-
摘要:
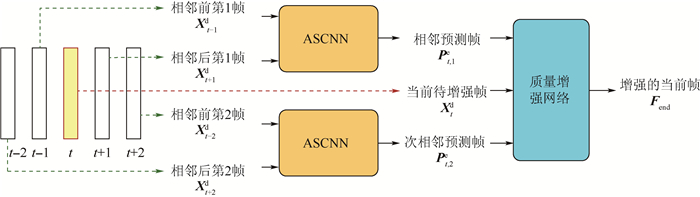
卷积神经网络(CNN)在视频增强方向取得了巨大的成功。现有的视频增强方法主要在空域探索图像内像素的相关性,忽略了连续帧之间的时域相似性。针对上述问题,提出一种基于时空域上下文学习的多帧质量增强方法(STMVE),即利用当前帧以及相邻多帧图像共同增强当前帧的质量。首先根据时域多帧图像直接预测得到当前帧的预测帧,然后利用预测帧对当前帧进行增强。其中,预测帧通过自适应可分离的卷积神经网络(ASCNN)得到;在后续增强中,设计了一种多帧卷积神经网络(MFCNN),利用早期融合架构来挖掘当前帧及其预测帧的时空域相关性,最终得到增强的当前帧。实验结果表明,所提出的STMVE方法在量化参数值37、32、27、22上,相对于H.265/HEVC,分别获得0.47、0.43、0.38、0.28 dB的性能增益;与多帧质量增强(MFQE)方法相比,平均获得0.17 dB的增益。
-
关键词:
- 时空域上下文学习 /
- 多帧质量增强(MFQE) /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 残差学习 /
- 预测帧
Abstract:Convolutional neural network (CNN) has achieved great success in the field of video enhancement. The existing video enhancement methods mainly explore the pixel correlations in spatial domain of an image, which ignores the temporal similarity between consecutive frames. To address the above issue, this paper proposes a multi-frame quality enhancement method, namely spatial-temporal multi-frame video enhancement (STMVE), through learning the spatial-temporal context of current frame. The basic idea of STMVE is utilizing the adjacent frames of current frame to help enhance the quality of current frame. To this end, the virtual frames of current frame are first predicted from its neighbouring frames and then current frame is enhanced by its virtual frames. And the adaptive separable convolutional neural network (ASCNN) is employed to generate the virtual frame. In the subsequent enhancement stage, a multi-frame CNN (MFCNN) is designed. An early-fusion CNN structure is developed to extract both temporal and spatial correlation between the current and virtual frames and output the enhanced current frame. The experimental results show that the proposed STMVE method obtains 0.47 dB, 0.43 dB, 0.38 dB and 0.28 dB PSNR gains compared with H.265/HEVC at quantized parameter values 37, 32, 27 and 22 respectively. Compared to the multi-frame quality enhancement (MFQE) method, an average 0.17 dB PSNR gain is obtained.
-
表 1 光流法(FlowNet 2.0)与ASCNN预处理时间对比
Table 1. Pre-processing time comparison of optical flow method (FlowNet 2.0) and ASCNN
序列 分辨率 预处理时间/s FlowNet 2.0 ASCNN BQSquare 416×240 255 108 PartyScene 832×480 1085 111 BQMall 832×480 1144 104 Johnny 1280×720 2203 116 平均耗时 1172 110 表 2 多帧质量增强网络结构
Table 2. Structure of proposed quality enhancement network
卷积层 滤波器大小 滤波器数量 步长 激活函数 Conv 1/2/3 3×3 64 1 Relu Conv 4 1×1 64 1 Relu 残差块×7 1×1 64 1 Relu 3×3 64 1 Relu 1×1 64 1 Relu Conv end 5×5 1 1 表 3 5种预处理方式所获得的PSNR性能指标对比
Table 3. PSNR performance indicator comparison by five pre-processing strategies
dB 序列 H.265/HEVC FlowNet 2.0(t-2, t+2) ASCNN(t-2, t+2) FlowNet 2.0(t-2, t+2)+ASCNN (t-2, t+2) FlowNet 2.0(t-2, t+2)+ASCNN (t-1, t+1) ASCNN(t-2, t+2)+ASCNN(t-1, t+1) BQMall 31.00 31.35 31.38 31.20 31.23 31.46 BasketballDrill 31.94 32.35 32.32 32.16 32.19 32.39 FourPeople 35.59 36.23 36.20 36.00 36.04 36.32 BQSquare 29.21 29.59 29.62 29.32 29.35 29.65 平均值 31.94 32.38 32.38 32.17 32.20 32.46 表 4 三种网络结构的PSNR性能指标对比
Table 4. PSNR performance indicator comparison of three network structures
dB 测试序列 直接融合 渐进融合 早期融合 BQMall 31.39 31.42 31.46 BasketballDrill 32.32 32.35 32.39 RaceHousesC 29.36 29.38 29.41 平均值 31.02 31.05 31.09 表 5 不同方法的PSNR性能指标对比
Table 5. Comparison of PSNR performance indicator among different methods
dB 量化参数 类别 测试序列 H.265/HEVC 单帧质量增强 STMVE方法 相对单帧的提升 相对H.265/HEVC的提升 37 C BasketballDrill 31.94 32.14 32.39 0.25 0.45 BQMall 31.00 31.17 31.46 0.29 0.46 PartyScene 27.73 27.73 27.94 0.21 0.21 RaceHorses 29.08 29.23 29.41 0.18 0.33 D BasketballPass 31.79 32.02 32.37 0.35 0.58 BlowingBubbles 29.19 29.30 29.51 0.21 0.32 BQSquare 29.21 29.28 29.65 0.37 0.44 RaceHorses 28.69 28.93 29.18 0.25 0.49 E FourPeople 35.59 36.03 36.32 0.29 0.73 Johnny 37.34 37.61 37.80 0.19 0.46 KristenAndSara 36.77 37.21 37.43 0.22 0.66 平均值 31.67 31.97 32.13 0.16 0.47 32 平均值 34.31 34.59 34.74 0.15 0.43 27 平均值 37.06 37.28 37.43 0.15 0.38 22 平均值 39.89 40.06 40.17 0.11 0.28 表 6 STMVE方法与MFQE的PSNR性能指标对比
Table 6. PSNR performance indicator comparison between proposed method and MFQE
dB 测试序列(36帧) MFQE STMVE方法 ΔPSNR PartyScene 26.95 27.39 0.44 BQMall 30.39 30.64 0.25 Johnny 36.84 36.87 0.03 BlowingBubbles 28.97 28.93 0.04 平均值 30.79 30.96 0.17 -
[1] CISCO.Cisco visual networking index: Global mobile data traffic forecast update[EB/OL]. (2019-02-18)[2019-07-08]. https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/solutions/collateral/service-provider/visual-networking-index-vni/white-paper-c11-738429.html. [2] DONG C, DENG Y, CHANGE LOY C, et al.Compression artifacts reduction by a deep convolutional network[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 576-584. [3] ZHANG K, ZUO W, CHEN Y, et al.Beyond a Gaussian denoiser:Residual learning of deep CNN for image denoising[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2017, 26(7):3142-3155. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2017.2662206 [4] YANG R, XU M, WANG Z.Decoder-side HEVC quality enhancement with scalable convolutional neural network[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo(ICME).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 817-822. [5] YANG R, XU M, WANG Z, et al.Multi-frame quality enhancement for compressed video[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 6664-6673. [6] NIKLAUS S, MAI L, LIU F.Video frame interpolation via adaptive separable convolution[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 261-270. [7] PARK W S, KIM M.CNN-based in-loop filtering for coding efficiency improvement[C]//2016 IEEE 12th Image, Video, and Multidimensional Signal Processing Workshop(IVMSP), 2016: 1-5. [8] JUNG C, JIAO L, QI H, et al.Image deblocking via sparse representation[J]. Signal Processing:Image Communication, 2012, 27(6):663-677. doi: 10.1016/j.image.2012.03.002 [9] WANG Z, LIU D, CHANG S, et al.D3: Deep dual-domain based fast restoration of jpeg-compressed images[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 2764-2772. [10] LI K, BARE B, YAN B.An efficient deep convolutional neural networks model for compressed image deblocking[C]//2017 IEEE International Conference on Multimedia and Expo (ICME).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 1320-1325. [11] LU G, OUYANG W, XU D, et al.Deep Kalman filtering network for video compression artifact reduction[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).Berlin: Springer, 2018: 568-584. [12] DAI Y, LIU D, WU F.A convolutional neural network approach for post-processing in HEVC intra coding[C]//International Conference on Multimedia Modeling.Berlin: Springer, 2017: 28-39. [13] TSAI R.Multiframe image restoration and registration[J]. Advance Computer Visual and Image Processing, 1984, 11(2):317-339. http://d.old.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical/dbch201411011 [14] PARK S C, PARK M K, KANG M G.Super-resolution image reconstruction:A technical overview[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Magazine, 2003, 20(3):21-36. doi: 10.1109/MSP.2003.1203207 [15] HUANG Y, WANG W, WANG L.Video super-resolution via bidirectional recurrent convolutional networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2018, 40(4):1015-1028. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2017.2701380 [16] LI D, WANG Z.Video superresolution via motion compensation and deep residual learning[J]. IEEE Transactions on Computational Imaging, 2017, 3(4):749-762. doi: 10.1109/TCI.2017.2671360 [17] ILG E, MAYER N, SAIKIA T, et al.FlowNet 2.0: Evolution of optical flow estimation with deep networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 2462-2470. [18] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al.Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. -







 下载:
下载: