-
摘要:
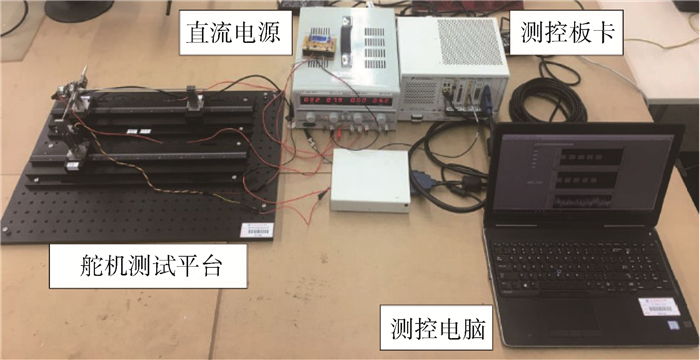
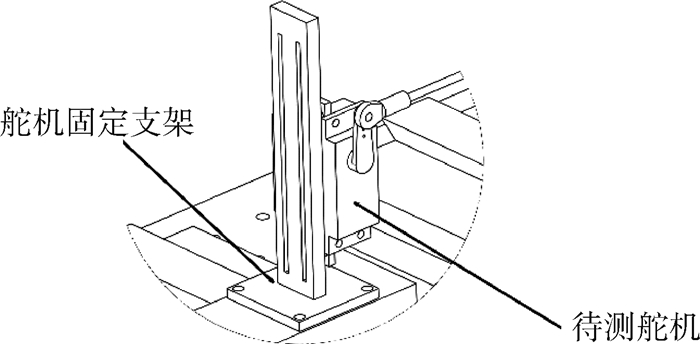
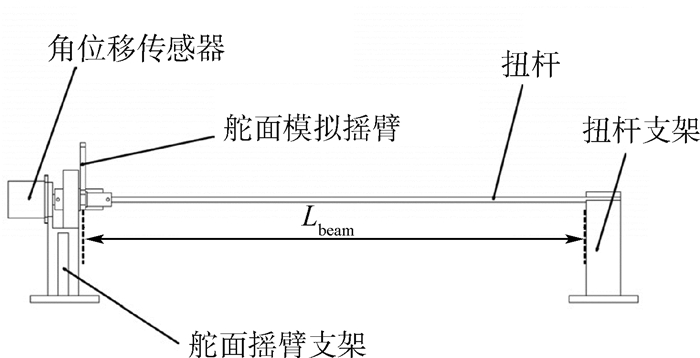
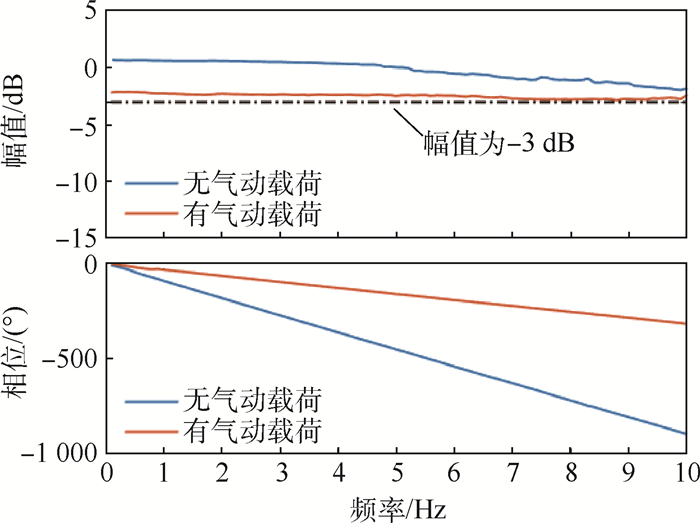
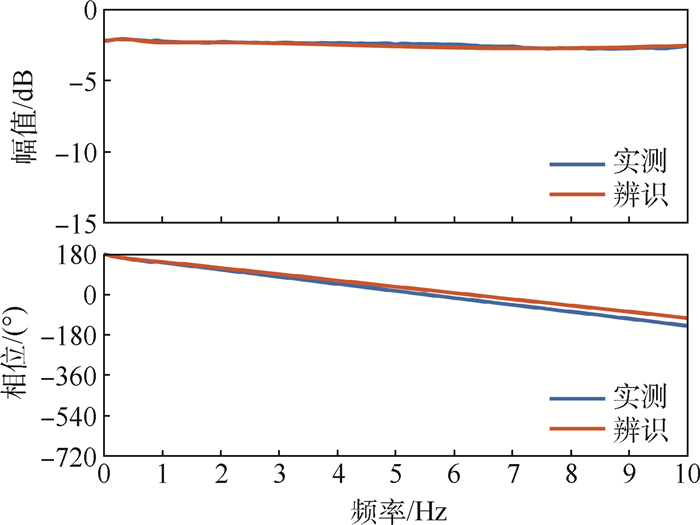
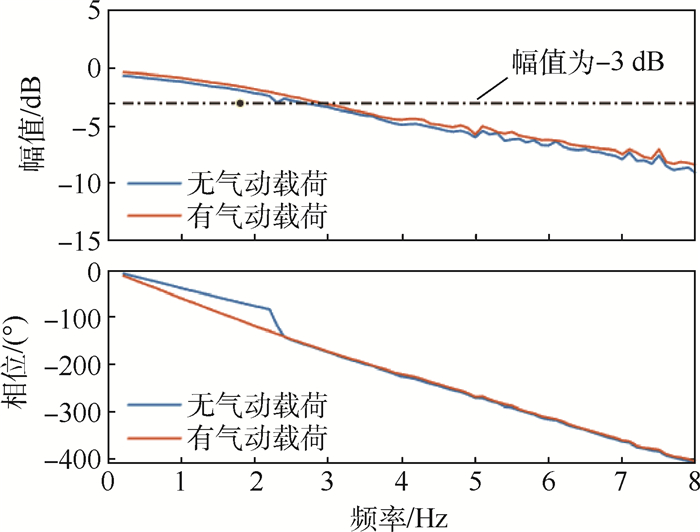
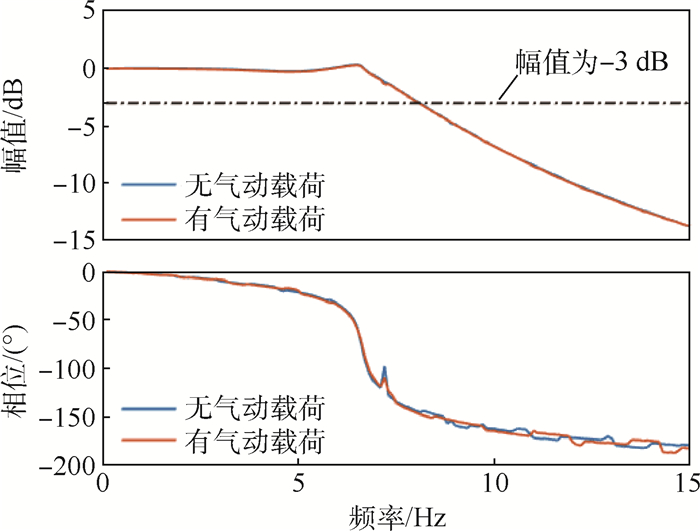
航模飞机受机体质量、机体空间和设计成本的限制,选用的小型航模舵机大多缺乏相应的频响特性指标,须在使用前完成频响特性测试。考虑舵面惯性载荷和气动载荷对舵机特性的影响,设计了舵机频响特性测试平台,可对大部分航模舵机和小型伺服电机进行空载或带载测试。针对常用的三款舵机进行频响特性测试,并采用子空间辨识获得舵机准确的数学模型。通过三款舵机频响特性对比得出,即使舵机的标称扭矩满足使用要求,负载增加也会改变舵机的幅频特性;舵机中存在的时滞时长随负载变化。而航模舵机常用的50 Hz PWM信号,也限制了舵机的带宽。
Abstract:Small actuators are chosen due to the limitation of model aircraft's weight, space and design cost, most of which are lack of frequency response characteristics that need to be tested. Considering the influence of inertial loads and aerodynamic loads of rudder, an platform for testing frequency response characteristics of actuator was designed and capable to perform tests with or without loads on rudder. Frequency response characteristics test was conducted for three types of frequently-used actuators. Subspace identification method is used to obtain precise mathematical model of actuator. The comparison among frequency response characteristics of three actuators indicated that even if the nominal torque of the actuator meets the requirements of use, the amplitude-frequency characteristics change with the increase of loads. The time delay in the actuator also varies with the load. Widely used 50 Hz PWM signal limits the bandwidth of the actuator.
-
Key words:
- actuator /
- subspace identification /
- actuator test /
- system identification /
- frequency characteristics
-
表 1 舵机频响特性测试平台参数
Table 1. Parameters of actuator frequency response characteristic test platform
参数 数值 舵面转动惯量/(kg·mm) 2.40 舵面铰链刚度/(N·m·(°)-1) 0.002 2 表 2 舵机频响特性测试参数
Table 2. Parameters of actuator frequency response characteristic test
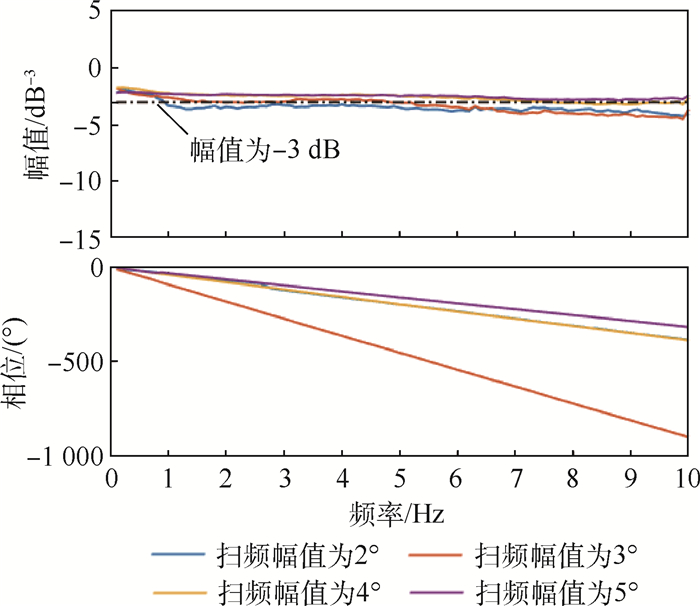
参数 航机A 航机B 航机C 采样率/Hz 50 50 1 000 扫频初始频率/Hz 0.2 0.1 0.1 扫频终止频率/Hz 8 10 15 步进步长/(Hz·次-1) 0.1 0.1 0.1 表 3 舵机频响特性测试结果
Table 3. Results of actuator frequency response characteristic test
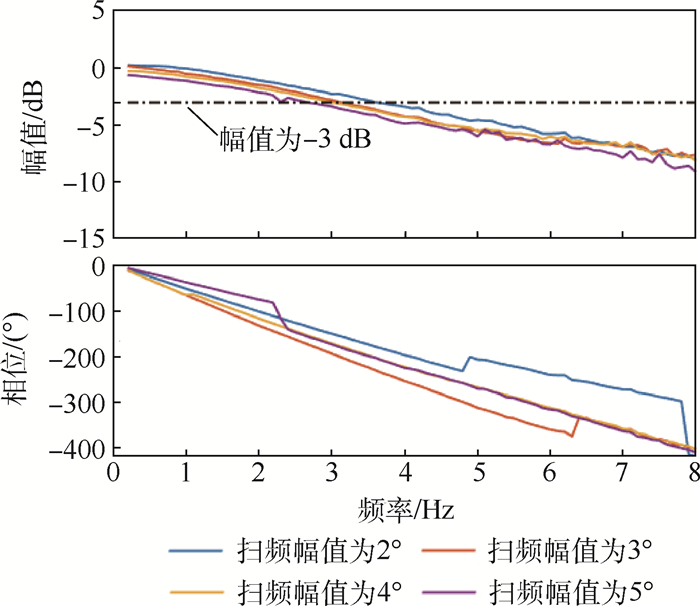
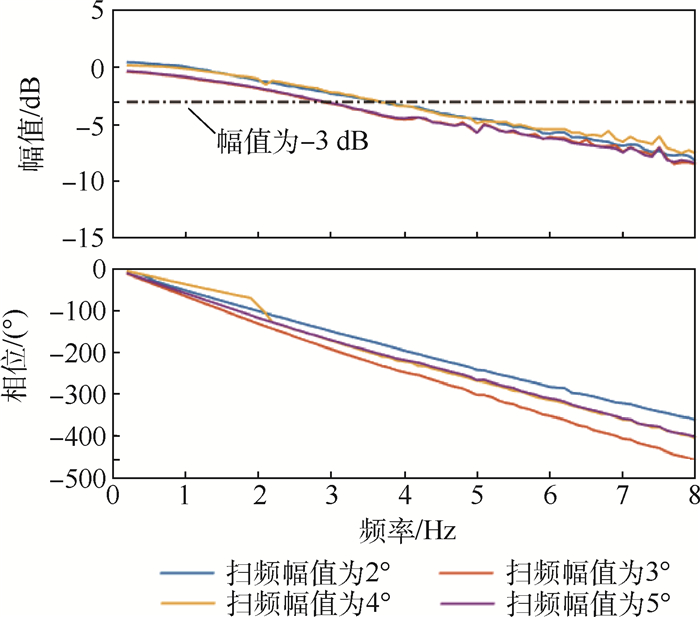
舵机 扫频幅值/(°) 无气动载荷带宽/Hz 有气动载荷带宽/Hz 时滞时长/s A 2 0.9 0.9 0.06~0.24 3 >10 1.6 4 >10 7.6 5 >10 >10 B 2 3.6 3.6 0.1 3 3.2 2.9 4 3.0 3.6 5 2.6 2.9 C 2 >15 >15 0.014 3 12.5 12.5 4 10.7 10.7 5 9.6 9.6 6 8.7 8.7 7 8.1 8.1 -
[1] 杨超.飞行器气动弹性原理[M].3版.北京:北京航空航天大学出版社, 2016:203-208.YANG C.Princple of aircraft aeroelasticity[M].3rd ed.Beijing:Beihang University Press, 2016:203-208(in Chinese). [2] 陈怀民, 庄皓玥, 马松辉, 等.基于试验的电动舵机模型辨识[J].航空计算技术, 2014, 44(4):6-9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2014.04.002CHEN H M, ZHUANG H Y, MA S H, et al.Model identification of electromechanical actuator based on tests[J].Aeronautical Computing Technique, 2014, 44(4):6-9(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-654X.2014.04.002 [3] 马敏, 周盛春, 王伯波, 等.关于飞行器的电动舵机伺服系统参数辨识[J].计算机仿真, 2016, 33(2):88-92. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2016.02.019MA M, ZHOU S C, WANG B B, et al.Parameter identification of electric actuator servo system on aircraft[J].Computer Simulation, 2016, 33(2):88-92(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9348.2016.02.019 [4] 朱萌, 曹国武, 张志伟, 等.基于Levy法的气动舵机参数辨识[J].弹箭与制导学报, 2011, 31(6):69-72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2011.06.020ZHU M, CAO G W, ZHANG Z W, et al.The system identification of pneumatic actuator based on Levy method[J].Journal of Projectiles, Rockets, Missiles and Guidance, 2011, 31(6):69-72(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-9728.2011.06.020 [5] 章家保, 刘慧, 贾宏光, 等.电动舵机伺服系统的模型辨识及其校正[J].光学精密工程, 2008, 16(10):1971-1976. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2008.10.030ZHANG J B, LIU H, JIA H G, et al.Model identification and corrector design for servo system of electromechanical actuator[J].Optics and Precision Engineering, 2008, 16(10):1971-1976(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-924X.2008.10.030 [6] 高素军.基于实测数据的系统辨识及实验研究[D].哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2006: 25-38.GAO S J.Research and experiment of system identification based on real-gained data[D].Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2006: 25-38(in Chinese). [7] MACIEJOWSKI J M.Guaranteed stability with subspace methods[J].System and Control Letters, 1995, 26(2):153-156. doi: 10.1016/0167-6911(95)00010-7 [8] OVERSCHEE P V, MOOR B D.Subspace identification for linear systems[M].Dordrecht:Kluwer Academic Publishers, 1996:8-11. [9] OVERSCHEE P V, MOOR B D.A unifying theorem for three subspace system identification algorithms[J].Automatica, Special Issue on Trends in System Identification, 1995, 31(12):1853-1864. [10] DE CALLAFON R, DE ROOVER D, VAN DEN HOF P.Multivariable least squares frequency domain identification using polynomial matrix fraction descriptions[C]//Proceedings of the 35th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 1996, 2: 2030-2035. [11] LJUNG L.System identification:Theory for the user[M].2nd ed.Upper Saddle River:Prentice Hall, 1999. [12] CLAES M, GRAHAM M R, CALLAFON R A.Frequency domain subspace identification of a tape servo system[J].Microsystem Technologies, 2007, 13(8-10):1439-1447. doi: 10.1007/s00542-007-0389-y [13] 张仁嘉.飞行器气动伺服弹性若干关键问题研究[D].北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2015: 101-102.ZHANG R J.Extensional research on several critical aeroservoelastic problems of air vehicles[D].Beijing: Beihang University, 2015: 101-102(in Chinese). [14] MCKELVEY T, AKCAY H, LJUNG L.Subspace-based multivariable system identification from frequency response data[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 1996, 41(7):960-979. doi: 10.1109/9.508900 [15] 黄超.柔性飞翼飞机颤振主动抑制系统建模、设计与验证[D].北京: 北京航空航天大学, 2018: 89-90.HUANG C.Modeling, design and verification of active flutter suppression system acting on flexible flying wing aircraft[D].Beijing: Beihang University, 2018: 89-90(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(5)
1. 王学进,董海迪,王淅娜. 一种便携式导弹电液伺服机构动态测试系统设计. 计算机测量与控制. 2024(05): 172-177+185 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 梁晓峰,乔禹淇,刘华峰,李强. 基于FPGA高适应性舵系统参数整定方法研究. 现代机械. 2024(03): 86-90 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 谢长川,朱立鹏,孟杨,冒森. 基于系统辨识的自适应变形机翼控制系统设计. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2023(10): 2761-2770 .  本站查看
本站查看4. 代桂成,范彦铭,李东辉,马宏图,梅莉. 通用飞机飞控系统地面验证试验平台研究. 西北工业大学学报. 2022(02): 391-400 .  百度学术
百度学术5. 杨阳,杨超,吴志刚,戴玉婷. 考虑舵机时滞的阵风减缓主动控制律设计. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2020(12): 2236-2244 .  本站查看
本站查看其他类型引用(6)
-








 下载:
下载:












 百度学术
百度学术

