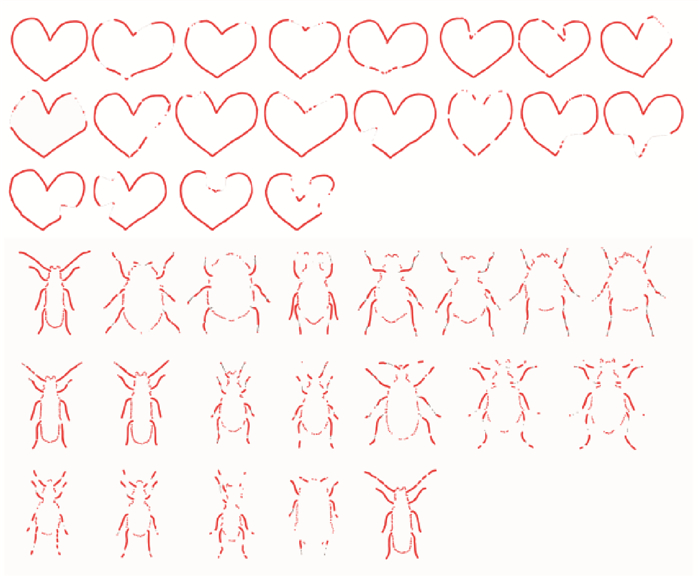-
摘要:
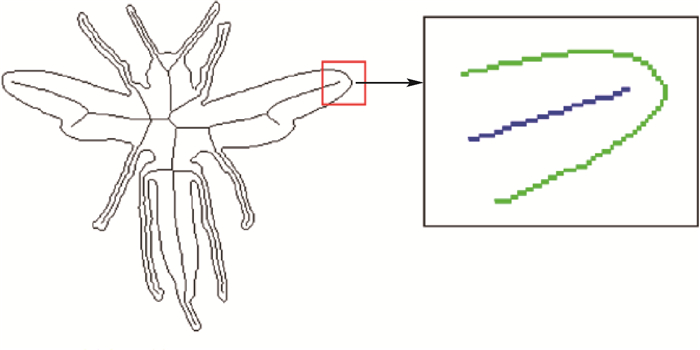
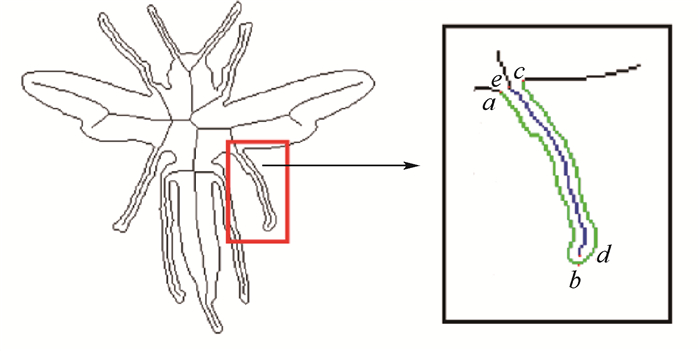
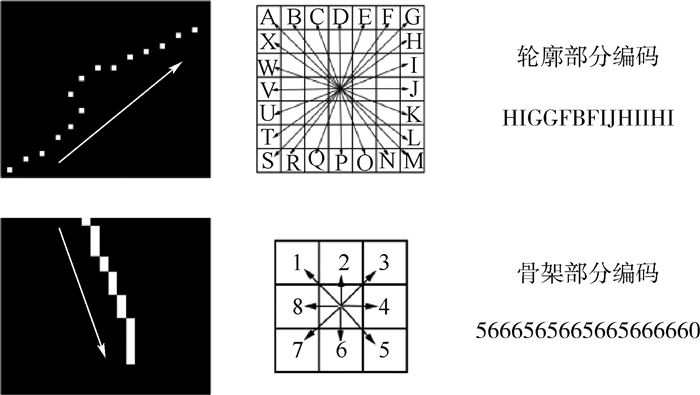
二维形状识别是物体识别中的一个基本问题,被广泛地应用于商标检索、指纹识别、物体定位、图像检索等多个领域。其中,基于生物信息学的二维形状识别是近期一个新的研究方向,基本思想是把二维形状的轮廓转化为生物信息序列,借助标准的生物信息序列分析工具来进行二维形状的匹配和识别。不过,利用轮廓进行信息序列编码存在编码冗余和编码准确性不高的问题,本文提出了一种新型的结合形状轮廓和骨架的序列编码方法。该方法利用骨架表示形状的细长分支,减少编码的冗余;并分别对轮廓和骨架进行不同类型的编码,具备编码简洁、后续匹配准确性高等优点。最后,本文在三个公开数据集上进行大量的形状识别实验,并与多种通用形状识别方法进行了比较。实验表明,本文方法在多个实验中均取得了较高的识别准确率,相比基本的形状特征描述方法,准确率提高了近5%。
Abstract:Two-dimensional shape recognition is a fundamental problem in object recognition, which is widely used in trademark retrieval, fingerprint recognition, object location, image retrieval and other fields. Recently, two-dimensional shape recognition based on bioinformatics has become a new research direction, whose basic idea is to transform the contour of a planar shape into a biological information sequence. The two-dimensional shape matching and recognition are then achieved by the standard alignment tools of such biological information sequence. However, the classic coding method still suffers from the problems of code redundancy and low accuracy. In this paper, we present a new coding method based on both the shape contour and skeleton sequence. Firstly, skeletons are used to represent slender branches of the shape to reduce coding redundancy. Secondly, the contour and skeleton are coded in different ways to compact the code and improve the matching accuracy. Finally, extensive shape recognition experiments are conducted on three public datasets and the proposed method is compared with a variety of shape recognition methods. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed method has achieved higher performance in several experiments, and the recognition accuracy rate is improved by nearly 5% compared with basic shape feature description methods.
-
表 1 MPEG-7数据集上牛眼比较法分类准确率对比
Table 1. Comparison of classification accuracy rate of bullseye method on MPEG-7 dataset
表 2 MPEG-7数据集上的分类准确率对比
Table 2. Comparison of classification accuracy rate on MPEG-7 dataset
表 3 ETH-80数据集上的分类准确率对比
Table 3. Comparison of classification accuracy rate on ETH-80 dataset
-
[1] BELONGIE S, MALIK J, PUZICHA J.Shape matching and object recognition using shape contexts[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2002, 24(4):509-522. doi: 10.1109/34.993558 [2] LING H, JACOBS W D.Shape classification using the inner-distance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(2):286-299. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.41 [3] LING H, YANG X, LATECKI J L.Balancing deformability and discriminability for shape matching[C]//11th European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2010, 6313(3): 411-424. [4] KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E.ImageNet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[C]//NIPS'12 Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2012: 1097-1105. [5] BICEGO M, LOVATO P.A bioinformatics approach to 2D shape classification[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2016, 145:59-69. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2015.11.011 [6] XU D, ALAMEDA-PINEDA X, SONG J, et al.Cross-paced representation learning with partial curricula for sketch-based image retrieval[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2018, 27(9):4410-4421. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2837381 [7] BISWAS S, AGGARWAL G, CHELLAPPA R.Efficient indexing for articulation invariant shape matching and retrieval[C]//2007 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 1-8. [8] BLUM H.A transformation for extracting new descriptors of shape[M]//WATHEN DUNN W.Models for the perception of speech and visual form model.Cavnbridge: MIT Press, 1967: 362-380. [9] 陈展展, 汤进, 罗斌, 等.基于最优子序列双射的骨架树匹配[J].计算机工程与应用, 2011, 41(7):162-165. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.07.047CHEN Z Z, TANG J, LUO B, et al.Skeleton tree matching based on optimal subsequence bijection[J]. Computer Engineering and Applications, 2011, 41(7):162-165(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.2011.07.047 [10] BAI X, LATECKI J L.Path similarity skeleton graph matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, 30(7):1282-1292. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.70769 [11] NEEDLEMAN S, WUNSCH C.A general method applicable to the search for similarities in the amino acid sequence of two proteins[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1970, 48(31):443-453. doi: 10.1016-0022-2836(70)90057-4/ [12] SMITH T, WATERMAN S M M.Identification of common molecular subsequences[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1981, 147(1):195-197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90087-5 [13] ALTSCHUL S, GISH W, MILLER W, et al.Basic local alignment search tool[J]. Journal of Molecular Biology, 1990, 2145(3):403-410. [14] LARKIN M, BLACKSHIELDS G, BROWN N, et al.Clustal w and clustal x version 2.0[J]. Bioinformatics, 2007, 23(21):2947-2948. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404 [15] MARIE R, LABBANI-IGBIDA O, MOUADDIB M E.The delta medial axis:A fast and robust algorithm for filtered skeleton extraction[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2016, 56:26-39. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2016.02.011 [16] GOS'CIEWSKA K, FREJLICHOWSKI D.Silhouette-based action recognition using simple shape descriptors[C]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science.Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 2018, 11114: 413-424. [17] BAI X, YANG X, LATECKI J L, et al.Learning context-sensitive shape similarity by graph transduction[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2009, 32(5):861-874. [18] WANG J, LI Y, BAI X, et al.Learning context-sensitive similarity by shortest path propagation[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2011, 44(10):2367-2374. [19] LIN L, ZENG K, LIU X, et al.Layered graph matching by composite cluster sampling with collaborative and competitive interactions[C]//2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2009: 1351-1358. [20] MCNEILL G, VIJAYAKUMAR S.Hierarchical procrustes matching for shape retrieval[C]//2006 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2006: 885-894. [21] DALIRI R M, TORRE V.Robust symbolic representation for shape recognition and retrieval[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2008, 41(5):1782-1798. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2007.10.020 [22] BAI X, LIU W, TU Z.Integrating contour and skeleton for shape classification[C]//2009 IEEE 12th International Conference on Computer Vision Workshops.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2009: 360-367. [23] SUN B K, SUPER J B.Classification of contour shapes using class segment sets[C]//2005 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2005: 727-733. [24] WANG X, FENG B, BAI X, et al.Bag of contour fragments for robust shape classification[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2014, 47(5):2116-2125. [25] LEIBE B, SCHIELE B.Analyzing appearance and contour based methods for object categorization[C]//2003 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2003: 409-415. [26] HU X R, JIA W, ZHAO Y, et al.Perceptually motivated morphological strategies for shape retrieval[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45(9):3222-3230. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2012.02.020 [27] DALIRI R M, TORRE V.Shape recognition based on Kernel-edit distance[J]. Computer Vision and Image Understanding, 2010, 114(10):1097-1103. doi: 10.1016/j.cviu.2010.07.002 [28] ATABAY A H.A convolutional neural network with a new architecture applied on leaf classification[J]. ⅡOAB Journal, 2016, 7(5):326-331. [29] GAO L, SONG J, NIE F, et al.Optimal graph learning with partial tags and multiple features for image and video annotation[C]//2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2015: 4371-4379. -








 下载:
下载: