-
摘要:
为了帮助航空公司合理规划航线网络,降低运输成本,从航空公司的角度出发,将机场容量看作到港和离港航班的函数,绘制了机场容量包络曲线。基于机场容量包络曲线构建了随机需求下多分配、非严格的两阶段混合整数随机规划模型,第1阶段确定网络的枢纽位置,第2阶段确定不同需求情形下城市对的运输路径和不同路径上的流量比例。当需求情形是离散变量时将两阶段模型转化为确定的等价规划。继而以东航为例选取13个机场对模型进行验证,并对运输成本折扣因子进行灵敏度分析。结果表明:在不同的折扣因子情形下选择的枢纽机场不同,折扣越大,选择的枢纽越多,网络总成本越低,且3种折扣因子情形下的枢纽选择与实际比较吻合;每种折扣因子情形下,当需求不同时航线网络的布局有所差异;对比需求确定和不确定下的模型结果差异,得出需求不确定下的网络总成本更低。可见需求不确定下的随机规划模型更加贴近实际,能够帮助航空公司规划符合实际情形的枢纽航线网络,并确定其在枢纽机场的容量份额。
Abstract:In order to help airlines plan route network reasonably and reduce operation cost, from the perspective of airlines, airport capacity is regarded as a function of arrival and departure flights to draw airport capacity envelope curve. Based on airport capacity envelope curve, a two-stage mixed integer stochastic programming model with multi-allocation and non-strictness under stochastic demand is established. In the first stage, the hub location of the network is determined, and in the second stage, the transportation routes of each city pair and the flow ratios of different routes under different demand scenarios are determined. When demand scenario is a discrete variable, the model is transformed into a deterministic equivalent programming. Then taking China Eastern Airlines as an example, 13 airports are selected to validate the model, and the sensitivity analysis of transportation cost discount factor is carried out. The results show that the hub airports selected under different discount factors are different, the larger the discount, the more the hub selected, the lower the total network cost, and the hub selected under three discount factor scenarios is in good agreement with the actual situation; in each discount factor case, when the demand is different, the layout of the route network is different; by comparing the model results between certain and uncertain demand, it is concluded that the total cost of the network is lower when the demand is uncertain. Therefore, the proposed stochastic programming model under uncertain demand is closer to reality, which can help airlines plan hub-and-spoke network that is in line with the actual situation, and determine their capacity share in hub airports.
-
Key words:
- airline /
- hub location /
- uncertain demand /
- airport capacity /
- stochastic planning
-
随着航空管制的放松,各个航空公司都在重建自己的航线网络,由点对点航线网络向中枢辐射式航线网络转变。中枢辐射式航线网络通过短途汇运、分运和长途、大容量转运,使得运输成本更低,经济效益更好。但在构建枢纽网络时,始发地与目的地(OD)需求不确定是困扰航空公司战略决策的主要原因。研究需求不确定下的枢纽选址与运输路径规划问题能够帮助航空公司确定最佳的运输方案以应对季节、市场等因素引起的OD需求波动,使其运营总成本最低。
对枢纽选址问题的设计与优化,O’Kelly[1]、Campbell[2]、Skorin-Kapov[3]、Ernst[4]等建立了经典的枢纽航线网络优化模型。之后学者在经典模型的基础上从枢纽机场容量限制、机场容量多水平决策、OD需求不确定性等角度做了逐步的推进。在枢纽机场容量限制方面,Yang[5]分别考虑枢纽机场总流量限制和枢纽机场中转流量限制,构建了2个混合整数线性规划模型,得出了不同容量限制情形下的枢纽选址差异。冯乾等[6]将枢纽选择和航线设计2个阶段综合考虑,用机场吞吐量衡量机场容量限制,提出了机场容量限制下的多分配枢纽航线网络设计方法。在机场容量多水平决策方面,Wu等[7-8]将机场容量看作离散变量,确定不同情形下的枢纽位置和路径流分配,得出不同容量限制情形下的最优网络。Correia等[9]在机场容量限制的基础上引入枢纽机场容量多水平决策。Zarei[10]在枢纽机场容量多水平决策的基础上引入枢纽之间的连接方式差异。Seyed等[11]从容量包络曲线的角度构建了枢纽机场容量多水平决策的混合整数规划模型(MILP)。在OD需求不确定性方面,Yang[12-13]和Chiu[13]考虑随机需求,构建了两阶段的随机规划模型,第1阶段解决枢纽选址问题,第2阶段在第1阶段枢纽选择的基础上确定不同需求情形下OD之间的路径和流量分配。Alumur等[14]同时考虑枢纽建设成本的不确定性和OD需求的不确定性,分别构建了单分配、多分配下的优化模型。Qin和Gao[15]、Contreras等[16]研究OD流量不确定情形下枢纽机场无容量限制的枢纽选址问题。胡青蜜和胡志华[17]运用随机规划方法研究不确定货流下的枢纽选址问题。
纵观国内外研究现状,对枢纽网络设计问题从机场容量限制、机场容量多水平决策和OD需求不确定性方面的研究主要存在以下3点不足:①现有研究主要从整个航空运输市场的角度考虑,但实际规划航线网络布局的是航空公司;②现有研究在确定枢纽机场容量时以机场的最大吞吐量作为容量,但是枢纽机场容量受多种因素影响,不同的时期容量可能不同;③现有研究在枢纽容量决策和OD需求不确定性方面独立研究。研究OD需求不确定性时,未考虑枢纽机场容量多水平决策,在对枢纽机场容量多水平决策研究时未考虑季节、时期等因素造成的OD需求不确定性。
本文从航空公司的角度出发,在机场容量一定的情况下,确定航空公司选择枢纽机场的最优所占份额。对枢纽机场总容量水平的确定,为了更切合实际,将机场容量看作离港和到港航班的函数,运用历史统计数据绘制机场容量包络曲线。同时考虑OD需求的不确定性,构建航空公司枢纽选址问题的多分配、非严格的两阶段混合整数随机规划模型,并运用实际航空公司数据对模型进行验证。
1. 机场容量包络曲线
枢纽机场的实际容量与天气、机场空域构型、跑道构型及数量、停靠的航班类别等多种因素有关。学者通常情况下根据历史数据将进离港航班之和的最大值表示为单位时间内枢纽机场的容量。对于一个真实的航线网络,实际容量比理论容量更加精确。单位时间内的机场容量应该表示为到港和离港航班数量的函数,而不是一个常数。这些函数是对历史数据形成的全部观测值的包络,从而构成了机场容量包络曲线。
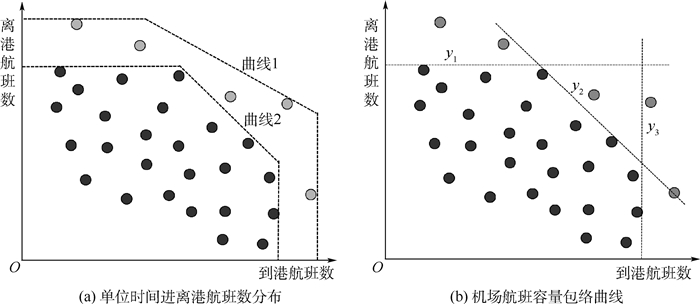
机场容量包络曲线根据一段时间内(1 h)的到达和离开的实际航班数量进行绘制。横轴表示到港航班数量,纵轴表示离港航班数量。一般情况下运用统计的方法去除低频率的观测值,通过拒绝一定比例的观测频率来绘制正确的枢纽机场容量包络曲线。如图 1(a)所示,曲线1表示基于统计数据观测到的机场容量包络曲线;曲线2表示修正后的机场容量包络曲线。图 1(b)中,y1、y2、y3共同构成了机场容量包络曲线。
2. 模型提出
本文采用有向图建模。假设网络中有N个节点,包括始发地、目的地和潜在枢纽。非枢纽节点之间既能中转也能直达运输。一个非枢纽节点可以连接多个枢纽点,并且规定两个非枢纽节点之间最多实现两次中转。
从航空公司枢纽选址问题的角度出发,基于机场容量包络曲线,考虑航空公司在枢纽机场的容量多水平决策,以及OD需求的不确定性,构建两阶段的随机规划模型。本文将需求的不确定性表示为随机变量。第1阶段以总的网络运输成本最低来确定枢纽的位置,第2阶段在第1阶段枢纽选址结果的基础上确定不同需求的运输路径和路径上的流量分配。
2.1 模型参数及变量
2.1.1 模型参数
模型参数定义如下:N为网络节点的集合;W为OD需求情形的集合;ω表示一种特定的情形,ω∈W,每种情形代表航空公司的一种OD需求情形;Tk为航空公司选择机场k作为枢纽的容量情形集合;S为机场容量包络曲线函数的线段s的集合,s∈S;hij(ω)为情形ω下节点i和j之间的需求;Cikmj(ω)为情形ω下节点i和j之间通过k、m中转的单位旅客运输成本;Cij为节点i和j之间直达运输的单位旅客运输成本;fkt为枢纽节点k在容量情形t下的建设成本;M为一个非常大的正数;ask为枢纽节点k在机场容量包络函数s下的到港系数;bsk为枢纽节点k在机场容量包络函数s下的离港系数;Uskmax为枢纽节点k在机场容量包络函数s下的最大容量;pkt为航空公司选择枢纽节点k情形t下的容量份额;Uskt为枢纽节点k在机场容量包络函数s、容量情形t下的容量,且Uskt=Uskmax·pkt;p(ω)为情形ω发生的概率;α(ω)为情形ω下非枢纽节点至枢纽节点运输成本折扣因子;β(ω)为情形ω下从一个枢纽节点至另一个枢纽节点运输成本折扣因子;γ(ω)为情形ω下枢纽节点至非枢纽节点运输成本折扣因子。
2.1.2 模型变量
模型变量定义如下:Zikmj(ω)为情形ω下节点i至节点j的旅客经过枢纽节点k、m中转的比例;Zij(ω)为情形ω下节点i至节点j的旅客直达运输的比例;Xkt为0-1变量,当航空公司选择节点k,容量情形t作为枢纽时等于1,否则等于0;Wkout(ω)为情形ω下枢纽节点k的离港流量;Wkin(ω)为情形ω下枢纽节点k的进港流量。
2.2 两阶段模型
枢纽建设是一个长期且耗资的工程,由季节、时期等因素引起的需求不确定性对枢纽节点的选择不产生影响。因此第1阶段模型中的变量Xkt不受需求不确定性的影响,第2阶段变量Zij(ω)、Zikmj(ω)取决于需求的不同情形。Z为目标函数值。
1) 第1阶段

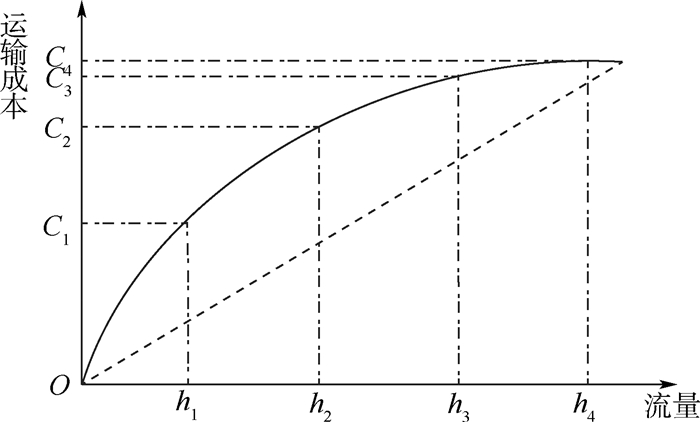
(1) s.t.

(2) 
(3) 式(1)中,

2) 第2阶段

(4) s.t.

(5) 
(6) 
(7) 
(8) 
(9) 
(10) 
(11) 
(12) 
(13) 
(14) 
(15) 第2阶段模型表示每种情形ω下的路径决策和流量分配决策。式(4)表示情形ω下所有OD中转和直达的总成本最小。式(5)确保OD之间的需求必须得到满足。式(6)~式(8)表示流变量之间的关系。其中式(6)、式(7)表示当节点k被选作枢纽时,流经节点k的运输应被看作中转运输;式(8)表示当节点k、m都是枢纽时,k和m之间的运输应被看作中转运输。式(9)表示当节点k不是枢纽时,经节点k中转的流量为0。式(10)表示流出节点k的流平衡约束。式(11)表示流入节点k的流平衡约束。式(12)表示容量约束,流经节点k的流量应小于节点k的容量。式(13)~式(15)表示变量域的限制。
针对需求不确定下枢纽选址和运输路径规划问题所构建的模型是一个两阶段模型,需要采用迭代算法求解。假设需求情形ω是离散变量,具有有限种可能的情形,每种情形以一定的概率发生。则两阶段的随机规划模型可以被写为确定的等价规划(Deterministic Equivalent Programming,DEP),如式(16)~式(29)所示。各式的含义等同于两阶段的随机规划模型。

(16) s.t.

(17) 
(18) 
(19) 
(20) 
(21) 
(22) 
(23) 
(24) 
(25) 
(26) 
(27) 
(28) 
(29) 在上述模型中,情形ω下路径的单位旅客运输成本表示为

(30) 式(30)表明在HS网络中,对于每种需求情形ω,节点i和j之间的整个运输成本包括汇运、转运、分运三部分。由于规模经济性的存在,随着路径流量的增加(h1增加至h4),单位运输成本逐渐降低,如图 2所示。
3. 算例分析
3.1 数据输入
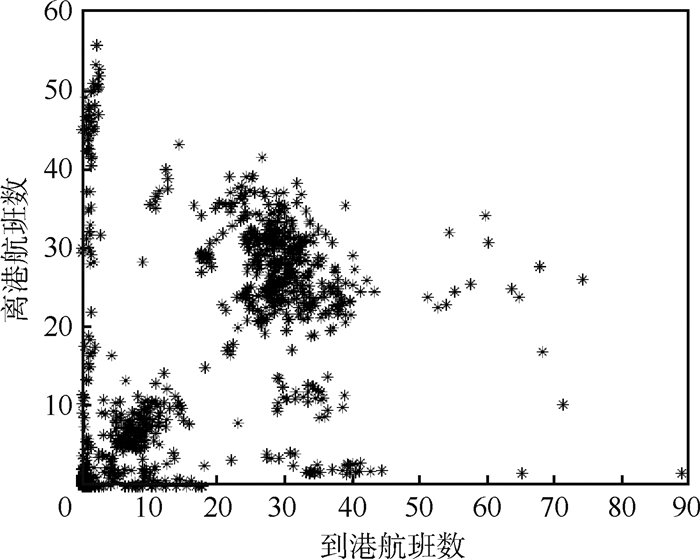
为了验证模型的有效性,本文以东航为例,选择13个主要省会机场研究航空公司枢纽网络设计问题。根据2016、2017两年的进离港航班数据,统计单位小时内的进离港航班数量如图 3所示(以西安机场为例)。为了获得机场的年旅客容量,设机场的日开放小时为18h,每航班的平均旅客数为180,则以旅客数表示的机场容量包络曲线如图 4所示。
13个机场旅客容量包络曲线的系数如表 1所示。
表 1 机场容量包络曲线系数Table 1. Airport capacity envelope curve coefficient机场
所在地机场
代码ask bsk Uskmax/(106人) a1k a2k a3k b1k b2k b3k U1kmax U2kmax U3kmax 深圳 SZX 1 0 1 0 1 0.882 40.64 39.29 63.69 西安 XIY 1 0 1 0 1 1.034 41.37 40.33 64.43 郑州 CGO 1 0 1 0 1 1.029 24.16 24.88 38.24 乌鲁木齐 URC 1 0 1 0 1 1.001 29.45 28.51 43.77 长沙 CSX 1 0 1 0 1 0.906 21.77 21.36 34.08 武汉 WUH 1 0 1 0 1 1.167 22.71 21.88 38.80 成都 CTU 1 0 1 0 1 0.862 40.54 39.19 58.77 浦东 PVG 1 0 1 0 1 1.013 55.88 54.64 80.25 南京 NKG 1 0 1 0 1 0.548 25.61 26.85 34.42 沈阳 SHE 1 0 1 0 1 0.618 25.51 23.43 32.95 北京 PEK 1 0 1 0 1 0.717 85.74 56.71 92.80 太原 TYN 1 0 1 0 1 0.530 15.86 13.69 19.60 昆明 KMG 1 0 1 0 1 0.713 48.52 43.34 64.20 在13个机场中,任意两个OD之间的需求,根据2017年实际运力乘以行业航线平均客座率估算。运力数据源于OAG(Official Airline Guide),客座率数据源于飞常准。东航在某些没有运力部署的OD上需求设为0。
本文对需求不同的考虑,只要根据航空公司的实际做法,即如何应对旺、平、淡季,在文中对应设立了高、中、低3个不同的需求场景。平季需求,即基准需求hij,采用OAG数据计算;高低等级需求按深航博士后创新实践基地研究,设为1.14hij和0.87hij。根据基地的研究,需求发生的概率由高等级至低等级依次为0.371、0.488和0.141。
根据OAG数据统计得出,东航在任意主协调机场的运力份额不超过20%,因此将航空公司在每个潜在枢纽机场能够得到的容量情形设置为机场容量包络曲线最大值的5%、10%、15%和20%。枢纽机场的建设成本与容量情形有关,用式(31)表示:

(31) 式中:ρk为一个常量参数,与机场的规模经济效应有关。当ρk>1时表示机场繁忙,航空公司增加在机场的容量份额就得付出更高的单位容量建设成本;当ρk < 1时表示机场不是繁忙机场,增加容量能够减少枢纽机场的单位容量建设成本。本文定义主协调机场SZX、XIY、URC、CSX、WUH、CTU、PVG、NKG、PEK、KMG为繁忙机场,设ρk=1.1;其余机场为非繁忙机场,设ρk=0.9。根据东航2017年公司年报,推断的枢纽机场建设成本如表 2所示。
表 2 不同容量情形下的枢纽建设成本Table 2. Hub construction cost under different capacity scenarios107元 机场代码 pk1=0.05 pk2=0.1 pk3=0.15 pk4=0.2 SZX 89 195.8 323.1 473.8 XIY 85 187 308.6 452.5 CGO 80 144 194.4 233.3 URC 68 149.6 246.8 362 CSX 73 160.6 265.0 388.7 WUH 82 180.4 297.7 436.6 CTU 88 193.6 319.4 468.5 PVG 90 198 326.7 479.2 NKG 78 171.6 283.1 415.3 SHE 75 135 182.3 218.7 PEK 95 209 344.9 505.8 TYN 73 131.4 177.4 212.9 KMG 88 193.6 319.4 468.5 假设每位旅客的单位运输成本相同,则任意2个OD之间的运输成本与航线距离成正比,因此用航线距离来计算其运输成本。
为验证折扣因子的灵敏度,计算3组不同折扣因子取值下的优化模型,取α=γ。根据Yang[12]的研究结果,α和γ的范围为0.7~0.9,β的范围为0.6~0.8。同时考虑网络的规模效应,OD需求越大,成本折扣越大。折扣因子的取值见表 3。
表 3 不同需求情形下的折扣因子Table 3. Discount factors for different demand scenarios需求
情形情形1 情形2 情形3 α1, γ1 β1 α2, γ2 β2 α3, γ3 β3 低 0.95 0.85 0.85 0.75 0.75 0.65 中 0.9 0.8 0.8 0.7 0.7 0.6 高 0.85 0.75 0.75 0.65 0.65 0.55 3.2 结果展示
运用MATLAB求解DEP模型,得到不同折扣因子情形下的枢纽选址结果如表 4所示。
表 4 折扣灵敏度下的枢纽选址结果Table 4. Results of hub location under discount sensitivity折扣因子
情形枢纽点
(容量水平)目标函数值/
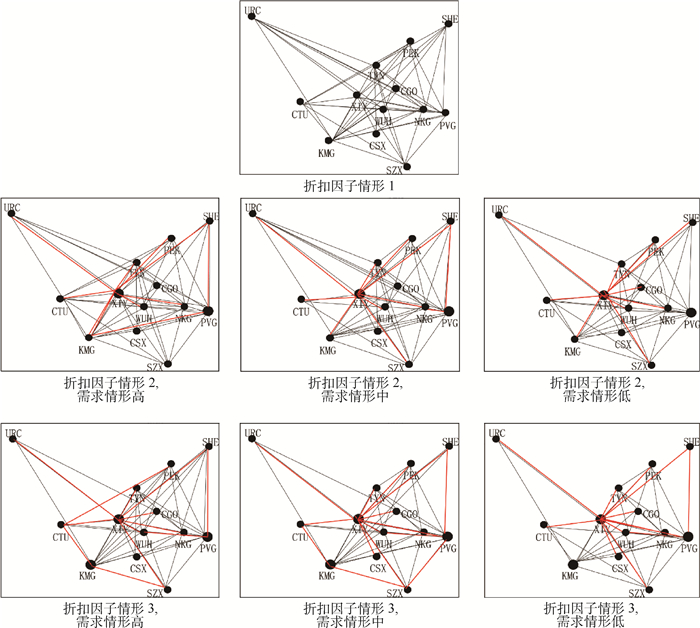
(1010元)情形1 无 2.31 情形2 XIY(10%)、PVG(5%) 2.27 情形3 XIY(10%)、PVG(5%)、KMG(10%) 2.11 通过对结果中的流变量值进行分析,绘制了不同需求情形、不同折扣因子情形下的航空公司航线网络,如图 5所示。图中的黑圆点表示不同折扣因子情形下的枢纽点。
由图 5可以看出,在折扣因子情形1下,由于折扣较小,折扣不足以抵消枢纽的建设成本,模型得出的网络是完全的点对点网络,任意2个节点之间直达运输。在折扣因子情形2下,选择XIY、PVG作为枢纽,选择的容量水平分别是10%、5%,网络中一部分OD直达运输,一部分OD通过枢纽中转运输。不同OD需求情形下的网络间存在较小的差异,随着需求的下降,原本直达或通过浦东机场中转运输的OD转向西安中转,这是因为中转和直达2种运输方式的成本存在差异,当受到中转成本最低的枢纽机场容量限制时,一些OD转向成本次低的路径运输,需求高的时候这种现象更加显著。在折扣因子情形3下,选择XIY、PVG、KMG 3个机场作为枢纽,选择的容量水平分别是10%、5%、10%。随着OD需求的变化,网络间的差异与折扣因子情形2下的变化趋势相同。
表 5、表 6分别列出了折扣因子情形2和折扣因子情形3下,不同OD需求情形下需要中转的OD、中转点和路径流比例,表中来回运输路径相同的城市之间只列一个OD。从表 5、表 6可以再次看出不同需求情形下OD的中转差异。表 5中的KMG-SHE、KMG-TYN、SZX-TYN,表 6中的WUH-SHE、PVG-URC、CTU-WUH、SZX-NKG都选择了2条路径,这是由于目标函数是整个网络总成本最小,不同容量的枢纽建设成本不同,模型会选择使得整个网络总成本最小的枢纽容量,因此这些OD会选择成本最低的路径运送一部分流量,剩余流量选择次低成本的路径运输。
表 5 折扣因子情形2下的中转情况Table 5. Transit in discount factor Case 2需求情形 OD 中转点 路径流比例 高 KMG-TYN XIY 0.3756 无 0.6244 KMG-SHE XIY 0.9825 PVG 0.0175 WUH-URC XIY 1 KMG-PEK XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 SHE-CTU XIY 1 中 TYN-SZX XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 KMG-PEK XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 SHE-CTU XIY 1 KMG-TYN XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 TUN-CTU XIY 1 SHE-NKG XIY 1 KMG-SHE XIY 1 SZX-TYN XIY 0.2678 无 0.7322 低 TYN-SZX XIY 1 URC-CGO XIY 1 KMG-TYN XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 NKG-CTU XIY 1 SHE-CTU XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 TYN-CTU XIY 1 KMG-SHE XIY 1 KMG-PEK XIY 1 表 6 折扣因子情形3下的中转情况Table 6. Transit in discount factor Case 3需求情形 OD 中转点 路径流比例 高 WUH-SHE PVG 0.2179 无 0.7821 SHE-CTU XIY 1 URC-CGO XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 CTU-SZX KMG 1 TYN-SZX XIY 1 TUN-CTU XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 TYN-URC XIY 1 SHE-WUH PVG 1 NKG-CTU XIY 1 中 CTU-SZX KMG 1 TYN-SZX XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 NKG-CTU XIY 1 URC-CGO XIY 1 PVG-URC XIY 0.6745 无 0.3255 SHE-CTU XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 TYN-CTU XIY 1 TYN-CSX XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 CTU-WUH XIY 0.9383 无 0.0617 SHE-WUH PVG 1 TYN-CTU XIY 1 SZX-NKG PVG 0.5016 无 0.4984 SHE-NKG PVG 1 低 TYN-SZX XIY 1 URC-CGO XIY 1 TYN-URC XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 PVG-URC XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 TYN-CSX XIY 1 CTU-WUH XIY 1 SHE-WUH PVG 1 NKG-CTU XIY 1 SHE-CTU XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 TYN-CTU XIY 1 SHE-NKG PVG 1 与随机规划模型相对应的是传统的确定性模型。传统的确定性模型包含2类:
1) 若每种需求情形发生的概率为1,将3种需求情形分别代到确定性模型中单独求解,得到3种不同的解,将这个解按照本文中的概率分布加权求和,即期望最优成本。但每一种情形下求得的枢纽选择可能不同,枢纽选择是航空公司的战略选择,较长一段时间内不会随需求而变。
2) 不同需求以一定概率发生,求得3种需求的期望值,将这一期望需求作为平均需求代入确定性模型可以得到一个最优的网络成本。
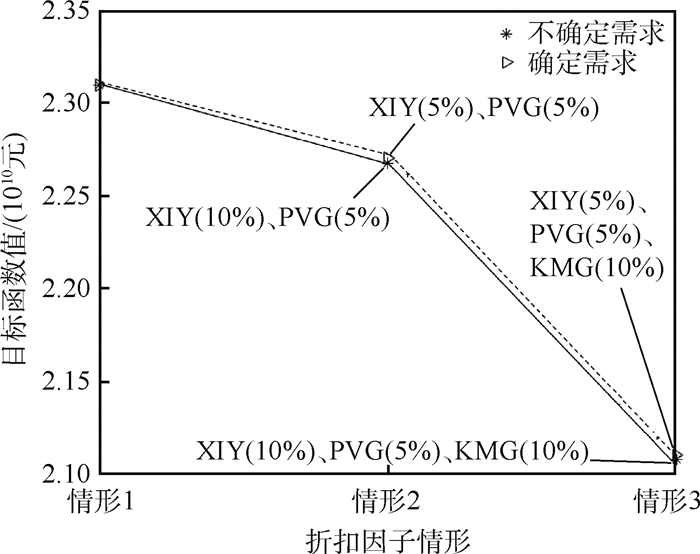
这2种模型,第1种成本上占优,但是若要达到最优成本,必须要视需求变动枢纽选择,对公司长期发展不利。因此本文中比对第2种确定性模型和DEP模型之间的成本和枢纽选择的差异, 如图 6所示。图中虚线上的枢纽表示确定需求下的选择,实线上的枢纽表示不确定需求下的选择,可以看出当折扣因子相同时,需求确定和不确定两种情况下枢纽选址结果存在差异,且不确定需求下的网络总成本更低。
4. 结论
1) 从航空公司的角度出发研究枢纽航线网络的选址问题,考虑OD需求的随机性和枢纽机场容量多水平决策,基于机场容量包络曲线,构建了随机需求下有容量限制的多分配、非严格的两阶段混合整数随机规划模型,并将两阶段模型转化为确定的等价规划。
2) 在考虑机场容量限制时,为了让模型更加贴近实际,将机场的容量表示为到港和离港航班的函数,绘制机场容量包络曲线,获得枢纽机场的容量限制。
3) 对运输成本折扣因子进行灵敏度分析,结果表明在不同的折扣因子情形下选择的枢纽机场不同,折扣越大,选择的枢纽越多,网络总成本越低。当折扣因子一定、需求不同时,OD的运输路径有所差异,流量分配也不同。
4) 通过对比需求确定和不确定下的结果差异,得出需求不确定下的网络总成本更低。说明随机规划模型更能适应航空公司的发展需求,帮助航空公司规划布局航线网络。
-
表 1 机场容量包络曲线系数
Table 1. Airport capacity envelope curve coefficient
机场
所在地机场
代码ask bsk Uskmax/(106人) a1k a2k a3k b1k b2k b3k U1kmax U2kmax U3kmax 深圳 SZX 1 0 1 0 1 0.882 40.64 39.29 63.69 西安 XIY 1 0 1 0 1 1.034 41.37 40.33 64.43 郑州 CGO 1 0 1 0 1 1.029 24.16 24.88 38.24 乌鲁木齐 URC 1 0 1 0 1 1.001 29.45 28.51 43.77 长沙 CSX 1 0 1 0 1 0.906 21.77 21.36 34.08 武汉 WUH 1 0 1 0 1 1.167 22.71 21.88 38.80 成都 CTU 1 0 1 0 1 0.862 40.54 39.19 58.77 浦东 PVG 1 0 1 0 1 1.013 55.88 54.64 80.25 南京 NKG 1 0 1 0 1 0.548 25.61 26.85 34.42 沈阳 SHE 1 0 1 0 1 0.618 25.51 23.43 32.95 北京 PEK 1 0 1 0 1 0.717 85.74 56.71 92.80 太原 TYN 1 0 1 0 1 0.530 15.86 13.69 19.60 昆明 KMG 1 0 1 0 1 0.713 48.52 43.34 64.20 表 2 不同容量情形下的枢纽建设成本
Table 2. Hub construction cost under different capacity scenarios
107元 机场代码 pk1=0.05 pk2=0.1 pk3=0.15 pk4=0.2 SZX 89 195.8 323.1 473.8 XIY 85 187 308.6 452.5 CGO 80 144 194.4 233.3 URC 68 149.6 246.8 362 CSX 73 160.6 265.0 388.7 WUH 82 180.4 297.7 436.6 CTU 88 193.6 319.4 468.5 PVG 90 198 326.7 479.2 NKG 78 171.6 283.1 415.3 SHE 75 135 182.3 218.7 PEK 95 209 344.9 505.8 TYN 73 131.4 177.4 212.9 KMG 88 193.6 319.4 468.5 表 3 不同需求情形下的折扣因子
Table 3. Discount factors for different demand scenarios
需求
情形情形1 情形2 情形3 α1, γ1 β1 α2, γ2 β2 α3, γ3 β3 低 0.95 0.85 0.85 0.75 0.75 0.65 中 0.9 0.8 0.8 0.7 0.7 0.6 高 0.85 0.75 0.75 0.65 0.65 0.55 表 4 折扣灵敏度下的枢纽选址结果
Table 4. Results of hub location under discount sensitivity
折扣因子
情形枢纽点
(容量水平)目标函数值/
(1010元)情形1 无 2.31 情形2 XIY(10%)、PVG(5%) 2.27 情形3 XIY(10%)、PVG(5%)、KMG(10%) 2.11 表 5 折扣因子情形2下的中转情况
Table 5. Transit in discount factor Case 2
需求情形 OD 中转点 路径流比例 高 KMG-TYN XIY 0.3756 无 0.6244 KMG-SHE XIY 0.9825 PVG 0.0175 WUH-URC XIY 1 KMG-PEK XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 SHE-CTU XIY 1 中 TYN-SZX XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 KMG-PEK XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 SHE-CTU XIY 1 KMG-TYN XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 TUN-CTU XIY 1 SHE-NKG XIY 1 KMG-SHE XIY 1 SZX-TYN XIY 0.2678 无 0.7322 低 TYN-SZX XIY 1 URC-CGO XIY 1 KMG-TYN XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 NKG-CTU XIY 1 SHE-CTU XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 TYN-CTU XIY 1 KMG-SHE XIY 1 KMG-PEK XIY 1 表 6 折扣因子情形3下的中转情况
Table 6. Transit in discount factor Case 3
需求情形 OD 中转点 路径流比例 高 WUH-SHE PVG 0.2179 无 0.7821 SHE-CTU XIY 1 URC-CGO XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 CTU-SZX KMG 1 TYN-SZX XIY 1 TUN-CTU XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 TYN-URC XIY 1 SHE-WUH PVG 1 NKG-CTU XIY 1 中 CTU-SZX KMG 1 TYN-SZX XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 NKG-CTU XIY 1 URC-CGO XIY 1 PVG-URC XIY 0.6745 无 0.3255 SHE-CTU XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 TYN-CTU XIY 1 TYN-CSX XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 CTU-WUH XIY 0.9383 无 0.0617 SHE-WUH PVG 1 TYN-CTU XIY 1 SZX-NKG PVG 0.5016 无 0.4984 SHE-NKG PVG 1 低 TYN-SZX XIY 1 URC-CGO XIY 1 TYN-URC XIY 1 WUH-URC XIY 1 PVG-URC XIY 1 NKG-URC XIY 1 TYN-CSX XIY 1 CTU-WUH XIY 1 SHE-WUH PVG 1 NKG-CTU XIY 1 SHE-CTU XIY 1 PEK-CTU XIY 1 TYN-CTU XIY 1 SHE-NKG PVG 1 -
[1] O'KELLY M E.A quadratic integer program for the location of interacting hub facilities[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 1987, 32(3):393-404. doi: 10.1016-S0377-2217(87)80007-3/ [2] CAMPBELL J F.Integer programming formulations of discrete hub location problems[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 1994, 72(2):387-405. [3] SKORIN-KAPOV D, SKORIN-KAPOV J, O'KELLY M E.Tight linear programming relaxations of uncapacitated p-hub median problems[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 1996, 94(3):582-593. [4] ERNST A, KRISHNAMOORTHY M.Efficient algorithms for the uncapacitated single allocation p-hub median problem[J].Location Science, 1996, 4(3):139-154. doi: 10.1016-S0966-8349(96)00011-3/ [5] YANG T H.Airline network design problem with different airport capacity constraints[J].Transportmetrica A:Transport Science, 2008, 4(1):33-49. [6] 冯乾, 乐美龙, 韩晓龙.机场容量限制下的多重分派枢纽航线网络设计[J].工业工程, 2015, 18(3):146-151.FENG Q, LE M L, HAN X L.Design of hub-and-spoke airline network based on capacitated constraints and multiple allocation[J].Industrial Engineering Journal, 2015, 18(3):146-151(in Chinese). [7] WU W W, ZHENG S L.Research on airline network design under hub airport capacity uncertainty[C]//14th COTA International Conference of Transportation Professionals, 2014: 3254-3266. [8] WU W W, ZHANG H Y, WEI W B.Optimal design of hub-and-spoke networks with access to regional hub airports:A case for the Chinese regional airport system[J].Transportmetrica A:Transport Science, 2017, 14(4):330-345. [9] CORREIA I, NICKEL S, SALDANHA-DA-GAMA F.Single-assignment hub location problems with multiple capacity levels[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 2010, 44(8):1047-1066. [10] ZAREI V.A multi-level capacity approach to the hub and spoke network[J].International Journal of Industrial Engineering & Production Research, 2013, 24(1):1-15. [11] SEYED S M, HOSSEIN K, ALI A K, et al.Airline hub-and-spoke network design based on airport capacity envelope curve:A practical view[J].Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2018, 125:375-393. [12] YANG T H.A two-stage stochastic model for airline network design with uncertain demand[J].Transportmetrica, 2010, 6(3):187-213. [13] YANG T H, CHIU T Y.Airline hub-and-spoke system design under stochastic demand and hub congestion[J].Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering, 2016, 33(2):69-76. [14] ALUMUR S A, NICKEL S, SALDANHA-DA-GAMA F.Hub location under uncertainty[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological, 2012, 46(4):529-543. [15] QIN Z F, GAO Y.Uncapacitated p-hub location problem with fixed costs and uncertain flows[J].Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 2017, 28(3):705-716. [16] CONTRERAS I, CORDEAU J F, LAPORTE G.Stochastic uncapacitated hub location[J].European Journal of Operational Research, 2011, 212(3):518-528. [17] 胡青蜜, 胡志华.考虑不确定货流及其影响的轴辐式网络随机规划模型[J].华中师范大学学报(自然科学版), 2014, 48(2):197-205.HU Q M, HU Z H.Stochastic programming model for flow uncertainty and its effects on hub-and-spoke network[J].Journal of Huazhong Normal University (Natural Science), 2014, 48(2):197-205(in Chinese). -








 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载: