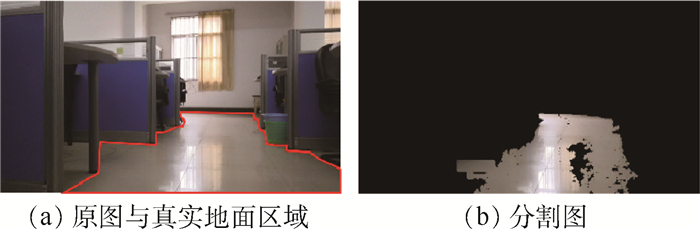
-
摘要:
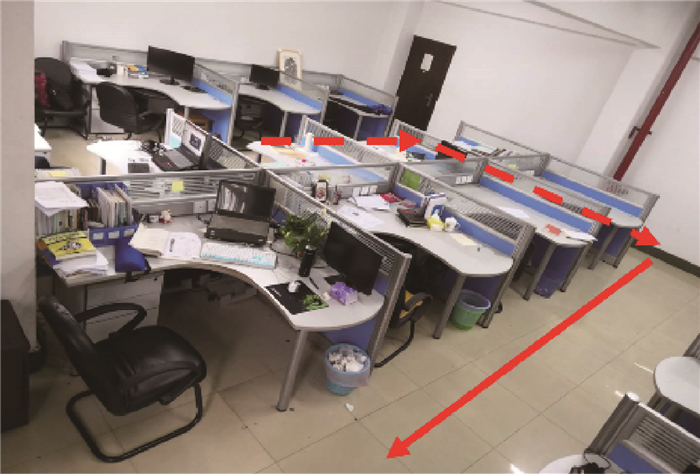
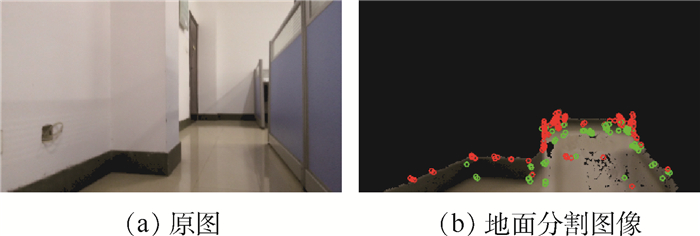
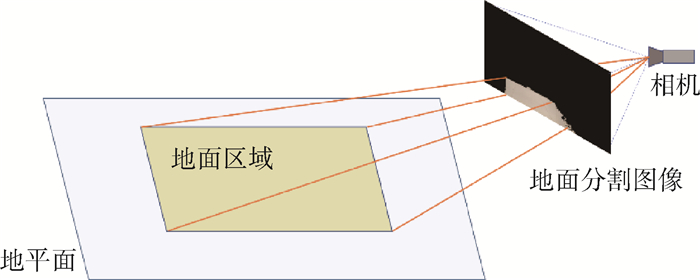
基于单目视觉的同步定位与建图(SLAM)是机器人领域中的一项热门技术。然而,在场景建图方面,由于其计算量较大,各主流方法还无法在低运算能力的平台上实现实时的场景建模。针对室内环境与小型机器人的特定情况,提出了一种新的可通行区域建模方法。该方法建立在单目特征点SLAM的基础上,通过HSV色彩空间内的图像自适应阈值分割获取地面分割图像,并与SLAM生成的稀疏点云进行交叉比对,进而获取地平面与准确的地面分割区域,再将地面分割区域反投影到地平面上,获取地面的稠密建模。在室内场景的实验中,所提方法的平均运算速度能达到21帧/s,速度约为ORB-SLAM的70%,能够满足移动平台的实时性要求。对于地平面位置的还原平均误差为5.8%,地面上道路宽度的建模误差在3.5%~12.8%。
Abstract:Monocular vision-based simultaneous localization and mapping (SLAM) is a popular technology in the field of robotics in recent years. However, due to the huge computation resource required by reconstruction, mainstream methods are not able to generate meaningful reconstruction of scene in real time on platforms with low computing power. This paper proposes a new fast passable area modeling method for the specific situation of indoor environment and small robots. The method is based on the monocular feature-based SLAM. Firstly, it obtains the road segmentation image through segmentation in the HSV color space with adaptive threshold. Then, the system cross-matches the segmentation with the sparse point cloud generated by SLAM, to obtain the ground plane and accurate ground segmentation area. Finally, it projects the ground segmentation area to the ground plane for dense modeling of the floor. In the experiment of indoor scene, the average calculation speed of the proposed method can reach 21 frames per second, and the speed is about 70% of ORB-SLAM, which can meet the real-time requirements of mobile platforms. The position error for the floor plane is 5.8% on average, and the modeling error of the road width is between 3.5% and 12.8%.
-
表 1 平均每帧运算时间
Table 1. Average operation time per frame
模块 运算时间/ms 本文方法 ORB-SLAM SLAM进程 31.21 32.30 图像分割 5.16 — 地面点云获取 1.54 — 拟合平面 0.13 — 分割图像筛选 1.84 — 地面稠密建模 7.80 — 总计 47.68 32.30 表 2 地平面位置还原精度
Table 2. Accuracy of ground plane position restoration
场景 实际距离/cm 拟合地平面距离/cm 误差/% 办公室 42.0 43.6 3.81 教室 42.0 38.7 -7.86 表 3 办公室地面建模精度
Table 3. Ground modeling accuracy of office
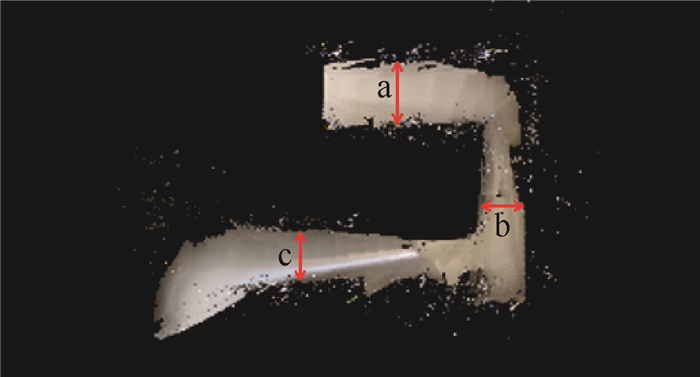
位置 实际距离/cm 模型距离/cm 误差/% a 135 129 4.4 b 112 108 3.5 c 128 116 10.3 表 4 教室地面建模精度
Table 4. Ground modeling accuracy of classroom
位置 实际距离/cm 模型距离/cm 误差/% a 82 85 3.6 b 77 81 5.2 c 70 61 12.8 -
[1] LI Z, TANG J.Weakly supervised deep metric learning for community-contributed image retrieval[J].IEEE Transactions on Multimedia, 2015, 17(11):1989-1999. doi: 10.1109/TMM.2015.2477035 [2] LIU H, ZHANG G, BAO H.A survey of monocular simultaneous localization and mapping[J].Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2016, 28(6):855-868. [3] TURAN M, ALMALIOGLU Y, ARAUJO H, et al.A non-rigid map fusion-based direct SLAM method for endoscopic capsule robots[J].International Journal of Intelligent Robotics and Applications, 2017, 1(4):399-409. doi: 10.1007/s41315-017-0036-4 [4] JAN S, GUMHOLD S, CREMERS D.Real-time dense geometry from a handheld camera[C]//Proceedings of the Pattern Recognition-32nd DAGM Symposium.Berlin: Springer, 2010: 22-24. [5] ENGEL J, KOLTUN V, CREMERS D.Direct sparse odometry[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2016, 40(3):611-625. [6] KIM J H, CADENA C, REID I.Direct semi-dense SLAM for rolling shutter cameras[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 1308-1315. [7] BAILEY T, NIETO J, GUIVANT J, et al.Consistency of the EKF-SLAM algorithm[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2006: 9-15. [8] PIRKER K, MATTHIAS R, BISCHOF H.CD-SLAM-Continuous localization and mapping in a dynamic world[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems(IROS).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 25-30. [9] GEE A P.MAYOL-CUEVAS W.Real-time model-based SLAM using line segments[C]//Proceedings of the International Symposium on Visual Computing.Berlin: Springer, 2006: 354-363. [10] NEWCOMBE R A, LOVEGROVE S J, DAVISON A J.DTAM: Dense tracking and mapping in real-time[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2011: 6-13. [11] ENGEL J, SCHÖPS T, CREMERS D.LSD-SLAM: Large-scale direct monocular SLAM[C]//Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).Berlin: Springer, 2014: 834-849. [12] TRIGGS B, MCLAUCHLAN P F, HARTLEY R I, et al.Bundle adjustment a modern synthesis[C]//Proceedings of the Vision Algorithms: Theory and Practice.Berlin: Springer, 2000: 298-372. [13] ULRICH I, NOURBAKHSH I R.Appearance-based place recognition for topological localization[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2000: 1023-1029. [14] DAVISON A J, REID I D, MOLTON N D, et al.MonoSLAM:Real-time single camera SLAM[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2007, 29(6):1052-1067. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2007.1049 [15] KLEIN G, MURRAY D.Parallel tracking and mapping for small AR workspaces[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE and ACM International Symposium on Mixed and Augmented Reality.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2007: 225-234. [16] MUR-ARTAL R, MONTIEL J M M, TARDÓS J D.ORB-SLAM:A versatile and accurate monocular SLAM System[J].IEEE Transactions Robotics, 2015, 31(5):1147-1163. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2015.2463671 [17] NEWCOMBE R A, DAVISON A J.Live dense reconstruction with a single moving camera[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR).Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2010: 1498-1505. [18] MURARTAL R, TARDOS J D.Probabilistic semi-dense mapping from highly accurate feature-based monocular SLAM[C]//Proceedings of the Robotics Science and Systems, 2015. [19] HINZMANN T, SCHNEIDER T, DYMCZYK M, et al.Robust map generation for fixed-wing UAVs with low-cost highly-oblique monocular cameras[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots & Systems.Piscataway, NJ: IEEE Press, 2016: 3261-3268. [20] 蒙山, 唐文名.单目SLAM直线匹配增强平面发现方法[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(4):660-666. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract14265.shtmlMENG S, TANG W M.Monocular SLAM linear matching enhanced plane discovery method[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(4):660-666(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/abstract/abstract14265.shtml [21] VON STUMBERG L, USENKO V, ENGEL J, et al.Autonomous exploration with a low-cost quadrocopter using semi-dense monocular SLAM[C]//Processing of the European Conference on Mobile Robots, 2017. [22] 蒋林, 郭晨, 朱志超.嵌入式平台上的三维重建算法研究[J].机械设计与制造, 2018, 330(8):264-266.JIANG L, GUO C, ZHU Z C.Research on 3D reconstruction algorithm based on embedded platform[J].Machinery Design & Manufacture, 2018, 330(8):264-266(in Chinese). [23] BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R.SegNet:A deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for scene segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017, 39(12):2481-2495. doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2016.2644615 [24] 黄寅.基于HSV颜色空间与形态学的车辆目标分割算法[J].大庆师范学院学报, 2017, 37(6):11-15.HUANG Y, Vehicle target segmentation algorithm based on HSV color space and morphology[J].Journal of Daqing Normal University, 2017, 37(6):11-15(in Chinese). [25] 闫敬文.数字图像处理:MATLAB版[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2011:125-127.YAN J W.Digital image processing by MATLAB[M].Beijing:National Defence Industry Press, 2011:125-127(in Chinese). [26] 李鹏飞, 吴海娥, 景军锋, 等.点云模型的噪声分类去噪算法[J].计算机工程与应用, 2016, 52(20):188-192. doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1603-0354LI P F, WU H E, JING J F, et al.Noise classification and denoising algorithm for point cloud model[J].Computer Engineering and Applications, 2016, 52(20):188-192(in Chinese). doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1603-0354 -








 下载:
下载: