-
摘要:
针对在确定空战威胁评估指标权重时,未考虑指标间的耦合性以及客观赋权法不能从逻辑视角体现指标相对评价对象真正的重要程度的问题,提出了一种基于灰色关联度、灰色关联深度的极大熵模型初步确定权值,再根据指标间灰色关联度以及确定的解耦阈值修正权值的方法。为了克服灰色关联分析法(GRA)和理想点接近法(TOPSIS)的缺点,提出了一种基于GRA-TOPSIS的目标威胁评估方法。首先,通过实例对比分析了指标采用数学模型与模糊处理后,对目标威胁评估结果的影响;其次,对比分析了采用GRA、TOPSIS以及GRA-TOPSIS、数学模型得出的目标威胁评估结果;最后,考虑不同决策者的主观偏好,得出不同的目标威胁评估结果。通过仿真验证了所提方法的有效性以及科学性。
-
关键词:
- 灰色关联深度 /
- 指标间灰色关联度 /
- 灰色关联分析法-理想点接近法(GRA-TOPSIS) /
- 极大熵 /
- 分辨系数
Abstract:In order to solve the problem that the coupling between indexes is not considered an the objective weighting method cannot reflect the true importance of indexes relative to evaluation objects from a logical perspective when calculating the weight of indexes in air combat threat assessment, a maximum entropy model based on grey relational degree and grey relational depth is proposed to determine the initial weight, and then the weight is modified according to the grey relational degree among indexes and the decoupling threshold. In order to overcome the shortcomings of grey relational analysis (GRA) and technique for order preference by similarity to solution (TOPSIS), a method of target threat assessment based on GRA-TOPSIS is proposed. First, the influence of mathematical model and fuzzy processing on the target threat assessment is analyzed through example. Second, the results of the target threat assessment using the GRA, TOPSIS, GRA-TOPSIS and mathematical models are compared and analyzed. Finally, different target threat assessment results are obtained by considering the subjective preference of different decision makers. Simulation proved the effectiveness and scientificity of the proposed method.
-
表 1 敌机的参数信息
Table 1. Enemy aircraft parameter information
目标 机型 作战意图 qB/(°) qR/(°) rr/km vr/(m·s-1) 1 F-16C 攻击 80 -45 50 300 2 F-16C 掩护 45 -45 70 325 3 F-5E 攻击 -60 80 60 320 4 F-15E 干扰 -45 15 60 330 表 2 灰色关联度
Table 2. Grey relational degree
敌机编号 正理想解灰色关联度 负理想解灰色关联度 相对贴近度 1 0.815 8 0.616 7 0.547 7 2 0.633 1 0.725 3 0.444 1 3 0.783 4 0.605 4 0.542 2 4 0.593 7 0.746 7 0.421 2 表 3 欧氏距离
Table 3. Euclidean distance
敌机编号 正理想解欧氏距离 负理想解欧氏距离 TOPSIS方法欧氏距离 1 0.353 6 0.629 1 0.394 4 2 0.529 3 0.424 5 0.590 9 3 0.330 3 0.604 1 0.387 8 4 0.543 0 0.521 3 0.546 9 表 4 无量纲化处理及威胁排序(α=0.5, β=0.5)
Table 4. Dimensionless processing and threat sorting(α=0.5, β=0.5)
敌机编号 正理想解灰色关联度 负理想解灰色关联度 正理想解欧氏距离 负理想解欧氏距离 正理想解贴近度 负理解贴近度 相对贴近度 威胁排序 1 1.000 0 0.825 9 0.651 2 1.000 0 1.000 0 0.738 6 0.574 2 2 2 0.776 0 0.971 4 0.974 7 0.674 9 0.725 5 0.973 1 0.427 1 4 3 0.960 3 0.810 8 0.608 3 0.960 3 0.960 3 0.709 6 0.575 1 1 4 0.727 7 1.000 0 1.000 0 0.828 6 0.778 2 1.000 0 0.437 6 3 表 5 四种方法相对贴近度与威胁排序比较
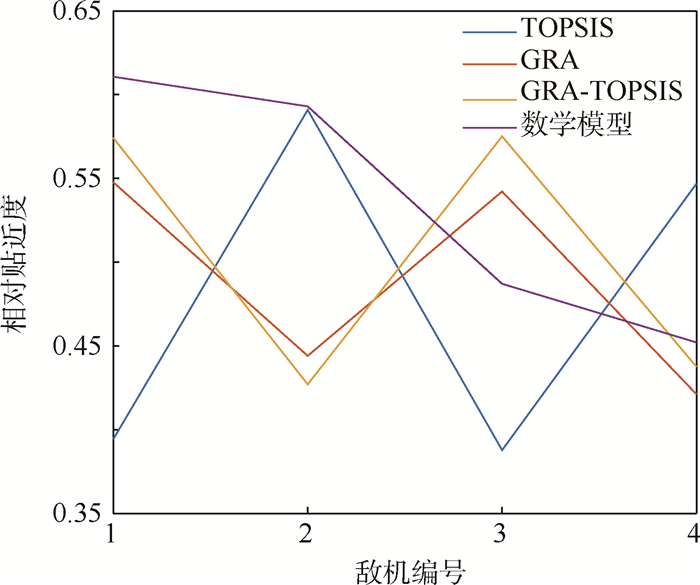
Table 5. Comparison of relative nearness degree and threat sorting of four methods
敌机编号 TOPSIS GRA GRA-TOPSIS 数学模型 相对贴近度 威胁排序 相对贴近度 威胁排序 相对贴近度 威胁排序 相对贴近度 威胁排序 1 0.394 4 3 0.547 7 1 0.574 2 2 0.610 7 1 2 0.590 9 1 0.444 1 3 0.427 1 4 0.593 0 2 3 0.387 8 4 0.542 2 2 0.575 1 1 0.487 1 3 4 0.546 9 2 0.421 2 4 0.437 6 3 0.452 1 4 表 6 α,β不同取值时目标威胁排序
Table 6. Target threat sorting at different values of α, β
