-
摘要:
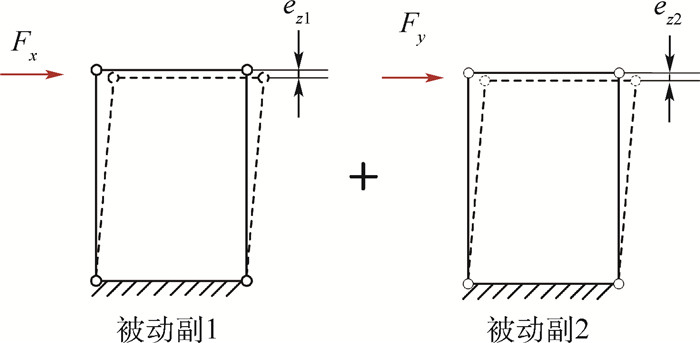
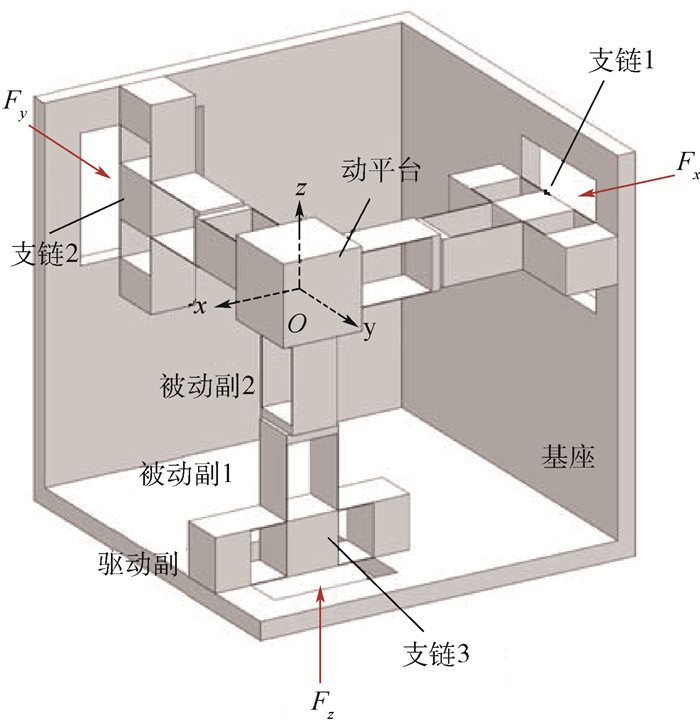
为解决现有空间平动柔性并联微定位平台(CPMS)结构布局不紧凑,且多轴驱动时各运动副的寄生运动相互累加,导致平台耦合误差增大的问题。首先,设计了一种基于柔性薄板的分布柔度式3-PPP型柔性并联微定位平台。其次,通过结构优化减小了平台的体积,并消除了支链中移动副寄生运动的累加现象。然后,基于柔度矩阵法建立了平台的输入刚度理论模型,并采用有限元仿真验证了理论模型的正确性;同时计算了平台的固有频率,并探究了其与柔性薄板尺寸参数之间的关系。最后,将结构优化前后的平台通过有限元仿真进行了对比分析。结果表明:结构优化后平台的体积减小了67%,且平台在单轴和多轴驱动时均具有更优的运动解耦特性和输入输出一致性。
-
关键词:
- 柔性并联微定位平台(CPMS) /
- 柔度矩阵 /
- 耦合误差 /
- 固有频率 /
- 有限元仿真
Abstract:The structure layouts of the existing spatial translational compliant parallel micro-positioning stages are not compact, and the parasitic motion of each kinematic joint accumulates during multi-axis actuation, which leads to the augment of cross-axis coupling error. In order to solve these problems, first, a distributed-compliance 3-PPP spatial translational compliant parallel micro-positioning stage (CPMS) based on compliant sheet was designed. Secondly, the stage volume was reduced, and the parasitic motion accumulation phenomenon of kinematic joints in each limb was eliminated by the way of structure optimization. Then, the theoretical model of input stiffness was deduced through compliance matrix method. The validity of the theoretical model was proved by finite element simulation. Besides, the natural frequency of the CPMS was calculated, and the relationship between natural frequency of the CPMS and size parameters of compliant sheet was explored. Finally, comparative analysis of the CPMS before and after structure optimization was conducted by finite element simulation. The results show that the volume of the CPMS is reduced by 67% after structure optimization, and the CPMS has better kinematic decoupling characteristic and input output consistency in both single-axis and multi-axis actuation.
-
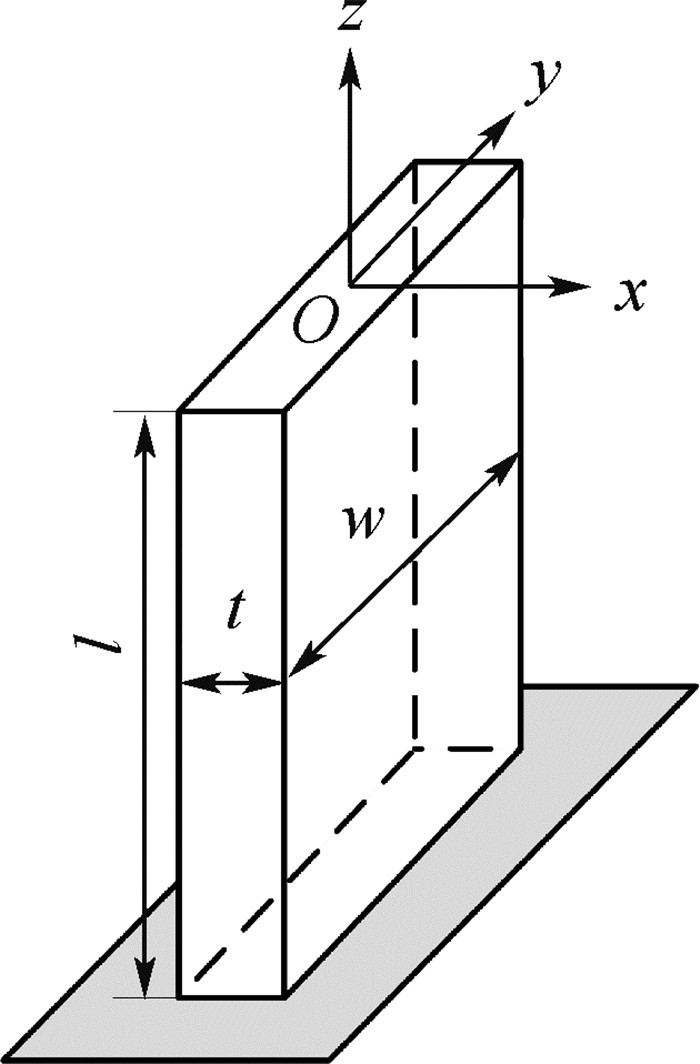
表 1 平台的尺寸参数
Table 1. Dimension parameters of stage
参数 数值/mm t 0.5 w 25 l 40 H 59 u1 45.5 u2 28.5 s 44 表 2 参考点位移的矩阵法计算值、仿真值及相对误差
Table 2. Matrix method calculation values, simulation values and relative error of reference point displacement
驱动力/N 参考点位移/μm 相对误差/% 理论计算值 仿真值 10 70.74 73.15 3.41 20 141.47 143.36 1.33 30 212.21 208.78 1.62 40 282.94 268.73 5.02 50 353.68 323.36 8.57 表 3 参考点位移非线性法计算值、仿真值及相对误差
Table 3. Nonlinear method calculation values, simulation values and relative error of reference point displacement
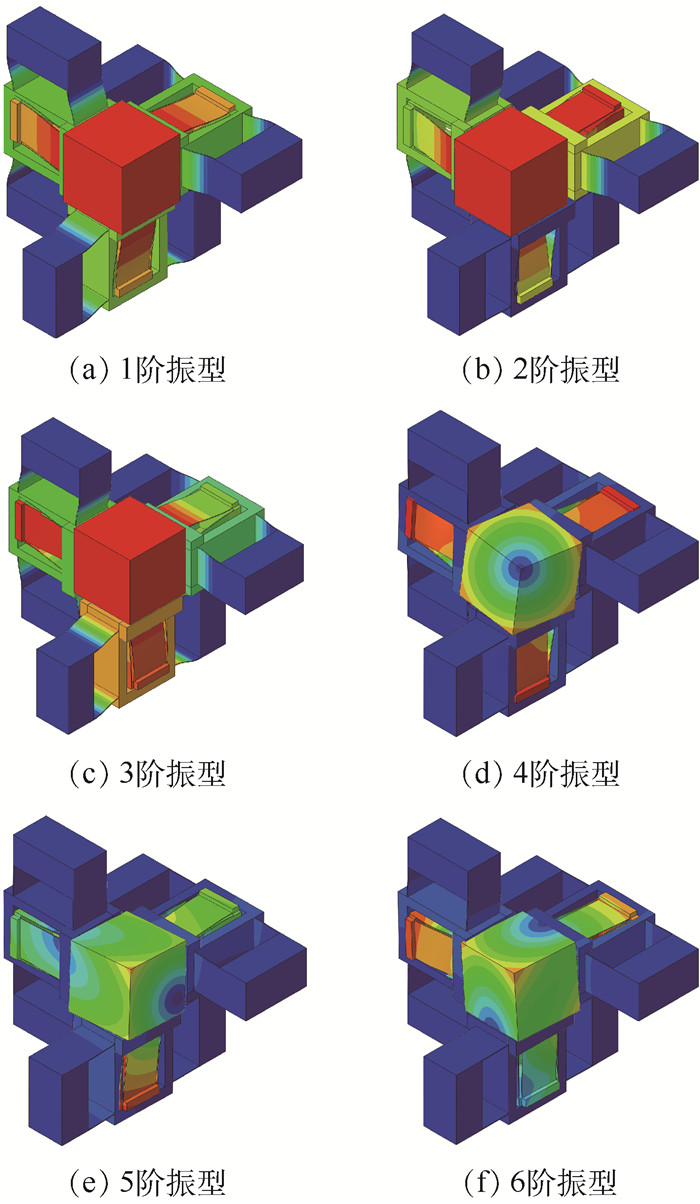
驱动力/N 参考点位移/μm 相对误差/% 理论计算值 仿真值 10 70.1 73.15 4.35 20 136.9 143.36 4.72 30 198.3 208.78 5.28 40 253.8 268.73 5.88 50 303.7 323.36 6.47 表 4 平台有限元分析的固有频率
Table 4. Natural frequency of stage obtained by finite element analysis
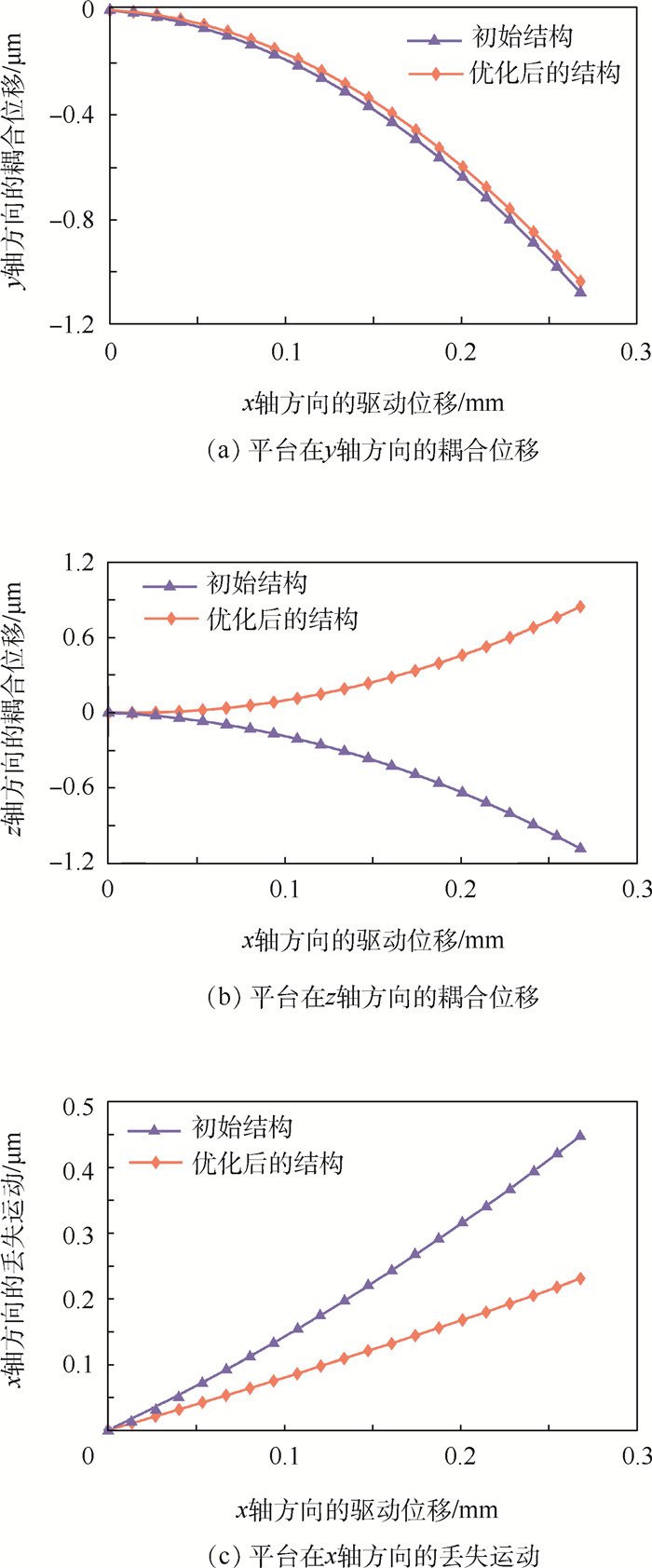
阶数 1阶 2阶 3阶 4阶 5阶 6阶 频率/Hz 94.49 94.49 94.49 694.13 700 700.13 表 5 单轴驱动时参考点的耦合位移与丢失运动
Table 5. Coupling displacement and lost motion of reference point with single-axis actuation
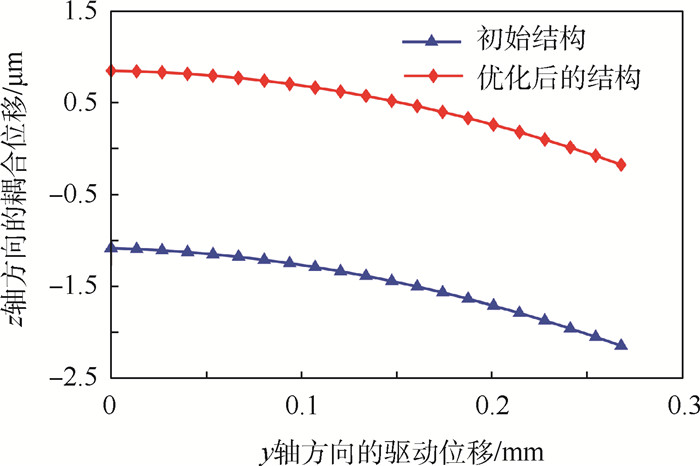
μm 平台结构 y轴方向的最大耦合位移 z轴方向的最大耦合位移 x轴方向的最大丢失运动 初始结构 -1.08 -1.09 0.45 优化后的结构 -1.04 0.85 0.23 -
[1] HOWELL L L.Compliant mechanisms[M].New York:John Wiley and Sons, 2001:2-14. [2] 张宪民, 胡凯, 王念峰, 等.基于并行策略的多材料柔顺机构多目标拓扑优化[J].机械工程学报, 2016, 52(19):1-8.ZHANG X M, HU K, WANG N F, etal.Multi-objectivetopology optimization of multiple materials compliant mechanisms based on parallel strategy[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 52(19):1-8(in Chinese). [3] 周睿, 周辉, 桂和利, 等.基于柔性铰链的二自由度微动平台分析及优化[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(9):199-207. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0706ZHOU R, ZHOU H, GUI H L, et al.Analysis and optimization of 2-DoF micro-positioning stage based on flexible hinges[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(9):199-207(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0706 [4] 于靖军, 郝广波, 陈贵敏, 等.柔性机构及其应用研究进展[J].机械工程学报, 2015, 51(13):53-68.YU J J, HAO G B, CHEN G M, et al.State-of-art of compliant mechanisms and their applications[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(13):53-68(in Chinese). [5] PAOLO D G, ALVISE B, PIERLUIGI B.New MEMS tweezers for the viscoelastic characterization of soft materials at the microscale[J].Micromachines, 2018, 9(1):15-37. [6] DSOUZA R D, NAVIN K P, THEODORIDIS T.Design fabrication and testing of a 2 DOF compliant flexural microgripper[J].Microsystem Technologies, 2018, 24(9):3867-3883. doi: 10.1007/s00542-018-3861-y [7] 曹毅, 刘凯, 桂和利, 等.二自由度开口型空间夹持机构研究[J].机械工程学报, 2018, 54(11):94-101.CAO Y, LIU K, GUI H L, et al.The research of one two-degree-of-freedom spatial gripper with opening[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(11):94-101(in Chinese). [8] LIN C, WU Z H, REN Y H, et al.Characteristic analysis of unidirectional multi-driven and large stroke micro/nano-transmission platform[J].Microsystem Technologies, 2017, 23(8):3389-3400. doi: 10.1007/s00542-016-3130-x [9] ÖZKALE B, PARREIRA R, BEKDEMIR A, et al.Modular soft robotic microdevices for dexterous biomanipulation[J].Lab on a Chip, 2019, 19(5):778-788. doi: 10.1039/C8LC01200H [10] LI C, WANG J, CHEN S C.Flexure-based dynamic-tunable five-axis nanopositioner for parallel nanomanufacturing[J].Precision Engineering, 2016, 45:423-434. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.04.002 [11] YONG Y K, MOHEIMANI S O R, KENTON B J, et al.Invited review article:High-speed flexure-guided nanopositioning:Mechanical design and control issues[J].Review of Scientific Instruments, 2012, 83(12):121101. doi: 10.1063/1.4765048 [12] ZHU Z, TO S, ZHU W L, et al.Optimum design of a piezo-actuated triaxial compliant mechanism for nanocutting[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 2018, 65(8):6362-6371. doi: 10.1109/TIE.2017.2787592 [13] WATANABE S, ANDO T.High-speed XYZ-nanopositioner for scanning ion conductance microscopy[J].Applied Physics Letters, 2017, 111(11):113106. doi: 10.1063/1.4993296 [14] HAO G B.Towards the design of monolithic decoupled XYZ compliant parallel mechanisms for multi-function applications[J].Mechanical Sciences, 2013, 4(2):291-302. doi: 10.5194/ms-4-291-2013 [15] 李海洋, 郝广波, 于靖军, 等.空间平动柔性并联机构的系统设计方法研究[J].机械工程学报, 2018, 54(13):57-65.LI H Y, HAO G B, YU J J, et al.Systematic approach to the design of spatial translational compliant parallel mechanisms[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2018, 54(13):57-65(in Chinese). [16] TANG X Y, CHEN I M, LI Q.Design and nonlinear modeling of a large-displacement XYZ flexure parallel mechanism with decoupled kinematic structure[J].Review of Scientific Instruments, 2006, 77(11):115101. doi: 10.1063/1.2364132 [17] AWTAR S, USTICK J, SEN S.An XYZ parallel-kinematic flexure mechanism with geometrically decoupled degrees of freedom[J].Journal of Mechanisms and Robotics, 2012, 5(1):015001. [18] LI Y M, XU Q S.Design and optimization of an XYZ parallel micromanipulator with flexure hinges[J].Journal of Intelligent and Robotic Systems, 2009, 55(4-5):377-402. doi: 10.1007/s10846-008-9300-z [19] YUE Y, GAO F, ZHAO X, et al.Relationship among input-force payload stiffness and displacement of a 3-DOF perpendicular parallel micro-manipulator[J].Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2010, 45(5):756-771. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2009.12.006 [20] WANG N, ZHANG Z Y, ZHANG X M, et al.Optimization of a 2-DOF micro-positioning stage using corrugated flexure units[J].Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2018, 121:683-696. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2017.11.021 [21] CHAO D H, ZONG G H, LIU R.Design of a 6-DOF compliant manipulator based on serial-parallel architecture[C]//2005 IEEE/ASME International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2005: 765-770. [22] KIM D, GWEON D G, SONG I, et al.Optimal design of a flexure hinge-based XYZ atomic force microscopy scanner for minimizing Abbe errors[J].Review of Scientific Instruments, 2005, 76(7):376-391. [23] XU Q S, ZHU X B, DONG Z G, et al.Nonlinear modeling and analysis of compliant mechanisms with circular flexure hinges based on quadrature beam elements[J].Proceedings of the Institution of Mechanical Engineers, Part C:Journal of Mechanical Engineering Science, 2019, 233(9):3277-3285. doi: 10.1177/0954406218802945 [24] LI Y M, WU Z G.Design analysis and simulation of a novel 3-DOF translational micromanipulator based on the PRB model[J].Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2016, 100:235-258. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2016.02.001 [25] SHE Y, MENG D S, SU H J, et al.Introducing mass parameters to pseudo-rigid-body models for precisely predicting dynamics of compliant mechanisms[J].Mechanism and Machine Theory, 2018, 126:273-294. doi: 10.1016/j.mechmachtheory.2018.04.005 [26] KOSEKI Y, TANIKAWA T, KOYACHI N, et al.Kinematic analysis of translational 3-DOF micro parallel mechanism using matrix method[J].IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems, 2000, 1(3):786-792. [27] TANG H, LI Y M.Design analysis and test of a novel 2-DOF nanopositioning system driven by dual mode[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2013, 29(3):650-662. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2013.2248536 [28] 余跃庆, 张亚涛, 张绪平, 等.柔顺微夹持机构理论分析与实验[J].农业机械学报, 2018, 49(11):393-398.YU Y Q, ZHANG Y T, ZHANG X P, et al.Theoretical analysis and experiment on compliant microgripper mechanism[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2018, 49(11):393-398(in Chinese). [29] HAO G B, LI H Y, KEMALCAN S, et al.Understanding coupled factors that affect the modelling accuracy of typical planar compliant mechanisms[J].Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering, 2016, 11(2):129-134. doi: 10.1007/s11465-016-0392-z [30] 杨志军, 白有盾, 陈新, 等.基于应力刚化效应的动态特性可调微动平台设计新方法[J].机械工程学报, 2015, 51(23):153-159.YANG Z J, BAI Y D, CHEN X, et al.A new design method of dynamic characteristics adjustable micro motion stage based on tension stiffening[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2015, 51(23):153-159(in Chinese). [31] XAVIER H, ROSS W, KONG X W.On a simplified nonlinear analytical model for the characterization and design optimization of a compliant XY micro-motion stage[J].Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing, 2018, 49:66-76. doi: 10.1016/j.rcim.2017.05.012 -







 下载:
下载: