-
摘要:
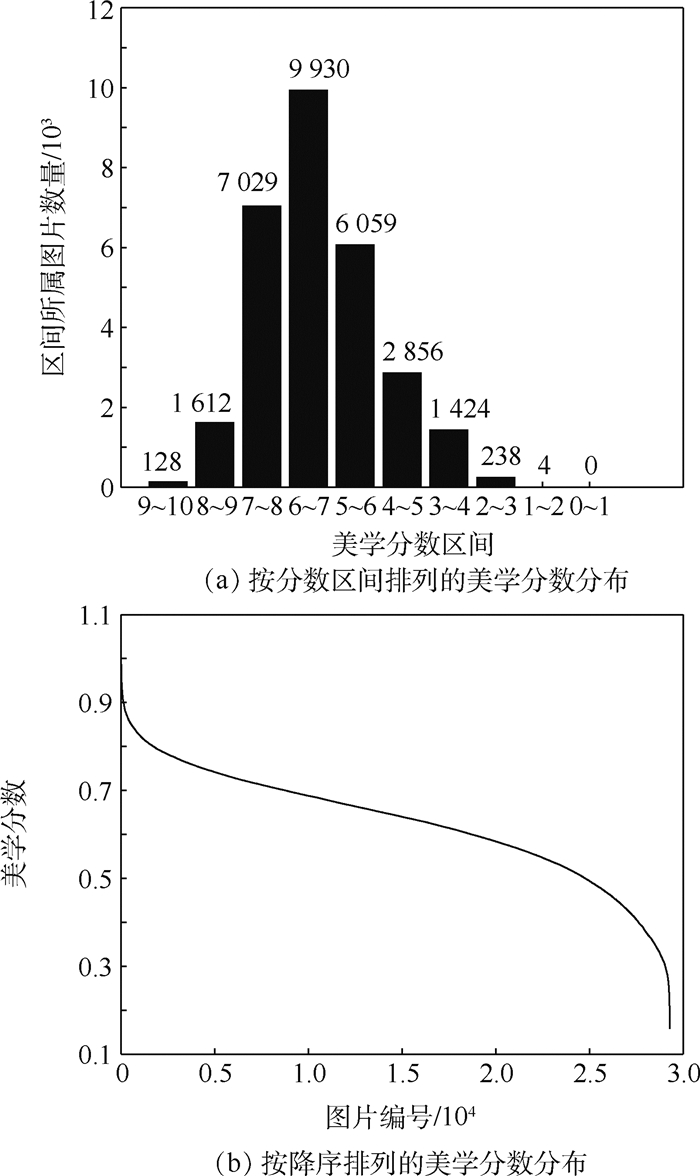
在对抗生成网络(GAN)这一概念的诞生及发展推动下,文本生成图像的研究取得进展和突破,但大部分的研究内容集中于提高生成图片稳定性和解析度的问题,提高生成结果美观度的研究则很少。而计算机视觉中另一项经典的课题——图像美观度评判的研究也在深度神经网络的推动下提出了一些成果可信度较高的美观度评判模型。本文借助美观度评判模型,对实现文本生成图像目标的GAN模型进行了改造,以期提高其生成图片的美观度指标。首先针对StackGAN++模型,通过选定的美观度评判模型从美学角度评估其生成结果;然后通过借助评判模型构造美学损失的方式对其进行优化。结果使得其生成图像的总体美学分数比原模型提高了3.17%,同时Inception Score提高了2.68%,证明所提方法具有一定效果,但仍存在一定缺陷和提升空间。
-
关键词:
- 文本生成图像 /
- 对抗生成网络(GAN) /
- 美观度评判 /
- StackGAN++ /
- 美学损失
Abstract:Due to the development of generative adversarial network (GAN), much progress has been achieved in the research of text-to-image synthesis. However, most of the researches focus on improving the stability and resolution of generated images rather than aesthetic quality. On the other hand, image aesthetic assessment research is also a classic task in computer vision field, and currently there exists several state-of-the-art models on image aesthetic assessment. In this work, we propose to improve the aesthetic quality of images generated by text-to-image GAN by incorporating an image aesthetic assessment model into a conditional GAN. We choose StackGAN++, a state-of-the-art text-to-image synthesis model, assess the aesthetic quality of images generated by it with a chosen aesthetic assessment model, then define a new loss function:aesthetic loss, and use it to improve StackGAN++. Compared with the original model, the total aesthetic score of generated images is improved by 3.17% and the inception score is improved by 2.68%, indicating that the proposed optimization is effective but still has several weaknesses that can be improved in future work.
-
表 1 不同生成数量情况下最高分数与前10平均分数
Table 1. Highest aesthetic score and average of top 10 aesthetic score when generating different quantities of images
图像生成数量 最高分数 前10平均分数 100 0.892 8 0.769 8 200 0.804 2 0.775 3 350 0.845 1 0.788 9 500 0.843 9 0.797 8 750 0.858 4 0.815 5 1 000 0.954 8 0.859 2 表 2 不同β取值对应模型的IS
Table 2. IS of models using different β
β IS 0 4.10±0.06 45 4.05±0.03 1 4.13±0.05 0.000 1 4.21±0.03 表 3 不同β取值对应模型的美学分数对比
Table 3. Comparison of aesthetic scores of models using different β
β 测试集平均分数 0 0.628 3 1 0.600 6 0.000 1 0.648 2 表 4 原模型与优化模型使用24条文本生成1 000张图像的平均美学分数对比
Table 4. Comparison of average aesthetic score of 1 000 images generated by original models and optimized models using 24 different texts
编号 平均美学分数 对比提升量 原模型 β= 0.000 1 1 0.592 9 0.619 2 +0.026 3 2 0.586 6 0.618 0 +0.031 4 3 0.567 1 0.617 0 +0.049 9 4 0.574 1 0.543 3 -0.030 8 5 0.581 9 0.551 5 -0.030 4 6 0.551 0 0.518 8 -0.032 2 7 0.602 4 0.622 1 +0.019 7 8 0.568 8 0.546 7 -0.022 1 9 0.598 7 0.627 9 +0.029 2 10 0.616 6 0.589 0 -0.027 6 11 0.600 8 0.613 8 +0.013 0 12 0.551 1 0.622 7 +0.071 6 13 0.700 7 0.691 3 -0.009 4 14 0.586 2 0.659 6 +0.073 4 15 0.586 8 0.623 2 +0.036 4 16 0.595 1 0.622 7 +0.027 6 17 0.621 7 0.634 5 +0.012 8 18 0.555 0 0.579 2 +0.024 2 19 0.585 9 0.597 4 +0.011 5 20 0.568 9 0.567 3 -0.001 6 21 0.598 8 0.640 5 +0.041 7 22 0.579 4 0.547 7 -0.031 7 23 0.558 7 0.593 0 +0.034 3 24 0.589 0 0.541 9 -0.047 1 -
[1] BODNAR C.Text to image synthesis using generative adversarial networks[EB/OL].(2018-05-02)[2019-07-08]. [2] GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M, et al.Generative adversarial nets[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.Cambridge: MIT Press, 2014: 2672-2680. [3] ZHANG H, XU T, LI H, et al.Stackgan++: Realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks[EB/OL].(2018-06-28)[2019-07-08]. [4] SALIMANS T, GOODFELLOW I, ZAREMBA W, et al.Improved techniques for training gans[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.Cambridge: MIT Press, 2016: 2234-2242. [5] LI Z, TANG J, MEI T.Deep collaborative embedding for social image understanding[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 41(9):2070-2083. [6] DENG Y, LOY C C, TANG X.Image aesthetic assessment:An experimental survey[J].IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2017, 34(4):80-106. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2017.2696576 [7] DATTA R, JOSHI D, LI J, et al.Studying aesthetics in photographic images using a computational approach[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2006: 288-301. doi: 10.1007/11744078_23 [8] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E.ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.Cambridge: MIT Press, 2012: 1097-1105. doi: 10.5555/2999134.2999257 [9] KONG S, SHEN X, LIN Z, et al.Photo aesthetics ranking network with attributes and content adaptation[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2016: 662-679. doi: 10.1007%2F978-3-319-46448-0_40 [10] CHOPRA S, HADSELL R, LECUN Y.Learning a similarity metric discriminatively, with application to face verification[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2005: 539-546. doi: 10.1109/CVPR.2005.202 [11] RADFORD A, METZ L, CHINTALA S.Unsupervised representation learning with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[EB/OL].(2016-01-07)[2019-07-08]. [12] SALIMANS T, GOODFELLOW I, ZAREMBA W, et al.Improved techniques for training gans[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.Cambridge: MIT Press, 2016: 2234-2242. [13] ARJOVSKY M, CHINTALA S, BOTTOU L.Wasserstein gan[EB/OL].(2017-12-06)[2019-07-08]. [14] MIRZA M, OSINDERO S.Conditional generative adversarial nets[EB/OL].(2014-11-06)[2019-07-08]. [15] REED S, AKATA Z, YAN X, et al.Generative adversarial text to image synthesis[EB/OL].(2016-06-05)[2019-07-08]. [16] ZHANG H, XU T, LI H, et al.Stackgan: Text to photo-realistic image synthesis with stacked generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 5907-5915. [17] XU T, ZHANG P, HUANG Q, et al.Attngan: Fine-grained text to image generation with attentional generative adversarial networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 1316-1324. [18] CHA M, GWON Y, KUNG H T.Adversarial nets with perceptual losses for text-to-image synthesis[C]//2017 IEEE 27th International Workshop on Machine Learning for Signal Processing (MLSP).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-6. [19] JOHNSON J, ALAHI A, LI F.Perceptual losses for real-time style transfer and super-resolution[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2016: 694-711. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-46475-6_43 [20] SZEGEDY C, VANHOUCKE V, IOFFE S, et al.Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 2818-2826. -







 下载:
下载:






