Structural feature representation and fusion of behavior recognition oriented human spatial cooperative motion
-
摘要:
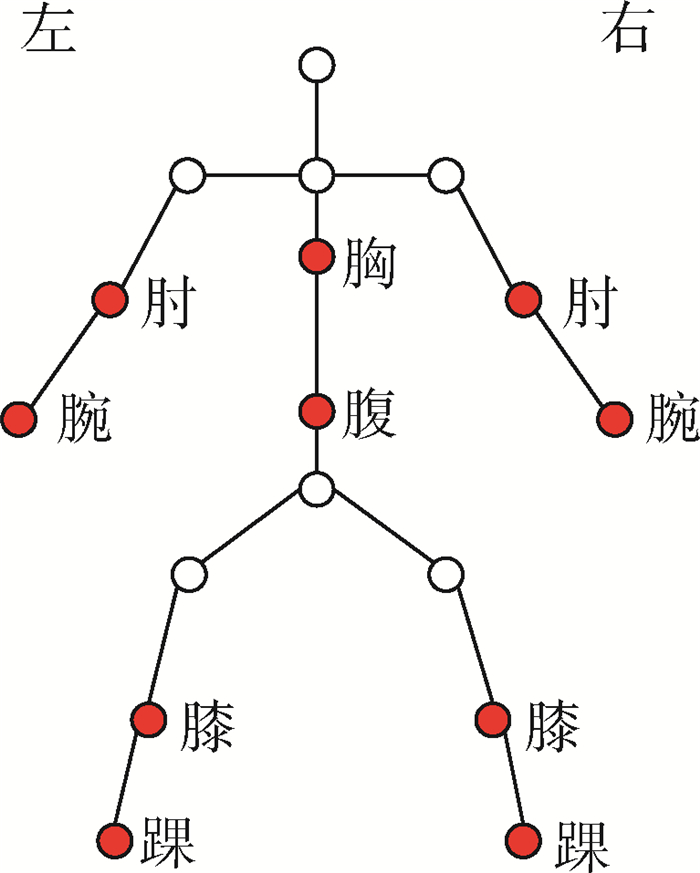
针对人体执行动作时不同身体部位之间的协同关系,提出了基于人体空间协同运动结构特征的行为识别方法。首先度量人体不同部位对完成动作的贡献度,并将不同部位的贡献度转变为协同运动结构特征模型。然后利用模型无监督、自适应地对不同身体部位的运动特征进行约束。在此基础上借鉴跨媒体检索方法JFSSL对不同模态的特征进行特征选择与多模态特征融合。实验表明,所提方法在自建的行为数据库上明显提高了开放测试的识别率,且计算过程简便,易于实现。
Abstract:In view of the synergistic relationship among different parts of the body when human body performs actions, a behavior recognition method based on human body spatial cooperative motion structural features is proposed. Firstly, the contribution of different parts of the human body to the completion of the action is measured, and the contribution of different parts of the human body is transformed into a structural feature model of cooperative motion. Then, the model is used to constrain the motion characteristics of different parts of the body self-adaptively without supervision. On this basis, feature selection and multi-modal feature fusion are carried out using JFSSL, a cross-media retrieval method. The experiments show that the recognition rate of the open test is obviously improved by the proposed method on the self-built behavior database. At the same time, the calculation process of the method is simple and easy to implement.
-
表 1 自建的行为数据库中的15个动作
Table 1. Fifteen actions in self-built behavior database
序号 类别 1 右高挥手 2 左高挥手 3 右水平挥手 4 左水平挥手 5 右手锤 6 右手抓 7 右手画叉 8 左手画叉 9 右手画圆 10 左手画圆 11 右脚前踢 12 左脚前踢 13 右脚侧踢 14 左脚侧踢 15 上下挥手 表 2 三轴加速度识别率
Table 2. Recognition rate of triaxial acceleration
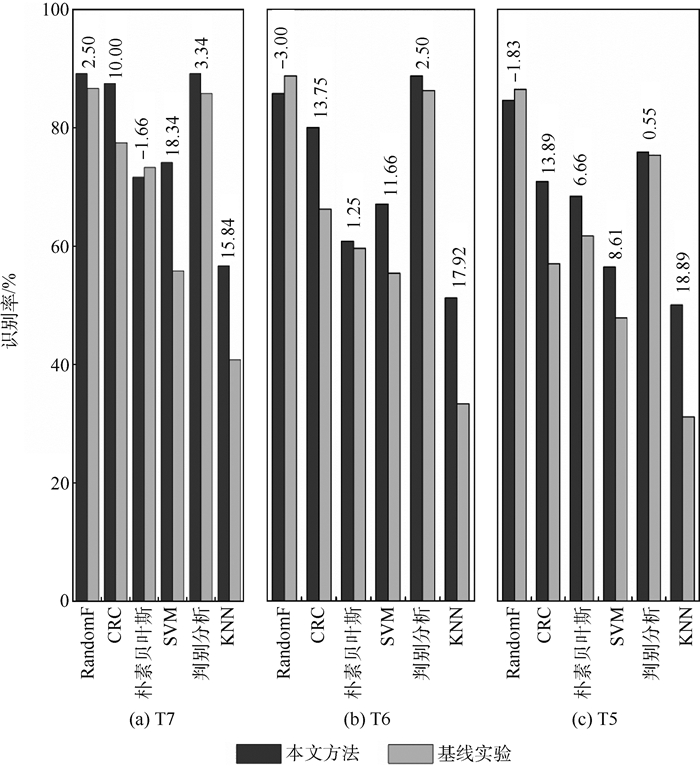
% 分类器 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 KNN 39.64 41.85 43.84 45.90 31.11 33.33 40.83 判别分析 92.21 95.80 97.07 97.40 75.28 86.25 85.83 SVM 60.31 65.45 70.13 71.10 47.78 55.42 55.83 朴素贝叶斯 77.45 77.57 78.78 80.00 61.67 59.58 73.33 CRC 81.92 85.07 86.27 89.07 56.94 66.25 77.50 RandomF 94.01 95.15 95.96 96.50 86.39 88.75 86.67 表 3 三轴加速度约束后的识别率
Table 3. Recognition rate of constrained triaxial acceleration
% 分类器 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 KNN 59.95 66.47 65.33 68.80 50.00 51.25 56.67 判别分析 92.59 95.07 96.89 97.20 75.83 88.75 89.17 SVM 71.31 76.33 77.96 78.93 56.39 67.08 74.17 朴素贝叶斯 75.68 78.47 78.58 80.80 68.33 60.83 71.67 CRC 86.56 89.00 90.04 92.93 70.83 80.00 87.50 RandomF 94.83 95.40 96.18 96.53 84.56 85.75 89.17 表 4 关节点位置识别率
Table 4. Recognition rate of joint point position
% 分类器 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 KNN 41.11 42.45 43.33 45.70 37.22 41.25 36.67 判别分析 94.16 91.93 60.40 96.50 86.90 68.33 90.00 SVM 61.95 67.73 71.18 75.43 49.17 60.83 71.67 朴素贝叶斯 84.68 87.43 89.22 90.30 83.33 87.92 85.00 CRC 71.67 80.60 83.11 85.57 73.33 84.17 85.83 RandomF 96.70 97.32 97.33 98.00 91.94 97.92 98.33 表 5 多模态特征选择与特征融合的识别率
Table 5. Recognition rate of multi-modal feature selection and feature fusion
% 分类器 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 KNN 77.31 84.25 88.27 89.23 89.72 92.08 88.33 判别分析 91.63 96.30 97.80 98.33 91.39 97.50 100.00 SVM 88.43 93.93 96.00 97.07 90.83 97.50 98.33 朴素贝叶斯 78.89 91.47 94.47 96.43 74.72 88.75 97.50 CRC 70.72 83.97 88.71 91.13 89.44 86.25 87.50 RandomF 88.85 93.52 94.84 95.93 82.71 88.40 97.04 表 6 融合约束后的三轴加速度数据特征与关节点位置数据特征识别率
Table 6. Recognition rate of triaxial acceleration feature and joint point position data feature after fusion constraints
% 分类器 T1 T2 T3 T4 T5 T6 T7 KNN 88.79 93.75 96.53 97.10 87.22 97.92 100.00 判别分析 89.84 96.07 97.80 98.17 90.83 98.33 100.00 SVM 89.07 94.88 96.51 97.90 88.33 98.33 100.00 朴素贝叶斯 80.09 90.65 94.96 95.83 79.44 95.42 100.00 CRC 86.85 93.75 96.16 97.50 87.22 97.08 100.00 RandomF 88.48 93.01 94.47 96.00 85.49 94.50 96.29 -
[1] LUVIZON D C, PICARD D, TABIA H.2D/3D pose estimation and action recognition using multitask deep learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 5137-5146. [2] FABIEN B, CHRISTIAN W, JULIEN M, et al.Glimpse clouds: Human activity recognition from unstructured feature points[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 469-478. [3] HOU R, CHEN C, MUBARAK S.Tube convolutional neural network (T-CNN) for action detection in videos[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision(ICCV).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 5822-5831. [4] CHEN C, JAFARI R, KEHTARNAVAZ N.Action recognition from depth sequences using depth motion maps-based local binary patterns[C]//IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Perss, 2015: 1092-1099. [5] XIA L, CHEN C, AGGARWAL J K.View invariant human action recognition using histograms of 3d joints[C]//2012 IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops(CVPRW).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 20-27. [6] HUSSEIN M E, TORKI M, GOWAYYED M A.Human action recognition using a temporal hierarchy of covariance descriptors on 3d joint locations[C]//23rd International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2013: 2466-2472. [7] 苏本跃, 蒋京, 汤庆丰, 等.基于函数型数据分析方法的人体动态行为识别[J].自动化学报, 2017, 43(5):866-876.SU B Y, JIANG J, TANG Q F, at al.Human dynamic action recognition based on functional data analysis[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2017, 43(5):866-876(in Chinese). [8] GRAVINA R, ALINIA P, GHASEMZADEH H, et al.Multi-sensor fusion in body sensor networks:State-of-the-art and research challenges[J]. Information Fusion, 2017, 35:68-80. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.09.005 [9] CHEN C, LIU K, KEHTARNAVAZ N.Real-time human action recogniti on based on depth motion maps[J]. Journal of Real-Time Image Processing, 2016, 12(1):155-163. doi: 10.1007/s11554-013-0370-1 [10] CHEN C, JAFARI R, KEHTARNAVAZ N.Improving human action recognition using fusion of depth camera and inertial sensors[J]. IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems, 2015, 45(1):51-61. doi: 10.1109/THMS.2014.2362520 [11] HAGHIGHAT M, ABDEL-MOTTALEB M, ALHALABI W.Fully automatic face normalization and single sample face recognition in unconstrained environments[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2016, 47:23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2015.10.047 [12] HAGHIGHAT M, ABDEL-MOTTALEB M, ALHALABI W.Discriminant correlation analysis:Real-time feature level fusion for multimodal biometric recognition[J]. IEEE Transactions on Information Forensics and Security, 2016, 11(9):1984-1996. doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2016.2569061 [13] 唐超, 王文剑, 李伟, 等.基于多学习器协同训练模型的人体行为识别方法[J].软件学报, 2015, 26(11):2939-2950.TANG C, WANG W J, LI W, et al.Multi-learner co-training model for human actioin recognition[J]. Journal of Software, 2015, 26(11):2939-2950(in Chinese). [14] SI C Y, JING Y, WANG W, et al.Skeleton-based action recognition with spatial reasoning and temporal stack learning[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).Berlin: Springer, 2018: 103-118. [15] LIU M Y, MENG F Y, CHEN C, et al.Joint dynamic pose image and space time reversal for human action recognition from videos[C]//33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Palo Alto: AAAI Press, 2019: 8762-8769. [16] 邓诗卓, 王波涛, 杨传贵, 等.CNN多位置穿戴式传感器人体活动识别[J].软件学报, 2019, 30(3):718-737.DENG S Z, WANG B T, YANG C G, et al.Convolutional neural networks for human activity recognition using multi-location wearable sensors[J]. Journal of Software, 2019, 30(3):718-737(in Chinese). [17] CHEN C, JAFARI R, KEHTARNAVAZ N.A real-time human action recognition system using depth and inertial sensor fusion[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2016, 16(3):773-781. doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2015.2487358 [18] 许艳, 侯振杰, 梁久祯, 等.权重融合深度图像与骨骼关键帧的行为识别[J].计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2018, 30(7):139-146.XU Y, HOU Z J, LIANG J Z, et al.Action recognition using weighted fusion of depth images and skeleton's key frames[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2018, 30(7):139-146(in Chinese). [19] WANG K, HE R, WANG L, et al.Joint feature selection and subspace learning for cross-modal retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2016, 38(10):2010-2023. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2015.2505311 [20] NIE F, HUANG H, CAI X, et al.Efficient and robust feature selection via joint ℓ2, 1-norms minimization[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems(NIPS).New York: Curran Associates, 2010: 1813-1821. [21] HE R, TIAN T N, WANG L, et al.L2, 1 regularized correntropy for robust feature selection[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition(CVPR).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2012: 2504-2511. [22] OFLI F, CHAUDHRY R, KURILLO G, et al.Berkeley MHAD: A comprehensive multimodal human action database[C]//2013 IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 53-60. [23] CHEN C, JAFARI R, KEHTARNAVAZ N.UTD-MHAD: A multimodal dataset for human action recognition utilizing a depth camera and a wearable inertial sensor[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Image Processing (ICIP).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 168-172. [24] CHEN C, ZHANG B G, HOU Z J, et al.Action recognition from depth sequences using weighted fusion of 2D and 3D auto-correlation of gradients features[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, 2017, 76(3):4651-4669. doi: 10.1007/s11042-016-3284-7 -








 下载:
下载: