Simultaneous inversion of fractal morphology and particle size distribution of soot aggregate based on light scattering intensity
-
摘要:
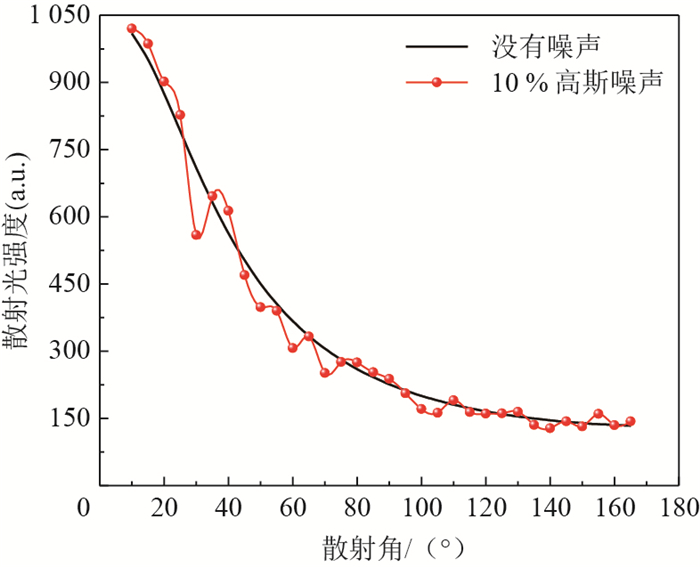
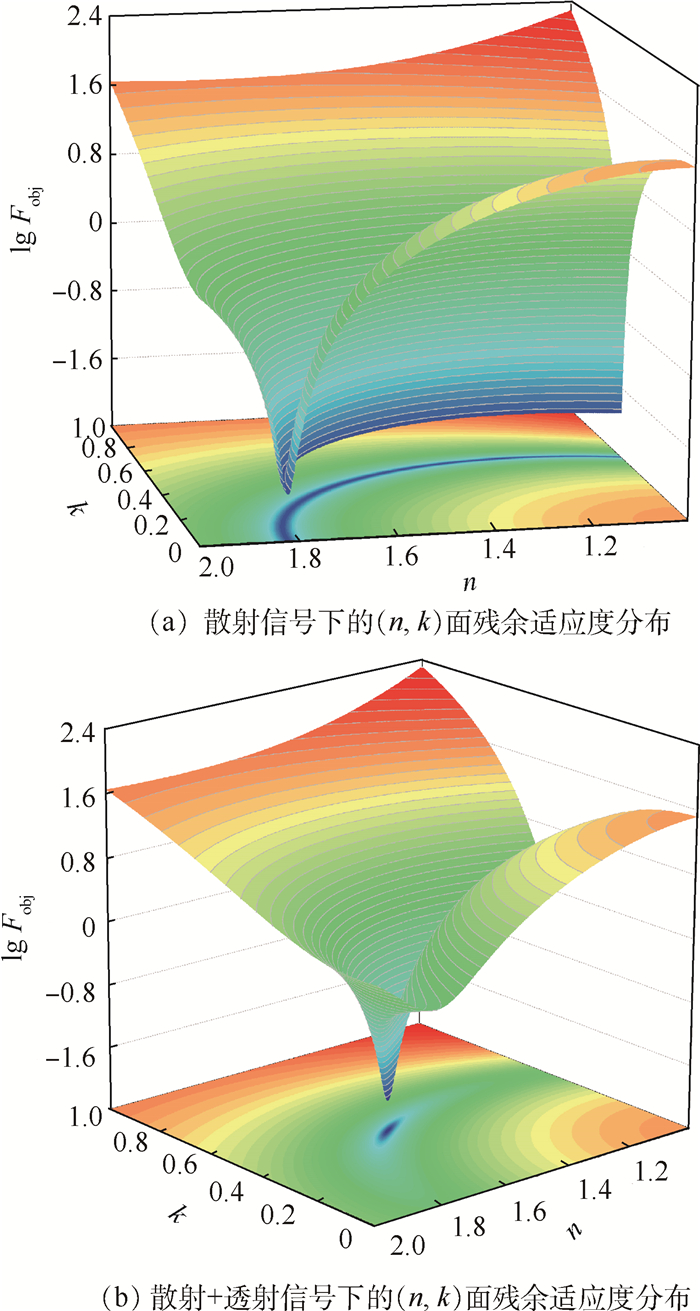
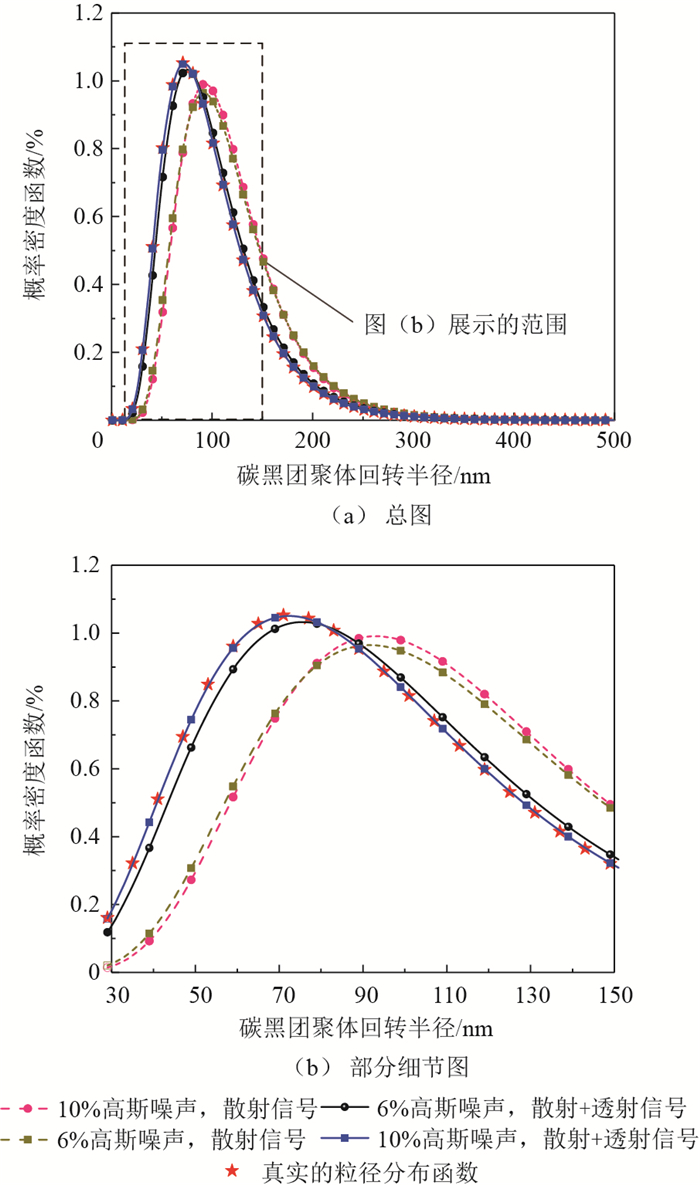
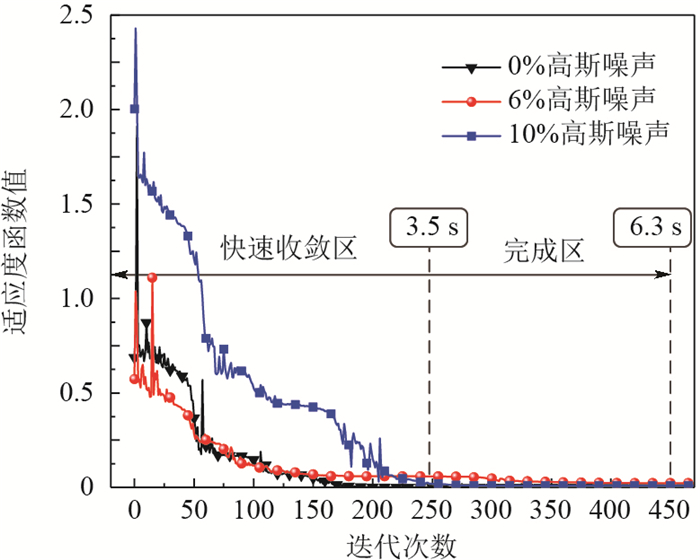
利用散射光信号实现碳黑团聚体分形结构和粒径分布参数的同时反演,在火焰辐射换热模拟和污染物测定方面有着重要应用价值。反演的正问题基于瑞利-德拜-甘斯多分散分形团聚体(RDG-PFA)散射理论,研究了2种信号方案,包括多角度散射及多角度散射-准直透射率。反演前,对比2种信号方案的残余适应度值分布发现,散射与透射信号同时使用有效减弱了反问题的病态性。反演过程基于协方差矩阵自适应的演化策略(CMA-ES)算法,该算法具有很强的局部搜索能力,为快速且稳定地反演各个目标参数提供了保障。反演结果表明了CMA-ES算法较大搜索空间内的可行性和普适性,同时也证明了采用多角度散射-准直透射率的组合信号有效提高了目标参数的反演精度。
Abstract:The use of light scattering signals to achieve the simultaneous inversion of the fractal morphology and particle size distribution parameters of soot aggregates have important application value in flame radiation heat transfer simulation and pollution control. The direct model of inversion is based on the Rayleigh-Debye-Gans Polydisperse Fractal Approximation (RDG-PFA) light scattering theory. Two signal schemes were investigated: multi-angle scattering, multi-angle scattering and collimated transmittance. Before the inversion, by comparing the residual fitness value distributions of the two signal schemes, it is found that the simultaneous use of scattering and transmission signals effectively reduces the ill-posedness of the inverse problem. The inversion process is based on the Covariance Matrix Adaptive Evolutionary Strategy (CMA-ES) algorithm, which has a strong local search capability and provides a guarantee for fast and stable inversion of each target parameter. The final inversion results demonstrate the feasibility and universality of the method in a large search space. And it is also proved that the combination of multi-angle scattering and collimated transmittance effectively improves the inversion accuracy of the target parameters.
-
Key words:
- light scattering /
- soot /
- aggregate /
- fractal dimension /
- inverse problems /
- optimization algorithm
-
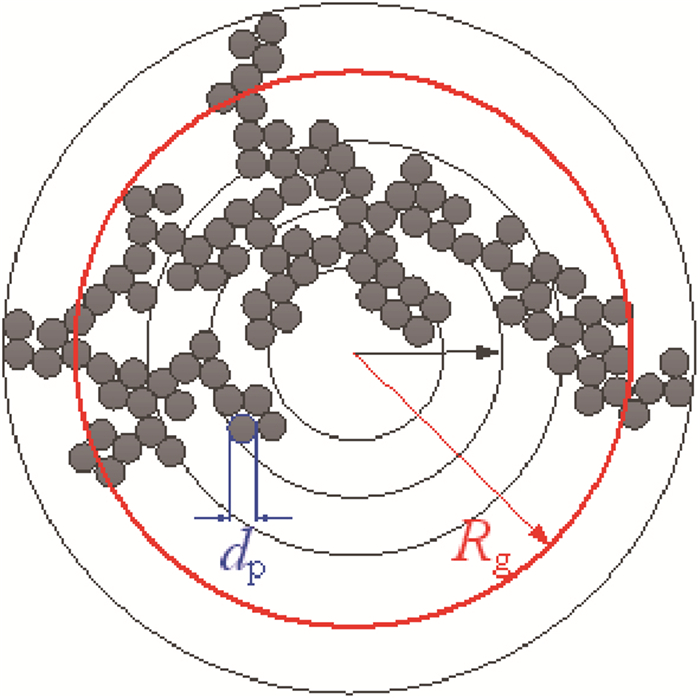
表 1 目标参数的真实值和搜索范围
Table 1. Original value and search range of target parameters
目标参数 真实值 搜索范围 C 0.8 [0, 10] Df 1.65 [1,3] μg/nm 90 [0, 500] σg 1.6 [0, 10] 表 2 CMA-ES算法的参数设定值
Table 2. Parameter value setting of CMA-ES algorithm
参数 设定值 maxgens 1000 eps 10-10 表 3 不同高斯噪声下使用不同信号方案的目标参数反演结果
Table 3. Inversion results of target parameters obtained by different signal schemes under different Gaussian noise
目标参数 真实值 高斯噪声/% 散射 散射+透射 平均结果 εrel/% 标准差 平均结果 εrel/% 标准差 C 0.8 0 0.8000 0 6.05×10-5 0.8000 0 1.10×10-4 6 0.8563 7.03 1.73×10-1 0.7929 0.89 6.19×10-2 10 0.8323 4.04 1.37×10-1 0.8010 0.12 1.03×10-1 Df 1.65 0 1.650 0 9.57×10-5 1.600 0 1.58×10-5 6 1.600 3.06 1.39×10-1 1.654 0.24 5.67×10-2 10 1.615 2.12 1.49×10-1 1.645 0.29 9.02×10-2 μg/nm 90 0 90.00 0 2.25×10-2 90.00 0 1.33×10-5 6 108.81 20.90 2.99×101 90.25 0.28 9.35 10 109.17 21.30 3.75×101 93.38 3.75 1.77×101 σg 1.6 0 1.600 0 1.10×10-4 1.650 0 2.29×10-3 6 1.513 5.45 1.48×10-1 1.600 0 3.79×10-2 10 1.491 6.78 2.05×10-1 1.584 0.97 7.03×10-2 -
[1] BOND T C, BERGSTROM R W.Light absorption by carbonaceous particles:An investigative review[J].Aerosol Science and Technology, 2006, 40(1):27-67. doi: 10.1080/02786820500421521 [2] 李红红.航空发动机二维模型燃烧室中碳黑颗粒生成数值模拟[D].南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2008: 1-3.LI H H.Research on numerical simulation of soot formation in a 2-D simplified gas turbine combustor[D].Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2008: 1-3(in Chinese). [3] 张群杰.航空发动机燃烧室中辐射换热的数值研究[D].沈阳: 沈阳航空航天大学, 2012: 1-3.ZHANG Q J.Numerical study of radiative transfer in areo-engine combustor[D].Shenyang: Shenyang Aerospace University, 2012: 1-3(in Chinese). [4] RAMANATHAN V, CARMICHAEL G.Global and regional climate changes due to black carbon[J].Nature Geoscience, 2008, 1(4):335-358. [5] GRAHAM T J, SCHLESINGER R B.Cardiovascular health and particulate vehicular emissions:A critical evaluation of the evidence[J].Air Quality Atmosphere & Health, 2010, 3(1):3-27. doi: 10.1007-s11869-009-0047-x/ [6] LUO J, ZHANG Y, ZHANG Q, et al.Sensitivity analysis of morphology on radiative properties of soot aerosols[J].Optics Express, 2018, 26(10):A420. doi: 10.1364/OE.26.00A420 [7] SORENSEN C M, CAI J, LU N.Light-scattering measurements of monomer size, monomers per aggregate, and fractal dimension for soot aggregates in flames[J].Applied Optics, 1992, 31(30):6547-6557. doi: 10.1364/AO.31.006547 [8] IYER S S, LITZINGER T A, LEE S Y, et al.Determination of soot scattering coefficient from extinction and three-angle scattering in a laminar diffusion flame[J].Combustion & Flame, 2007, 149(1-2):206-216. [9] LINK O, SNELLING D R, THOMSON K A, et al.Development of absolute intensity multi-angle light scattering for the determination of polydisperse soot aggregate properties[J].Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2011, 33(1):847-854. [10] AMIN H M F, ROBERTS W L.Soot measurements by two angle scattering and extinction in an N2-diluted ethylene/air counterflow diffusion flame from 2 to 5 atm[J].Proceedings of the Combustion Institute, 2016, 36(1):861-869. [11] MOGHADDAM S T, HADWIN P J, DAUN K J.Soot aggregate sizing through multiangle elastic light scattering:Influence of model error[J].Journal of Aerosol Science, 2017, 111:36-50. doi: 10.1016/j.jaerosci.2017.06.003 [12] SORENSEN C M.Light scattering by fractal aggregates:A review[J].Aerosol Science and Technology, 2001, 35(2):648-687. doi: 10.1080/02786820117868 [13] MISHCHENKO M I, TRAVIS L D, LACIS A A.Scattering, absorption, and emission of light by small particles[M].Cambridge:Cambridge University Press, 2002:101-442. [14] OLTMANN H, REIMANN J, WILL S.Wide-angle light scattering (WALS) for soot aggregate characterization[J].Combustion & Flame, 2010, 157(3):516-522. [15] OLTMANN H, REIMANN J, WILL S.Single-shot measurement of soot aggregate sizes by wide-angle light scattering (WALS)[J].Applied Physics B, 2012, 106(1):171-183. [16] HANSEN N.The CMA evolution strategy: A tutorial[EB/OL].(2016-04-04)[2019-06-20]. [17] DALZELL W H, SAROFIM A F.Optical constants of soot and their application to heat-flux calculations[J].Journal of Heat Transfer, 1969, 91(1):100-104. doi: 10.1115/1.3580063 -







 下载:
下载: