Formation control for high-order linear swarm systems with complex communication conditions
-
摘要:
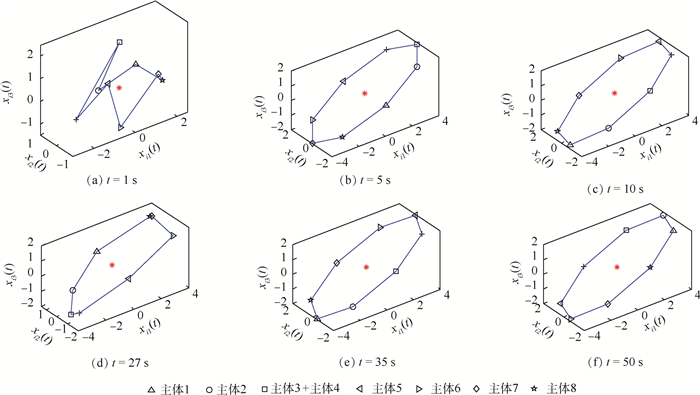
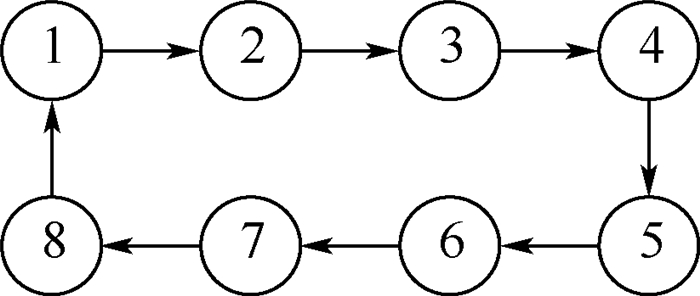
针对时变时延、拓扑不确定和外部扰动等复杂通信条件下的高阶线性群系统编队控制问题进行研究。首先,建立了群系统编队控制问题的数学描述,并基于一致性最近邻原则给出了编队控制协议框架。其次,提出了群系统实现编队的充要条件。通过状态分解和变量代换,给出了约束条件下,编队控制协议的设计方法。同时,为得到群系统所允许最大时延边界,引入自由权矩阵,得到了保守性较小的线性矩阵不等式(LMI)判据条件。仿真实验验证了编队控制方法对于有界时变时延、拓扑不确定以及外部扰动具有一定的鲁棒性。
Abstract:The formation control problems for high-order linear swarm systems with time-varying delays, topology uncertainties and external disturbances are investigated. Firstly, the mathematical description of the formation control for swarm systems is established, and the formation control protocol is proposed based on the consensus nearest neighbor principle. Secondly, the necessary and sufficient conditions for swarm systems to achieve the formation are presented. By decomposing the state and using the variable substitution method, the design method of formation protocol is given under the constrained conditions. Furthermore, in order to get the upper bound of the time-varying delays, the free-weighting matrices are introduced, and the linear matrix inequality (LMI) criteria with lower conservation are obtained. Finally, numerical examples and simulation results are given to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed method. The formation control method is robust for bounded time-varying delays, topology uncertainties and external disturbances.
-
-
[1] KOPFSTEDT T, MUKAI M, FUJITA M.Control of formations of UAVs for surveillance and reconnaissance missions[C]//Proceedings of the 17th World Congress.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 6-11. [2] NIGAM N, BIENIAWSKI S, KROO I, et al.Control of multiple UAVs for persistent surveillance:Algorithm and flight test results[J].IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2012, 20(5):1236-1251. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2011.2167331 [3] SHAMES I, FIDAN B, ANDERSON B D.Close target reconnaissance using autonomous UAV formations[C]//Proceedings of the 47th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 1729-1734. [4] PACK D J, DELIMA P, TOUSSAINT G J.Cooperative control of UAVs for localization of intermittently emitting mobile targets[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics.Part B:Cybernetics, 2009, 39(4):959-970. doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2008.2010865 [5] KANTOR G, SINGH S, PETERSON R, et al.Distributed search and rescue with robot and sensor teams[J].Springer Tracts in Advanced Robotics, 2003, 24:529-538. [6] HURTADO J E, ROBINETT R D I, DOHRMANN C R, et al.Decentralized control for a swarm of vehicles performing source localization[J].Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2004, 41:1-18. [7] YAN W S, FANG X P, LI J B.Formation optimization for AUV localization with range-dependent measurements noise[J].IEEE Communications Letters, 2014, 18(9):1579-1582. doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2014.2344033 [8] SIVAKUMAR A, TAN C K Y.UAV swarm coordination using cooperative control for establishing a wireless communications backbone[C]//International Conference on Autonomous Agents & Multi-agent Systems.Red Hook, NY: IFAAMAS, 2010: 1157-1164. [9] SOBIESIAK L A, DAMAREN C J.Lorentz-augmented spacecraft formation reconfiguration[J].IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2016, 24(2):514-524. [10] ZHU S Q, WANG D W, LOW C B.Cooperative control of multiple UAVs for moving source seeking[J].Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems, 2014, 74:333-346. [11] WANG P K C. Navigation strategies for multiple autonomous mobile robots moving in formation[J].Journal of Robotic Systems, 1991, 8(2):177-195. doi: 10.1002/rob.4620080204 [12] DESAI J P, OSTROWSKI J, KUMAR V.Modeling and control of formations of non-holonomic mobile robots[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 2001, 17(6):905-908. doi: 10.1109/70.976023 [13] BALCH T, ARKIN R.Behavior-based formation control for multi-robot teams[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics and Automation, 1998, 14(6):926-939. doi: 10.1109/70.736776 [14] LEWIS M, TAN K.High precision formation control of mobile robots using virtual structures[J].Autonomous Robots, 1997, 4(4):387-403. doi: 10.1023/A:1008814708459 [15] REN W.Consensus strategies for cooperative control of vehicle formation[J].IET Control Theory and Application, 2007, 1(2):505-512. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta:20050401 [16] REN W, SORENSEN N.Distributed coordination architecture for multi-robot formation control[J].Robotics and Autonomous Systems, 2008, 56(4):324-333. doi: 10.1016/j.robot.2007.08.005 [17] FAX J A, MURRAY R M.Information flow and cooperative control of vehicle formations[C]//15th IFAC World Congress.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2002: 115-120. [18] LIN Z Y, FRANCIS B, MAGGIORE M.Necessary and sufficient graphical conditions for formation control of unicycles[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(1):121-127. [19] FENG X, LONG W, JIE C, et al.Finite-time formation control for multi-agent systems[J].Automatica, 2009, 45(11):2605-2611. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2009.07.012 [20] SEO J, AHN C, KIM Y.Controller design for UAV formation flight using consensus based decentralized approach[C]//Proceedings of AIAA Infotech@Aerospace Conference.Reston: AIAA, 2009: 1-11. [21] DONG X W, YU B C, SHI Z Y, et al.Time-varying formation control for unmanned aerial vehicles:Theories and applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology, 2015, 23(1):340-348. doi: 10.1109/TCST.2014.2314460 [22] LAFFERRIERE G, WILLIAMS A, CAUGHMAN J, et al.Decentralized control of vehicle formations[J].Systems and Control Letters, 2005, 54(9):899-910. doi: 10.1016/j.sysconle.2005.02.004 [23] MA C Q, ZHANG J F.On formability of linear continuous-time multi-agent systems[J].Journal of Systems Science and Complexity, 2012, 25(1):13-29. doi: 10.1007/s11424-012-0108-3 [24] LIU C L, TIAN Y P.Formation control of multi-agent systems with heterogeneous communication delays[J].International Journal of Systems Science, 2009, 40(6):627-636. doi: 10.1080/00207720902755762 [25] RUDY C G, NEJAT O.Stability of formation control using a consensus protocol under directed communications with two time delays and delay scheduling[J].International Journal of Systems Science, 2016, 47(2):433-449. [26] QIN L G, HE X, ZHOU D H.Distributed proportion-integration-derivation formation control for second-order multi-agent systems with communication time delays[J].Neurocomputing, 2017, 267:271-282. doi: 10.1016/j.neucom.2017.05.088 [27] ABDELKADER A, ABDELHAMID T.Formation control of VTOL unmanned aerial vehicles with communication delays[J].Automatica, 2011, 47(11):2383-2394. doi: 10.1016/j.automatica.2011.08.042 [28] LU X Q, AUSTIN F, CHEN S H.Formation control for second-order multi-agent systems with time-varying delays under directed topology[J].Communications in Nonlinear Science and Numerical Simulation, 2012, 17(3):1382-1391. doi: 10.1016/j.cnsns.2011.07.029 [29] DONG X W, XI J X, LU G, et al.Formation control for high-order linear time-invariant multi-agent systems with time delays[J].IEEE Transactions on Control of Network Systems, 2014, 1(3):232-240. doi: 10.1109/TCNS.2014.2337972 [30] XUE D, YAO J, WANG J, et al.Formation control of multi-agent systems with stochastic switching topology and time-varying communication delays[J].IET Control Theory and Applications, 2013, 7(13):1689-1698. doi: 10.1049/iet-cta.2011.0325 [31] XUE R B, CAI G H.Formation flight control of multi-UAV system with communication constraints[J].Journal of Aerospace Technology and Management, 2016, 8(2):203-210. doi: 10.5028/jatm.v8i2.608 [32] 马培蓓, 雷明, 纪军, 等.均等通信时滞下多UAV协同编队控制[J].航空学报, 2017, 38(S1):721551.MA P B, LEI M, JI J, et al.Control of multi-UAV cooperative formation with equality communication time-delay[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2017, 38(S1):721551(in Chinese). [33] LI X S.Control for formation of multi-agent systems with time-varying delays and uncertainties based on LMI[J].Automatika, 2016, 57(2):441-451. doi: 10.7305/automatika.2016.10.1012 [34] XI J X, YAO Z C, LIU G B, et al.Robust L2 consensus of high-order swarm systems with time-varying delays[J].Control and Cybernetics, 2014, 43(1), 59-77. [35] DONG X W, XI J X, SHI Z Y, et al.Practical consensus for high-order linear time-invariant swarm systems with interaction uncertainties, time-varying delays and external disturbances[J].International Journal of Systems Science, 2013, 44(10):1843-1856. doi: 10.1080/00207721.2012.670296 [36] REN W, BEARD R W.Consensus seeking in multiagent systems under dynamically changing interaction topologies[J].IEEE Transactions on Automatic Control, 2005, 50(5):655-661. doi: 10.1109/TAC.2005.846556 [37] LIU W, ZHOU S L, WU Q P, et al.H∞ consensus of multi-agent systems in directed networks with Lipschitz non-linear dynamics[J].Transactions of the Institute of Measurement and Control, 2016, 39(12):1877-1884. [38] BOYD S, GHAOUI L E, FERON E, et al.Linear matrix inequalities in system and control theory[M].Philadelphia, PA:SIAM, 1994. [39] GU K.A further refinement of discretized Lyapunov functional method for the stability of time-delay systems[J].International Journal of Control, 2001, 74(10):967-976. doi: 10.1080/00207170110047190 [40] PETERSEN I R, HOLLOT C V.A Riccati equation approach to the stabilization of uncertain linear systems[J].Automatica, 1986, 22(4):397-411. doi: 10.1016/0005-1098(86)90045-2 [41] BEE O C E O.Matrix analysis[M].New York:Cambridge University Press, 1985. [42] XI J X, SHI Z Y, ZHONG Y S.Consensus analysis and design for high-order linear swarm systems with time-varying delays[J].Physica A, 2011, 390(23-24):4114-4123. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2011.06.045 -







 下载:
下载: