-
摘要:
为进一步研究回归模型中高维数据的降维方法,提出基于Gram-Schmidt变换的新的有监督变量聚类(SCV-GS)方法。该方法未采用以潜变量为聚类中心的层次聚类,而是借用变量扫描思想,依次挑出对响应变量有重要贡献的关键变量,并将其作为聚类中心。SCV-GS方法基于Gram-Schmidt变换,对变量之间的高度相关性进行批量处理,并得到聚类结果;同时,结合偏最小二乘思想,提出新的同一性度量,并以此来选取最佳聚合参数。SCV-GS不仅可以快速得到变量聚类结果,而且可识别出对响应变量的解释及预测起关键作用的变量类。仿真表明该聚类方法运算速度显著提升,而且所得潜变量对应的回归系数的估计结果与对照方法表现一致;实例分析表明该方法具有更好的解释性和预测能力。
-
关键词:
- 降维 /
- 变量聚类 /
- 回归 /
- 高度相关 /
- Gram-Schmidt变换
Abstract:In order to study the dimension reduction method of high-dimensional data based on regression model further, and the supervised clustering of variables algorithm based on Gram-Schmidt transformation (SCV-GS) is proposed. SCV-GS uses the key variables selected in turn by the variable screening idea as the clustering center, which is different from the hierarchical variable clustering around latent variables. High correlation among variables is processed based on Gram-Schmidt transformation and the clustering results are obtained. At the same time, combined with the concept of partial least squares, a new criterion for "homogeneity" is proposed to select the optimal clustering parameters. SCV-GS can not only get the variable clustering results quickly, but also identify the most relevant variable groups and in what kind of structure the variables work to influence the response variable. Simulation results show that the calculation speed is significantly improved by SCV-GS, and the estimated regression coefficients corresponding to the latent variables are consistent with the comparison method. Real data analysis shows that SCV-GS performs better in interpretation and prediction.
-
Key words:
- dimension reduction /
- variable clustering /
- regression /
- high correlation /
- Gram-Schmidt transformation
-
随着信息技术的快速发展和大数据时代的来临,数据信息的收集与存储变得极其便捷,各行各业已经形成规模巨大、亟待开发的数据。如何灵活运用这些数据宝藏,快捷有效地探究数据的本质特征与运行规律,这已经成为大数据分析中的重要课题,催生出新一轮统计数据建模理论与方法的创新高潮。其中建立回归模型或分类模型是最常用的统计分析方法之一,而此类模型通常面临两大挑战:第一,在成千上万维的变量中可能仅有少数变量起关键作用,即变量维数p远远大于关键变量的维数d;第二,变量之间往往存在高度相关性。对此,需要对数据进行降维处理。文献中基于回归模型的高维数据降维技术主要包含2种方法:第1种是变量选择(或称特征筛选), 即从原始变量集合中筛选出维数较小的变量子集。这类方法包括经典的惩罚类方法(如LASSO(Leaset Absolute Shringe and Selection Operator)[1]、elastic-net[2]等)和扫描类方法[3-4]。这类方法可以达到很好的预测效果,但在进行变量筛选的同时可能会忽略掉与关键变量强相关的重要变量,导致模型解释性的缺失。第2种是进行变量综合,即将原始p维变量投影到低维空间,得到原始变量的线性组合,再将这些组合作为潜变量(latent variable)进行回归建模。比如经典的主成分回归、偏最小二乘回归等。这类方法虽考虑了变量之间的高度相关性,同时实现了降维,但因其将所有变量都考虑进来,为模型的解释性增加了困难。
为了兼顾两类数据降维方法的优点,实现既能挑选出关键变量,又能将变量之间的高度相关性考虑进来,一些稀疏综合方法被相继提出,比如稀疏主成分分析(Sparse Principal Component Aanlysis, SPCA)方法[5]、稀疏偏最小二乘(Sparse Partial Least Squares regression, SPLS)[6]等。此类方法通过将原始变量进行稀疏组合,得到稀疏潜变量,再进行建模。另一种思路是对所有变量进行聚类。2016年,Chen和Vigneau[7]首次提出“有监督变量聚类”,以求同时提升模型的预测性与解释性,该方法与SPCA、SPLS有所区别,其目标是实现对所有变量的聚类,同时从变量类中筛选出对模型预测性能起关键作用的变量组。本文第2节将详细介绍有监督变量聚类方法。
事实上,由于变量聚类有助于探索多元数据的内部结构,便于后续的解释和分析。因此,在Chen和Vigneau[7]之前,已有相关学者对变量聚类进行探索研究。只是在此之前的变量聚类大多属于“无监督变量聚类”。在20世纪70年代,Jolliffe[8]总结了对变量的层次聚类的步骤。首先定义2个类之间的相似度;然后从每个变量自成一类开始, 对所有类计算两两之间的相似性;最后将相似性最大的2个类合并为一类,循环上述步骤,直到所有变量聚为一类。Hastie等[9]提出了Tree harvesting方法,并将其应用于基因数据的分析研究。Tree harvesting方法对p维变量施加层次聚类法,由此可得到2p-1个变量类;然后采用向前法,在每一步中,挑选当前候选类中最小化残差平方和的变量类,将2p-1个变量类依次以变量平均的形式加入模型。Tree harvesting方法思想朴素,步骤简单。之后Vigneau和Qannari[10]对变量聚类进行了深入的研究, 提出围绕潜变量的聚类,并给出K个类的聚类算法,目标为最大化所有类潜变量与对应的各类中自变量的相关程度T。求解方法是迭代算法, 在聚类的不同阶段允许变量xj进来或出去,在每一个阶段会增大准则T的值。当前有关变量聚类研究的文献相对较少,主要是Vigneau和Qannari团队在研究,且多数为无监督变量聚类。Vigneau等[11-12]给出了围绕潜变量聚类的R程序,并将变量聚类扩展至含缺失数据的情形,Cariou等[13]将围绕潜变量的聚类方法应用于结构方程模型中。
Vigneau等[7, 10]提出的聚类方法均围绕潜变量展开。具体来说,是希望同时找到K个变量类和K个潜变量,使得每个变量类与对应的潜变量具有强相关。但由于该方法步骤复杂,且包含多次重复循环,因此计算速度较低。为此,本文提出了一种新的快速有监督变量聚类方法。具体地,该方法借用变量扫描思想,依次挑出关键变量,并将其作为聚类中心;基于Gram-Schmidt变换,对变量之间的高度相关性进行批量处理;同时,结合偏最小二乘思想,提出新的同一性度量,并以此来选取最佳聚合参数。因此,它不仅可以快速得到变量聚类结果,以及变量是以什么样的结构对响应变量起作用的。
1. 有监督变量聚类
Chen和Vigneau[7]首次提出基于回归模型的有监督围绕潜变量的变量聚类(SCV-LV)方法。本文采用层次聚类法,通过最大化提取出的变量组的组内相关性以及最大化变量组对响应变量y的贡献,依次迭代提取出一系列变量组。聚类准则为:最大化变量组的全局同一性,同时根据响应变量来控制变量组局部同一性的损失。聚类目标是:得到变量之间的聚类信息,提升模型的预测能力,同时提升模型的可解释性。做法是:首先将响应变量y和所有解释变量{x1, x2, …, xp}放一起,然后进行层次聚类。得到多层聚类结果后,接着确定最佳聚合水平,即选出满足要求的最优一层聚类结果。具体做法如下:
步骤1 初始化。
将y和所有解释变量{x1, x2, …, xp}放一起,即U={x1, x2, …, xp, y}。
步骤2 对U进行层次聚类。
需将初始的p+1个类,一层一层聚类,直到所有p+1个变量成为一类。从上一层到下一层的过程中(例如, 从p+1个类到p个类的过程),有Cp+12种可能性, 此时需选取全局同一性下降最小的那一种。假设当前层有K个变量类, 记作G1, G2, …, GK,则全局同一性定义为该层各组所得潜变量ck与对应各组中各个变量之间的相关性之和,其中潜变量是对应变量组中所含变量的线性组合ck=Gkvk, vk为组合系数向量。
全局同一性准则T的表达式为

(1) 式中:Gk为变量组Gk中所含变量的个数。
容易证明最大化准则T所得潜变量ck恰好为Gk中变量所得的第一主成分, 因此该准则等价于最大化各变量组协方差矩阵的第一特征值, 即


(2) 因此,从当前聚类层到下一聚类层的划分依据为:将Δ取最小值时对应的2个类合并为一类。
步骤3 确定最佳聚合水平。
得到各个层的聚类结果后,为了确定最佳一层聚合水平,需要选取局部同一性变化最小的一层。考虑第l-1层及第l层中y所在的变量组,并记对应的潜变量为cl-1和cl。则局部同一性定义为

(3) 式中:n为样本容量;c*/j为变量xj在与y合并(第l层)之前(第l-1层)所在的变量组对应的潜变量。于是相邻两层之间的局部同一性变化率为

(4) 可以看出局部同一性准则反映了2个相邻聚合水平同一性的损失比率。给定损失阈值,最佳聚合水平定义为l*=max l(Γl≤γ),γ通常设为5%或10%。
SCV-LV方法虽然可以达到很好的聚类效果,但其步骤复杂,计算量庞大,导致计算成本过高。本文将结合变量扫描的思想,同时借助Gram-Schmidt变换,提出一种新的快速有监督变量聚类算法。
2. 基于Gram-Schmidt变换的回归模型的快速变量聚类
本节首先介绍Gram-Schmidt变换及其信息分解准则,然后提出新的快速有监督变量聚类算法。该算法借用变量扫描思想,依次挑出关键变量;同时基于Gram-Schmidt变换,对变量之间的高度相关性进行批量处理。最后给出基于变量聚类的回归模型。
2.1 Gram-Schmidt变换
Gram-Schmidt变换作为线性代数中的经典算法[14-15],已被应用于多种领域。比如,Chen等[16]将之应用于非线性系统的识别;Stoppiglia等[17]首次提出基于Gram-Schmidt变换的特征选择;王惠文等[18-19]提出了基于Gram-Schmidt过程的回归模型及判别模型的变量筛选方法;Liu等[20]研究了基于Gram-Schmidt过程的函数型数据回归模型的变量扫描。
给定n×p矩阵M=[w1, w2, …, wp], M的秩为s(s≤min(n, p)),则Gram-Schmidt正交化过程将wj转换为uj:

(5) 式中:

易知,在所得到的uj(j=1, 2, …, p)中,有s个非零向量,其余均为零向量。设u、w分别为变量u、w的样本实现,可证wk所携带的信息可以分解为两部分:一部分由uk承载,另一部分由wk和ul(l=1, 2, …, k-1)共同承担。wk携带的信息有如下分解准则:

(6) uk的方差满足:

(7) 式中:Var表示变量对应的样本方差;Cor表示样本相关系数。其中Var(uk)=ukTuk/n, 且

从信息分解式(5)可知,经过Gram-Schmidt变换后,uk承载的信息量不会多于原始变量wk承载的信息量。而且,wk携带的信息量恰好等于原始变量wk和变换后的变量uk之间的样本相关系数的平方和。因此由uk承载的信息可以由Cor(wk, ul)间接表示,式(5)和式(6)称为Gram-Schmidt变换的信息分解准则。
2.2 基于Gram-Schmidt变换的变量聚类
本文将结合扫描思想,提出基于Gram-Schmidt变换的新的有监督变量聚类(SCV-GS)方法。假设收集的样本数据为y=[y1, y2, …, yn]T, Xn×p=[x1, x2, …, xn]T, 其中xi=[xi1, xi2, …, xip]T。不失一般性,假设响应变量和解释变量分别经过中心化和标准化处理:

(8) SCV-GS方法步骤如下:
步骤1 变量扫描。
对于初始变量集Λ(0)={x1(0), x2(0), …, xp(0)}={x1, x2, …, xp},设k=1,利用回归系数的显著性检验,将最解释响应变量y的自变量挑出来。
1) 对任意xj(k-1)∈Λ(k-1), 关于y做一元回归,可得回归系数

2) 计算Tj(k-1),其中Tj(k-1)为

(9) 式中:

3) 计算




步骤2 变量聚类。
1) 将所有其余变量


(10) 2) 根据信息分解准则式(6),衡量变换后的变量xj(k)与原始变量的相似性。不失一般性,假设x1, x2, …, xk, xk+1是对应于z1, z2, …, zk, xj(k)的原始变量。接下来判断xj(k)所对应的原始变量能否被看作冗余变量。
需注意的是,xj(k)所对应的样本可能为零向量,即不再承担任何信息,因此与之对应的原始变量xk+1可被看作冗余变量。另外,若xj(k)的方差近似于零,xk+1也可被看作冗余,即认为该变量的信息几乎可由其他之前的变量代表,可将之与上一步挑出的GS变量zk所对应的原始变量聚成一组,得到第k组变量。为了判断某变量能否被当作冗余,即Cor(xk+1, xj(k))是否为零,这里引入相关性检验,采用Fisher Z变换[21]:

(11) Gaussian情形下可得如下准则:
准则1 对于原假设H0:ρ(xk+1, xj(k))=0和双边备择假设HA:ρ(xk+1, xj(k))≠0,若

3) 根据方差分解式(5)、式(6)和准则1,判断xj(k)能否被看作冗余变量,同时更新




步骤3 在步骤1和步骤2迭代结束后,提取潜变量LV。
这里潜变量的提取可考虑两种方法:主成分分析和偏最小二乘回归。
注:相关性检验显著性水平的确定。在变量聚类过程中,将经过Gram-Schmidt变换后,通过相关性检验(即被看作无信息的变量,满足


(12) 式中:X为p维变量集合;v为p维投影向量。
受偏最小二乘准则启发,这里提出一种新的同一性准则,称之为“综合偏最小二乘准则”:

(13) 式中:LVk为第k个变量组对应的第一偏最小二乘成分。于是将综合偏最小二乘准则(12)作为选取α的最优准则,即在给定的α范围内,选取使得综合偏最小二乘准则(12)最大化的那个α值。
2.3 基于Gram-Schmidt变换变量聚类的预测
在变量聚类算法结束后,可以得到一系列的变量组。每个变量组Gk可由对应的潜变量LVk来表示,其中LVk为第k组变量的线性组合,即LVk=Xkvk。这里Xk为变量组Gk中的pk个变量对应的n×pk维数据矩阵,组合系数向量vk=[vk1, vk2, …, vkpk]T为Xk的第一特征向量。由算法可知,LV1代表了与y最相关的一组变量,最后一组LVK则代表了最不解释y的一组变量。
因此,得到有监督变量聚类的结果后,接下来对各个潜变量采用向前扫描法[4]。设最终扫描得到m(m≤K)个潜变量,则最终回归模型为

(14) 由此还可同时得到回归模型关于原始变量的回归系数。
3. 仿真研究
3.1 仿真设置
本文参考Chen和Vigneau[7]的仿真设置。设样本容量n=50, 变量维数p=80,变量分成5个组:G1, G2, G3, G4, G5。每组变量由隐变量Zk(k=1, 2, …, 5)生成。各组中变量个数为G1=20, G2=20, G3=10, G4=10, G5=20。隐变量Z1、Z2、Z3、Z4和Z5之间的相关系数设置为

变量xj由Zk生成,即

其中:sj∈{+1, -1};εj~N(0, 0.42)。
考虑如下模型:

(15) 即响应变量y只与变量组G1、G2和G3有关,而且变量的重要性为G1>G3>G2。下面将仿真生成100组数据,对每组数据施行SCV-LV方法和SCV-GS方法。
3.2 仿真结果
仿真考虑如下指标:变量聚类结果的准确性,聚类算法运行时间,变量类对应的回归系数β的估计。
1) 变量聚类结果的准确性
在100次仿真结果中,SCV-LV方法可以得到100次正确聚类结果;而SCV-GS方法所得结果稍有差错。表 1展示了施行SCV-GS方法后各变量在所得5个变量组中出现的频次。可以看出,对于原仿真设置中的第1组变量(x1~x20),100次仿真实验中,除了有一次未将变量(x17, x19)包含在内,第1组聚类结果与真实设置一致。第2组聚类结果有97次聚类成功,100次聚类结果中出现原本来自第2组的变量落入第3组的情形,主要是由于仿真设置中第2组变量与第3组变量之间存在较强的相关性(相关系数为0.5)。类似的,第3组变量也出现两次误入第2类的情形。第4组变量及第5组变量在100次实验中,聚类结果完全正确。
表 1 SCV-GS方法变量聚类结果Table 1. Variable clustering results by SCV-GS变量 G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 x1 100 0 0 0 0 x2 100 0 0 0 0 x3 100 0 0 0 0 x4 100 0 0 0 0 x5 100 0 0 0 0 x6 100 0 0 0 0 x7 100 0 0 0 0 x8 100 0 0 0 0 x9 100 0 0 0 0 x10 100 0 0 0 0 x11 100 0 0 0 0 x12 100 0 0 0 0 x13 100 0 0 0 0 x14 100 0 0 0 0 x15 100 0 0 0 0 x16 100 0 0 0 0 x17 99 0 0 0 0 x18 100 0 0 0 0 x19 99 0 0 0 0 x20 100 0 0 0 0 x21 0 97 2 0 0 x22 0 100 0 0 0 x23 0 99 1 0 0 x24 0 100 0 0 0 x25 0 99 0 0 0 x26 0 100 0 0 0 x27 0 99 1 0 0 x28 0 98 1 0 0 x29 0 99 0 0 0 x30 0 99 1 0 0 x31 0 99 1 0 0 x32 0 98 2 0 0 x33 0 99 1 0 0 x34 0 100 0 0 0 x35 0 100 0 0 0 x36 0 100 0 0 0 x37 0 100 0 0 0 x38 0 99 0 0 1 x39 0 100 0 0 0 x40 0 100 0 0 0 x41 0 0 100 0 0 x42 0 0 100 0 0 x43 0 0 100 0 0 x44 0 0 100 0 0 x45 0 0 100 0 0 x46 0 1 99 0 0 x47 0 0 99 0 1 x48 0 0 100 0 0 x49 0 0 100 0 0 x50 0 0 100 0 0 x51 0 0 0 100 0 x52 0 0 0 100 0 x53 0 0 0 100 0 x54 0 0 0 100 0 x55 0 0 0 100 0 x56 0 0 0 100 0 x57 0 0 0 100 0 x58 0 0 0 100 0 x59 0 0 0 100 0 x60 0 0 0 100 0 x61 0 0 0 0 100 x62 0 0 0 0 100 x63 0 0 0 0 100 x64 0 0 0 0 100 x65 0 0 0 0 100 x66 0 0 0 0 100 x67 0 0 0 0 100 x68 0 0 0 0 100 x69 0 0 0 0 100 x70 0 0 0 0 100 x71 0 0 0 0 100 x72 0 0 0 0 100 x73 0 0 0 0 100 x74 0 0 0 0 100 x75 0 0 0 0 100 x76 0 0 0 0 100 x77 0 0 0 0 100 x78 0 0 0 0 100 x79 0 0 0 0 100 x80 0 0 0 0 100 2) 聚类算法运行时间
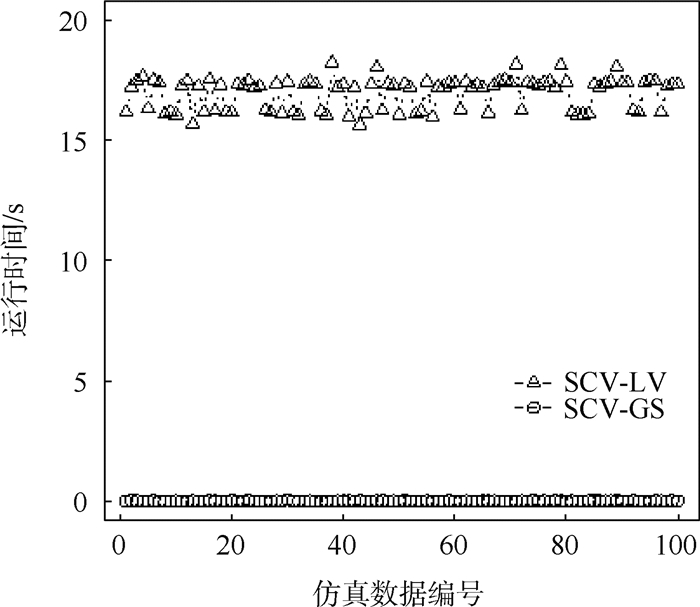
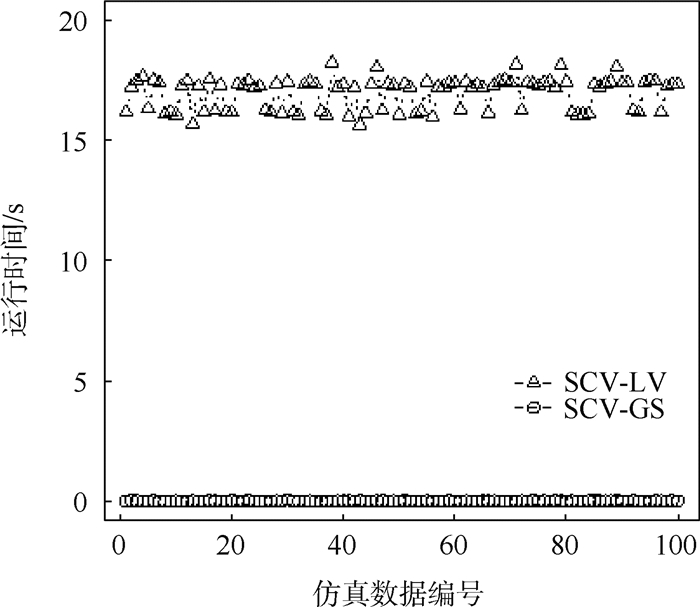
在100次仿真实验中,SCV-LV方法运行时间均在15 s以上;本文提出的SCV-GS算法运行时间不超过0.1 s,而且非常稳定。运行时间结果详细对比图参见图 1。
3) 变量类对应的回归系数的估计
表 2分别给出经SCV-LV方法和SCV-GS方法进行变量聚类后,由向前扫描法所得潜变量对应的回归系数相对于真值(6, 1.5, 2)的估计结果(包含估计值的偏差和标准差)。这里
 表 2 SCV-LV与SCV-GS方法所得潜变量回归系数的估计结果Table 2. Estimated regression coefficients by SCV-LVand SCV-GS as a function of latent variables
表 2 SCV-LV与SCV-GS方法所得潜变量回归系数的估计结果Table 2. Estimated regression coefficients by SCV-LVand SCV-GS as a function of latent variables方法 


SCV-LV -0.07(0.44) -0.08(0.43) 0.03(0.28) SCV-GS -0.10 (0.44) -0.10(0.43) 0.02(0.28) 4. 实例分析
为了进一步验证方法的有效性,下面分别考察SCV-LV及SCV-GS方法在实例数据上的表现。
该数据集选自1/2中的教育数据集。数据来自1996—1999年美国新闻“美国最佳大学”和美国教育部综合高等教育数据系统(IPEDS),共涉及94所高校。因变量Y为1996—1998年全国大学体育协会(NCAA)高等大学中的平均6年毕业率,19个解释变量包含学校情况、学生的个人情况和学生在校际育项目中的表现。分析目的是找出影响毕业率的重要决定因素。
对该数据集分别施行SCV-LV和SCV-GS方法,结果表明SCV-GS优于SCV-LV方法。表 3给出了具体聚类结果。表 3中指标K表示聚类后所得变量类的数目,“
 表 3 SCV-LV与SCV-GS方法作用于实例数据集所得结果Table 3. Results on real dataset by SCV-LV and SCV-GS
表 3 SCV-LV与SCV-GS方法作用于实例数据集所得结果Table 3. Results on real dataset by SCV-LV and SCV-GS方法 K 
变量 SCV-LV 1 0.83 x1~x19 SCV-GS 16 0.87 x2, x3 5. 结论
在预测模型中,随着自变量维数的急剧式增大,模型的解释性和稳定性都将受到影响,有监督变量聚类有助于解决此问题。本文提出了一种基于Gram-Schmidt变换的新的有监督变量聚类方法,具有以下优点:
1) 避开层次聚类,且未采用围绕潜变量的思想。
2) 可实现较为准确的变量聚类。
3) 借助Gram-Schmidt变换,可以显著提高变量聚类方法的运行时间。
4) 结合偏最小二乘回归,提出新的聚合同一性准则。
5) 可扩展至其他模型,比如基于判别模型的有监督变量聚类,基于复杂数据的变量聚类等。
-
表 1 SCV-GS方法变量聚类结果
Table 1. Variable clustering results by SCV-GS
变量 G1 G2 G3 G4 G5 x1 100 0 0 0 0 x2 100 0 0 0 0 x3 100 0 0 0 0 x4 100 0 0 0 0 x5 100 0 0 0 0 x6 100 0 0 0 0 x7 100 0 0 0 0 x8 100 0 0 0 0 x9 100 0 0 0 0 x10 100 0 0 0 0 x11 100 0 0 0 0 x12 100 0 0 0 0 x13 100 0 0 0 0 x14 100 0 0 0 0 x15 100 0 0 0 0 x16 100 0 0 0 0 x17 99 0 0 0 0 x18 100 0 0 0 0 x19 99 0 0 0 0 x20 100 0 0 0 0 x21 0 97 2 0 0 x22 0 100 0 0 0 x23 0 99 1 0 0 x24 0 100 0 0 0 x25 0 99 0 0 0 x26 0 100 0 0 0 x27 0 99 1 0 0 x28 0 98 1 0 0 x29 0 99 0 0 0 x30 0 99 1 0 0 x31 0 99 1 0 0 x32 0 98 2 0 0 x33 0 99 1 0 0 x34 0 100 0 0 0 x35 0 100 0 0 0 x36 0 100 0 0 0 x37 0 100 0 0 0 x38 0 99 0 0 1 x39 0 100 0 0 0 x40 0 100 0 0 0 x41 0 0 100 0 0 x42 0 0 100 0 0 x43 0 0 100 0 0 x44 0 0 100 0 0 x45 0 0 100 0 0 x46 0 1 99 0 0 x47 0 0 99 0 1 x48 0 0 100 0 0 x49 0 0 100 0 0 x50 0 0 100 0 0 x51 0 0 0 100 0 x52 0 0 0 100 0 x53 0 0 0 100 0 x54 0 0 0 100 0 x55 0 0 0 100 0 x56 0 0 0 100 0 x57 0 0 0 100 0 x58 0 0 0 100 0 x59 0 0 0 100 0 x60 0 0 0 100 0 x61 0 0 0 0 100 x62 0 0 0 0 100 x63 0 0 0 0 100 x64 0 0 0 0 100 x65 0 0 0 0 100 x66 0 0 0 0 100 x67 0 0 0 0 100 x68 0 0 0 0 100 x69 0 0 0 0 100 x70 0 0 0 0 100 x71 0 0 0 0 100 x72 0 0 0 0 100 x73 0 0 0 0 100 x74 0 0 0 0 100 x75 0 0 0 0 100 x76 0 0 0 0 100 x77 0 0 0 0 100 x78 0 0 0 0 100 x79 0 0 0 0 100 x80 0 0 0 0 100 表 2 SCV-LV与SCV-GS方法所得潜变量回归系数的估计结果
Table 2. Estimated regression coefficients by SCV-LVand SCV-GS as a function of latent variables
方法 


SCV-LV -0.07(0.44) -0.08(0.43) 0.03(0.28) SCV-GS -0.10 (0.44) -0.10(0.43) 0.02(0.28) 表 3 SCV-LV与SCV-GS方法作用于实例数据集所得结果
Table 3. Results on real dataset by SCV-LV and SCV-GS
方法 K 
变量 SCV-LV 1 0.83 x1~x19 SCV-GS 16 0.87 x2, x3 -
[1] TIBSHIRANI R.Regression shrinkage and selection via the lasso:A retrospective[J].Journal of the Royal Statistical Society:Series B(Statistica Methodology), 2011, 73(3):273-282. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2011.00771.x [2] ZOU H, HASTIE T.Regularization and variable selection via the elastic net[J].Journal of the Royal Statistical Society:Series B(Statistical Methodology), 2005, 67(2):301-320. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2005.00503.x [3] FAN J Q, LV J C.Sure independence screening for ultrahigh dimensional feature space[J].Journal of the Royal Statistical Society:Series B(Statistical Methodology), 2008, 70(5):849-911. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2008.00674.x [4] WANG H S.Forward regression for ultra-high dimensional variable screening[J].Journal of the American Statistical Association, 2009, 104(488):1512-1524. doi: 10.1198/jasa.2008.tm08516 [5] ZOU H, HASTIE T, TIBSHIRANI R.Sparse principal component analysis[J].Journal of Computational and Graphical Statistics, 2006, 15(2):265-286. doi: 10.1198/106186006X113430 [6] CHUN H, KELEŞ S.Sparse partial least squares regression for simultaneous dimension reduction and variable selection[J].Journal of the Royal Statistical Society:Series B(Statistical Methodology), 2010, 72(1):3-25. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9868.2009.00723.x [7] CHEN M K, VIGNEAU E.Supervised clustering of variables[J].Advances in Data Analysis and Classification, 2016, 10(1):85-101. [8] JOLLIFFE I T.Discarding variables in a principal component analysis.I:Artificial data[J].Applied Statistics, 1972, 21(2):160-173. doi: 10.2307/2346488 [9] HASTIE T, TIBSHIRANI R, BOTSTEIN D, et al.Supervised harvesting of expression trees[J].Genome Biology, 2001, 2(1):research0003-1. [10] VIGNEAU E, QANNARI E.Clustering of variables around latent components[J].Communications in Statistics-Simulation and Computation, 2003, 32(4):1131-1150. doi: 10.1081/SAC-120023882 [11] VIGNEAU E, CHEN M, QANNARI E M.ClustVarLV:An R package for the clustering of variables around latent variables[J].The R Journal, 2015, 7(2):134-148. doi: 10.32614/RJ-2015-026 [12] VIGNEAU E.Segmentation of a panel of consumers with missing data[J].Food Quality and Preference, 2018, 67:10-17. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2017.04.010 [13] CARIOU V, QANNARI E M, RUTLEDGE D N, et al.ComDim:From multiblock data analysis to path modeling[J].Food Quality and Preference, 2018, 67:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2017.02.012 [14] BJÖRCK Å.Numerics of gram-schmidt orthogonalization[J].Linear Algebra and Its Applications, 1994, 197-198:297-316. doi: 10.1016/0024-3795(94)90493-6 [15] LEON S J, BJÖRCK A, GANDER W.Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization:100 years and more[J].Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications, 2013, 20:492-532. doi: 10.1002/nla.1839 [16] CHEN S, BILLINGS S A, LUO W.Orthogonal least squares methods and their application to non-linear system identification[J].International Journal of Control, 1989, 50(5):1873-1896. doi: 10.1080/00207178908953472 [17] STOPPIGLIA H, DREYFUS G, DUBOIS R, et al.Ranking a random feature for variable and feature selection[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2003, 3:1399-1414. [18] 王惠文, 仪彬, 叶明.基于主基底分析的变量筛选[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2008, 34(11):1288-1291. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8983.shtmlWANG H W, YI B, YE M.Variable selection based on principal basis analysis[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008, 34(11):1288-1291(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract8983.shtml [19] 王惠文, 陈梅玲, SAPORTA G.基于Gram-Schmidt过程的判别变量筛选方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 37(8):958-961. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract12041.shtmlWANG H W, CHEN M L, SAPORTA G.Variable selection in discriminant analysis based on Gram-Schmidt process[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011, 37(8):958-961(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract12041.shtml [20] LIU R P, WANG H W, WANG S S.Functional variable selection via Gram-Schmidt orthogonalization for multiple functional linear regression[J].Journal of Statistical Computation and Simulation, 2018, 88(18):3664-3680. doi: 10.1080/00949655.2018.1530776 [21] FISHER R.On the probable error of a coefficient of correlation deduced from a small sample[J].Metron, 1921, 1(4):3-32. [22] FRANK L E, FRIEDMAN J H.A statistical view of some chemometrics regression tools[J].Technometrics, 1993, 35(2):109-135. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1993.10485033 [23] MANGOLD W D, BEAN L, ADAMS D.The impact of intercollegiate athletics on graduation rates among major ncaa division I universities:Implications for college persistence theory and practice[J].Journal of Higher Education, 2003, 74(5):540-562. 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(4)
-







 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载: