Tongue image segmentation algorithm based on deep convolutional neural network and fully conditional random fields
-
摘要:
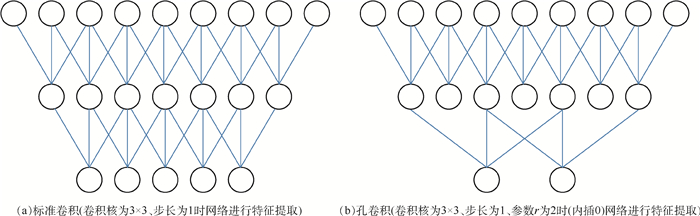
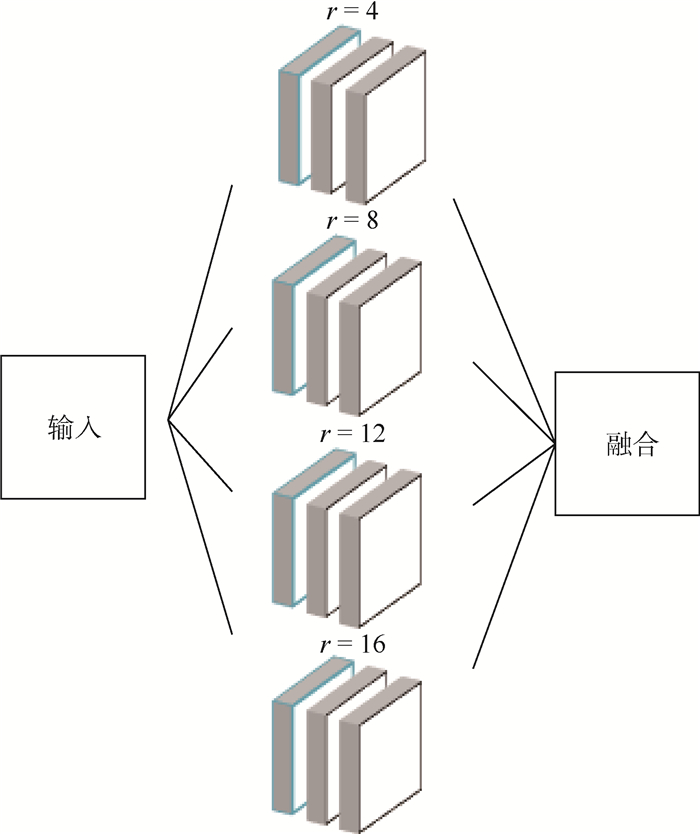
针对中医舌诊中舌体分割不准确、分割速度较慢且需要人工标定候选区域等问题,提出了一种端到端的舌图像分割算法。与传统舌图像分割算法相比,所提算法可以得到更为准确的分割结果,并且不需要人工操作。首先,使用孔卷积算法,可以在不增加参数的条件下扩大网络的特征图谱。其次,使用孔卷积空间金字塔池化(ASPP)模块,令网络通过不同的感受野学习舌图像的多尺度特征。最后,将深度卷积神经网络(DCNN)和全连接的条件随机场(CRF)相结合,细化分割后的舌体边缘。实验结果表明:所提算法优于传统舌图像分割算法和主流的深度卷积神经网络,具有较高的分割精度,平均交并比达到了95.41%。
-
关键词:
- 深度学习 /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 语义分割 /
- 舌图像 /
- 条件随机场(CRF)
Abstract:The disadvantage of tongue image segmentation in traditional Chinese medicine are low accuracy, slow segmentation speed and manual calibration of candidate regions.To solve these problems, we propose an end-to-end tongue image segmentation algorithm. Compared with the traditional tongue segmentation algorithm, more accurate segmentation results can be obtained by the proposed method which does not need any manual operation. Firstly, the atrous convolution algorithm is used to increase the feature map of the network without increasing the parameters. Secondly, the atrous spatial pyramid pooling (ASPP) module is used to enable the network to learn the multi-scale feature of the tongue image through different receptive fields. Finally, the deep convolutional neural networks (DCNN) are combined with fully connected conditional random fields (CRF) to refine the edge of the segmented tongue image. The experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms traditional tongue image segmentation algorithm and popular DCNN with higher segmentation accuracy, and the mean intersection over union reaches 95.41%.
-
表 1 三个数据集的图片数量
Table 1. Number of images on three datasets
数据集 类型 图片数量 PASCAL VOC 2012 训练 10 582 验证 1 449 测试 1 456 Tongue dataset 1 训练 1 440 测试 250 Tongue dataset 2 训练 160 测试 40 表 2 不同尺寸和参数的孔卷积对网络性能的影响
Table 2. Effect of atrous convolution with different size and parameters on network performance
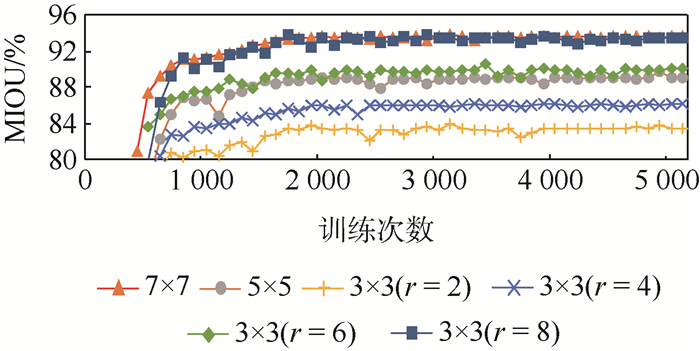
核尺寸 r 参数数量/106 时间/s MIOU/% 7×7 2 134.3 1.57 93.29 5×5 2 94.6 2.47 89.16 3×3 2 20.5 4.92 83.47 3×3 4 20.5 4.92 86.13 3×3 6 20.5 4.92 90.06 3×3 8 20.5 4.92 93.27 表 3 不同参数的ASPP模块对网络性能的影响
Table 3. Effect of different parameters of ASPP module on network performance
方法 各通道参数 MIOU/% 单分支 8 93.27 ASPP-2 (2, 4, 6, 8) 94.18 ASPP-4 (4, 8, 12, 16) 95.41 ASPP-6 (6, 12, 18, 24) 94.79 ASPP-8 (8, 16, 24, 32) 94.57 表 4 不同模块对网络性能的影响
Table 4. Effect of different modules on network performance
单分支 ASPP CRF MIOU/% Tongue dataset 1 Tongue dataset 2 √ 92.48 90.87 √ √ 93.27 91.21 √ 94.36 92.54 √ √ 95.41 93.75 表 5 不同算法在舌图像数据集上的分割结果
Table 5. Segmentation results on tongue image dataset by different algorithms
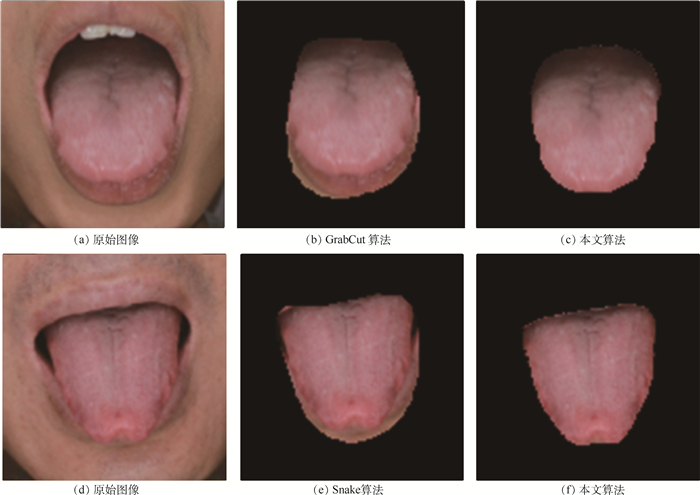
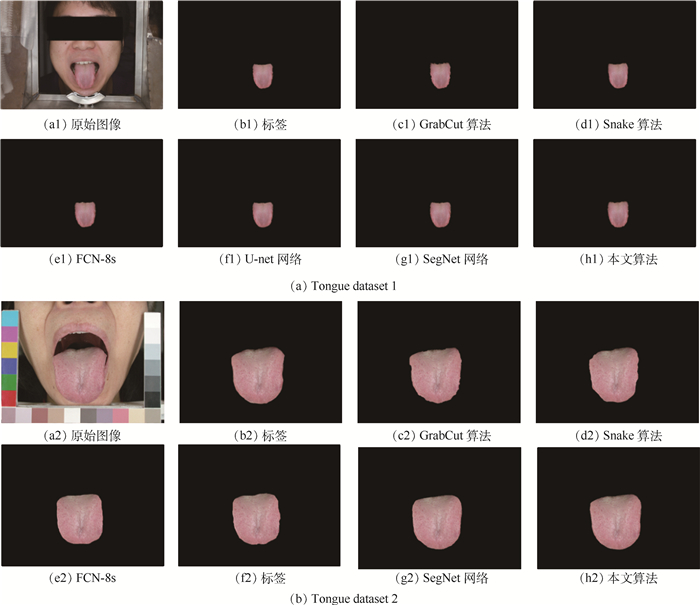
算法 Tongue dataset 1 Tongue dataset 2 PA/% MPA/% MIOU/% 时间/s PA/% MPA/% MIOU/% 时间/s GrabCut[7] 96.22 95.47 83.89 7.25 96.63 95.38 86.81 6.87 Snake[4] 97.15 96.39 90.43 6.33 98.50 96.71 93.54 6.57 FCN-8s[18] 97.36 96.04 91.37 0.37 96.84 95.27 90.36 0.31 U-net[27] 98.65 96.88 93.69 0.68 97.83 96.19 92.17 0.64 SegNet[20] 99.71 98.09 94.81 0.48 98.02 96.51 92.63 0.42 本文算法 99.85 98.29 95.41 0.83 98.97 97.60 93.75 0.75 -
[1] SHEN L S, WANG A M, WEI B G, et al.Image analysis for tongue characterization[J].Acta Electronica Sinica, 2001, 12(3):317-323. [2] 张灵, 秦鉴.基于灰度投影和阈值自动选取的舌像分割方法[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(9):1638-1641. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2010.09.027ZHANG L, QIN J.Tongue-image segmentation based on gray projection and threshold-adaptive method[J].Journal of Clinical Rehabilitative Tissue Engineering Research, 2010, 14(9):1638-1641(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-8225.2010.09.027 [3] 李丹霞, 韦玉科.基于自适应阈值的舌像分割方法[J].计算机技术与发展, 2011, 21(9):63-65. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2011.09.016LI D X, WEI Y K.Tongue image segmentation method based on adaptive thresholds[J].Computer Technology & Development, 2011, 21(9):63-65(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2011.09.016 [4] KASS M, WITKIN A, TERZOPOULOS D.Snakes:Active, contour models[J].International Journal of Computer Vision, 1988, 1(4):321-331. doi: 10.1007/BF00133570 [5] 傅之成, 李晓强, 李福凤.基于径向边缘检测和Snake模型的舌像分割[J].中国图象图形学报, 2019, 14(4):688-693.FU Z C, LI X Q, LI F F.Tongue image segmentation based on snake model and radial edge detection[J].Journal of Image & Graphics, 2009, 14(4):688-693(in Chinese). [6] LI Q L, XUE Y Q, WANG J Y, et al.Automated tongue segmentation algorithm based on hyperspectral image[J].Journal of Infrared & Millimeter Waves, 2007, 26(1):77-80. [7] ROTHER C, KOLMOGOROV V, BLAKE A.GrabCut:Interactive foreground extraction using iterated graph cuts[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics, 2004, 23(3):309-314. doi: 10.1145/1015706.1015720 [8] 韦玉科, 范鹏, 曾贵.改进的GrabCut方法在舌诊系统中的应用[J].传感器与微系统, 2014, 33(10):157-160.WEI Y K, FAN P, ZENG G.Application of improved GrabCut method in tongue diagnosis system[J].Transducer & Microsystem Technologies, 2014, 33(10):157-160(in Chinese). [9] 陈善超, 符红光, 王颖.改进的一种图论分割方法在舌像分割中的应用[J].计算机工程与应用, 2012, 48(5):201-203. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2012.05.058CHEN S C, FU H G, WANG Y.Application of improved graph theory image segmentation algorithm in tongue image segmentation[J].Computer Engineering & Applications, 2012, 48(5):201-203(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2012.05.058 [10] GUO J Y, YANG Y K, WU Q W, et al.Adaptive active contour model based automatic tongue image segmentation[C]//International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, Biomedical Engineering and Informatics, 2017: 1386-1390. [11] SHI M J, LI G Z, LI F F.C2G2FSnake:Automatic tongue image segmentation utilizing prior knowledge[J].Science China:Information Sciences, 2013, 56(9):1-14. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-JFXG201309014.htm [12] LIN B Q, XIE J W, LI C H.Deeptongue: Tongue segmentation via resnet[C]//IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 1035-1039. [13] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G.ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2013: 1097-1105. [14] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A.Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[EB/OL].(2014-09-04)[2019-01-28]. [15] GIRSHICK R, DONAHUE J, DARRELL T, et al.Rich feature hierarchies for accurate object detection and semantic segmentation[C]//IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2014: 580-587. [16] GIRSHICK R.Fast R-CNN[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 15801732. [17] REN S Q, HE K M, GIRSHICK R, et al.Faster R-CNN:Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(6):1137-1149. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2577031 [18] SHELHAMER E, JONATHAN L, TREVOR D.Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(4):640-651. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2572683 [19] NOH H, HONG S, HAN B.Learning deconvolution network for semantic segmentation[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 1520-1528. [20] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R.SegNet:A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12):2481-2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [21] CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I, et al.DeepLab:Semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets, atrous convolution, and fully connected CRFs[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4):834-848. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2699184 [22] LI J, XU B C, BAN X J.A tongue image segmentation method based on enhanced HSV convolutional neural network[C]//International Conference on Cooperative Design, Visualization and Engineering.Berlin: Springer, 2017: 252-260. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-66805-5_32 [23] QU P L, ZHANG H, ZHUO L, et al.Automatic tongue image segmentation for traditional Chinese medicine using deep neural network[C]//Intelligent Computing Theories and Application.Berlin: Springer, 2017: 247-259. doi: 10.1007%2F978-3-319-63309-1_23 [24] HOSCHNEIDER M, KRONLAND-MARTINET R, MORLET J, et al.A real-time algorithm for signal analysis with the help of the wavelet transform[C]//Wavelets: Time-Frequency Methods Phase Space, 1989: 289-297. doi: 10.1007%2F978-3-642-75988-8_28 [25] PHILIPP K, KOLTUN V.Efficient inference in fully connected CRFs with Gaussian edge potentials[J].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2011, 24(1):109-117. [26] HARIHARAN B, ARBELAEZ P, BOURDEV L, et al.Semantic contours from inverse detectors[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 991-998. [27] RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T.U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C]//International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Berlin: Springer, 2015: 234-241. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-24574-4_28 -








 下载:
下载: