A technology for generation of space object optical image based on 3D point cloud model
-
摘要:
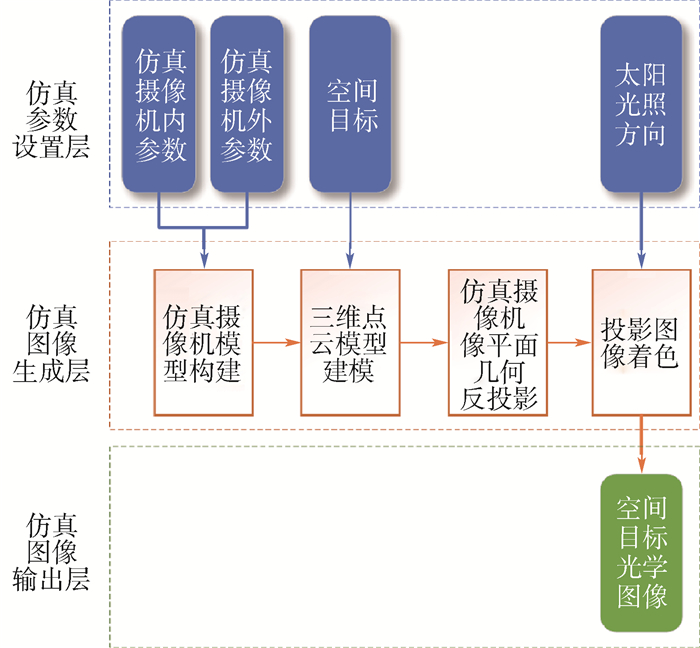
空间探测任务中大量先验图像数据的缺乏,使得基于光学图像的态势感知和导航算法无法被有效定量测试和评估。针对此问题,提出了一种基于三维点云模型和射影变换基本理论的空间目标光学图像生成方法。在完成对空间目标三维点云模型和仿真摄像机模型构建基础之上,利用射影变换基本理论依次计算像平面所有像素点与空间目标三维点云模型空间点的对应关系,并基于Lambertian漫反射模型和相对应空间目标三维点云模型空间点的光照方向,得到所有像素点的灰度值,从而生成给定空间目标的光学图像。大量仿真实验表明:与传统的基于解析模型的仿真图像生成方法相比,所提的空间目标光学图像生成技术能够以更快的速度生成更加真实的仿真图像,且生成的仿真图像可以广泛应用于椭圆拟合、陨石坑检测、着陆器视觉导航、航天器交会对接、空间目标跟踪等典型空间应用算法的定性与定量评估。
Abstract:The lack of the prior image data in the space exploration tasks makes it difficult to quantitatively test and evaluate the situation awareness and navigation algorithms based on the optical images. Accordingly, in this paper, we present an algorithm for generating the synthetic space object optical image based on the 3D point cloud model and the basic theory of the projective transformation. First, the 3D point cloud model of the space object and the optical camera model were constructed. Then, the corresponding pairs between all the pixels in the image plane and the space points of the 3D point cloud model were obtained via the basic theory of projective transformation, and subsequently the intensity of each pixel in the image plane was calculated by the lighting direction of its corresponding space point and the Lambertian reflection model, and finally the simulated image was generated. A great deal of simulation experiments demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can produce the more vivid simulated images rapidly than the traditional analytical image generation algorithm, and the generated images can be applied to testing and evaluating the typical space application algorithms qualitatively and quantitatively, such as ellipse fitting, crater detection, optical navigation landing on the planet, automated rendezvous and docking of spacecraft, 3D tracking of spacecraft, and so on.
-
Key words:
- space object /
- simulated image /
- point cloud model /
- projective transformation /
- artificial intelligence
-
表 1 着陆器视觉导航算法验证实验精度
Table 1. Experimental accuracy of lander visual navigation algorithm verification
导航误差 Rheasilvia小行星 月球近地表面 位置误差/m 0.01 0.012 0.02 0.019 0.015 0.009 姿态误差/rad 0.01 0.014 0.03 0.009 0.013 0.021 表 2 航天器交会对接算法验证实验精度
Table 2. Experimental accuracy of spacecraft rendezvous and docking algorithm verification
位姿误差 Triana卫星 Aurora卫星 位置误差/m 0.02 0.019 0.017 0.021 0.009 0.018 姿态误差/rad 0.03 0.008 0.09 0.022 0.016 0.013 表 3 不同分类器在陨石坑图像数据集和飞行器图像数据集上的分类结果
Table 3. Classification results of different classifiers on crater dataset and spacecraft dataset
图像数据集 分类器类型 P R F1 陨石坑 CNN 0.91 0.90 0.91 AdaBoost 0.85 0.82 0.83 飞行器 CNN 0.93 0.91 0.92 AdaBoost 0.87 0.83 0.85 -
[1] XIANG Y, SCHMIDT T, NARAYANAN V, et al.PoseCNN: A convolutional neural network for 6D object pose estimation in cluttered scenes[EB/OL].(2017-11-01)[2019-04-01].http://export.arxiv.org/abs/1711.00199. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320796892_PoseCNN_A_Convolutional_Neural_Network_for_6D_Object_Pose_Estimation_in_Cluttered_Scenes [2] LIU C, HU W.Real-time geometric fitting and pose estimation for surface of revolution[J].Pattern Recognition, 2019, 85:90-108. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2018.08.002 [3] CRIVELLARO A, RAD M, VERDIE Y, et al.Robust 3D object tracking from monocular images using stable parts[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(6):1465-1479. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2708711 [4] YU M, CUI H, TIAN Y.A new approach based on crater detection and matching for visual navigation in planetary landing[J].Advances in Space Research, 2014, 53(12):1810-1821. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2013.04.011 [5] ZHANG H, JIANG Z, ELGAMMAL A.Satellite recognition and pose estimation using homeomorphic manifold analysis[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2015, 51(1):785-792. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.130744 [6] ESA.Pinpoint vision-based landings on moon, mars and asteroids[EB/OL].(2013-05-29)[2019-04-01].http://www.esa.int/Our_Activities/Space_Engineering_Technology/Pinpoint_vision-based_landings_on_Moon_Mars_and_asteroids. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/317345295_A_new_experimental_facility_for_testing_of_vision-based_GNC_algorithms_for_planetary_landing [7] GSA.TRON-Testbed for robotic optical navigation[EB/OL].(2017-03-29)[2019-04-01].http://www.ngcaerospace.com/space-systems/test-validation-services. [8] NGC.High-fidelity hardware-in-the-loop emulators[EB/OL].(2017-03-29)[2019-04-01].http://www.ngcaerospace.com/space-systems/test-validation-services/. [9] PARKES S M, MARTIN I.Virtual lunar landscapes for testing vision-guided lunar landers[C]//IEEE International Conference on Information Visualization.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1999: 122-127. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/3811947_Virtual_Lunar_Landscapes_for_Testing_Vision-Guided_Lunar_Landers [10] STAR-Dundee.PANGU-Planet and asteroid natural scene generation utility[EB/OL].(2017-02-08)[2019-04-01].https://www.star-dundee.com/products/pangu-planet-and-asteroid-natural-scene-generation-utility. [11] LU T, HU W, JIANG Z.An effective algorithm for generation of crater gray image[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Virtual Environments for Measurement Systems and Applications.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-6. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/290194684_An_effective_algorithm_for_generation_of_crater_gray_image [12] SU Q, ZHAO Y, WU F, et al.Simulation of high resolution lunar's Sinus Iridum terrain[C]//IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 2589-2592. [13] LI J S, LIU W M, LAN C Z, et al.Fast algorithm for lunar craters simulation[M].Berlin:Springer, 2011. [14] 张玥, 李清毅, 许晓霞.月球表面地形数学建模方法[J].航天器环境工程, 2007, 24(6):341-343. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2007.06.002ZHANG Y, LI Q Y, XU X X.Mathematical modeling of lunar surface terrain[J].Spacecraft Environment Engineering, 2007, 24(6):341-343(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1379.2007.06.002 [15] 陈宝林.最优化理论与算法[M].2版.北京:清华大学出版社, 2005:10-23.CHEN B L.Theory and algorithms of optimization[M].2rd ed.Beijing:Tsinghua University Press, 2005:10-23(in Chinese). [16] 吴福朝.计算机视觉中的数学方法[M].北京:科学出版社, 2008:255-266.WU F C.Mathematics in computer vision[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2008:255-266(in Chinese). [17] AKENINE-MOLLER T, HAINES E.实时计算机图形学[M].2版.普建涛, 译.北京: 北京大学出版社, 2004: 40-50.AKENINE-MOLLER T, HAINES E.Real time graphics[M].2nd ed.PU J T, translated.Beijing: Peking University Press, 2004: 40-50(in Chinese). [18] NASA.Vesta[EB/OL].(2017-04-28)[2019-04-01].https://nasa3d.arc.nasa.gov/detail/vesta. [19] NASA.Eros[EB/OL].(2017-04-28)[2019-04-01].https://nasa3d.arc.nasa.gov/detail/eros. [20] The Planetary Society.Mosaic of the asteroid Vesta from the Dawn spacecraft[EB/OL].(2017-04-28)[2019-04-01].http://www.planetary.org/multimedia/space-images/small-bodies/vesta_mosaic_0006121-6124.html/. [21] Wikipedia.433 Eros[EB/OL].(2017-04-28)[2019-04-01].https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/433_Eros. [22] LU T, HU W, LIU C, et al.Effective ellipse detector with polygonal curve and likelihood ratio test[J].IET Computer Vision, 2015, 9(6):914-925. doi: 10.1049/iet-cvi.2014.0347 [23] LU C, HU W.Effective method for ellipse extraction and integration for spacecraft images[J].Optical Engineering, 2013, 52(5):057002. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.52.5.057002 [24] LU T, HU W, LIU C, et al.Relative pose estimation of a lander using crater detection and matching[J].Optical Engineering, 2016, 55(2):023102. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.55.2.023102 [25] LIU C, HU W.Relative pose estimation for cylinder-shaped spacecrafts using single image[J].IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2014, 50(4):3036-3056. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2014.120757 [26] COHEN J P, LO H Z, LU T, et al.Crater detection via convolutional neural networks[EB/OL].(2016-01-05)[2019-04-01].https://arxiv.org/abs/1601.00978. [27] DING W, STEPINSKI T F, MU Y, et al.Sub-kilometer crater discovery with boosting and transfer learning[J].ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems and Technology, 2011, 2(4):39. http://sil.uc.edu/pdfFiles/tist11.pdf -







 下载:
下载: