Transient numerical simulations of flow rate into and out of two-phase temperature control accumulator
-
摘要:
两相控温型储液器是泵驱两相流体回路(MPTL)系统中的一个重要部件,承担着工质存储、供给、气液分离及精密控温的作用。采用Navier-Stokes方程建立了MPTL系统瞬态模拟的仿真模型,可用于研究热源功率变化时储液器与主回路的动态传热和传质特性。通过仿真与试验对比发现,数值模型的流量误差在±10%以内,验证了模型的有效性和准确度。数值模拟结果表明:热源开关机时,储液器与主回路发生工质交换,气液两相的温度和压力受到影响,系统的流阻也受到影响;随着热源功率的增加,工质交换速率和交换总量随之增加,储液器内气液两相的温度和压力变化趋势随之增大。该模型可用于研究不同工作条件下的流量、温度和干度的变化特性,指导MPTL设计,并在系统搭建前预测系统特性。
-
关键词:
- 泵驱两相流体回路(MPTL) /
- 两相控温型储液器 /
- 精密控温 /
- 传热传质 /
- 数值模拟
Abstract:Two-phase temperature control accumulator (hereinafter referred to as accumulator) is the key component of mechanically pumped two-phase loop (MPTL) system, which acts like the brain of MPTL system. The accumulator has the functions of storage and supplying of working fluid, gas-liquid separation and precise temperature controlling. In order to study the dynamic behavior of heat and mass transfer between accumulator and MPTL system in response to heat load variations, a transient numerical simulation model is developed for MPTL system by using the Navier-Stokes equations. By comparison between simulation and test results, it is found that the flow rate error of numerical model is in the range of ±10%, which verifies the validity and accuracy of the model. The simulation results show that accumulator will exchange fluid with the main loop in response to heat load variations. In this case, the temperature and pressure of two-phase fluid in accumulator, and the total system flow resistance will be affected. The rate and amount of mass transfer between accumulator and main loop will increase with the increase of heat power, and the same increase will occur for the variation trend of temperature and pressure of two-phase fluid in the accumulator. The model can be used to study the variation characteristics of flow rate, temperature, and quality under different operating conditions, which can also be used to design MPTL system and to predict the system characteristics before a system has been built.
-
随着航天技术的不断发展,热控系统面临着微小尺寸、高控温精度和温度均匀性、大面积热收集、高热流等问题的挑战,而泵驱两相流体回路(Mechanically Pumped Two-phase Loop,MPTL)技术的发展可以很好地解决这些航天热控难题[1]。MPTL技术具有传热功率大、传输距离远、控温精度高(可以实现±0.2 K~±1 mK的控温精度)等优点,特别适用于大功率激光器、大型遥感器、活动天线等要求具有高温度稳定度热源的热控[1-3]。相比于毛细泵驱流体回路(LHP和CPL),MPTL技术可以用于解决高功率和分散热源的散热难题,其稳定性和工作特性更好[4]。
MPTL技术的研究始于20世纪80年代,主要经历了如下几个发展阶段:19世纪80年代,Oren、Stalmach、Haslett与Delil[5-8]等对MPTL技术的基础理论进行了研究,并通过理论公式推导验证了该技术应用的可行性;1997年,日本NASDA和TOSHIBA公司通过航天飞机STS-85任务对MPTL进行了首次搭载[9];1999年,俄罗斯在国际空间站俄罗斯段上对MPTL技术开展了为期2个月的试验,对关键试验特性进行了验证,结果表明该技术在航天上应用切实可行[10];2011年,荷兰国家航空中心、中山大学等多家单位联合研制的阿尔法磁谱仪探测器使用了MPTL系统,是该技术在轨的首次应用,其对探测器内192个硅微条进行温度控制,控温的稳定性达到了±0.2℃,迄今应用已超7年[11];2016年,中国空间技术研究院通过搭载的方式验证了MPTL系统用于高热流密度散热的可行性,热源的最高热流密度可以达到271 W/cm2[12]。以上研究、搭载和应用均验证了MPTL技术用于航天热控系统的可行性及其优异的传热与控温性能。
在MPTL系统中,储液器起着至关重要的作用,其相当于系统的“大脑”,承担着工质存储、供给、气液分离及精密控温的作用。目前,储液器有2类设计方法,分别为压力控制型和两相控温型[13]。压力控制型储液器由气体部分(通常为惰性气体)和液体部分组成,通过改变气侧部分的压力,实现内部波纹管的移动,进而实现工质的交换;两相控温型储液器的内部为两相饱和态工质,通过控制储液器内饱和流体的温度,即可实现压力的控制,并可实现工质与主回路之间的交换。压力控制型储液器结构复杂,通常需要采用主动的电磁阀或复杂的电-机械控制,其寿命和可靠性远低于结构简单的两相控温型储液器。因此,两相控温型储液器更受青睐,MPTL技术一般选择其作为系统的控温组件。
为了实现储液器的控温与控液功能,储液器与主回路之间存在复杂的传热传质的耦合过程。对于该过程,国内外的研究者开展了一系列研究。黄臻成等[14]通过数值模拟研究了储液器与主回路之间的耦合特性,揭示了两者之间的相互扰动;莫冬传等[15]建立了MPTL系统的Simulink模型,研究了储液器与主回路之间的热质耦合过程,并指出储液器和主回路间连接管道的缓冲作用对耦合特性的影响不可忽视;van Gerner等[16-17]建立了储液器进出流量模拟的系统级瞬态模型,研究了CO2和R134a两种不同工质的交换特性,并对影响工质交换热性的因素进行了分析。然而,目前对储液器与主回路之间的动态传热传质过程的数值模拟,均对物理模型进行了一定的简化,未考虑储液器内气液两相之间的相互影响,缺少储液器与回路之间耦合特性的研究。
基于此,本文建立了储液器与主回路耦合的系统级瞬态模型,通过该模型研究了储液器与主回路之间的传热传质特性。首先,给出了MPTL系统的组成原理与数学模型;然后,比较了仿真和试验测试结果,并对储液器与主回路之间的传热传质过程进行了讨论和分析;最后,给出了热源功率变化时,储液器和系统的参数均受到影响以及功率增加会对储液器内的参数造成影响结论。
1. 分析和模型
1.1 系统组成
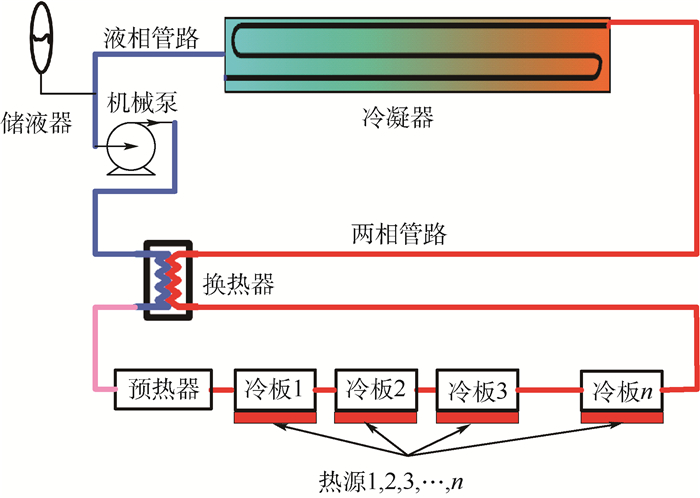
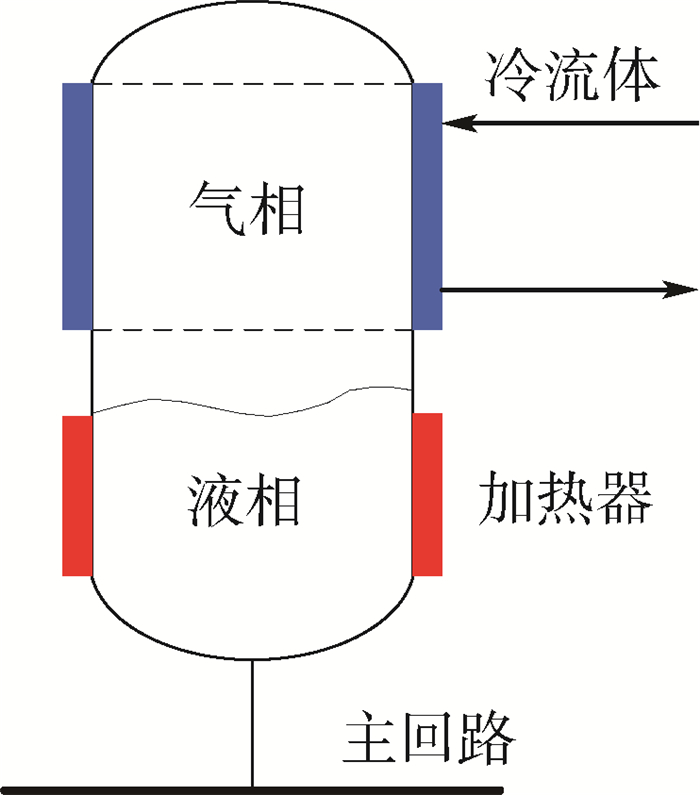
MPTL系统是利用机械泵驱动工质在循环流动过程中进行热量的收集、运输、排散的系统,其组成如图 1所示。为了实现热量的排散和多热源的温度控制,MPTL系统通过机械泵产生动力,机械泵出口的液相工质经换热器和预热器加热至饱和态,而后进入串联的冷板与热源进行换热,流经各片冷板的工质始终处于气液两相状态,其温度始终为对应压力下的饱和温度,吸收热量后的工质进入冷凝器将热量排放至热沉并重新回到液相状态进入机械泵完成一个循环。
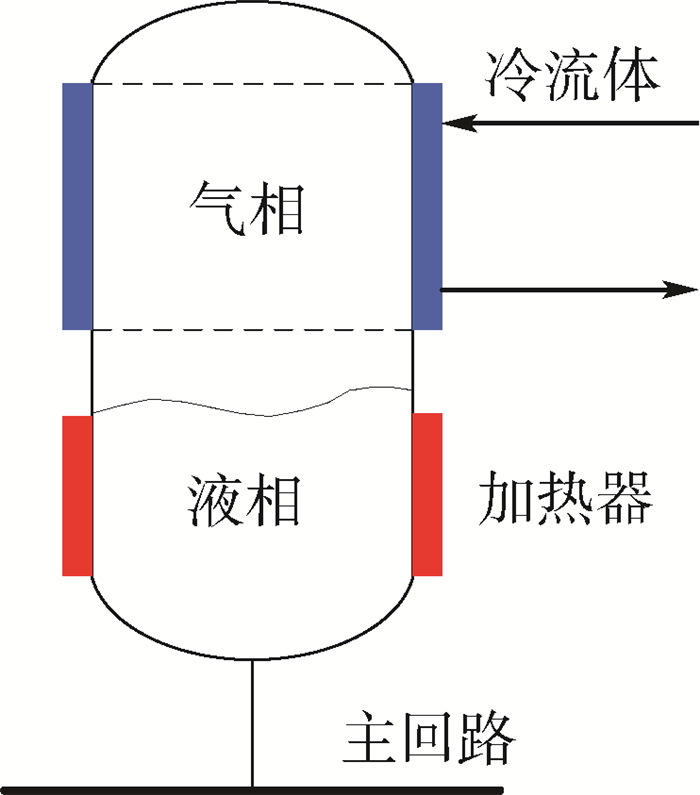
图 2给出了储液器的示意图,其内部流体由气液两相构成。对于两相流体,饱和压力与饱和温度是线性相关的,压力(温度)的升高/下降可以通过加热/制冷控制气相的增加/减少来实现。对于间歇性工作的热源,当热源功率增加时,回路内的液相工质将转变为气相,气相体积将大幅增加,此时回路内部多余的液相工质则会流入储液器进行存储;反之,当热源功率减小时,回路内的气相工质将转变为液相,气相体积将大幅减小,此时回路内不足的工质则会由储液器进行补充。当储液器向主回路补充工质时,为避免泵的气蚀,需保证进入到主回路内的流体为纯液态。在地面应用时,液相和气相在重力作用下会自动实现分离;在空间应用时,需要采用特殊的毛细结构实现气液分离,确保排出的流体为纯液态。
1.2 数值模型
MPTL系统的流动与传热可以由积分形式的Navier-Stokes方程描述[18]:

(1) 
(2) 
(3) 式中:ρ、u、p、g、e、q和n分别为密度、速度、压力、重力加速度、内能、热通量和法向量;V、A和t分别为体积、面积和时间。
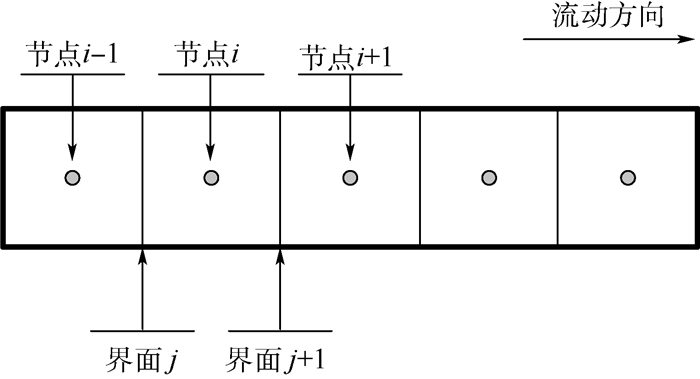
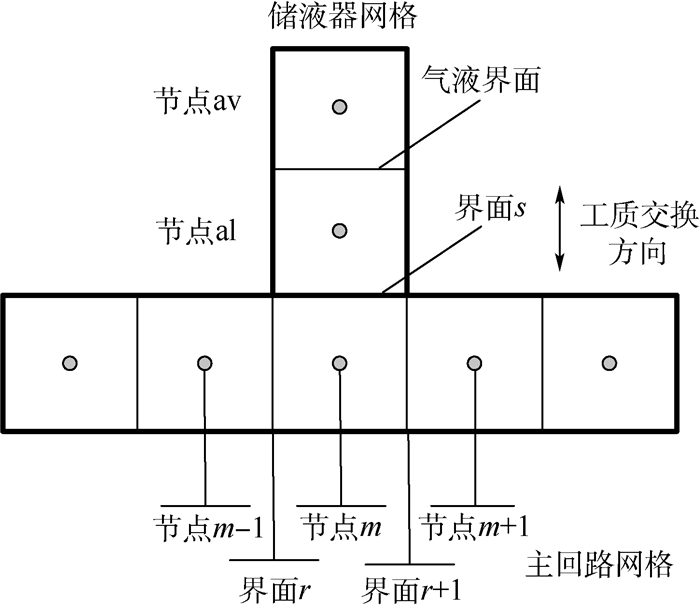
本文采用交错网格的方法对模型进行离散[19],即将压力、温度、干度及所有标量与物性参数定义在主节点上,而将矢量函数速度按其分量分别定义在错开主节点半个步长的主控制容积的界面上,图 3给出了主回路网格划分示意图。MPTL系统的管路、预热器、冷板和冷凝器被划分为一些小的体积节点,每一个体积节点包含一个中心位置的节点和两个节点之间共享的界面。
对式(1)积分得到

(4) 式中:i表示网格节点,j表示界面,j=i-1/2,j=i+1/2;u表示标量速度。
由于质量流量ṁ=ρuA,式(4)可以写为

(5) 在式(2)中,对左边第1项积分得到

(6) 式中:li+1, i为节点i和i+1之间的距离。
式(2)左边第2项表示流体进出网格所引起的动量的变化量,在本文的模型中,引起流体动量变化量的因素主要为流动摩擦引起的压力降,即左边第2项可以表示为

(7) 式中:fj+1为界面j+1的摩擦系数。
对式(2)中的右边第1项,采用空间一阶格式离散得到

(8) 由此,式(2)变为

(9) 在式(3)中,由于e+p/ρ=h,h表示比焓, 左边第2项和右边第2项可以合并为

(10) 忽略重力引起的能量变化,且加载的热量


(11) 单相压降依据文献[18]计算,两相压降的关系式由Friedel模型给出,该模型考虑了重力加速度、表面张力等影响因子,模型的预测结果与试验的误差较小[20],

在储液器中,区别于单相流体的热力学平衡态,其内部存在的状态为非平衡的状态,即气液两相对应不同的热力学状态,且两相之间存在着动态的传热传质过程。为了模拟相态的非平衡,储液器内的气相和液相采用了2个控制方程[23],即

(12) 
(13) 式中:mal为储液器内液相质量;ṁq为工质交换流量;Cpl为液相比热;Tal为液相温度;Tl为过冷液温度;Δmal, av/Δt为气液交换速率;hlv为汽化潜热;ρv为气相密度;ρl为液相密度;UlT为液相换热系数;AsT为气液交界面面积;TI为界面温度;mav为储液器内气相质量;Cpv为气相比热;Tav为气相温度;UvT为液相换热系数;

当主回路的热源状态发生变化时(如热源开机或关机),会引起主回路内的压力和温度场发生变化。在储液器与主回路的连接处(见图 4),当连接点压力下降时,储液器内的液体会流入到主回路中,反之,当连接点压力上升时,主回路内的液体会流入到储液器中。流入或流出的液体会影响到储液器的温度或压力。
储液器节点的压力根据式(14)计算得到:

(14) 式(14)忽略重力影响,下标al和m分别表示储液器液相和网格m,下标s表示储液器与主回路的交界面。
管路与储液器相连的节点m,连续方程式(1)变为

(15) 在储液器与主回路连接的节点m,动量和能量方程(式(2)和式(3))变为

(16) 
(17) 式(16)忽略了储液器与主回路工质交换时主回路的影响,hal为储液器液相的比焓,下标r和s+1分别表示网格m的前后2个界面。
除储液器外,预热器、冷板和冷凝器内涉及了气液相变过程,主要包括:①预热器内,工质从过冷态加热到饱和态的过程;②冷板内,工质以饱和态吸收热源,引起干度增加;③冷凝器内,释放热量,工质从饱和态变为过冷态。在这些组件内,通过将计算得到的比焓与饱和液相比焓进行比较,判断工质是否为过冷态或饱和态,即

(18) 式中:hl_sat为饱和液相比焓;Tf为流体温度;Tsat为饱和温度,与当地压力相关;x为干度。
MPTL系统各个组件的壳体、内部流动的工质均离散为小单元。预热器和冷板需要通过热源进行加热,壳体和工质之间均通过对流换热方式传递热量。对于与外界有热量交换的组件,将沿流动方向进行划分,每个节点加载相应的热量。对于冷凝器,网格划分与冷板划分方法类似,将管壁和工质进行划分,管壁节点和工质节点一一对应。机械泵提供工质在回路中循环的驱动力,为使系统能够运行,机械泵提供的扬程大于所有零件的阻力之和。
1.3 工质属性
本文MPTL系统的工质为液氨,该工质为航天热管或环路热管的常用工质,具有汽化潜热大、传热效率高、性质稳定的优点。在本文的计算模型中,所有与氨工质热物性相关的参数,如气液两相的密度、黏度、饱和压力、液体表面张力、汽化潜热和热导率等参数,均来源于美国NIST的REFPROP数据库。
1.4 计算参数和条件
模型的计算参数如表 1所示。本文中使用的预热器和冷板的类型均为平板型小通道换热器,内部流道为2 mm×1.5 mm的矩形截面,在计算模型中,等效为圆管进行计算;加载到预热器和冷板上的热量,均匀分配到每一个计算节点上;冷凝器管路与冷凝器的接触换热系数、储液器与冷源的接触换热均通过实验室的稳态接触热阻测试仪测试得到。
表 1 模型与试验参数Table 1. Parameters of model and test组件 描述 机械泵 流量:1 g/s 储液器 体积:200 mL;控温温度:(20±0.3)℃;加热功率:10 W 预热器 材料:不锈钢;加热功率:50 W;数量:2个 冷板 材料:不锈钢;数量:4个 冷凝器 温度:(10±0.5)℃ 管路 材料:不锈钢;外径:0.003 m;内径:0.002 m 模型的初始条件为:T=20℃,干度x=0,压力p=0.86MPa(20℃对应的饱和压力)。模型的边界条件包括:①储液器壁面温度,Taw=(20±0.3)℃;②热沉温度,Tcon=(10±0.5)℃;③管路轴向导数,∂Ttube/∂a=0。
1.5 数值计算方法
式(5)、式(9)~式(17)构成的数学模型,变量随时间的变化率采用一阶格式离散;压力、流量和比焓参数的离散采用全隐格式,其他参数采用显式格式。
主回路每个节点的求解变量包括p、ṁ、h;储液器的求解变量包括Tal、Tav、ṁq,其他变量可以通过REFPROP数据库或根据与求解变量之间的函数关系得到。求解问题的节点数目为N+1(N表示主回路节点个数,1表示储液器节点),每个节点上的方程数目为3个,求解变量为3个,因此所求解问题组成的离散方程组包含3(N+1)个方程,3(N+1)个变量。利用Newton-Rapson方法将非线性方程组线性化,然后通过高斯迭代方法进行求解,当满足给定的收敛判据时,迭代结束。迭代判据为ε=10-6。在迭代中,如果迭代次数超过10次仍未收敛,在计算中采用降低时间步的方式开始新迭代循环。
2. 试验验证装置
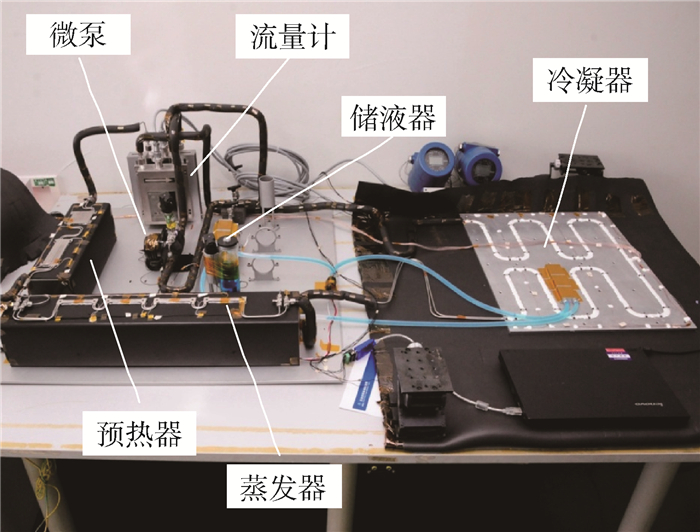
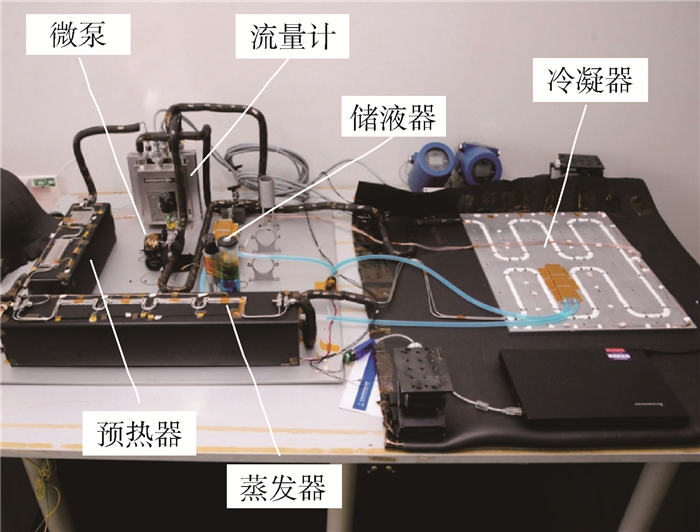
图 5给出了MPTL系统试验装置的照片,试验参数如表 1所示。储液器是一个两相控温型储液器,内部包含毛细结构装置,可同时满足地面和微重力环境下的应用,储液器的外表面布置了加热和制冷装置,可以实现对储液器的精密控温;2个预热器和4个冷板均为小通道平板型冷板,并串联应用在主回路中。机械泵的类型为齿轮泵(型号:Micropump GA-V21),在机械泵的出入口分别设置了2台型号相同的柯氏流量计(型号:首科实华DMF-1),并通过2个流量计的差值,获得储液器的进出流量。为了降低MPTL系统与环境的漏热,所有的管路都包覆了保温材料。
3. 结果和讨论
3.1 仿真与试验结果对比
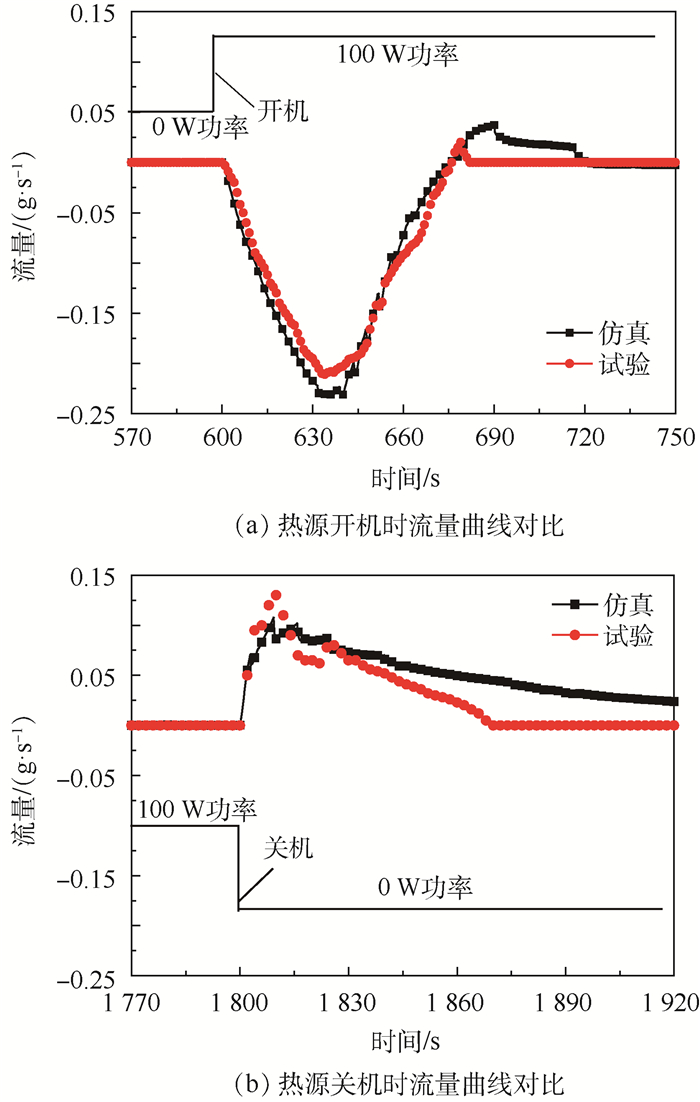
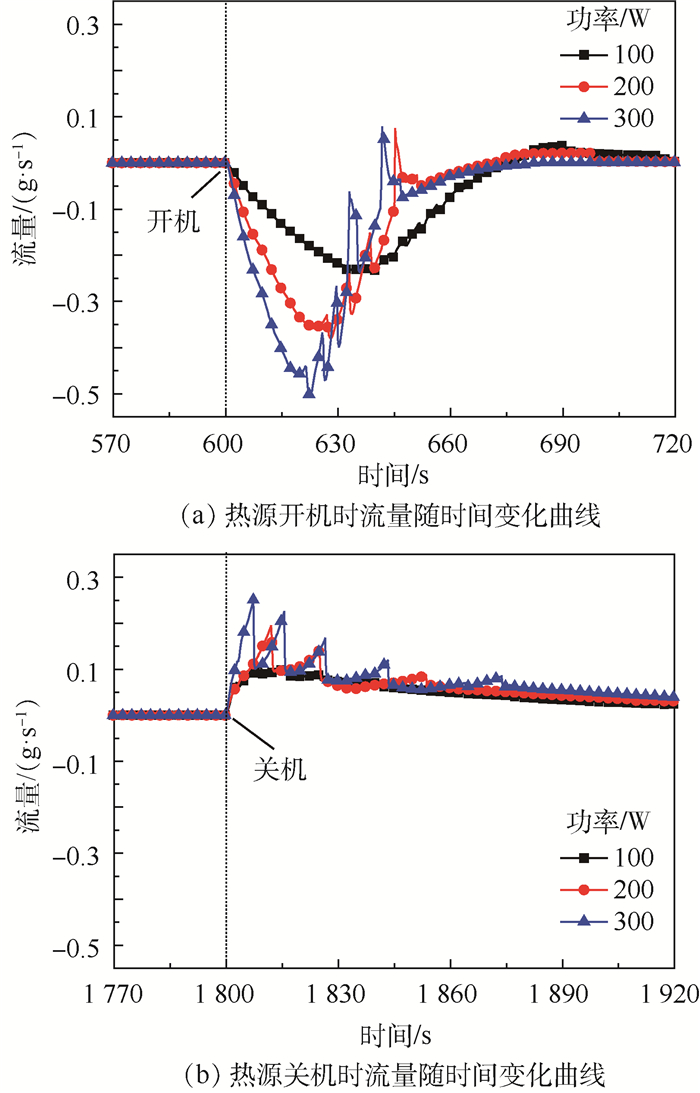
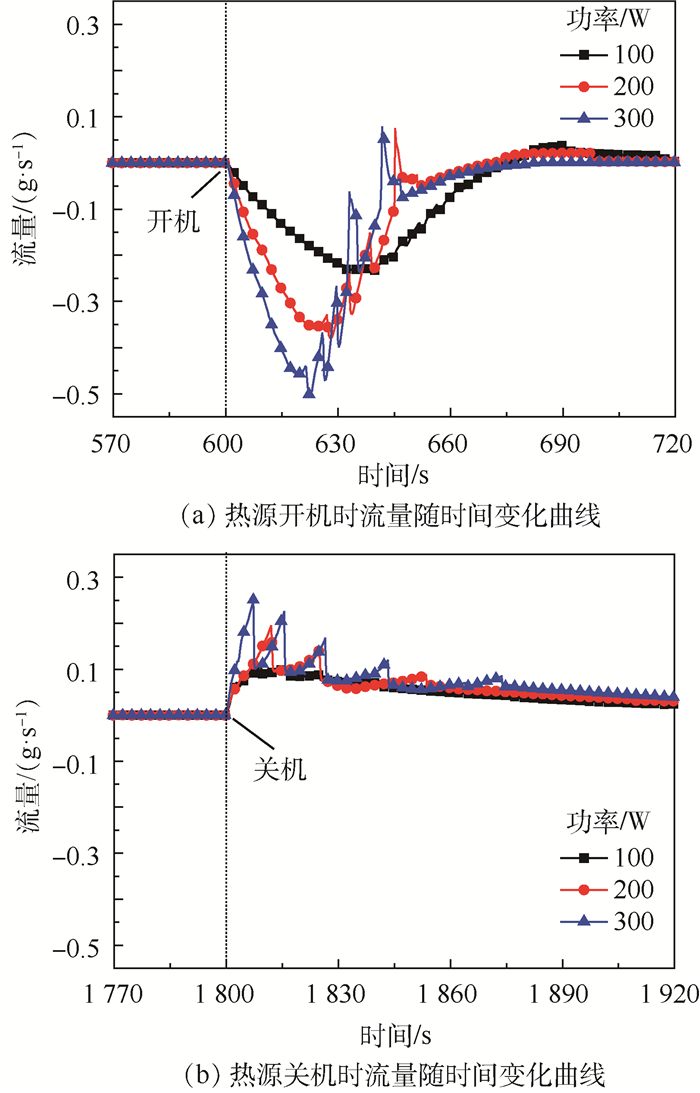
图 6给出了热源功率变化时,储液器与主回路工质交换的数值模拟与试验结果的对比。通过对比可以发现,数值模拟与试验结果吻合较好,两者结果在整体上变化趋势基本一致,进出流量的极大值误差在±10%以内,但仿真预测的总交换量偏大,主要是由于仿真时忽略了储液器与加热器之间的热阻及储液器本身热容的影响。热源开机时,冷板内会有大量的蒸气瞬间生成,生成的蒸气会迅速占据冷板下游回路内液体的空间,导致主回路内的液体被迫进入到储液器,此时的流量值为负值,表示液体从主回路进入到储液器内,如图 6(a)所示;热源关机时,冷板内的蒸气含量会瞬间减少,冷板下游回路内被蒸气占据的空间又会迅速被储液器回流的液体给填充,从而导致了储液器内的液体回流至主回路,此时流量值为正值,表示液体从储液器进入到主回路,如图 6(b)所示;热源功率不发生变化时,储液器与主回路之间的工质交换量为零。通过仿真与试验的对比,验证了模型的有效性和准确度,该模型可以用于预测MPTL系统的瞬态工作特性,并可用于理解和分析MPTL系统的工作特性。
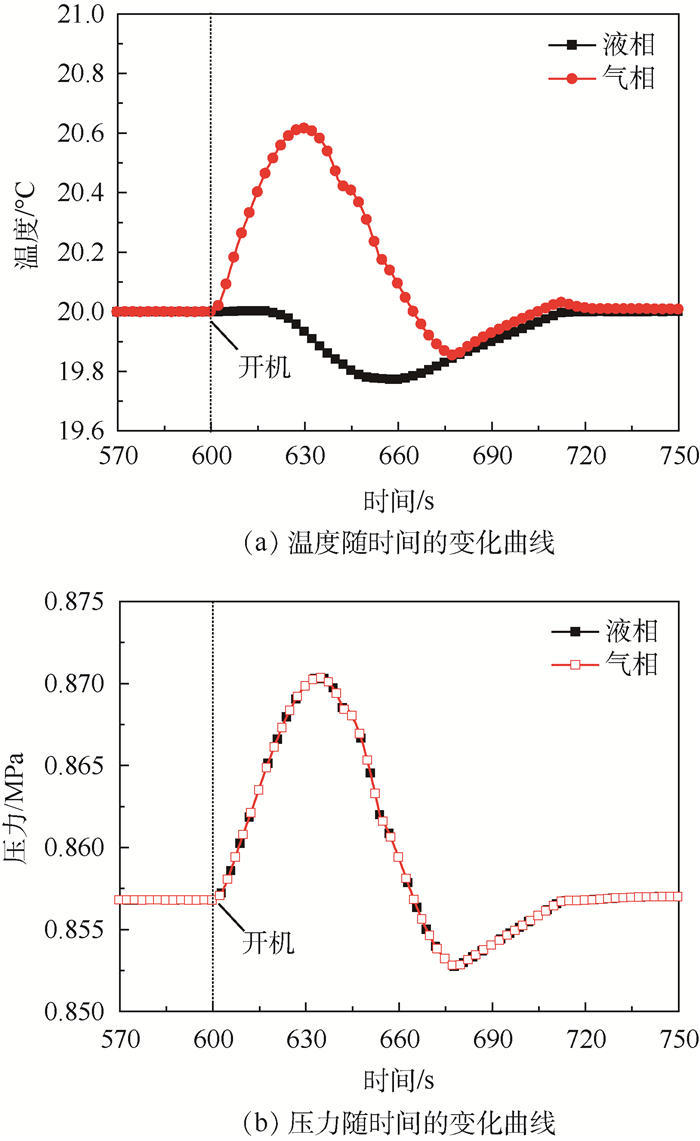
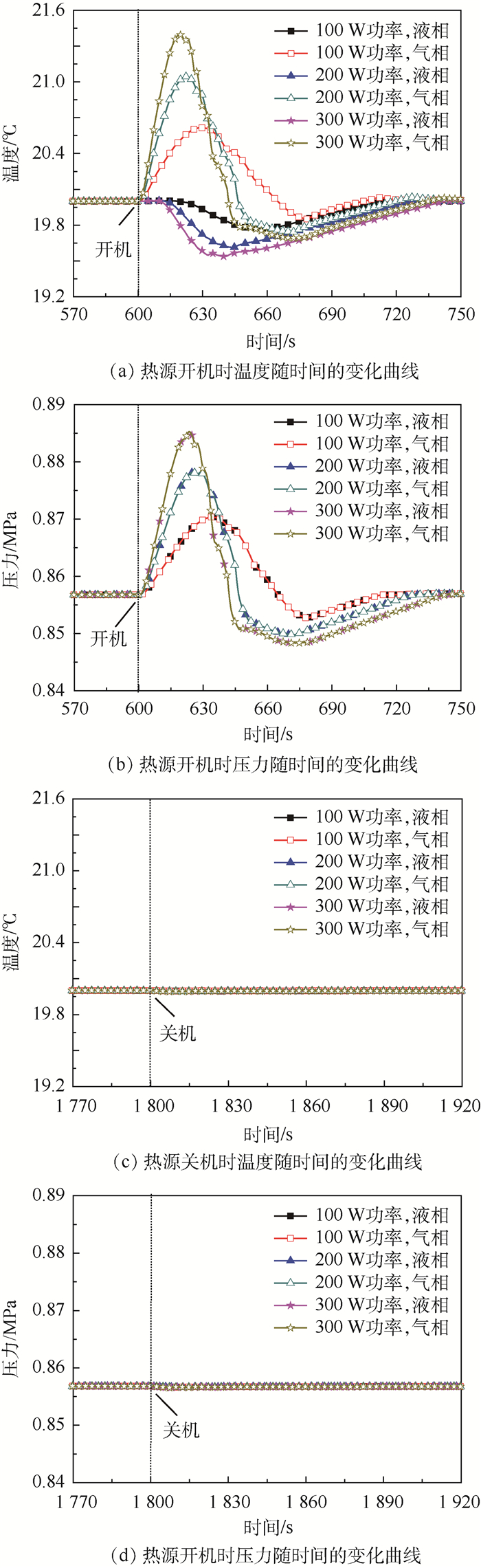
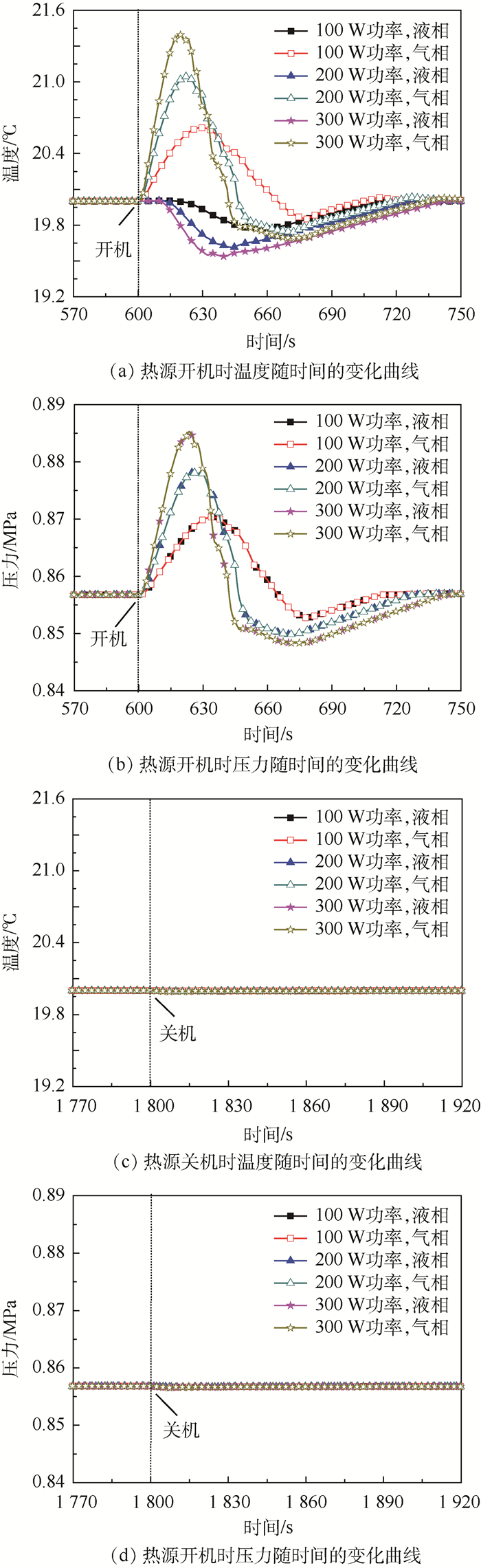
图 7给出了热源开机时,储液器内气液两相的温度和压力随时间的变化曲线。热源开机时,气液两相的温度和压力变化范围较大,且气相和液相的温度变化趋势差别较大,压力变化趋势差别较小。对于图 7(a)所示的气液两相温度的变化趋势,从主回路流入到储液器内的过冷液体,首先与储液器的液相进行混合,导致气相空间快速被压缩,气相温度快速上升,当流入量达到最大值时,气相的温度升高值达到最大为0.6℃,随后流入量逐渐减小,由于气液两相在交界面进行换热的作用,气相温度逐渐减小,直至与液相温度变化趋势一致;相比于气相温度的变化趋势,受液相热容较大的影响,液相温度的下降相对有些延迟,且温度下降速率也比较缓慢,液相温度下降的最大值为0.25℃。通过图 7(b)所示的气液两相压力的变化趋势可以发现,两者之间的变化趋势吻合较好,且变化趋势与气相饱和温度对应的压力变化趋势基本一致,这表明储液器内的工作温度是由内部的气相温度决定的。
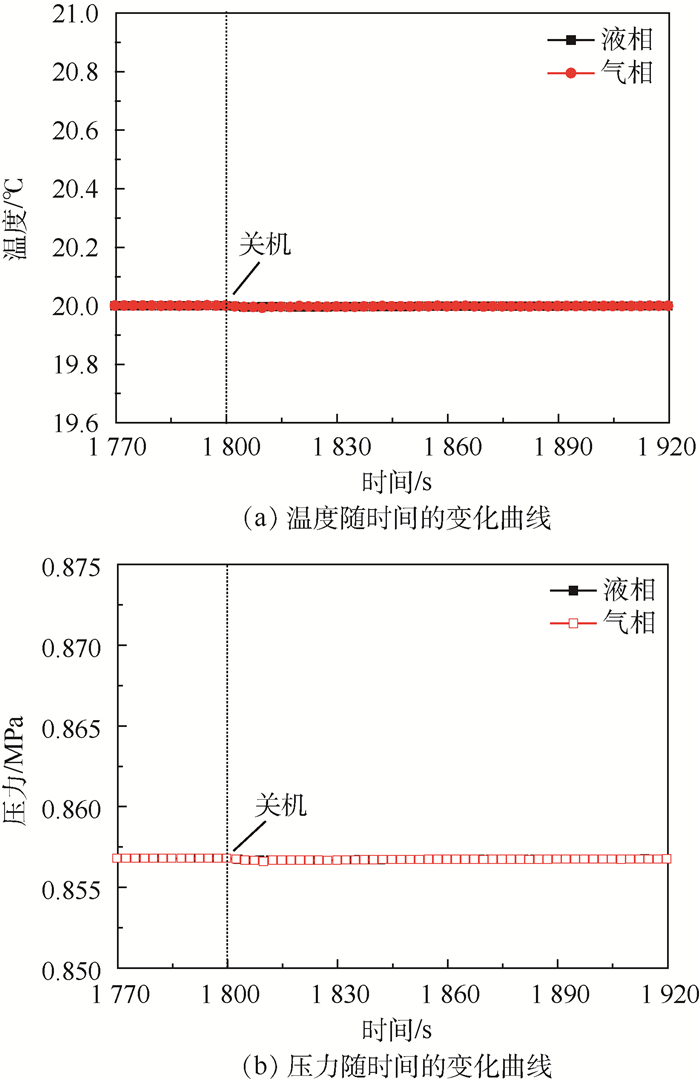
图 8为热源关机时,储液器内气液两相的温度和压力随时间的变化曲线。与热源开机时的变化趋势不同,热源关机时,气液两相温度和压力变化较小,且变化趋势一致,主要由于从储液器回流至主回路的速率相对较小,气相空间的变化速率相对较小,进而导致气相温度和压力的变化较小。
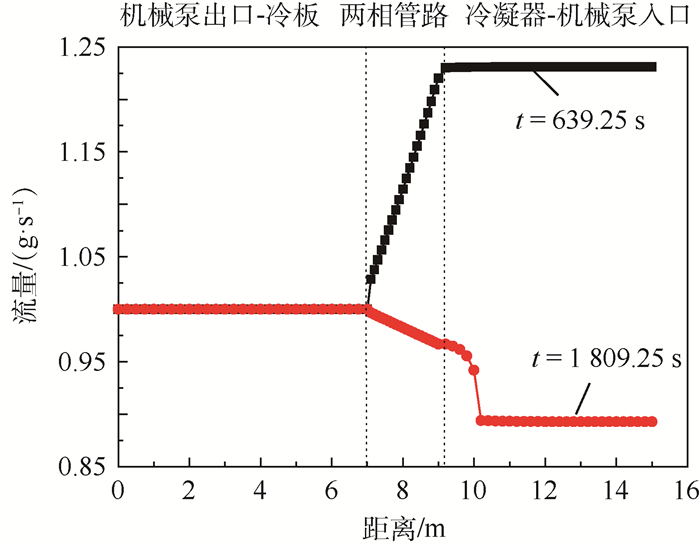
图 9给出了2个不同时刻的系统流量随距离的变化趋势,分别对应了流入和流出储液器流量的最大值。热源开机和关机后,机械泵出口到冷板出口的流量保持不变,其余位置的流量受到了开关机状态的影响。热源开机后,冷板出口与冷凝器连接的两相段管路,流量以近似线性的关系增加,冷凝器入口至机械泵入口位置的流量保持不变,且为回路流量的最大值,这可以理解为:冷板出口流体的干度不断增加,即气相的比例不断增加,由于气相流速相对较快(相同流量、不同密度),冷板下游的流体被不断加速,从而导致了两相段流量的增加,当流体流入到冷凝器时,干度下降,流体的加速过程被终止,进而导致冷凝器内的流速最大,当流经储液器支路时,多余的流体将流入到储液器;热源关机后,冷板下游的干度将下降,流体被不断减速,流量不断减小,当流体流入冷凝器时,干度进一步减小,当流体的干度降为零时,即流体变为纯液态时,流量降为最小值,此时,储液器将对主回路进行回流补液。
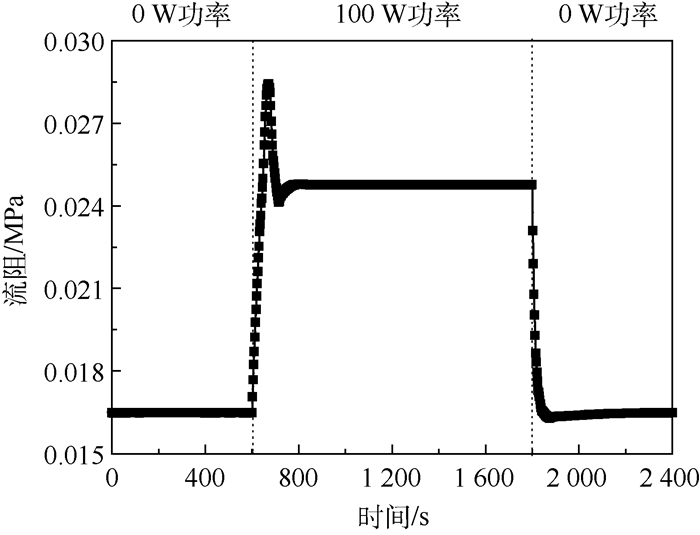
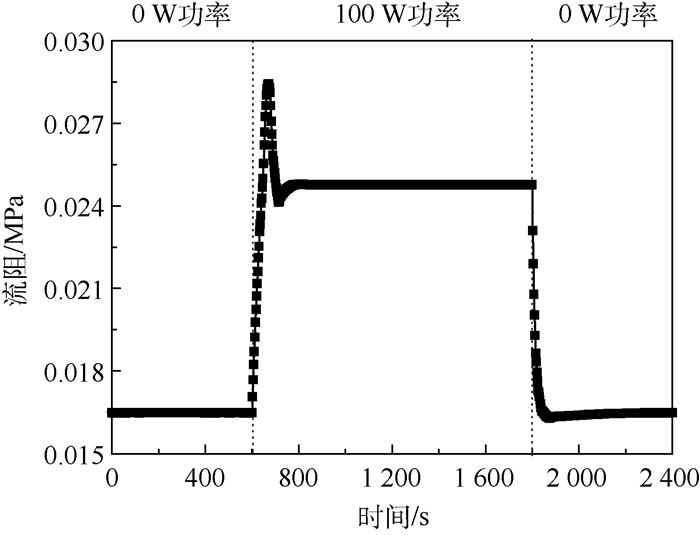
图 10为系统流阻随时间的变化趋势。热源开机后,两相管路和冷凝器处的流量将不断增加,导致系统的流阻突然增大,出现一个“尖峰”,尖峰持续的时间与主回路流入储液器持续的时间一致;当主回路与储液器工质交换过程停止后,系统的流阻有所回落,并一直持续至热源关机;热源关机后,两相管路和冷凝器处的流量和干度不断较小,导致系统的流阻快速回落至较小值。
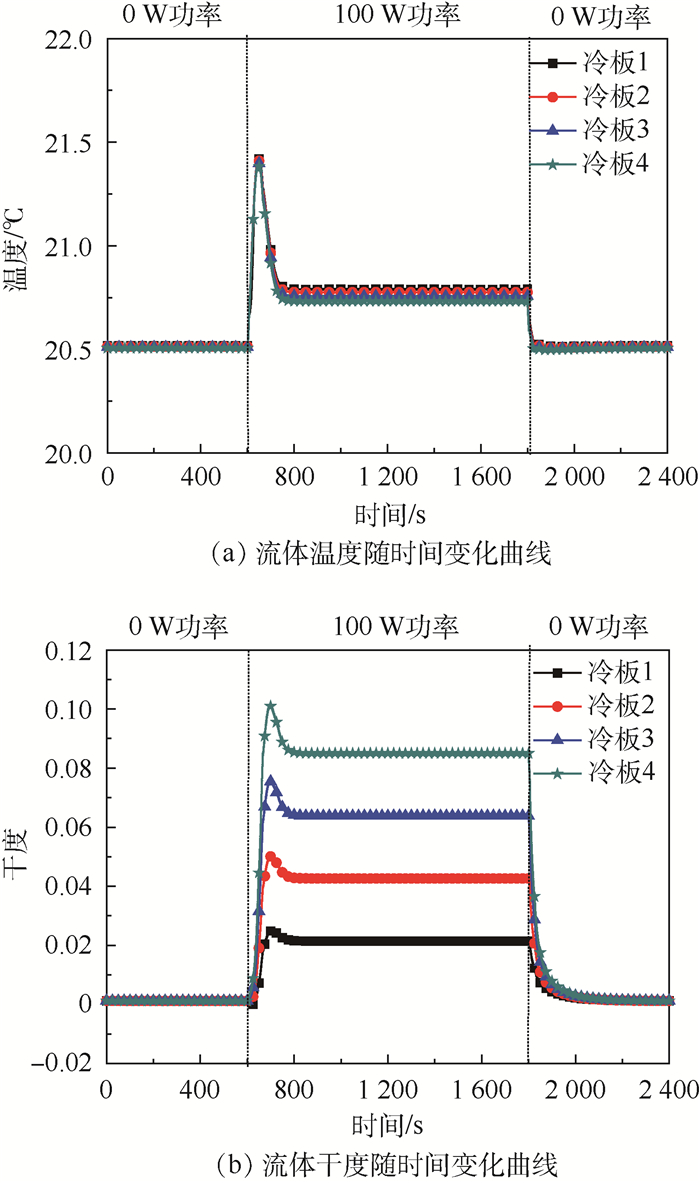
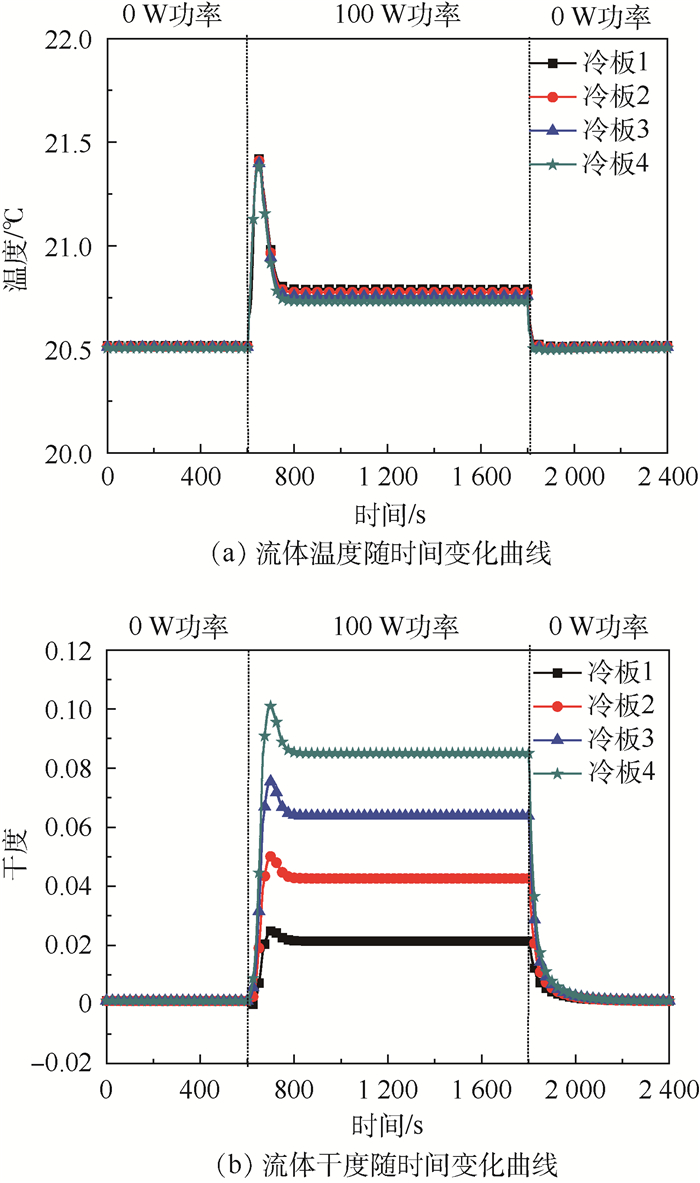
图 11为冷板内流体的温度和干度随时间的变化趋势。热源开机后,一方面,主回路多余的液体流入储液器,造成储液器内气相体积压缩,饱和温度上升;另一方面,冷板下游的流量迅速增加,导致系统的流阻迅速增加,2个原因共同造成冷板的饱和温度出现“尖峰”,温升约0.9℃;当工质交换过程停止后,冷板的温度回落至20.7℃,并持续至热源关机;热源关机后,冷板流体的温度回落至20.5℃。从图 11(b)可以发现,热源开机时,受储液器饱和压力和系统流阻变化的影响,冷板内流体的干度也受到了影响,每个冷板均出现了“尖峰”,变化值随冷板的顺序逐渐增大。
3.2 不同功率下的计算结果
图 12为不同功率下储液器的进出流量随时间的变化曲线。从图 12(a)可以发现,热源开机后,随着冷板加载功率的增加,工质从主回路流入到储液器流量的斜率随之增大,流量的最大值随之增加,表明从主回路进入到储液器工质的流量不断增加,这主要是由于功率增加时,冷板出口流体的干度不断增加,冷凝器上两相管路的长度不断增加,流体的平均速率不断增加而导致的;从图 12(b)可以发现,热源关机后,随着冷板加载功率的增加,工质从储液器流回主回路的流量也不断增加,但相对热源开机时的变化速率较小。此外,通过图 12可以发现,热源开关机时,随着加载功率的增大,储液器进出流量的波动均随之增大,这主要是由于随着加载功率的增大,储液器与主回路的工质交换量随之增大,进而导致储液器的温度变化随之增大,然而为维持储液器温度的稳定,控温(制冷或加热)装置的功率也随着增大,加载的功率会对工质交换量产生影响,导致进出流量出现波动,且波动随着功率增大而增加。
图 13为不同功率下储液器内气液两相温度和压力随时间的变化曲线。热源开机后,随着功率的增加,气相温度和压力的上升值随之增加,液相温度的下降值随之增加,这是由于随着功率的增加,从主回路进入到储液器内的流量和总量不断增加,气相压缩的空间随之增加,液相的总量随之增加导致的;热源关机后,气液两相的温度和压力随功率增加的变化相对较小,这是由于从储液器流回主回路的流量相对较小,且时间较长,斜率较小,瞬间从液相流回主回路的流量较小,液相和气相的体积变化速率小导致的。
4. 结论
本文通过数值模拟,研究了储液器与主回路的工质交换特性、储液器内气液两相温度和压力以及主回路的变化特性。主要结论如下:
1) 通过仿真与试验的对比,发现数值模型的预测的流量误差在±10%以内,模型可以用于预测储液器与主回路的瞬态工作特性。
2) 热源功率变化时,储液器内气液两相的温度和压力将受到影响,回路内的流量将发生变化,系统的流阻、冷板内的温度和干度将出现“尖峰”。
3) 随着热源功率的增加,工质交换速率和交换总量随之增加,储液器内饱和温度和饱和压力变化趋势随之增加。
模型可以用于预测MPTL系统的瞬态特性,并用于预测和理解MPTL系统的工作性能。
-
表 1 模型与试验参数
Table 1. Parameters of model and test
组件 描述 机械泵 流量:1 g/s 储液器 体积:200 mL;控温温度:(20±0.3)℃;加热功率:10 W 预热器 材料:不锈钢;加热功率:50 W;数量:2个 冷板 材料:不锈钢;数量:4个 冷凝器 温度:(10±0.5)℃ 管路 材料:不锈钢;外径:0.003 m;内径:0.002 m -
[1] JOHANES V E, GERNER V H J, BENTHEM V R C, et al.Component developments in Europe for mechanically pumped loop systems(MPLS) for cooling applications in space[C]//46th International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2016: 1-14. [2] 鲁盼, 赵振明, 颜吟雪.高分辨率遥感相机CCD器件精密热控制[J].航天返回与遥感, 2014, 35(4):59-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2014.04.008LU P, ZHAO Z M, YAN Y X.Precise thermal control of CCD in high resolution remote sensing[J].Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2014, 35(4):59-66(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2014.04.008 [3] 童叶龙, 李国强, 余雷, 等.CCD组件的热分析和热实验[J].航天返回与遥感, 2014, 35(5):46-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2014.05.007TONG Y L, LI G Q, YU L, et al.Heat dissipation and precise temperature control for high-power CCD assembly[J].Spacecraft Recovery & Remote Sensing, 2014, 35(5):46-53(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-8518.2014.05.007 [4] ELLIS M C, KURWITZ R C.Development of a pumped two-phase system for spacecraft thermal control[C]//46th International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2016: 1-16. [5] OREN J A.Study of thermal management for space platform applications: NASA CR-165307[R].Washington, D.C.: NASA, 1981. [6] STALMACH D D, OREN J A.Systems evaluation of thermal bus concepts: NASA CR-167774[R].Washington, D.C.: NASA, 1982. [7] HASLETT B.Space station technology 1983: NASA CP-2293[R].Washington, D.C.: NASA, 1983. [8] DELIL A A M.Some considerations concerning two-phase flow thermal bus systems for spacecraft: NLR-RL-84-028[R].Amsterdam: NLR, 1984. [9] RYOSUKE F, MASATAKA Y, MASAYUKI N, et al.Experiment configuration and preliminary results of two-phase fluid loop experiment (TPFLEX)-STS-85 mission payload[J].Acta Astronautica, 2002, 50(4):217-224. doi: 10.1016/S0094-5765(01)00159-X [10] BLECLNOV S M, DESYATOV A K, VEZHNEVETS P D, et al.Experimental flight facility-two-phase heat transfer model in the Russian segment of the international space station[C]//Proceedings of Aviation and Spacecraft Industry and Technology, 1999: N13. [11] JOHANES V E, PAUW A, DONK G V.AMS02 tracker thermal control cooling system test results of the AMS02 thermal vacuum test in the LSS at ESA ESTEC[C]//42nd International Conference on Environmental system, 2012: 1-14. [12] 于新刚, 徐侃, 苗建印, 等.高热流散热泵驱两相流体回路设计及飞行验证[J].宇航学报, 2017, 38(2):192-197. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.02.011YU X G, XU K, MIAO J Y, et al.Design and on-board validation of pumped two-phase fluid loop for high heat flux removal[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2017, 38(2):192-197(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2017.02.011 [13] JONI T.Modeling a two-phase mechanically pumped loop[D].Enscheda: University of Twente, 2014: 14-26. [14] HUANG Z C, HE Z H, MO D C, et al.Coupling between an accumulator and a loop in a mechanically pumped carbon dioxide two-phase loop[J].Microgravity Science and Technology, 2011, 21(Supp1):23-29. [15] 莫冬传, 黄臻成, VAN ES J, 等.机械泵驱动两相环路热控系统的储液器与主回路耦合特性分析[C]//中国工程热物理学会多相流学术会议, 2012: 1206124.MO D C, HUANG Z C, VAN ES J, et al.Coupling properties between accumulator and main loop of mechanically pumped two phase loop[C]//Chinese Society of Engineering Thermophysics Multiphase Flow Conference, 2012: 1206124(in Chinese). [16] VAN GERNER H J, BRAAKSMA N.Transient modelling of pumped two-phase cooling systems: Comparison between experiment and simulation[C]//46th International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2016: 1-15. [17] VAN GERNER H J, BOLDER H J, BOLDER R, et al.Transient modelling of pumped two-phase cooling systems: Comparison between experiment and simulation with R134a[C]//47th International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2017: 1-10. [18] 庄礼贤, 尹协远, 马晖扬.流体力学[M].2版.合肥:中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009:65-89.ZHUANG L X, YIN X Y, MA H Y.Fluid mechanics[M].2nd ed.Hefei:University of Science and Technology of China Press, 2009:65-89(in Chinese). [19] 陶文铨.数值计算传热学的近代进展[M].北京:科学出版社, 2000:181-192.TAO W Q.Advances in computational heat transfer[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2000:181-192(in Chinese). [20] FRIEDEL L.Improved friction pressure drop correlation for horizontal and vertical two-phase pipe flow[C]//European Two-Phase Flow Group Meeting, 1979: 485-492. [21] 弗兰克P.英克鲁佩勒, 大卫P.德维特, 狄奥多尔L.伯格曼, 等.传热和传质基本原理[M].葛新石, 叶宏, 译.北京: 化学工业出版社, 2011: 297-332.INCROPERA F P, DEWITT D P, BERGMAN T L, et al.Fundamentals of heat and mass transfer[M].GE X S, YE H, translated.Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2011: 297-332(in Chinese). [22] SHAH M M.Prediction of heat transfer during boiling of cryogenics fluids flowing in tubes[J].Cryogenics, 1984, 24(5):231-236. doi: 10.1016/0011-2275(84)90148-6 [23] LEONID V J, MARCO M, CLAUDIO F.Advanced design of a "low-cost" loop heat pipe[C]//39th International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2009: 1-12. 期刊类型引用(4)
1. 孟庆亮,赵振明,陈祥贵,朱许. 航天遥感器用泵驱两相流体回路热真空试验研究. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2023(03): 559-568 .  本站查看
本站查看2. 苏炳志,王磊,张红伟,汪海涵,石璐璐. 基于修正似然滤波的无人机编队相对导航方法. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2023(03): 569-579 .  本站查看
本站查看3. 褚雯霄,吕义高,王耀霆,王秋旺. 星载有源相控阵天线热控技术研究进展. 华中科技大学学报(自然科学版). 2022(12): 106-120 .  百度学术
百度学术4. 孟庆亮,赵振明,张焕冬,杨涛,赵宇,于峰. 航天遥感器用机械泵驱动两相流体回路工作特性试验研究. 中国科学:技术科学. 2020(11): 1474-1486 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(1)
-








 下载:
下载:













 下载:
下载:




 百度学术
百度学术