手术器械时存在的定位范围有限等问题,提出了一种拓展EM工作空间的方法。根据误差指示值调整磁场发生器,使得传感器一直处于最佳工作区域内,提升了EM的定位精度。
下一步将考虑在临床应用中,磁场发生器移动对手术设备、医生、病人的影响,结合手术室环境对磁场发生器移动的限制条件,得到误差指示值超出预设阈值时,磁场发生器具体的移动路径。
-
表 1 不同场景下不同算法的位置误差和姿态误差
Table 1. Position error and orientation error with different scenes for various algorithms
场景 位置误差/m, 姿态误差/(°) PoseNet[11] Bayesian DS[15] LSTM-Pose[13] VidLoc[12] Hourglass[14] BiLocNet Chess 0.32, 8.12 0.28, 7.05 0.24, 5.77 0.18, N/A 0.15, 6.17 0.13, 5.13 Fire 0.47, 14.4 0.43, 12.52 0.34, 11.9 0.26, N/A 0.27, 10.84 0.29, 10.48 Heads 0.29, 12.0 0.25, 12.72 0.21, 13.7 0.14, N/A 0.19, 11.63 0.16, 12.67 Office 0.48, 7.68 0.30, 8.92 0.30, 8.08 0.26, N/A 0.21, 8.48 0.25, 6.82 Pupkin 0.47, 8.42 0.36, 7.53 0.33, 7.00 0.36, N/A 0.25, 8.12 0.25, 5.23 Kitchen 0.59, 8.64 0.45, 9.80 0.37, 8.83 0.32, N/A 0.27, 10.15 0.26, 6.95 Stairs 0.47, 13.8 0.42, 13.06 0.40, 13.7 0.26, N/A 0.29, 12.46 0.33, 9.86 均值 0.44, 10.44 0.35, 10.22 0.31, 9.85 0.25, N/A 0.23, 9.69 0.23, 8.16 表 2 不同预测器的网络精度对比
Table 2. Comparison of network precision of different estimators
预测器 位置误差/m 姿态误差/(°) 全连接预测器 0.26 8.03 GAP预测器 0.14 5.21 多尺度位姿预测器 0.13 5.13 表 3 α权重损失函数与σ权重损失函数的网络精度对比
Table 3. Comparison of network precision between α weights loss function and σ weights loss function
损失函数 位置误差/m 姿态误差/(°) α权重 0.19 6.55 σ权重 0.17 5.64 表 4 有无迁移学习的网络精度对比
Table 4. Comparison of network precision with and without transfer learning
有无迁移学习 位置误差/m 姿态误差/(°) 有 0.32 10.64 无 0.29 10.48 -
[1] CHEN D M, BAATZ G, KOSER K, et al.City-scale landmark identification on mobile devices[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 12258110. [2] TORII A, SIVIC J, PAJDLA T, et al.Visual place recognition with repetitive structures[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 883-890. [3] SCHINDLER G, BROWN M, SZELISKI R.City-scale location recognition[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 1-7. [4] ARTH C, PIRCHHEIM C, VENTURA J, et al.Instant outdoor localization and SLAM initialization from 2.5 D maps[J].IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 2015, 21(11):1309-1318. doi: 10.1109/TVCG.2015.2459772 [5] POGLITSCH C, ARTH C, SCHMALSTIEG D, et al.A particle filter approach to outdoor localization using image-based rendering[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality(ISMAR).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 132-135. [6] SATTLER T, LEIBE B, KOBBELT L.Improving image-based localization by active correspondence search[C]//Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2012: 752-765. [7] LI Y, SNAVELY N, HUTTENLOCHER D, et al.Worldwide pose estimation using 3D point clouds[C]//Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2012: 15-29. [8] CHOUDHARY S, NARAYANAN P J.Visibility probability structure from SFM datasets and applications[C]//Proceedings of European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2012: 130-143. [9] SVARM L, ENQVIST O, OSKARSSON M, et al.Accurate localization and pose estimation for large 3D models[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 532-539. [10] SHOTTON J, GLOCKER B, ZACH C, et al.Scene coordinate regression forests for camera relocalization in RGB-D images[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 2930-2937. [11] KENDALL A, GRIMES M, CIPOLLA R.PoseNet: A convolutional network for real-time 6-DOF camera relocalization[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 2938-2946. [12] WALCH F, HAZIRBAS C, LEAL-TAIXÉ L, et al.Image-based localization with spatial LSTMs[EB/OL].(2016-11-23)[2018-12-25]. [13] CLARK R, WANG S, MARKHAM A, et al.VidLoc: A deep spatio-temporal model for 6-DOF video-clip relocalization[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 6856-6864. [14] KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R.Modelling uncertainty in deep learning forcamera relocalization[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 4762-4769. [15] MELEKHOV I, YLIOINAS J, KANNALA J, et al.Image-based localization using hourglass networks[EB/OL].(2017-08-24)[2018-12-25]. [16] LI R, LIU Q, GUI J, et al.Indoor relocalization in challenging environments with dual-stream convolutional neural networks[J].IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering, 2018, 15(2):651-662. doi: 10.1109/TASE.2017.2664920 [17] RADWAN N, VALADA A, BURGARD W.Vlocnet++: Deep multitask learning for semantic visual localization and odometry[EB/OL].(2016-10-11)[2018-12-25]. [18] BRAHMBHATT S, GU J, KIM K, et al.Geometry-aware learning of maps for camera localization[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 2616-2625. [19] LI X, YLIOINAS J, KANNALA J.Full-frame scene coordinate regression for image-based localization[EB/OL].(2018-01-25)[2018-12-25]. [20] LASKAR Z, MELEKHOV I, KALIA S, et al.Camera relocalization by computing pairwise relative poses using convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 929-938. [21] KENDALL A, GAL Y, CIPOLLA R.Multi-task learning using uncertainty to weigh losses for scene geometry and semantics[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 7482-7491. [22] SZEGEDY C, IOFFE S, VANHOUCKE V, et al.Inception-v4, inception-resnet and the impact of residual connections on learning[C]//Thirty-First AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2017: 4-12. [23] KENDALL A, GAL Y.What uncertainties do we need in Bayesian deep learning for computer vision [EB/OL].(2017-10-05)[2018-12-26]. [24] IZADI S, KIM D, HILLIGES O, et al.KinectFusion: Real-time 3D reconstruction and interaction using a moving depth camera[C]//Proceedings of the 24th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology.New York: ACM, 2011: 559-568. [25] HE K M, ROSS G, PIOTR D.Rethinking imagenet pre-training[EB/OL].(2015-11-21)[2018-12-25]. [26] WU Y X, HE K M.Group normalization[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), 2018, 3-19. 期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王宝元. 基于传播路径特性分析的电磁信号局放源定位方法研究. 宁夏师范学院学报. 2020(04): 24-29 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 毕津滔,张永德,孙波涛. 基于电磁跟踪与超声图像的介入机器人穿刺导航方法及实验研究. 仪器仪表学报. 2019(07): 253-262 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(5)
-








 下载:
下载:









 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术