-
摘要:
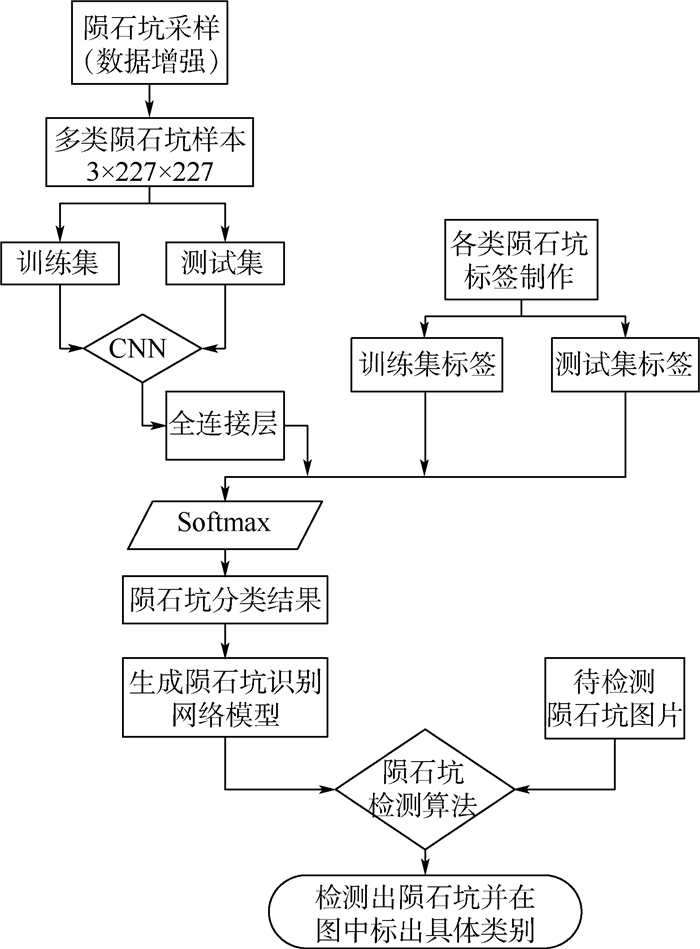
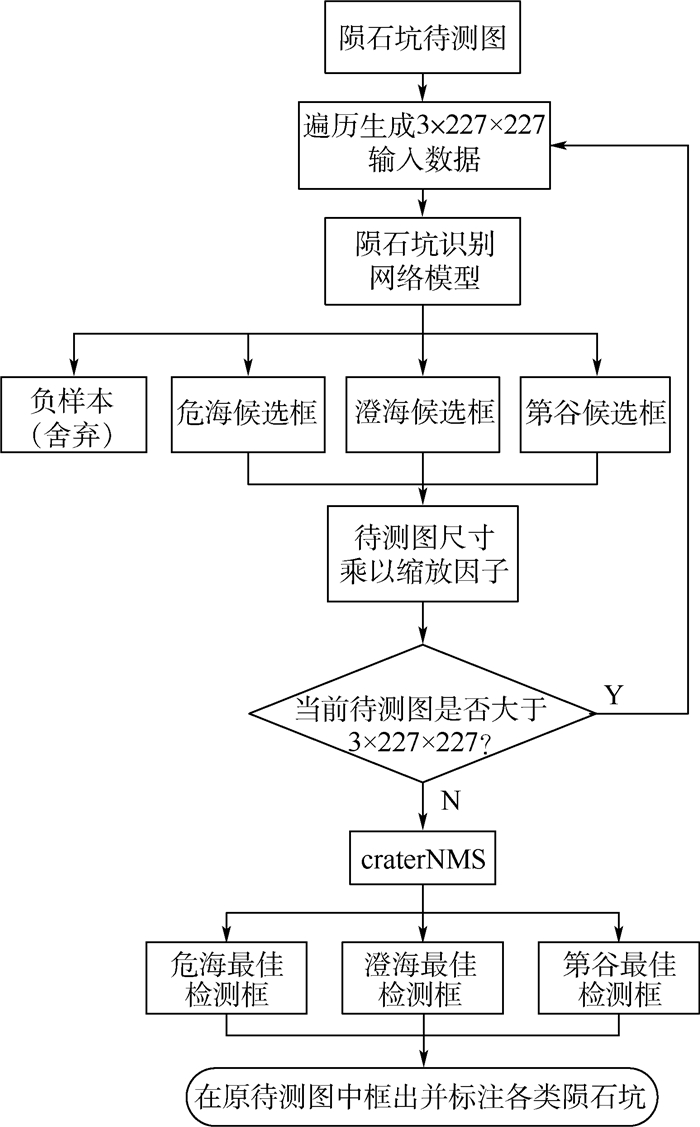
陨石坑是天体表面最为显著的地形特征,传统陨石坑识别方法主要是对小型陨石坑正负样本的二分类问题研究,且效率和精度均不高。以星体宏观视角下的大型陨石坑作为研究对象,结合图像处理和神经网络等方面的知识,创建了来自不同数据源的陨石坑样本数据库,研究了数据源对网络模型泛化能力的影响,提出了一种效率更高的陨石坑多分类识别方法。在非极大值抑制(NMS)算法基础上,提出了一种精度更高的陨石坑检测算法。经过参数优化和实验验证,构建的基于深度学习的多尺度多分类陨石坑自动识别网络框架取得了较高的准确率,在同源验证集上识别率可达0.985,在异源验证集上识别率可达0.863,并且有效改善了目标检测时检测框冗余及误检测的问题。
-
关键词:
- 深度学习 /
- 卷积神经网络 /
- 陨石坑识别 /
- 非极大值抑制(NMS)算法 /
- 目标检测
Abstract:Craters are the most significant topographic features on the surface of celestial bodies. The traditional method of craters identification is mainly to study the dichotomy of positive and negative samples of small craters, with low efficiency and accuracy. This paper takes large craters under the macroscopic view of the planet as the research object, combines the knowledge of digital image processing and neural network, creates a crater sample library of different data sources to study the influence of data source on network model generalization ability, and proposes a more efficient crater multi-classification identification method. Based on the Non-Maximum Suppression (NMS) algorithm, a higher precision crater detection algorithm is proposed. Through parameter optimization and experimental verification, the multi-scale and multi-classification craters automatic recognition network framework based on deep learning constructed in this paper achieves a high accuracy rate, with the recognition rate up to 0.985 on homologous verification set and 0.863 on heterogeneous verification set, and effectively improves the redundancy of detection box and false detection in target detection.
-
表 1 数据增强后各类样本数
Table 1. Number of different types of samples after data augmentation
样本类别 Ncrater Ccrater NCcrater 危海 10 000 10 000 20 000 澄海 8 500 10 000 18 500 第谷 8 500 10 000 18 500 负样本 16 000 25 000 41 000 总数 43 000 55 000 98 000 表 2 计算机配置参数
Table 2. Computer configuration parameters
计算机配置 具体参数 中央处理器(CPU) Intel(R) Xeon(R) W-2125 CPU @ 4.00 GHz 图形处理器(GPU) NVIDIA GeForce GTX 1070 操作系统 64位Windows10操作系统 运行内存 16 GB 表 3 样本数据集Ncrater训练结果
Table 3. Training results of sample data set Ncrater
优化方法 训练时间/s 准确率 最低损失代价 SGD 1 401 0.998 6 0.007 7 AdaDelta 1 423 0.998 1 0.007 8 Adam 1 414 0.997 8 0.008 8 RMSprop 1 418 0.997 9 0.009 1 表 4 样本数据集Ccrater训练结果
Table 4. Training results of sample data set Ccrater
优化方法 训练时间/s 准确率 最低损失代价 SGD 1 523 0.997 6 0.009 5 AdaDelta 1 533 0.997 1 0.011 2 Adam 1 550 0.996 3 0.015 2 RMSprop 1 551 0.997 2 0.012 5 表 5 样本数据集NCcrater训练结果
Table 5. Training results of sample data set NCcrater
优化方法 训练时间/s 准确率 最低损失代价 SGD 2 124 0.998 6 0.005 4 AdaDelta 2 199 0.995 9 0.012 7 Adam 2 139 0.994 6 0.017 9 RMSprop 2 163 0.993 9 0.016 7 表 6 验证集中各类样本数
Table 6. Number of different types of samples in verification set
样本类别 VNcrater VCcrater 危海 40 50 澄海 40 50 第谷 40 50 负样本 80 100 总数 200 250 表 7 验证集VNcrater上的识别准确率
Table 7. Identification accuracy on verification set VNcrater
样本类别 Nnet Cnet NCnet 危海 1.000 0.625 0.975 澄海 0.975 0.825 1.000 第谷 1.000 1.000 1.000 负样本 0.963 1.000 0.987 总准确率 0.985 0.863 0.991 表 8 验证集VCcrater上的识别准确率
Table 8. Identification accuracy on verification set VCcrater
样本类别 Nnet Cnet NCnet 危海 0.580 0.720 0.820 澄海 0.680 0.980 0.980 第谷 0.640 0.980 1.000 负样本 0.810 1.000 0.980 总准确率 0.678 0.920 0.945 表 9 三种检测算法数据分析
Table 9. Data analysis of three detection algorithms
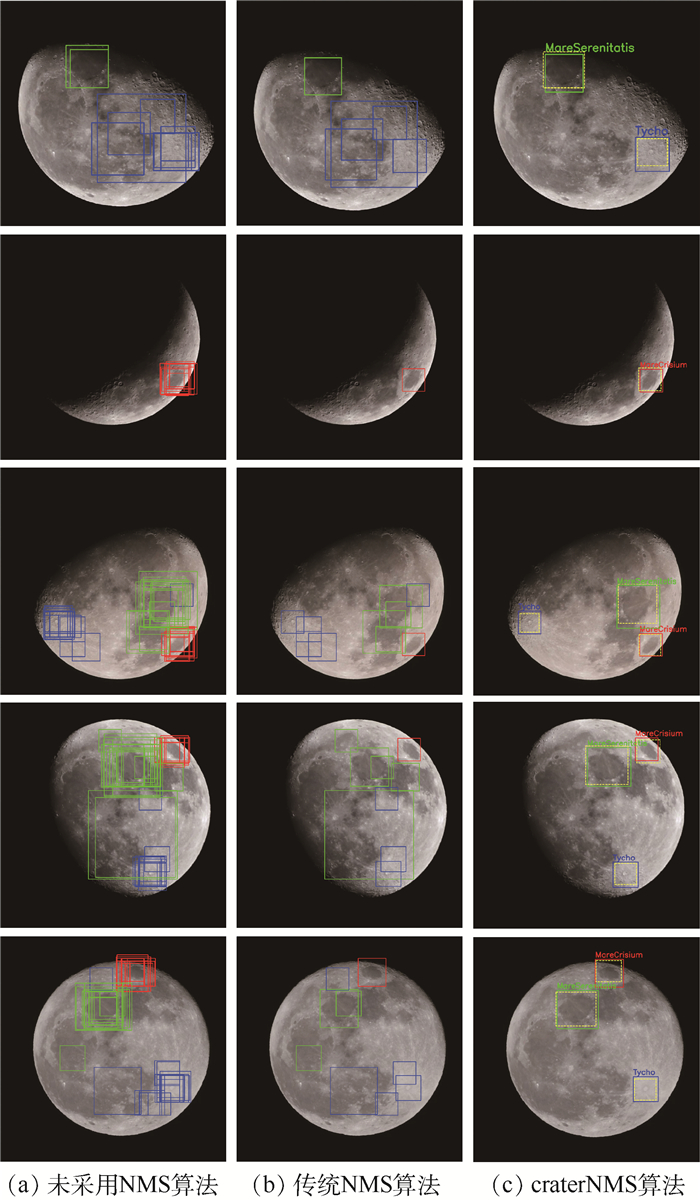
检测算法 P R 未采用NMS算法 0.825 18 传统NMS算法 0.886 6 craterNMS算法 1 0 -
[1] GROUP C A T W, ARVIDSON R E, BOYCE J, et al.Standard techniques for presentation and analysis of crater size-frequency data[J].Icarus, 1979, 37(2):467-474. doi: 10.1016/0019-1035(79)90009-5 [2] PALAFOX L F, HAMILTON C W, SCHEIDT S P, et al.Automated detection of geological landforms on Mars using convolutional neural networks[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2017, 101:48-56. [3] CHENG Y, JOHNSON A E, MATTHIES L H, et al.Optical landmark detection for spacecraft navigation[C]//Proceedings of the 13th Annual AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, 2003: 1785-1803. [4] SAWABE Y, MATSUNAGA T, ROKUGAWA S.Automated detection and classification of lunar craters using multiple approaches[J].Advances in Space Research, 2006, 37(1):21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2005.08.022 [5] KIM J R, MULLER J, VAN GASSELT S, et al.Automated crater detection, a new tool for Mars cartography and chronology[J].Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 2005, 71(10):1205-1217. [6] 冯军华, 崔祜涛, 崔平远, 等.行星表面陨石坑检测与匹配方法[J].航空学报, 2010, 31(9):1858-1863.FENG J H, CUI H T, CUI P Y, et al.Autonomous crater detection and matching on planetary surface[J].Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2010, 31(9):1858-1863(in Chinese). [7] DING M, CAO Y F, WU Q X.Method of passive image based crater autonomous detection[J].Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2009, 22(3):301-306. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(08)60103-X [8] CRACKNELL M J, READING A M.Geological mapping using remote sensing data: A comparison of five machine learning algorithms, their response to variations in the spatial distribution of training data and the use of explicit spatial information[J].Computers & Geosciences, 2014, 63:22-33. [9] CHRISTOFF N, MANOLOVA A, JORDA L, et al.Morphological crater classification via convolutional neural network with application on MOLA data[C]//Advances in Neural Networks and Applications 2018, 2018: 1-5. [10] BARATA T, ALVES E I, SARAIVA J, et al.Automatic recognition of impact craters on the surface of Mars[C]//International Conference Image Analysis and Recognition.Berlin: Springer, 2004: 489-496. [11] BOUKERCHA A, AL-TAMEEMI A, GRUMPE A, et al.Automatic crater recognition using machine learning with different features and their combination[C]//Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, 2014, 45: 2842. [12] SILBURT A, ALI-DIB M, ZHU C, et al.Lunar crater identification via deep learning[J].Icarus, 2019, 317:27-38. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2018.06.022 [13] WRIGHT E.SVS: Moon phase and libration, 2018[EB/OL].(2019-01-28)[2019-06-12]. [14] HEAD J W, ADAMS J B, MCCORD T B, et al.Regional stratigraphy and geologic history of Mare Crisium[C]//Mare Crisium: The View From Luna 24, 1978: 43-74. [15] WATTERS T R, KONOPLIV A S.The topography and gravity of Mare Serenitatis:Implications for subsidence of the mare surface[J].Planetary and Space Science, 2001, 49(7):743-748. doi: 10.1016/S0032-0633(01)00007-1 [16] SOLOMON S C, HEAD J W.Vertical movement in mare basins:Relation to mare emplacement, basin tectonics, and lunar thermal history[J].Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 1979, 84(B4):1667-1682. doi: 10.1029/JB084iB04p01667 [17] SCHULTZ P H, STAID M I, PIETERS C M.Lunar activity from recent gas release[J].Nature, 2006, 444(7116):184-186. doi: 10.1038/nature05303 [18] KRVGER T, VAN DER BOGERT C H, HIESINGER H.Geomorphologic mapping of the lunar crater Tycho and its impact melt deposits[J].Icarus, 2016, 273:164-181. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2016.02.018 [19] ZHANG K, ZUO W, CHEN Y, et al.Beyond a Gaussian denoiser:Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7):3142-3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 [20] DONG C, LOY C C, HE K, et al.Image super-resolution using deep convolutional networks[J].IEEE transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2015, 38(2):295-307. [21] LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T.Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3431-3440. [22] MALTEZOS E, DOULAMIS N, DOULAMIS A, et al.Deep convolutional neural networks for building extraction from orthoimages and dense image matching point clouds[J].Journal of Applied Remote Sensing, 2017, 11(4):42620. [23] ZHANG N, DONAHUE J, GIRSHICK R, et al.Part-based R-CNNs for fine-grained category detection[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2014: 834-849. [24] 黄洁, 姜志国, 张浩鹏, 等.基于卷积神经网络的遥感图像舰船目标检测[J]北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(9):1841-1848. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0755HUAGN J, JIANG Z G, ZHANG H P, et al.Ship object detection in remote sensing images using convolutional neural networks[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(9):1841-1848(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0755 [25] JIAO L, LIANG M, CHEN H, et al.Deep fully convolutional network-based spatial distribution prediction for hyperspectral image classification[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2017, 55(10):5585-5599. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2017.2710079 [26] 韩京冶, 许福, 陈志泊, 等.一种基于深度学习的交互式电话号码识别方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(5):1074-1080. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0357HAN J Y, XU F, CHEN Z B, et al.A deep learning based interactive recognition method for telephone numbers[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(5):1074-1080(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0357 [27] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E.Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012: 1097-1105. [28] RIEDMILLER M, BRAUN H.A direct adaptive method for faster backpropagation learning: The RPROP algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Neural Networks.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1993: 586-591. [29] ZEILER M D, FERGUS R.Visualizing and understanding convolutional networks[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2014: 818-833. [30] ZEILER M D.ADADELTA: An adaptive learning rate method[EB/OL].(2012-12-22)[2019-06-20]. [31] KINGMA D P, BA J.Adam: A method for stochastic optimization[EB/OL].(2014-12-22)[2019-06-20]. [32] TIELEMAN T, HINTON G.RMSPROP:Divide the gradient by a running average of its recent magnitude[J].Neural Networks for Machine Learning, 2012, 4:26-30. -








 下载:
下载: