-
摘要:
在不同宽高比显示设备上的图像观看体验通常受到图像重定向操作方法的影响。为了提高重定向图像主观感知与客观评估之间的一致性,提出了基于多尺度失真感知特征(MSDA)的客观重定向图像质量评估(RIQA)方法。语义失真和细节失真经常出现在图像的不同尺度上,因此从图像的不同尺度中提取失真感知特征。提出了一个描述原始图像和重定向图像之间的宽高比相似度(ARS)的精确度量。此外,使用视觉注意力融合图来模拟人类视觉系统对图像的主观关注度。在2个基准数据库上的实验结果表明,所提出的MSDA方法的肯德尔排名相关系数(KRCC)、皮尔逊线性相关系数(PLCC)和斯皮尔曼秩次相关系数(SRCC)指标分别比对比方法中最优方法提高4.1%、1.8%和4.5%。
-
关键词:
- 图像重定向 /
- 重定向图像质量评估(RIQA) /
- 视觉注意力融合 /
- 宽高比相似度(ARS) /
- 多尺度
Abstract:The subjective visual experience of viewing images using a variety of display devices is usually affected by image retargeting operation. To improve the consistency between subjective perception and objective assessment for the retargeted images, we present an objective retargeted image quality assessment (RIQA) method based on multi-scale distortion-aware (MSDA) features. Because semantic distortion and detail distortion appear on different scales of the image, we propose to extract distortion-aware features from multiple scales of the image. Specifically, we present an accurate measurement for the aspect ratio similarity (ARS) between the original and retargeted images. Furthermore, we use a fused visual attention map to simulate the subjective attention of the human visual system to the image. The experimental results on the two benchmark databases show that the Kendall rank correlation coefficient (KRCC), Pearson linear correlation coefficient (PLCC), and Spearman rank-order correlation coefficient (SRCC) indicators of the proposed MSDA method are 4.1%, 1.8%, and 4.5% higher than the optimal method in the comparative methods, respectively.
-
表 1 MIT数据库性能对比
Table 1. Performance comparison on MIT database
方法 KRCC KRCC均值 KRCC标准差 p-val 线条 人脸 前景物体 纹理 几何结构 对称结构 BDS 0.040 0.190 0.167 0.060 -0.004 -0.012 0.083 0.268 0.017 SIFTflow 0.097 0.252 0.218 0.161 0.085 0.071 0.145 0.262 0.031 EMD 0.220 0.262 0.226 0.107 0.237 0.500 0.251 0.272 1×10-5 CSim 0.097 0.290 0.293 0.161 0.053 0.150 0.164 0.263 0.028 PGDIL 0.431 0.390 0.389 0.286 0.438 0.523 0.415 0.296 6×10-10 ARS 0.463 0.519 0.444 0.330 0.505 0.464 0.452 0.283 1×10-11 MLF 0.486 0.605 0.544 0.384 0.536 0.536 0.512 0.251 1×10-14 MSDA 0.511 0.633 0.539 0.455 0.571 0.535 0.533 0.265 9×10-21 表 2 MIT数据库特征分析
Table 2. Feature analysis on MIT database
方法 线条 人脸 前景物体 纹理 几何结构 对称结构 KRCC均值 KRCC标准差 QARS+QEGS+QFBS 0.503 0.614 0.532 0.420 0.554 0.500 0.525 0.260 QIAR8+QEGS+QFBS 0.506 0.610 0.456 0.528 0.571 0.512 0.527 0.269 QIAR16+QEGS+QFBS 0.503 0.643 0.455 0.552 0.558 0.512 0.531 0.267 MSDA 0.511 0.633 0.539 0.455 0.571 0.535 0.533 0.265 表 3 CUHK数据库性能对比
Table 3. Performance comparison on CUHK database
方法 PLCC SRCC RMSE OR BDS 0.289 6 0.288 7 12.922 0.216 4 SIFTflow 0.314 1 0.289 9 12.817 0.142 6 EMD 0.276 0 0.290 4 12.977 0.169 6 CSim 0.437 4 0.566 2 12.141 0.152 0 PGDIL 0.540 3 0.540 9 11.361 0.152 0 ARS 0.683 5 0.669 3 9.855 0.070 2 MLF 0.757 7 0.738 3 8.525 0.029 4 MSDA 0.771 3 0.771 7 8.593 0.035 0 表 4 CUHK数据库特征分析
Table 4. Feature analysis on CUHK database
方法 PLCC SRCC RMSE OR QARS+QEGS+QFBS 0.761 0 0.758 5 8.759 6 0.046 8 QIAR8+QEGS+QFBS 0.763 9 0.769 4 8.713 0 0.040 9 QIAR16+QEGS+QFBS 0.770 9 0.766 3 8.599 0.040 9 MSDA 0.771 3 0.771 7 8.593 0.035 0 表 5 MIT数据库不同块尺度特征组合
Table 5. Different block scale feature combinations on MIT database
组合 KRCC均值 KRCC标准差 QIAR8+QIAR16 0.533 0.265 QIAR8+QIAR32 0.529 0.260 QIAR16+QIAR32 0.525 0.267 表 6 CUHK数据库不同块尺度特征组合
Table 6. Different block scale feature combinations on CUHK database
组合 PLCC SRCC RMSE OR QIAR8+QIAR16 0.771 3 0.771 7 8.593 0 0.035 0 QIAR8+QIAR32 0.754 1 0.753 7 8.865 8 0.040 9 QIAR16+QIAR32 0.767 7 0.766 6 8.652 2 0.035 0 表 7 MIT数据库不同显著性检测算法实验结果对比
Table 7. Comparison of experimental results of detection algorithms with different saliency on MIT database
-
[1] RUBINSTEIN M, SHAMIR A, AVIDAN S.Multi-operator media retargeting[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2009, 28(3):23. [2] AVIDAN S, SHAMIR A.Seam carving for content-aware image resizing[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2007, 26(3):10. doi: 10.1145/1276377.1276390 [3] PRITCH Y, KAV-VENAKI E, PELEG S.Shift-map image editing[C]//IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2009: 151-158. [4] WANG Y S, TAI C L, SORKINE O, et al.Optimized scale-and-stretch for image resizing[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2008, 27(5):118. [5] KRÄHENBVHL P, LANG M, HORNUNG A, et al.A system for retargeting of streaming video[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2008, 28(5):126. doi: 10.1038-clpt.2011.14/ [6] WOLF L, GUTTMANN M, COHEN-OR D.Non-homogeneous content-driven video-retargeting[C]//IEEE 11th International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 1-6. [7] RUBINSTEIN M, GUTIERREZ D, SORKINE O, et al.A comparative study of image retargeting[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2010, 29(6):160. [8] MA L, LIN W, DENG C, et al.Image retargeting quality assessment:A study of subjective scores and objective metrics[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2012, 6(6):626-639. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2012.2211996 [9] SIMAKOV D, CASPI Y, SHECHTMAN E, et al.Summarizing visual data using bidirectional similarity[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2008: 1-8. [10] LIU Y J, LUO X, XUAN Y M, et al.Image retargeting quality assessment[J].Computer Graphics Forum, 2011, 30(2):583-592. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2011.01881.x [11] ZHANG Y, FANG Y, LIN W, et al.Backward registration based aspect ratio similarity for image retargeting quality assessment[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2016, 25(9):4286-4297. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2016.2585884 [12] ZHANG Y, LIN W, LI Q, et al.Multiple-level feature-based measure for retargeted image quality[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(1):451-463. [13] ZHANG S, NIU Y Z, LIN J W, et al.Visual attention fusion framework for image retargeting quality assessment[J].IOP Conference Series:Earth and Environmental Science, 2019, 234(1):12-64. [14] CHEN Z, LIN J, LIAO N, et al.Full reference quality assessment for image retargeting based on natural scene statistics modeling and bi-directional saliency similarity[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(11):5138-5148. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2736422 [15] FANG Y, CHEN Z, LIN W, et al.Saliency detection in the compressed domain for adaptive image retargeting[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2012, 21(9):3888-3901. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2012.2199126 [16] QIN Y, LU H, XU Y, et al.Saliency detection via cellular automata[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 110-119. [17] JOACHIMS T.Training linear SVMs in linear time[C]//ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery & Data Mining.New York: ACM, 2006: 217-226. [18] LIU C, YUEN J, TORRALBA A.SIFT flow:Dense correspondence across scenes and its applications[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2010, 33(5):978-994. [19] PELE O, WERMAN M.Fast and robust earth mover's distances[C]//IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2009: 460-467. [20] HSU C C, LIN C W, FANG Y, et al.Objective quality assessment for image retargeting based on perceptual geometric distortion and information loss[J].IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2014, 8(3):377-389. doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2014.2311884 [21] KENDALL M G.A new measure of rank correlation[J].Biometrika, 1938, 30(1):81-93. [22] DONG W, ZHOU N, PAUL J C, et al.Optimized image resizing using seam carving and scaling[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2009, 28(5):125. [23] KARNI Z, FREEDMAN D, GOTSMAN C.Energy-based image deformation[J].Computer Graphics Forum, 2009, 28(5):1257-1268. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-8659.2009.01503.x [24] WANG Z, LU L, BOVIK A C.Video quality assessment based on structural distortion measurement[J].Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2004, 19(2):121-132. doi: 10.1016/S0923-5965(03)00076-6 [25] SHEIKH H R, SABIR M F, BOVIK A C.A statistical evaluation of recent full reference image quality assessment algorithms[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2006, 15(11):3440-3451. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2006.881959 [26] WU Z, SU L, HUANG Q M.Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection[EB/OL].(2018-04-18)[2019-07-09]. 期刊类型引用(3)
1. 胡波,谢国庆,李雷达,李静,杨嘉琛,路文,高新波. 图像重定向质量评价的研究进展. 中国图象图形学报. 2024(01): 22-44 .  百度学术
百度学术2. 孙令翠,冯辉宗. 基于编码量化参数调节的图像清晰化处理. 计算机仿真. 2022(04): 180-184 .  百度学术
百度学术3. 赵莉,张克旺. 基于傅里叶描述子的实装战技图像典型特征相似度检测方法. 南京理工大学学报. 2022(04): 406-411 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(3)
-







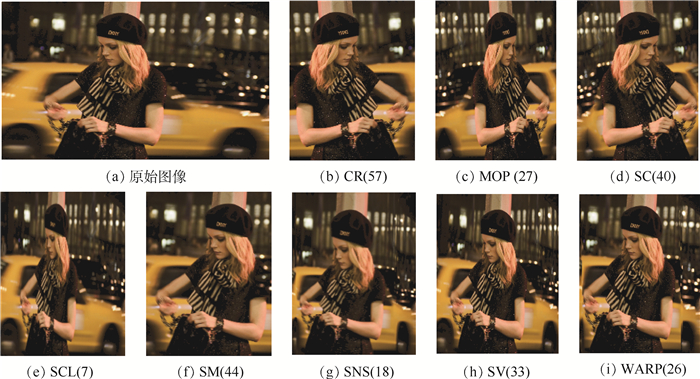
 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术