敌机编号 α=0.2,β=0.8 α=0.4,β=0.6 α=0.7,β=0.3 正理想解贴近度 负理想解贴近度 相对贴近度 正理想解贴近度 负理想解贴近度 相对贴近度 正理想解贴近度 负理想解贴近度 相对贴近度 1 1.000 0 0.825 9 0.547 7 1.000 0 0.756 0 0.569 5 1.000 0 0.703 6 0.575 2 2 0.776 0 0.971 4 0.444 1 0.735 6 0.972 7 0.430 6 0.705 2 0.973 7 0.420 2 3 0.960 3 0.810 8 0.542 2 0.960 3 0.729 8 0.568 2 0.960 3 0.669 1 0.575 1 4 0.727 7 1.000 0 0.421 2 0.768 1 1.000 0 0.434 4 0.798 4 1.000 0 0.443 9 排序 1>3>2>4 1>3>4>2 1>3>4>2 -
[1] 孙海文, 谢晓方, 孙涛, 等.小样本数据缺失状态下DBN舰艇编队防空目标威胁评估方法[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 44(6):1300-1308.SUN H W, XIE X F, SUN T, et al.Threat assessment DBN under method of warships formation air defense based on the condition of small sample data missing[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 44(6):1300-1308(in Chinese). [2] 王昱, 章卫国, 傅莉, 等.基于不确定性信息的空战威胁评估方法[J].西北工业大学学报, 2016, 34(2):299-305.WANG Y, ZHANG W G, FU L, et al.A method of threat assessment for aerial combat using uncertain information[J].Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2016, 34(2):299-305(in Chinese). [3] 黄大荣, 郭安学, 李云生, 等.基于专家知识属性重要度的集群目标威胁评估方法[J].兵工学报, 2009, 30(10):1357-1362.HUANG D R, GUO A X, LI Y S, et al.An object-group threat assessment method based on attribute significance of multi-field expert systems[J].Acta Armamentarii, 2009, 30(10):1357-1362(in Chinese). [4] 程岳, 王宝树.基于分级多层黑板模型的态势估计系统结构研究[J].计算机应用研究, 2002, 19(6):29-31. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2002.06.009CHENG Y, WANG B S.The study of situation assessment architecture based on a multi-level and multi-hierarchical blackboard model[J].Application Research of Computer, 2002, 19(6):29-31(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3695.2002.06.009 [5] 张浩为, 谢军伟, 葛佳昂, 等.改进TOPSIS的多态融合直觉模糊威胁评估[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(10):2263-2269. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.16ZHANG H W, XIE J W, GE J A, et al.Intuitionistic fuzzy set threat assessment based TOPSIS and multiple times fusion on improved[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(10):2263-2269(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.16 [6] 徐西蒙, 杨任农, 符颖, 等.基ELM_AdaBoost强预测器的空战目标威胁评估[J].系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40(8):1760-1768.XU X M, YANG R N, FU Y, et al.Target threat assessment in air combat based on ELM AdaBoost strong predictor[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(8):1760-1768(in Chinese). [7] FENG L Y, XUE Q, LIU M X.Threat evaluation model of targets based on information entropy and fuzzy optimization theory[C]//2011 IEEE International Conference on Industrial Engineering and Engineering Management.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 1789-1793. [8] ZHANG H Y, LI Y J, ZHANG K, et al.Hazard degree identification of goafs based on scale effect of structure by RS-TOPSIS method[J].Journal of Central South University, 2015, 22:684-692. doi: 10.1007/s11771-015-2571-1 [9] 杨远志, 王红卫, 索中英, 等.基于粗糙集-逼近理想解排序的辐射源威胁排序方法[J].兵工学报, 2016, 37(5):945-952. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.05.024YANG Y Z, WANG H W, SUO Z Y, et al.An emitter threat evaluating method based on rough set and TOPSIS[J].Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(5):945-952(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2016.05.024 [10] 张莹, 王红卫, 郭晓陶, 等.基于GIFSS-TOPSIS的辐射源威胁评估方法[J].火力与指挥控制, 2018, 43(4):37-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2018.04.009ZHANG Y, WANG H W, GUO X T, et al.Emitter threat evaluating method based on GIFSS and TOPSIS[J].Fire Control & Command Control, 2018, 43(4):37-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2018.04.009 [11] 李陆军, 丁建江, 吕金建, 等.基于TOPSIS和灰色关联度的弹道目标威胁评估方法[J].电光与控制, 2017, 24(9):6-10LI L J, DING J J, LYU J J, et al.Threat assessment to ballistic missile based on TOPSIS optimization and grey correlation degree[J].Electronic Optics & Control, 2017, 24(9):6-10(in Chinese). [12] 张永利, 计文平, 刘楠楠.基于熵权-TOPSIS-灰色关联的目标威胁评估研究[J].现代防御技术, 2016, 44(1):72-78. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2016.01.013ZHANG Y L, JI W P, LIU N N.Target threat evaluation based on entropy weight-TOPSIS-grey correlation[J].Modern Defense Technology, 2016, 44(1):72-78(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-086x.2016.01.013 [13] 刘思峰, 党耀国, 方志根, 等.灰色系统理论及其应用[M].北京:科学出版社, 2010:256-257.LIU S F, DANG Y G, FANG Z G, et al.Grey system theory and its application[M].Beijing:Science Press, 2010:256-257(in Chinese). [14] 董卓宁, 卢俊言, 肖霄.基于灰色区间关联的UCAV自主决策方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2013, 39(11):1536-1541. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2013/V39/I11/1536DONG Z N, LU J Y, XIAO X.Decision-making approach to UCAV based on gray interval relative theory[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2013, 39(11):1536-1541(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2013/V39/I11/1536 [15] 胡杰, 曹林平, 黄长强.基于扩展不完备信息的无人战斗机综合战术灰色粗决策方法[J].兵工学报, 2010, 31(9):32-36.HU J, CAO L P, HUANG C Q.A synthesized tactical gray rough decision-making method for UCAV based on extended incomplete information[J].Acta Armamentarii, 2010, 31(9):32-36(in Chinese). [16] 赵永, 李为民, 刘彬, 等.基于改进灰色关联法的高超声速目标威胁评估模型[J].探测与控制学报, 2014, 36(5):80-85.ZHAO Y, LI W M, LIU B, et al.Hypersonic target threat evaluation model based on improved gray relation analysis[J].Journal of Detection & Control, 2014, 36(5):80-85(in Chinese). [17] 高永, 向锦武.超视距多机协同空战目标分配算法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2007, 33(3):286-289. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2007.03.009GAO Y, XIANG J W.Target assignment in BVR air combat[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2007, 33(3):286-289(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5965.2007.03.009 [18] 陈强, 周先雁.岩锚梁稳定性影响因素模糊灰色关联分析模型及其应用[J].中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 46(9):3487-3495. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZNGD201509044.htmCHEN Q, ZHOU X Y.Fuzzy grey relation analysis model on influence factors for stability of rock-bolt crane girder and its application[J].Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2015, 46(9):3487-3495(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZNGD201509044.htm [19] 罗滇生, 别少勇, 庞振国, 等.考虑指标关联的配电网设备利用率综合评价[J].电力系统及其自动化学报, 2017, 29(10):73-79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.10.013LUO D S, BIE S Y, PANG Z G, et al.Comprehensive evaluation on the utilization rate of distribution network equipment considering the relevance among indexes[J].Proceedings of the CSU-EPSA, 2017, 29(10):73-79(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-8930.2017.10.013 -








 下载:
下载: