-
摘要:
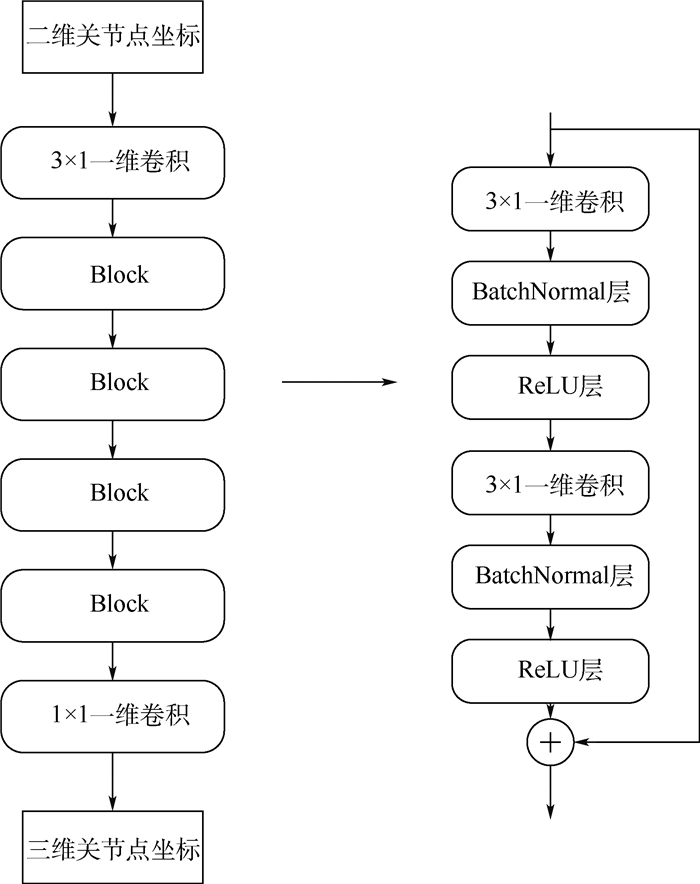
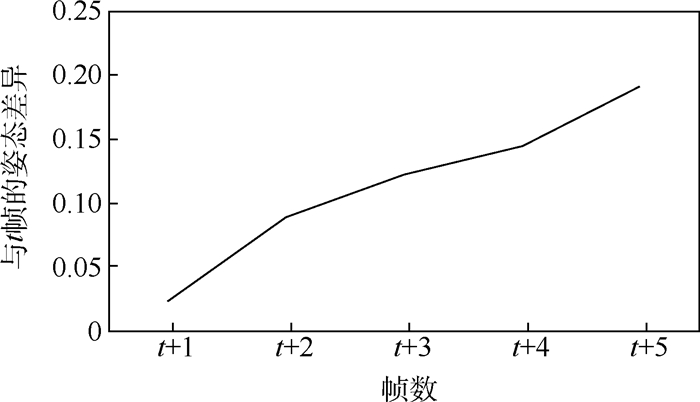
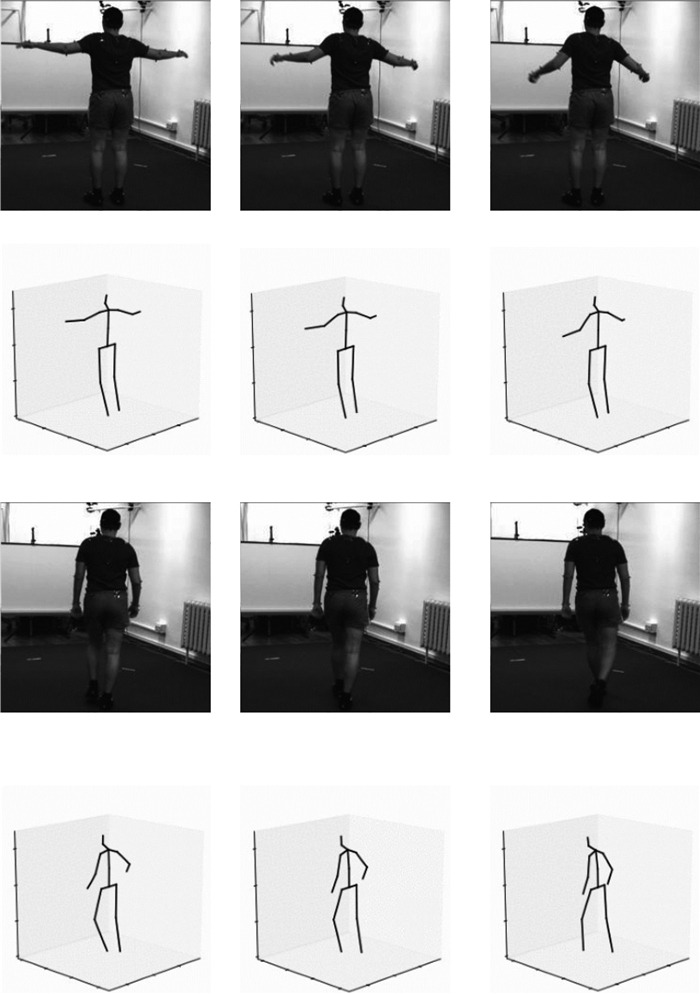
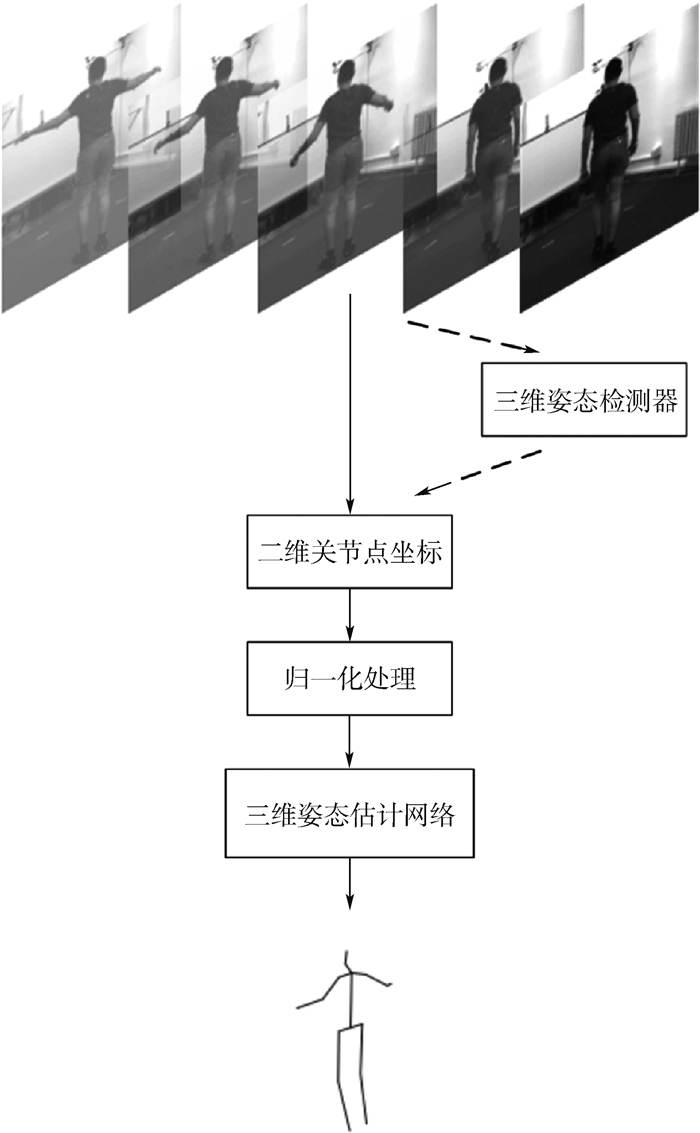
已有的三维人体姿态估计方法侧重于通过单帧图像来估计人体的三维姿态,忽略了视频中前后帧之间的相关性,因此,通过挖掘视频在时间维度上的信息可以进一步提高三维人体姿态估计的准确率。基于此,设计了一种可以充分提取视频时序信息的卷积神经网络结构,在获得高精度的同时也具有消耗计算资源小的优点,仅仅使用二维关节点的坐标为输入即可恢复完整的三维人体姿态。然后提出了一种新的损失函数利用相邻帧间人体姿态的连续性,来改进视频序列中三维姿态估计的平滑性,同时也解决了因缺少帧间信息而导致准确率下降的问题。通过在公开数据集Human3.6M上进行测试,实验结果表明本文方法相比目前的基准三维姿态估计算法的平均测试误差降低了1.2 mm,对于视频序列的三维人体姿态估计有着较高的准确率。
Abstract:The existing 3D human pose estimation method focuses on estimating the 3D pose of the human body through a single frame image, while ignoring the correlation between the front and back frames in the video. Therefore, by investigating the information of the video in the time dimension, the accuracy of the 3D human pose estimation can be further improved. Based on this, the convolutional neural network structure that can fully extract the temporal information in the video is designed. It has the advantage of low computational resources and high precision. The complete 3D human pose can be restored only by using the coordinates of the 2D articulation point as input. Furthermore, a new loss function is proposed, which uses the continuity of human pose between adjacent frames to improve the smoothness of 3D pose estimation in video sequences, and also solves the problem of accuracy degradation due to lack of inter-frame information. By testing on the Human 3.6M dataset, the experimental results indicate that the average test error of the proposed method is 1.2 mm lower than that of the current standard 3D pose estimation algorithm, and the proposed method has a high accuracy for the 3D human pose estimation of video sequences.
-
表 1 网络模型参数量
Table 1. Parameter number of network model
残差模块数 浮点运算次数/百万 参数个数/百万 平均误差/mm 2 76.9 8.5 46.6 3 114.6 12.7 45.8 4 152.4 16.9 44.7 5 190.2 21.1 45.5 表 2 各种三维姿态误差
Table 2. Various three-dimensional pose errors
方法 姿态误差/mm 平均误差/mm 指路 讨论 吃饭 问候 打电话 照相 摆姿势 购买 坐 坐下 抽烟 等待 遛狗 走路 散步 几何约束方法 文献[6] 54.8 60.7 58.2 71.4 62.0 65.5 53.9 55.6 75.2 115.6 64.2 66.0 51.4 63.2 55.3 64.9 单幅图像方法 文献[7] 58.6 64.6 63.7 62.4 66.9 70.7 57.7 62.5 76.8 103.5 65.7 61.6 69.0 56.4 59.5 66.9 二维姿态推断方法 文献[15] 48.5 54.4 54.4 52.0 59.4 65.3 49.9 52.9 65.8 71.1 56.6 52.9 60.9 44.7 47.8 56.2 文献[12] 53.3 46.8 58.6 61.2 56.0 76.1 58.1 48.9 55.6 73.4 60.3 62.2 61.9 35.8 51.1 57.5 文献[16] 52.8 54.8 54.2 54.3 61.8 67.2 53.1 53.6 71.7 86.7 61.5 53.4 61.6 47.1 53.4 48.3 文献[1] 37.7 44.4 40.3 42.1 48.2 54.9 44.4 42.1 54.6 58.0 45.1 46.4 47.6 36.4 40.4 45.5 本文方法(真实值输入) 35.4 43.0 37.9 40.0 44.4 52.1 41.7 40.4 51.8 68.4 42.0 46.0 47.4 36.4 38.4 44.3 本文方法(CPN检测器输入) 50.2 52.7 53.3 54.9 56.7 69.4 50.7 51.2 66.6 83.2 56.4 53.9 61.3 44.9 49.2 57.0 表 3 不同网络结构测试误差
Table 3. Testing errors of different network structures
网络结构 平均误差/mm 误差变化/mm 原始网络 44.3 加入Dropout(0.1) 54.8 +10.5 删除BN层 59.2 +14.9 删除残差连接 44.9 +0.6 -
[1] BO L, SMINCHISESCU C.Twin gaussian processes for structured prediction[J].International Journal of Computer Vision, 2010, 87(1-2):28. doi: 10.1007/s11263-008-0204-y [2] RADWAN I, DHALL A, GOECKE R.Monocular image 3D human pose estimation under self-occlusion[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2013: 1888-1895. [3] ZHOU X, HUANG Q, SUN X, et al.Towards 3D human pose estimation in the wild: A weakly supervised approach[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 398-407. [4] PAVLAKOS G, ZHOU X, DERPANIS K G, et al.Coarse-to-fine volumetric prediction for single-image 3D human pose[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 7025-7034. [5] NEWELL A, YANG K, DENG J.Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2016: 483-499. [6] PAVLAKOS G, HU L, ZHOU X, et al.Learning to estimate 3D human pose and shape from a single color image[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 459-468. [7] ROGEZ G, SCHMID C.Mocap-guided data augmentation for 3D pose estimation in the wild[C]//Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2016: 3108-3116. [8] VAROL G, ROMERO J, MARTIN X, et al.Learning from synthetic humans[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 109-117. [9] CHEN C H, RAMANAN D.3D human pose estimation=2D pose estimation+matching[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 7035-7043. [10] BOGO F, KANAZAWA A, LASSNER C, et al.Keep it SMPL: Automatic estimation of 3D human pose and shape from a single image[C]//European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2016: 561-578. [11] PISHCHULIN L, INSAFUTDINOV E, TANG S, et al.Deepcut: Joint subset partition and labeling for multiperson pose estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 4929-4937. [12] LOPER M, MAHMOOD N, ROMERO J, et al.SMPL:A skinned multi-person linear model[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics(TOG), 2015, 34(6):248. [13] LUVIZON D C, PICARD D, TABIA H.2D/3D pose estimation and action recognition using multitask deep learning[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 5137-5146. [14] MORENO-NOGUER F.3D human pose estimation from a single image via distance matrix regression[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 2823-2832. [15] ZHOU X, ZHU M, LEONARDOS S, et al.Sparseness meets deepness: 3D human pose estimation from monocular video[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 4966-4975. [16] MARTINEZ J, HOSSAIN R, ROMERO J, et al.A simple yet effective baseline for 3D human pose estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2017: 2640-2649. [17] DROVER D, MV R, CHEN C H, et al.Can 3D pose be learned from 2D projections alone [C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision(ECCV).Berlin: Springer, 2018: 78-94. [18] OORD A, DIELEMAN S, ZEN H, et al.WaveNet: A generative model for raw audio[EB/OL].(2016-09-19)[2019-06-13].https: //arxiv.org/abs/1609.03499. [19] HE K, ZHANG X, REN S, et al.Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 770-778. [20] IONESCU C, PAPAVA D, OLARU V, et al.Human3.6 M:Large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3D human sensing in natural environments[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2013, 36(7):1325-1339. [21] CHEN Y, WANG Z, PENG Y, et al.Cascaded pyramid network for multi-person pose estimation[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2018: 7103-7112. [22] SRIVASTAVA N, HINTON G, KRIZHEVSKY A, et al.Dropout:A simple way to prevent neural networks from overfitting[J].The Journal of Machine Learning Research, 2014, 15(1):1929-1958. -







 下载:
下载: