Reentry trajectory optimization for hypersonic vehicle based on adaptive pseudospectral method
-
摘要:
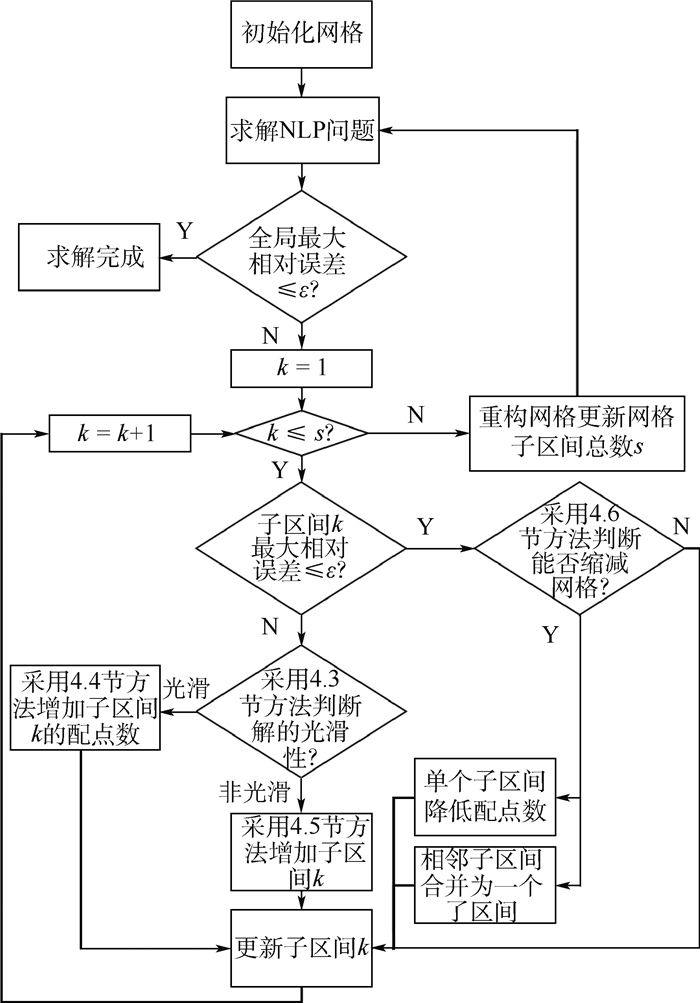
针对高超声速飞行器再入轨迹优化问题,建立考虑地球自转的三自由度再入运动方程,以美国通用空天飞行器为对象建立再入约束模型。采用Legendre-Gauss-Radau配点对3种典型优化问题:最大纵程、最大横程及最小航迹角变化率问题进行离散,将连续时间最优控制问题转化为非线性规划问题。基于Legendre多项式近似理论,引入衰减系数构建相对误差估计关系式,并以此提出一种有效的自适应网格重构策略。最终获得了3种典型再入轨迹优化问题的最优解。仿真结果表明,该算法的求解结果与变步长Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg法积分一致。相比传统自适应伪谱法,其配点和区间分配更合理,迭代次数少,求解速度高,且对人工参数不敏感。
-
关键词:
- 高超声速飞行器 /
- 复杂约束 /
- 轨迹优化 /
- 自适应伪谱法 /
- Legendre系数
Abstract:In order to solve the reentry trajectory optimization for hypersonic vehicle, a three-degree-of-freedom reentry kinematic equation considering the earth rotation was established, and a reentry constraint model was built, which took America's universal space vehicle as the object. Firstly, Legendre-Gauss-Radau points were employed to transform the continuous-time optimal control problem into a nonlinear programming problem, and three typical optimization problems including maximum downrange, maximum crossrange and minimum change rate of path angle were discretized. Secondly, an estimation relational expression of relative error relying on decay rate of Legendre polynomial approximation was established, and an effective adaptive mesh refinement strategy was proposed. Finally, three typical reentry trajectory optimization problems were well solved. The simulation results show that the result solved by the proposed method is consistent with the integral of variable-step-size Runge-Kutta-Fehlberg method. Compared to the traditional adaptive pseudospectral method, the proposed method achieves more reasonable mesh refinement, less mesh iteration numbers, faster computation speed and less sensitivity to the user-specified parameters.
