-
摘要:
触摸屏上的触觉再现技术增加了人机交互的真实感和丰富性。在触觉再现中,掩蔽效应改变了触觉感知特性(绝对阈值和分辨阈值),影响了触觉渲染模型的准确性及触觉再现效果的真实性。基于机械振动、空气压膜与静电力三元融合的触觉再现装置,采用“三下一上”的实验方法,研究5种不同幅度的机械振动触觉反馈作为掩蔽刺激时,空气压膜触觉反馈感知特性的变化。与静电力触觉反馈作为目标刺激时感知特性的变化进行比较,得出如下结论:在绝对阈值方面,当机械振动驱动电压幅度由0 V增加到100 V时,空气压膜绝对阈值由34.30 V增加到46.41 V,增加了35.31%,增长幅度为静电力绝对阈值增长幅度的14.95%;在分辨阈值方面,当机械振动驱动电压幅度由0 V增加到100 V时,空气压膜分辨阈值在(15.21±0.67)V范围内浮动,变化趋势与静电力触觉反馈基本相同。
Abstract:Tactile reproduction technology on touch screens enhances the sense of reality and richness of users' interaction experience. In the process of tactile reproduction, masking effect changes tactile perception characteristics (both absolute threshold and differential threshold), and influences the accuracy of tactile rendering model and the reality of tactile reproduction effect. Based on tactile reproduction device with mechanical vibration, squeeze film effect and electrostatic force, through "three-down-one-up" experimental method, we studied tactile feedback perception characteristics of squeeze film effect when the tactile feedback of five kinds of mechanical vibrations with different amplitudes were taken as masking stimulus. We also compared the results with those targeted by electrostatic force. The conclusions are drawn as follow:In terms of absolute threshold, when the mechanical vibration stimulation intensity increases from 0 V to 100 V, the absolute threshold of squeeze film effect increases 35.31%, from 34.30 V to 46.41 V, and the increase is 14.95% of the electrostatic absolute threshold growth. In terms of the differential thresholds, when the mechanical vibration stimulation intensity increases from 0 V to 100 V, the differential thresholds of squeeze film effect float within the range of (15.21±0.67) V, similar as the changing trend of electrostatic force tactile feedback.
-
触摸屏上的触觉再现技术是人工智能与人机交互的前沿技术,可以广泛应用于辅助医疗、网络娱乐、教育教学、军事仿真等重要领域。通过平面触觉再现技术, 人们裸指触摸智能手机、平板电脑时能够感受到虚拟物体的形状、轮廓、纹理等物理属性,增强了交互过程的真实感和沉浸感。目前应用于触摸屏上的触觉再现方式主要有空气压膜式[1-4]、静电力式[5-6]、机械振动式[7-9]以及融合空气压膜与静电力式[10-11]、融合机械振动与静电力式[12]。
掩蔽效应存在于视觉[13]、听觉[14-15]和触觉[16-17]等不同的感觉模式中。在触觉再现中,掩蔽效应可以定义为当一种或者多种触觉反馈同时工作时,一种触觉反馈(掩蔽刺激)效果对另一种触觉反馈(目标刺激)效果的影响。掩蔽刺激影响触觉反馈感知特性(绝对阈值与分辨阈值)变化[18]。触觉反馈感知特性的变化会影响触觉再现渲染方法中驱动信号的选择方式和加载方式,进而影响触觉渲染模型建立的准确性和触觉再现效果的真实性。
在触觉再现中,关于掩蔽效应的研究可以分为两类。一类为掩蔽刺激和目标刺激为同一种触觉反馈方式时,掩蔽效应对触觉感知特性的影响。Craig[19]以机械振动为掩蔽刺激,以同频的机械振动为目标刺激,研究没有掩蔽刺激和存在3种不同幅度的掩蔽刺激情况下,机械振动分辨阈值的变化,提出了一种能够解释韦伯函数随着掩蔽强度的变化而增加并预测掩蔽阈值的模型。Vardar等[20]研究了静电力掩蔽刺激对触摸屏上显示的静电力触觉感知的影响,发现感知阈值随着掩蔽刺激水平的增加以线性函数形式增加;并探究了掩蔽刺激效应对边缘锐度感知的影响,探究得出锐度感知取决于背景和前景刺激之间的局部对比度,可以逐渐降低背景边缘附近的电振动幅度,使边缘感觉更加清晰,或者可以使用高频电振动信号作为边缘,低频信号作为背景来增强边缘的清晰度。
另一类关于掩蔽效应的研究为掩蔽刺激和目标刺激为不同种触觉反馈方式。目前这一方面研究仍处于起步阶段。Ryu等[21]研究了以机械振动作为掩蔽刺激,静电力作为目标刺激时,机械振动对静电力感知阈值的影响,其研究结果表明随着机械振动刺激强度的增加,静电力绝对阈值以斜坡函数形式增加,分辨阈值没有显著变化。静电力触觉再现方式通过指尖与加有电信号的电容屏之间产生静电吸引力改变手指与电容屏之间的摩擦,达到增大切向触觉反馈力的效果。空气压膜作为另外一种平面终端触觉反馈方式,其通过指尖与贴有压电陶瓷片的电容屏之间产生挤压气膜来改变电容屏表面的摩擦,达到减小切向触觉反馈力的效果。空气压膜和静电力触觉反馈均改变切向反馈力,但由于其工作原理及触觉反馈效果的差异,机械振动作为掩蔽刺激时对静电力感知阈值影响的结论可能并不适用于空气压膜。
本文基于融合机械振动、空气压膜与静电力的多媒体触觉再现装置,研究机械振动作为掩蔽刺激时对空气压膜绝对阈值和分辨阈值的影响。创新性研究工作概括如下:首先,采用“三下一上”的实验方法,研究了5种不同幅度的机械振动作为掩蔽刺激时,空气压膜感知阈值的变化。研究发现,随着机械振动驱动电压幅度的增加, 空气压膜绝对阈值由34.30 V增加到46.41 V,增加了35.31%,分辨阈值无明显变化。其次探究了机械振动掩蔽刺激对静电力和空气压膜感知阈值影响的差异性。随着机械振动驱动电压幅度的增加, 静电力绝对阈值由35.5 V增加到116.5 V,比空气压膜绝对阈值变化的更为显著,分辨阈值无明显变化。绝对阈值以及分辨阈值的变化会对触觉渲染方法建模参数产生影响,感知特性的研究对在融合装置上探究真实性更高的触觉渲染方法有参考价值。
1. 融合机械振动、空气压膜与静电力的触觉再现装置
1.1 再现原理
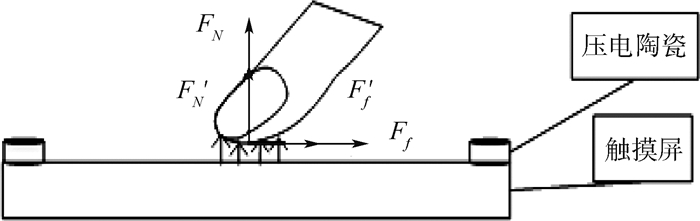
机械振动的原理如图 1所示,图中:Fn为单个机械振动源产生的法向力,振动源工作在低频,其产生的机械波在触摸屏表面传播,从而使手指受到相应的法向力F′n,调节驱动信号的大小,即可改变手指受到法向力的大小。
空气压膜的原理如图 2所示,不激励压电陶瓷时,手指所受到的屏幕的支持力为FN,受到的摩擦力为Ff;激励压电陶瓷时,压电陶瓷带动单点电容屏高频振动,在手指尖和单点电容屏之间形成了挤压气膜,导致手指受到的支持力F′N变小,所受到的摩擦力变小,达到了减小切向力的效果。调节驱动信号幅度的大小,即可改变手指受到切向力的大小。
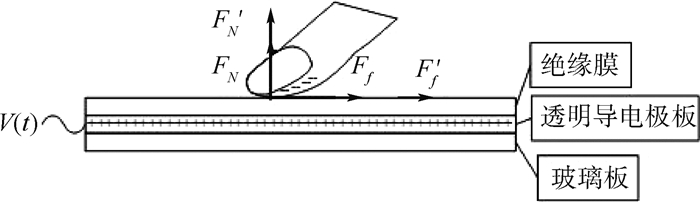
静电力的原理如图 3所示,单点电容屏通过产生静电力改变手指受到的切向力,主要起到增大摩擦力的作用。不施加驱动信号V(t)时手指所受到的屏幕的支持力为FN,受到的摩擦力为Ff;施加驱动信号V(t)时,指尖内的组织液和导电极板形成一个电容结构,当手指在屏幕上滑动时,手指受到一个静电吸引力Fe,导致屏幕对手指的支持力增大F′N=FN+Fe,手指所受的摩擦力也增大,达到了改变手指受到的切向力的效果;改变施加在导电极板上的驱动信号V(t),就会导致手指受到的吸引力发生变化,进而控制切向力的变化程度。
融合机械振动、空气压膜与静电力触觉再现装置将反馈力从一个维度扩展到两个维度,手指静止时可以通过振动源的振动来产生触觉感受,手指运动时,可以结合静电力与机械振动、空气压膜与机械振动来改变手指受到的切向力与法向力,突破了静电力只在运动过程中有反馈作用的限制,实现了切向力既可以增大又可以减小的双向调节。
1.2 再现装置整体结构
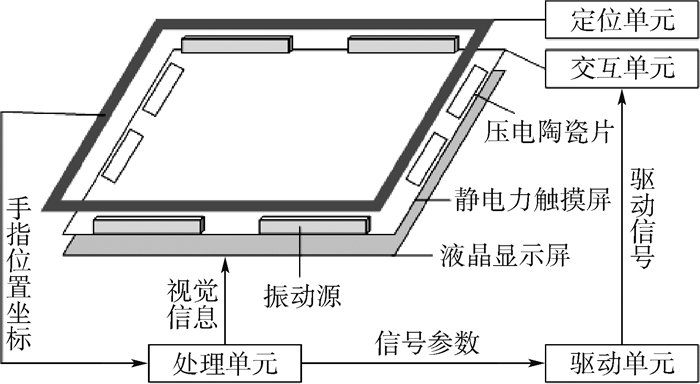
融合机械振动、空气压膜与静电力触觉再现装置主要结构包括定位单元、处理单元、驱动单元和交互单元4个部分,装置的结构示意图如图 4所示。定位单元采用红外定位,可以实时获取手指位置坐标,然后将获取的手指位置坐标发送给处理单元。处理单元,包括各种多媒体终端,用于输出视觉信息,同时对手指位置处的图像进行渲染得到触觉驱动信号参数,并将该参数发送到驱动单元。驱动单元,根据接收的驱动信号参数产生相应的静电力、空气压膜与机械振动3种触觉反馈的驱动信号,实现单点电容屏的触觉反馈功能与手指定位功能的分时复用。交互单元,包括静电力触摸屏、压电陶瓷片与振动源,接收驱动单元的驱动信号并呈现相应的触觉反馈,改变手指受到的切向力和法向力,从而实现三维的触觉再现感受。
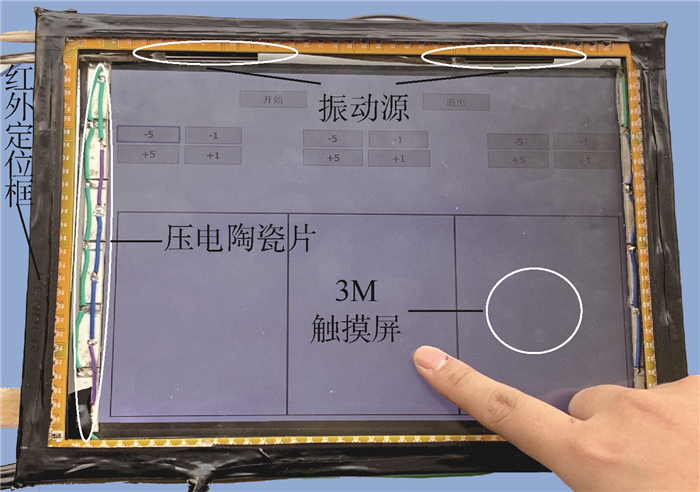
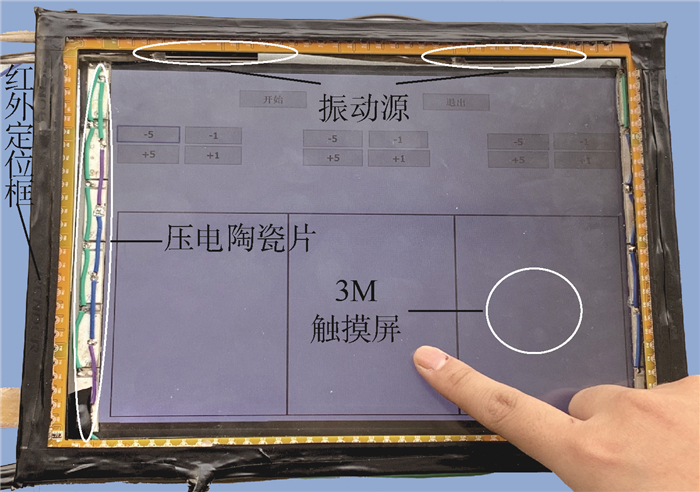
融合机械振动、空气压膜与静电力的触觉再现装置的实物图如图 5所示。
装置最底层是Microsoft Surface Pro 3,作为处理单元。粘贴在Surface上面的是3M触摸屏,3M触摸屏产生切向的静电力触觉反馈,起到增大摩擦的效果。粘贴在3M触摸屏短边两侧的是压电陶瓷片,压电陶瓷产生切向的空气压膜触觉反馈,起到减小摩擦的效果。粘贴在3M触摸屏长边两侧的是振动源,振动源产生法向的机械振动触觉反馈。粘贴在3M触摸屏一周的是红外定位框,红外定位框作为定位单元。
2. 机械振动对空气压膜感知阈值的影响
触觉感知阈值包括触觉感知的绝对阈值以及分辨阈值,绝对阈值是指刚能引起触觉感觉的最小刺激信号幅度,分辨阈值是指在刺激引起触觉感觉之后人体能感觉到刺激强度变化的最小幅度间隔。本节以机械振动为掩蔽刺激,空气压膜为目标刺激,研究5种不同幅度的机械振动掩蔽刺激下空气压膜感知阈值的变化。
2.1 机械振动对空气压膜绝对阈值的影响
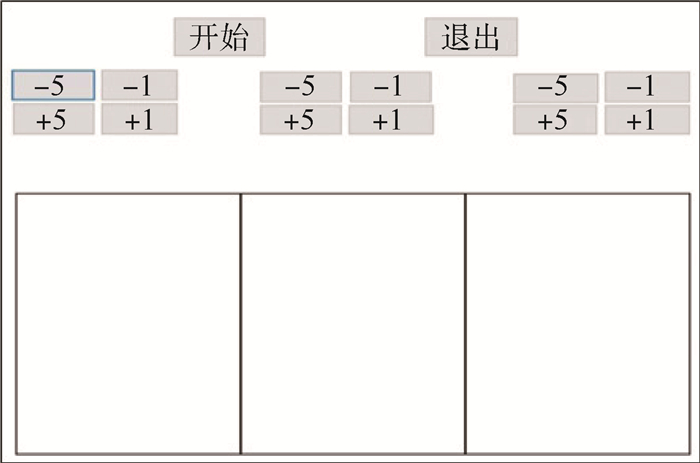
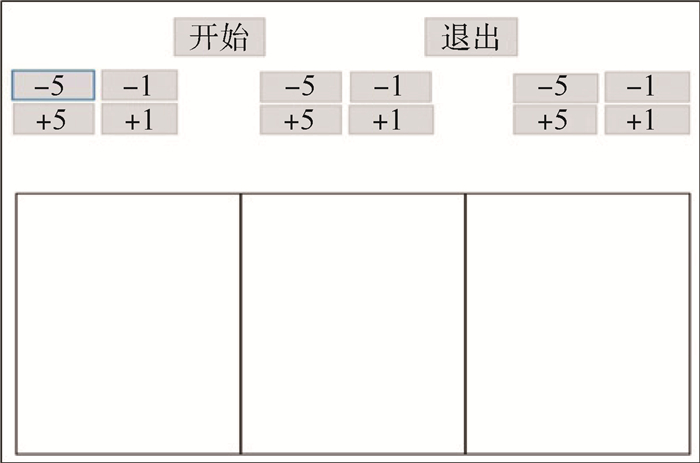
对于所有实验,使用相同的实验界面,如图 6所示。实验界面划分为3个区域,随机选择其中1个区域提供测试刺激(空气压膜和机械振动触觉反馈),另外2个区域提供参考刺激(机械振动触觉反馈)。
采用“三下一上”的方法,获取机械振动触觉反馈的绝对阈值为20.46 V,机械振动触觉反馈的分辨阈值为11.61 V。因此选取大于机械振动触觉反馈分辨阈值的驱动电压幅度20 V为间隔,在20、40、60、80、100 V 5种不同机械振动驱动电压幅度下探究机械振动触觉反馈对空气压膜和静电力感知阈值的影响。
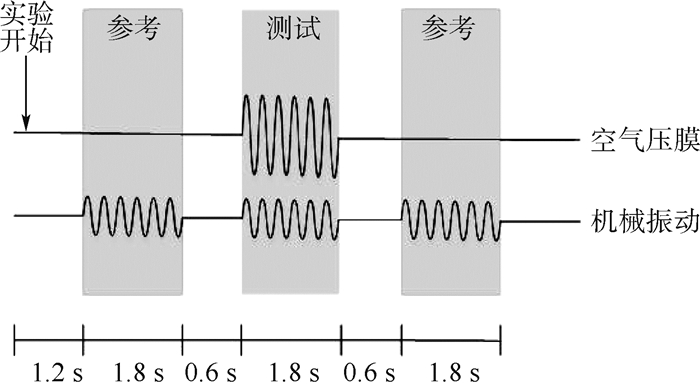
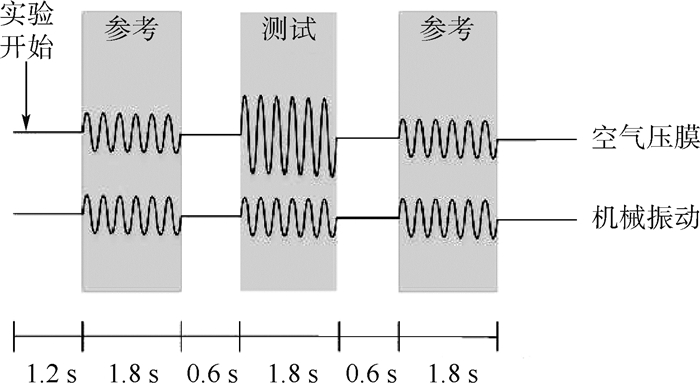
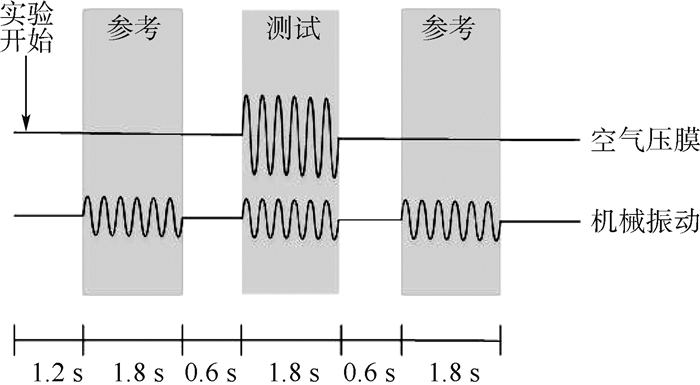
实验过程中实验者同时受到测试刺激和参考刺激,如图 7所示,空气压膜触觉反馈仅在测试刺激中提供,机械振动触觉反馈则在测试刺激和参考刺激中都提供。空气压膜刺激波形选用正弦波,测试频率为41 400 Hz,此频率为谐振频率;机械振动刺激测试频率选用220 Hz,此频率为实验者的敏感频率,波形选用正弦波,其振幅在0 ~100 V的范围内以20 V为间隔变化。每一种刺激都持续1.8 s,相邻刺激间隔0.6 s。
实验过程采用“三下一上”的实验方法,具体方法如下:实验过程中测试刺激信号电压值从空气压膜触觉反馈最大驱动电压值160 V开始,在3个区域中任选1个区域施加测试刺激(机械振动和空气压膜触觉反馈),其他2个区域施加参考刺激(机械振动触觉反馈)。实验者通过反复触摸3个区域对比触觉感受,作答哪个区域为测试刺激区域。若实验者作答的测试信号存在区域为刺激信号施加区域即为答对,当实验者连续给出3个正确的响应时,驱动信号电压以20 V的幅度逐次递减;直到参与者提交一个不正确的响应后,电压幅值停止减小,转变为从该电压开始以10 V的幅度逐次增加;当实验者连续给出3个正确的响应时,电压幅值停止增加,从该电压值处开始以4 V的幅度逐次递减。电压由下降转为上升或者由上升转为下降都称为是一次“反转”,实验过程中进行了10次反转,以获得尽可能准确的绝对阈值。
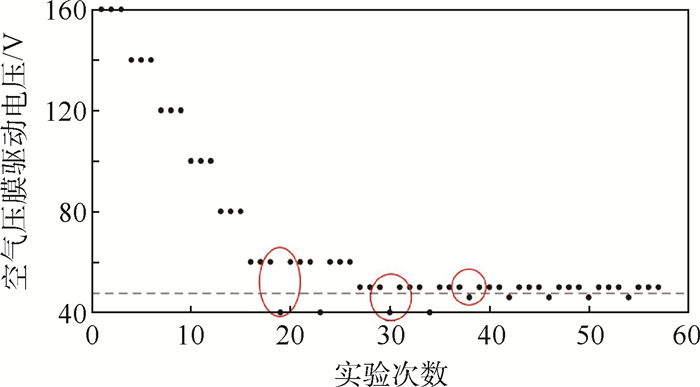
利用一个实验者的一组数据对“三下一上”实验过程进行说明,如图 8所示。空气压膜触觉反馈起始驱动电压为160 V,以20 V为间隔变化,该实验者在60 V和40 V之间经历3次反转后变成以10 V为间隔变化,该实验者在50 V和40 V之间经历3次反转后变成以4 V为间隔变化,实验者在50 V与46 V之间经历10次反转后确定绝对阈值为48 V。
实验过程中邀请12名实验者,平均年龄为26岁。所有的实验者都经过预实验训练,并且实验过程中均用右手操作。室内温度和湿度分别保持在23 ~ 28℃和35%~55%。为了减少外界环境对实验结果的影响,采用异丙醇清洁显示屏和受试者的手指。
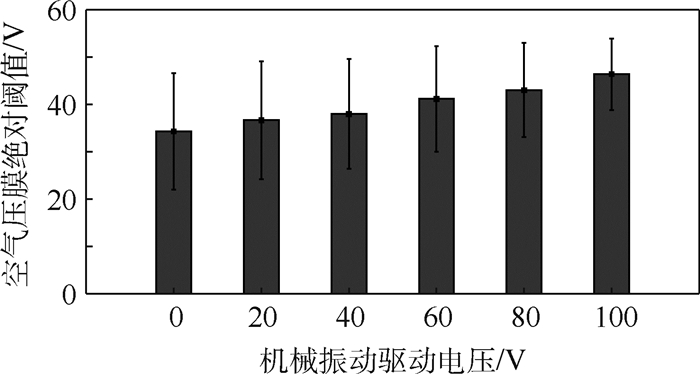
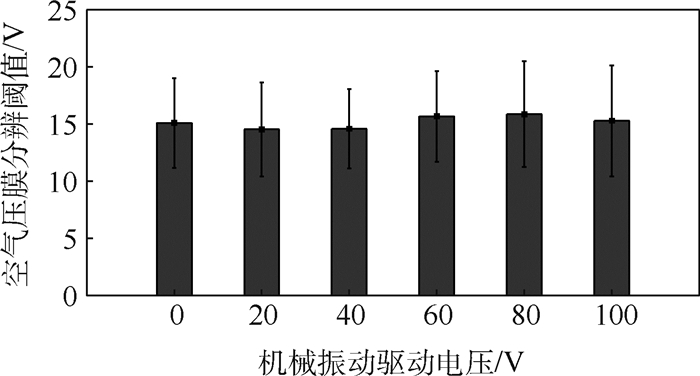
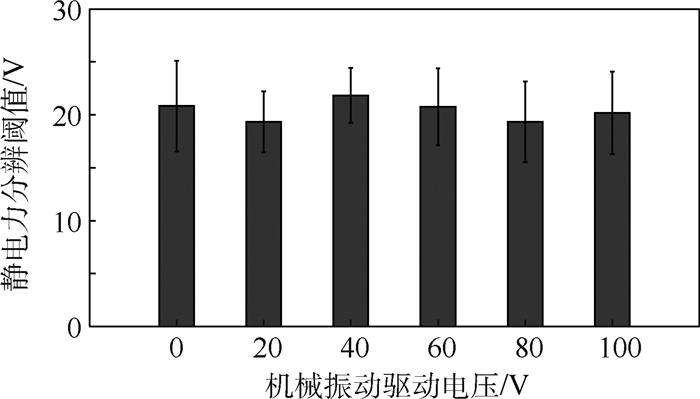
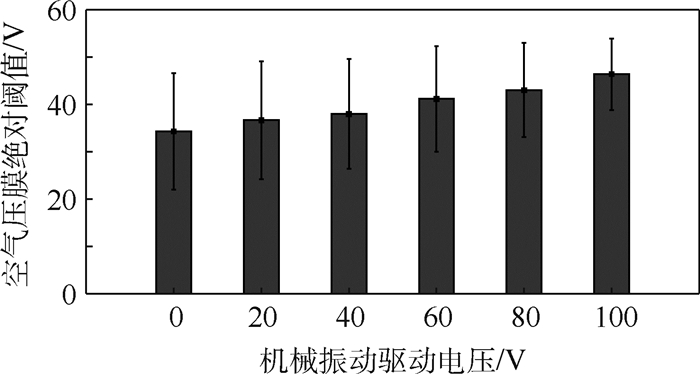
采用“三下一上”的方法,获取机械振动触觉反馈刺激下空气压膜的绝对阈值,如图 9所示。结果表明,在无机械振动刺激的情况下,空气压膜的绝对阈值是34.30 V,随着机械振动刺激驱动电压幅度的增加空气压膜的绝对阈值小幅度增加。当机械振动刺激的驱动电压幅度达到100 V时,空气压膜的绝对阈值增加到46.41 V,相对于没有机械振动作为掩蔽刺激时的绝对阈值增加了35.31%。
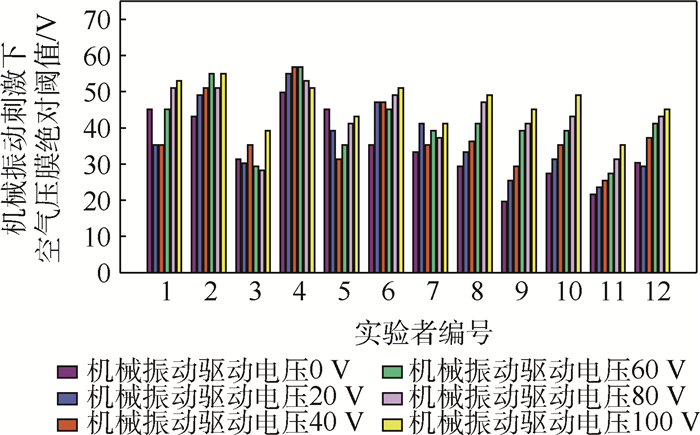
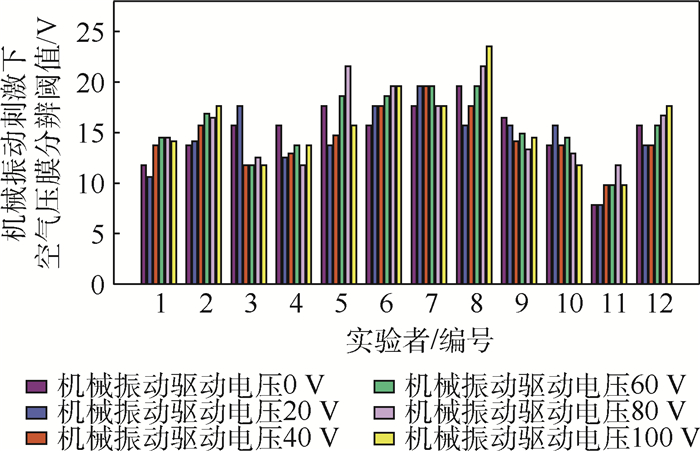
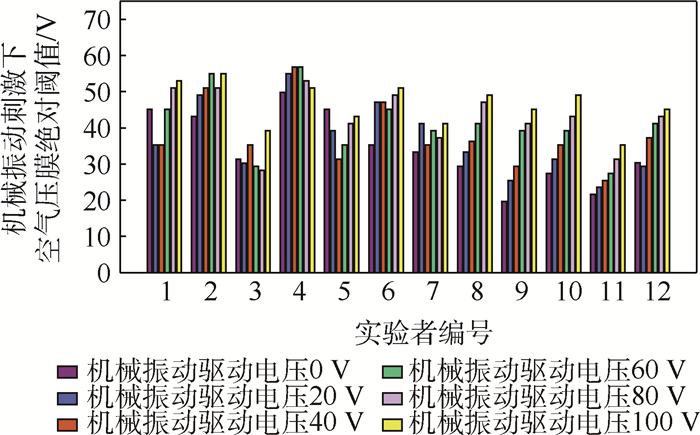
12名实验者在不同幅度机械振动刺激下空气压膜绝对阈值感知结果如图 10所示。从图中可以看出,第3名实验者的触觉感知能力最强,在不同幅度机械振动驱动电压刺激下都表现出较低的绝对阈值;第4名实验者的触觉感知能力较弱,在不同幅度机械振动驱动电压刺激下都表现出较高的绝对阈值;第1名和第5名实验者不同幅度机械振动驱动电压刺激下绝对感知阈值差异较大;第2名、第6名和第8~12名实验者均表现出随着机械振动驱动电压幅度增大绝对阈值逐渐增加的趋势。
2.2 机械振动对空气压膜分辨阈值的影响
实验环境及实验者同2.1节所述,在分辨阈值测量中,预先设计好参考刺激,参考刺激的电压值依赖于机械振动刺激下空气压膜触觉反馈绝对阈值的最大值。由绝对阈值实验结果得:空气压膜触觉反馈参考刺激电压值选为50 V。实验过程中实验者同时受到测试刺激和参考刺激。
如图 11所示,每一种刺激都持续1.8 s,相邻刺激间间隔0.6 s,与绝对阈值测量实验不同的是不仅在测试刺激中提供空气压膜触觉反馈,也在参考刺激中提供电压值恒定为50 V的空气压膜触觉反馈,该电压高于机械振动掩蔽刺激下空气压膜绝对阈值的最大值。空气压膜刺激波形选用正弦波,测试频率为41 400 Hz,此频率为谐振频率;机械振动刺激测试频率选用220 Hz,此频率为实验者的敏感频率,波形选用正弦波,机械振动驱动电压幅度在0 ~100 V的范围内以20 V为间隔变化。
实验采用“三下一上”的实验方法,具体方法如下:实验过程中测试刺激信号电压值从空气压膜触觉反馈最大电压值160V开始,在3个区域中任选1个区域施加测试刺激(机械振动和160 V的空气压膜触觉反馈),其他2个区域施加参考刺激(机械振动和恒定为50 V的空气压膜触觉反馈)。实验者通过反复触摸3个区域对比哪个区域的空气压膜触觉反馈更强一些,作答哪个区域为测试刺激区域。若实验者作答的测试信号存在区域为实际测试刺激信号施加区域即为答对,当实验者连续给出3个正确的响应时,驱动信号电压以20 V的幅度逐次递减;直到参与者提交一个不正确的响应后,电压幅值停止减小,转变为从该电压开始以10 V的幅度逐次增加;当实验者连续给出3个正确的响应时,电压幅值停止增加,从该电压值处开始以4 V的幅度逐次递减。电压由下降转为上升或者由上升转为下降都称为是一次“反转”,实验过程中进行了10次反转,对10次反转电压数据求平均,再减去空气压膜参考刺激50 V即获得尽可能准确的分辨阈值。
采用“三下一上”的实验方法,获取机械振动掩蔽刺激下空气压膜的分辨阈值,如图 12所示。结果表明,无机械振动刺激时空气压膜的分辨阈值是15.10 V,随着机械振动刺激驱动电压幅度的增大,空气压膜分辨阈值在(15.21±0.67) V范围内浮动,总体趋势无明显变化。
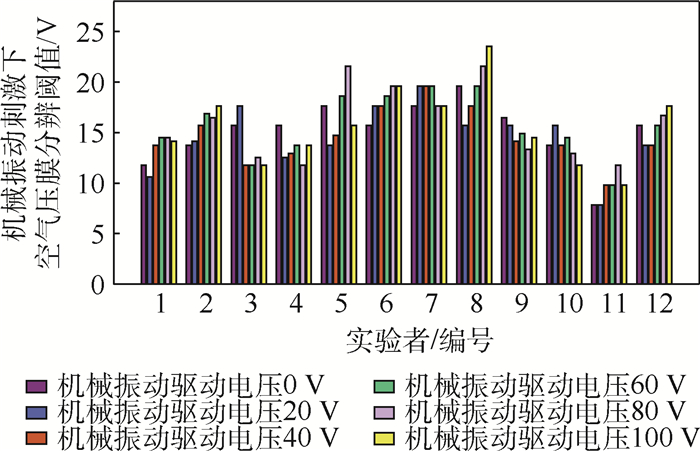
12名实验者在不同幅度机械振动刺激下空气压膜分辨阈值感知结果如图 13所示。从图中可以看出,第11名实验者对空气压膜触觉反馈的感知能力较强,表现出较低的分辨阈值水平。第6~8名实验者对空气压膜触觉反馈的感知能力较弱,表现出较高的分辨阈值水平。第3名实验者在40、60、80、100 V机械振动驱动电压刺激下空气压膜分辨阈值变化不明显,第7名实验者在不同机械振动驱动电压刺激下只表现出2种相近水平的分辨阈值,其他实验者均在不同幅度机械振动驱动电压刺激下表现出一定差异性空气压膜分辨阈值。
3. 机械振动对不同目标刺激感知阈值的影响
空气压膜触觉反馈与静电力触觉反馈同为触摸屏上重要的切向触觉反馈方式。静电力触觉再现方式敏感频率为120 Hz,其通过指尖与加有电信号的电容屏之间产生静电吸引力改变手指与电容屏之间的摩擦,达到增大切向触觉反馈力的效果。空气压膜触觉反馈方式,谐振频率为41 400 Hz,其通过指尖与贴有压电陶瓷片的电容屏之间产生挤压气膜改变电容屏表面的摩擦,达到减小切向触觉反馈的效果。由于其工作原理及频率的差异,机械振动作为掩蔽刺激对空气压膜和静电力感知阈值的影响可能存在差异性,下面将探究这种差异性,并对差异性原理进行分析。
3.1 机械振动对静电力感知阈值的影响
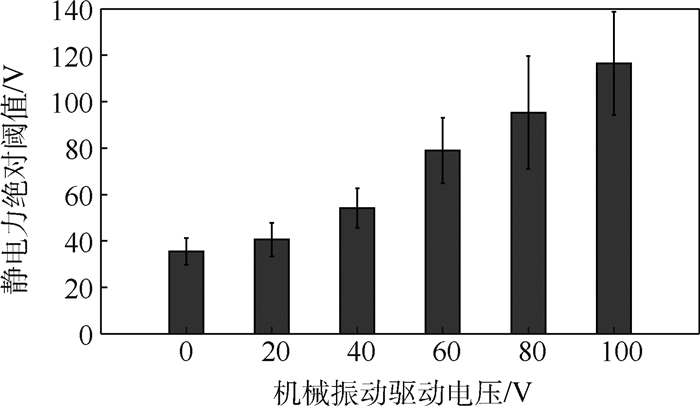
实验设计与步骤与2.1节相似,采用“三下一上”的实验方法,测量机械振动掩蔽刺激对静电力绝对阈值与分辨阈值的影响。在绝对阈值测量中,将静电力触觉反馈的初始电压幅值设为最大幅度400 V。除测试刺激用静电力代替空气压膜之外,其他条件与实验2.1节相同。采用“三下一上”的实验方法,获取不同幅度机械振动刺激时静电力的绝对阈值,如图 14所示。结果表明无机械振动刺激时静电力绝对阈值为35.50 V,随着机械振动刺激驱动电压幅度的增加静电力绝对阈值趋于斜坡式增加,当机械振动驱动电压幅度增加到100 V时,对应静电力的绝对阈值增加到116.5 V,是无机械振动作为掩蔽刺激时静电力绝对阈值的3.28倍。
采用与2.2节相同的实验方法,研究了机械振动掩蔽刺激对静电力分辨阈值的影响。分辨阈值测量中,预先设计好参考刺激,参考刺激的电压值依赖于机械振动刺激下静电力触觉反馈绝对阈值的最大值。由绝对阈值实验结果得静电力触觉反馈参考刺激电压值为120 V。采用“三下一上”的实验方法,获取不同幅度机械振动刺激下静电力的分辨阈值,如图 15所示。结果表明,没有机械振动刺激时静电力的分辨阈值是20.83 V,在不同幅度机械振动刺激下静电力分辨阈值在(20.58±1.25) V范围内浮动。随着机械振动刺激电压幅度的增加静电力分辨阈值基本趋于稳定。验证了Ryu等[21]关于静电力触觉反馈的实验结果,绝对阈值与分辨阈值的变化趋势与文献[21]中一致。
3.2 机械振动对空气压膜及静电力感知阈值影响的对比
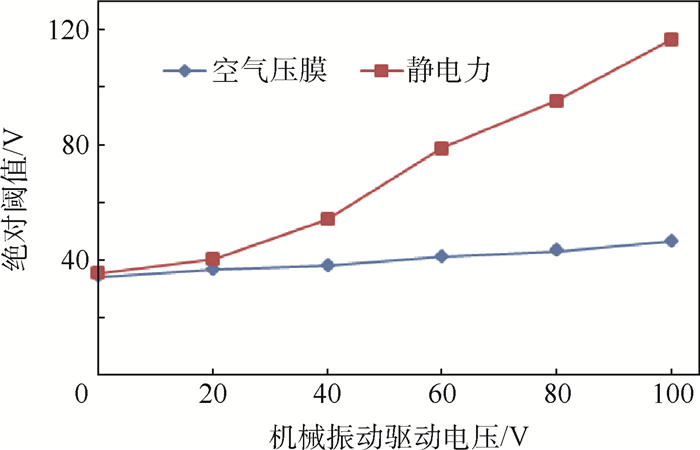
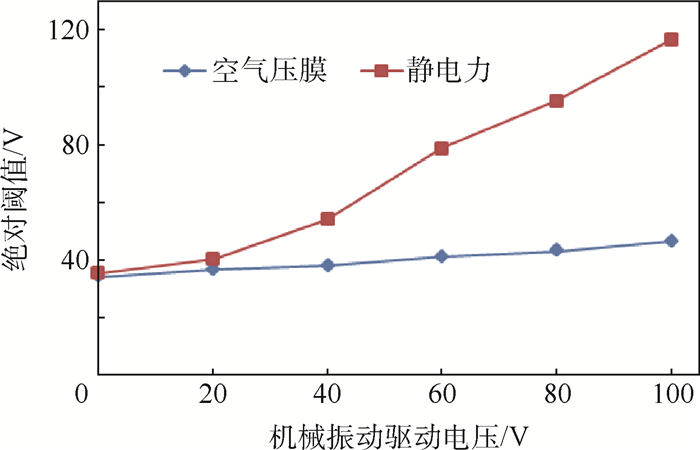
本文研究了机械振动对空气压膜及静电力触觉反馈绝对阈值的影响,如图 16所示。在无机械振动刺激的情况下,空气压膜和静电力触觉反馈绝对阈值分别是34.30 V和35.50 V,随着机械振动驱动电压幅度的增加空气压膜绝对阈值小幅度增加,当机械振动驱动电压幅度增加到100 V时,空气压膜的绝对阈值增加到46.41 V,相对于没有机械振动作为掩蔽刺激时的绝对阈值增加了35.31%。对于静电力触觉反馈,其绝对阈值随着机械振动驱动电压幅度的增加趋于斜坡式增加,当机械振动驱动电压幅度增加到100 V时,对应静电力触觉反馈的绝对阈值增加到116.5 V,是无机械振动作为掩蔽刺激时静电力绝对阈值的3.28倍。
采用两因素重复测量方差分析法,判断不同目标刺激(空气压膜和静电力)随着掩蔽刺激(机械振动)电压变化对实验者绝对阈值的影响。方差分析的数据为不同触觉反馈模式下绝对阈值的变化值,即每种情况下相对于没有掩蔽刺激(机械振动驱动电压幅度为0 V)的差值。经过Mauchiy’s球形检验,对于交互项目标刺激类型×掩蔽刺激电压,因变量不满足球形假设(P < 0.05),使用Greenhouse-Geisser方法校正。目标刺激类型和掩蔽刺激电压的交互作用对绝对阈值的影响具有统计学意义,F(1.668,18.347)=19.582,P < 0.001。因此,对2个受试者内因素目标刺激类型和掩蔽刺激电压进行单独效应的检验。在掩蔽刺激电压为20、40、60、80、100 V时,空气压膜作为目标刺激与静电力作为目标刺激的绝对阈值均具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。在空气压膜触觉反馈作为目标刺激中,对于受试者内因素掩蔽刺激电压,因变量不符合球形假设(P < 0.05),使用Greenhouse-Geisser方法校正。掩蔽刺激电压对绝对阈值变化的单独效应具有统计学意义,F(1.910, 21.013)=11.422,P < 0.05。在静电力触觉反馈作为目标刺激中,对于受试者内因素掩蔽刺激电压,因变量不符合球形假设(P < 0.05),使用Greenhouse-Geisser方法校正。掩蔽刺激电压对绝对阈值变化的单独效应具有统计学意义,F(1.532, 16.852)=23.489,P < 0.001。
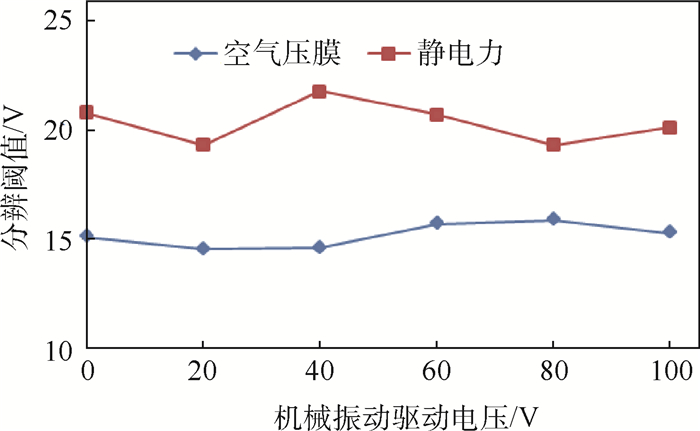
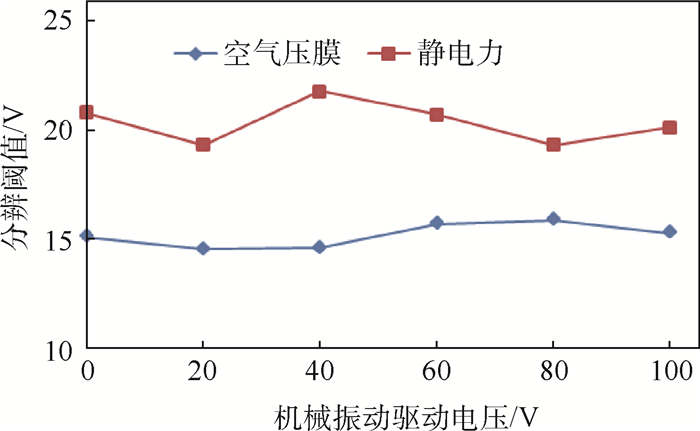
本文研究了机械振动对空气压膜及静电力触觉反馈分辨阈值的影响,如图 17所示。对于空气压膜触觉反馈,无机械振动刺激时其分辨阈值是15.10 V,随着机械振动驱动电压幅度的增大,空气压膜分辨阈值在(15.21±0.67) V范围内浮动,总体趋势无明显变化。对于静电力触觉反馈,不同幅度机械振动驱动电压下静电力分辨阈值在(20.58±1.25) V范围内浮动,相比空气压膜的分辨阈值变化范围稍大一些。
采用两因素重复测量方差分析法,判断不同掩蔽刺激电压下目标刺激(空气压膜和静电力)对实验者分辨阈值的影响。目标刺激类型和掩蔽刺激电压的交互作用对分辨阈值的影响没有统计学意义,F(2.773,30.508)=1.829,P>0.05。因此需解读2个受试者内因素(目标刺激类型和掩蔽刺激电压)的主效应。目标刺激类型对分辨阈值的主效应不具有统计学意义,F(1,11)=0.196,P>0.05。掩蔽刺激电压对分辨阈值的主效应不具有统计学意义,F(2.511,27.623)=0.732,P>0.05。
空气压膜触觉反馈和静电力触觉反馈都是触摸屏上重要的切向触觉反馈方式,同为机械振动作为掩蔽刺激时其感知阈值的变化却不相同,分析其原因,认为工作频率引起了感知特性的差异。在研究过程中所使用的触觉反馈工作频率分别为:机械振动敏感频率220 Hz, 空气压膜谐振频率41 400 Hz,静电力敏感频率120 Hz。从数据分析结果可以看出,机械振动掩蔽刺激对低频目标刺激感知特性的影响比对高频目标刺激感知特性的影响更大些。
4. 结论
1) 研究不同幅度机械振动作为掩蔽刺激对空气压膜绝对阈值的影响。结果表明,随着机械振动驱动电压幅度的增加空气压膜绝对阈值由34.30 V增加到46.41 V,增加了35.31%。
2) 研究不同幅度机械振动作为掩蔽刺激对空气压膜分辨阈值的影响。结果表明,随着机械振动驱动电压幅度的增加空气压膜分辨阈值在(15.21±0.67) V范围内浮动,总体趋势无明显变化。
3) 研究机械振动对静电力感知阈值的影响,随着机械振动驱动电压幅度的增加静电力绝对阈值由35.50 V增加到116.5 V,扩大为原来的3.28倍,比空气压膜绝对阈值变化显著。静电力分辨阈值在(20.58±1.25) V范围内浮动,与空气压膜分辨阈值变化趋势基本相同。
4) 对比机械振动对空气压膜及静电力触觉感知特性影响的差异性,发现掩蔽刺激对低频目标刺激感知特性的影响比高频目标刺激更明显。
5) 掩蔽效应会对目标刺激的绝对阈值以及分辨阈值产生相应影响。在采用联合机械振动与空气压膜、联合机械振动与静电力的触觉渲染方法时,要考虑由掩蔽效应带来的绝对阈值与分辨阈值变化,重新考量驱动信号的起始电压和分布间隔,建立联合渲染方法下的触觉反馈心理物理模型及渲染算法映射关系。本文对在融合装置上探究真实性更高的触觉渲染方法具有重要的参考意义。
-
-
[1] KALANTARI F, GRISONI L, REKIK Y, et al.Finding the minimum perceivable size of a tactile element on an ultrasonic based haptic tablet[C]//ACM International Conference on Interactive Surfaces and Spaces.New York: ACM, 2016: 379-384. [2] WINFIELD L, GLASSMIRE J, COLGATE J E, et al.T-pad: Tactile pattern display through variable friction reduction[C]//Symposium on Haptic Interfaces for Virtual Environment and Teleoperator Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 421-426. [3] MARCHUK N D, COLGATE J E, PESHKIN M A.Friction measurements on a large area TPaD[C]//2010 IEEE Haptics Symposium.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2010: 317-320. [4] CASSET F, DANEL J S, CHAPPAZ C, et al.Low voltage actuated plate for haptic applications with PZT thin-film[C]//The 17th International Conference on Solid-State Sensors, Actuators and Microsystems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 2733-2736. [5] BAU O, POUPYREV I, ISRAR A, et al.TeslaTouch: Electrovibration for touch surfaces[C]//Proceedings of the 23nd Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology.New York: ACM, 2010: 283-292. [6] KIM S C, ISRAR A, POUPYREV I.Tactile rendering of 3D features on touch surfaces[C]//Proceedings of the 26th Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology.New York: ACM, 2013: 531-538. [7] YATANI K, TRUONG K N.SemFeel: A user interface with semantic tactile feedback for mobile touch-screen devices[C]//Proceedings of the 22nd Annual ACM Symposium on User Interface Software and Technology.New York: ACM, 2009: 111-120. [8] YANG G H, JIN M, JIN Y, et al.T-mobile: Vibrotactile display pad with spatial and directional information for hand-held device[C]//2010 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2010: 5245-5250. [9] KIM S Y, KIM J C.Vibrotactile rendering for a traveling vibrotactile wave based on a haptic processor[J].IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2012, 5(1):14-20. doi: 10.1109/TOH.2011.72 [10] VEZZOLI E, MESSAOUD W B, AMBERG M, et al.Physical and perceptual independence of ultrasonic vibration and electrovibration for friction modulation[J].IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2015, 8(2):235-239. doi: 10.1109/TOH.2015.2430353 [11] SMITH T A, GORLEWICZ J L.HUE: A hybrid ultrasonic and electrostatic variable friction touchscreen[C]//World Haptics Conference.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 635-640. [12] ITO K, OKAMOTO S, ELFEKEY H, et al.A texture display using vibrotactile and electrostatic friction stimuli surpasses one based on either type of stimulus[C]//IEEE International Conference on Systems, Man and Cybernetics.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 2343-2348. [13] LEGGE G E, FOLEY J M.Contrast masking in human vision[J].Journal of the Optical Society of America, 1980, 70(12):1458-1471. doi: 10.1364/JOSA.70.001458 [14] HELLMAN R P.Loudness function of a 1000-cps tone in the presence of a masking noise[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1964, 36(9):1618-1627. doi: 10.1121/1.1919255 [15] CARHART R, TILLMAN T W, GREETIS E S.Perceptual masking in multiple sound backgrounds[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1969, 45(3):694-703. doi: 10.1121/1.1911445 [16] HAMER R D, VERRILLO R T, ZWISLOCKI J J.Vibrotacile masking of Pacinian and non Pacinian channels[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 1998, 73(4):1293-1303. [17] CRAIG J C.Difference threshold for intensity of tactile stimuli[J].Perception & Psychophysics, 1972, 11(2):150-152. [18] IDE M.Tactile stimulation can suppress visual perception[J].Scientific Reports, 2013, 3(12):3453-3460. [19] CRAIG J C.Vibrotactile difference thresholds for intensity and the effect of a masking stimulus[J].Attention Perception & Psychophysics, 1974, 15(1):123-127. [20] VARDAR Y, GÜÇLÜ B, BASDOGAN C.Tactile masking by electrovibration[J].IEEE Transactions on Haptics, 2018, 11(4):623-635. doi: 10.1109/TOH.2018.2855124 [21] RYU S, PYO D, LIM S C, et al.Mechanical vibration influences the perception of electrovibration[J].Scientific Reports, 2018, 8(1):4555-4564. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-22865-x 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 李晓峰,焦云雷,郭晨亮,孟庆昕,许江涛,盆洪民. 微型展开铰链的蜗卷弹簧盲区装配操作方法. 航天制造技术. 2021(02): 57-59+66 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(5)
-








 下载:
下载:

















 下载:
下载:







 百度学术
百度学术