-
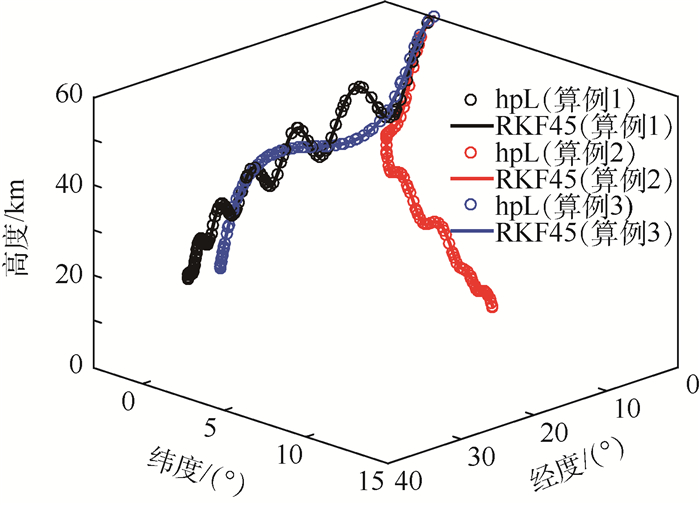
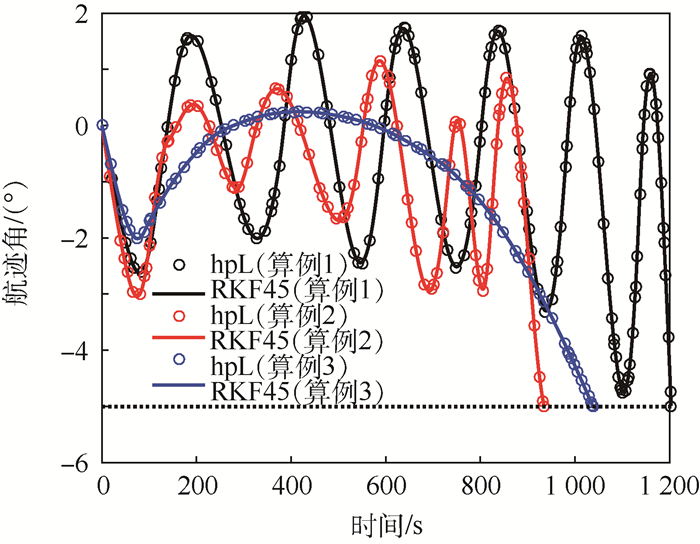
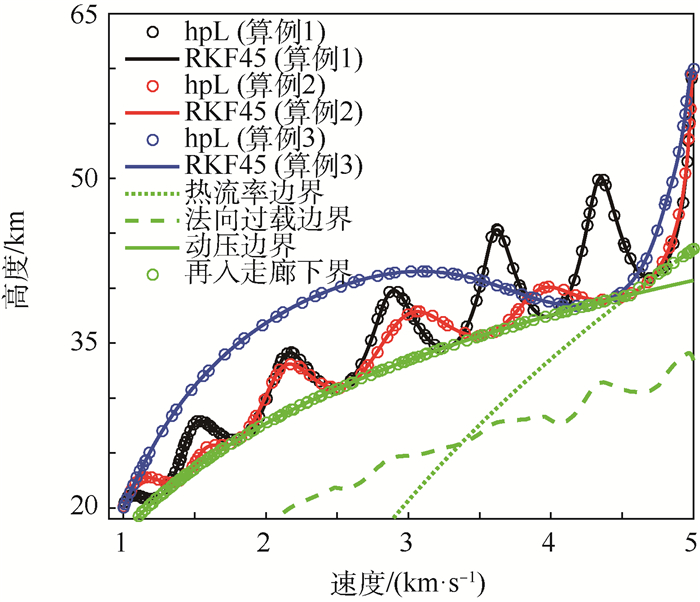
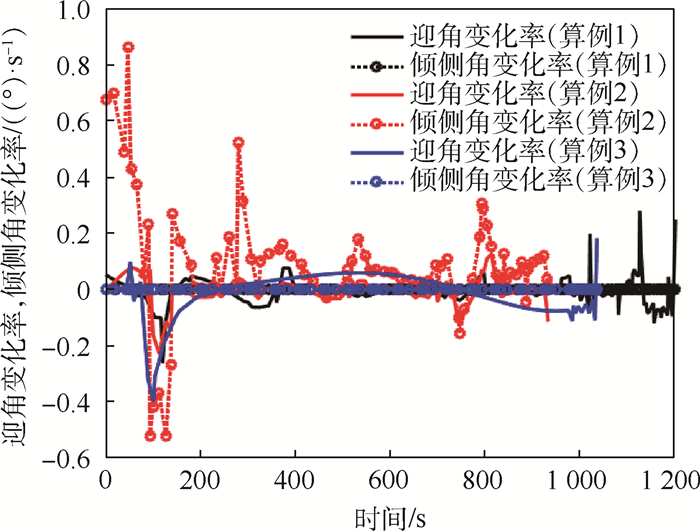
表 1 算例设置
Table 1. Setup of calculation examples
算例 状态 权重系数 1 最大纵程 w1=1,w2=0,w3=0 2 最大横程 w1=0,w2=1,w3=0 3 最小航迹角变化 w1=0,w2=0,w3=1 表 2 边界条件设置
Table 2. Setup of boundary conditions
参数 初始 末端 高度h/km 60 20 经度θ/(°) 0 自由 纬度ϕ/(°) 0 自由 速度V/(km·s-1) 5 1 航迹角γ/(°) 0 5 航向角ψ/(°) 90 自由 表 3 不同算法轨迹优化结果
Table 3. Trajectory optimization results by different methods
算法 算例 误差容限ε 衰减容限υε 区间配点限制 配点总数 区间总数 网格迭代次数 平均求解时间(5次)/s 性能指标 hpL 1 10-4 0.25 [3, 10] 130 33 3 3.520 1 -0.112 9 hpL 1 10-4 0.5 [3, 10] 122 37 4 3.878 5 -0.112 8 hpL 1 10-5 0.25 [3, 10] 209 30 5 7.467 0 -0.112 8 hp 1 10-4 [3, 10] 132 39 5 4.462 8 -0.112 8 hp 1 10-5 [3, 10] 250 58 13 56.272 2 -0.112 8 ph 1 10-4 [3, 10] 105 20 4 42.716 9 -0.112 6 ph 1 10-4 [3, 6] 114 28 4 4.461 6 -0.112 6 ph 1 10-5 [3, 6] 273 67 7 10.378 1 -0.112 9 hpL 2 10-4 0.25 [3, 10] 79 20 4 3.270 8 -0.014 8 hpL 2 10-4 0.5 [3, 10] 96 26 4 3.784 4 -0.014 8 hpL 2 10-5 0.25 [3, 10] 126 23 3 2.997 0 -0.014 8 hp 2 10-4 [3, 10] 82 23 4 3.059 3 -0.014 8 hp 2 10-5 [3, 10] 155 40 7 10.297 3 -0.014 8 ph 2 10-4 [3, 10] 79 20 4 6.972 8 -0.014 8 ph 2 10-4 [3, 6] 81 22 4 5.901 6 -0.014 8 ph 2 10-5 [3, 6] 152 34 5 5.333 2 -0.014 8 hpL 3 10-4 0.25 [3, 10] 65 20 4 11.745 5 0.467 8×10-4 hpL 3 10-4 0.5 [3, 10] 65 20 4 12.306 4 0.4678×10-4 hpL 3 10-5 0.25 [3, 10] 91 21 6 15.380 1 0.467 2×10-4 hp 3 10-4 [3, 10] 70 22 4 34.250 6 0.467 2×10-4 hp 3 10-5 [3, 10] 86 26 8 19.334 9 0.467 2×10-4 ph 3 10-4 [3, 10] 66 20 3 83.696 5 0.467 8×10-4 ph 3 10-4 [3, 6] 69 22 4 21.790 3 0.467 8×10-4 ph 3 10-5 [3, 6] 89 26 5 17.796 7 0.467 2×10-4 -
[1] 雍恩米, 陈磊, 唐国金.高超声速无动力远程滑翔飞行器多约束条件下的轨迹快速生成[J].宇航学报, 2008, 29(2):397-406. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2008.02.002YONG E M, CHEN L, TANG G J.A survey of numerical methods for trajectory optimization of spacecraft[J].Journal of Astronautics, 2008, 29(2):397-406(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2008.02.002 [2] GILL P E, MURRAY W, SAUNDERS M A.SNOPT:An SQP algorithm for large-scale constrained optimization[J].SIAM review, 2005, 47(1):99-131. doi: 10.1137/S0036144504446096 [3] WÄCHTER A, BIEGLER L T.On the implementation of an interior-point filter line-search algorithmfor large-scale nonlinear programming[J].Mathematical Programming, 2006, 106(1):25-57. doi: 10.1007/s10107-004-0559-y [4] BYRD R H, NOCEDAL J, WALTZ R A, et al.Knitro:An integrated package for nonlinear optimization[J].Large-Scale Nonlinear Optimization, 2006, 83:35-59. [5] PONTRYAGIN L S.Mathematical theory of optimal processes[M].New York:Routledge, 2018. [6] BETTS J T.Practical methods for optimal control and estimation using nonlinear programming[M].Philadelphia:SIAM, 2010. [7] BENSON D A, HUNTINGTON G T, THORVALDSEN T P, et al.Direct trajectory optimization and costate estimation via an orthogonal collocation method[J].Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2006, 29(6):1435-1440. doi: 10.2514/1.20478 [8] DARBY C L, GARG D, RAO A V.Costate estimation using multiple-interval pseudospectral methods[J].Journal of Spacecraft Rockets, 2011, 48(5):856-866. doi: 10.2514/1.A32040 [9] GARG D, PATTERSON M, HAGER W W, et al.A unified framework for the numerical solution of optimal control problems using pseudospectral methods[J].Automatica, 2010, 46(11):1843-1851. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2010.06.048 [10] PATTERSON M A, RAO A V.Exploiting sparsity in direct collocation pseudospectral methods for solving optimal control problems[J].Journal of Spacecraft Rockets, 2012, 49(2):364-377. [11] CANUTO C, HUSSAINI M Y, QUARTERONI A, et al.Spectral methods in fluid dynamics[M].New York:Springer Science & Business Media, 2012. [12] DARBY C L, HAGER W W, RAO A V.An hp-adaptive pseudospectral method for solving optimal control problems[J].Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 2011, 32(4):476-502. doi: 10.1002/oca.957 [13] PATTERSON M A, HAGER W W, RAO A V.A ph mesh refinement method for optimal control[J].Optimal Control Applications and Methods, 2015, 36(4):398-421. doi: 10.1002/oca.2114 [14] LIU F J, HAGER W W, RAO A V.Adaptive mesh refinement for optimal control using nonsmoothness detection and mesh size reduction[J].Journal of the Franklin Institude, 2015, 352(10):4081-4106. doi: 10.1016/j.jfranklin.2015.05.028 [15] PHILLIPS T H.A common aero vehicle (CAV) model, description, and employment guide[R].[S.L.]: Schafer Corporation for AFRL and AFSPC, 2003. [16] SHEN J, TANG T, WANG L L.Spectral methods:algorithms, analysis and applications[M].New York:Springer Science & Business Media, 2011:55-85. [17] WANG H, XIANG S.On the convergence rates of legendre approximation[J].Mathematicas of Computation, 2012, 81(278):861-877. -







 下载:
下载: