-
摘要:
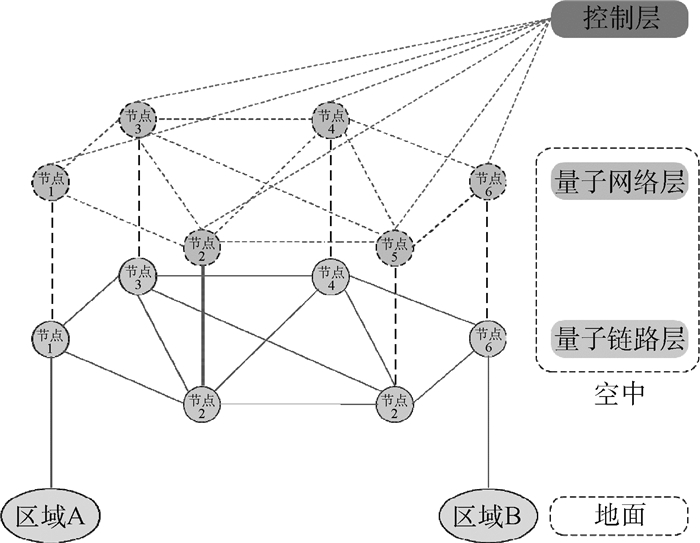
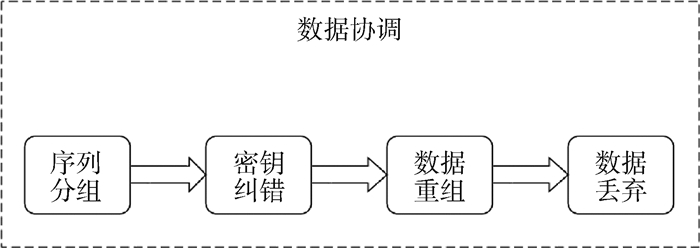
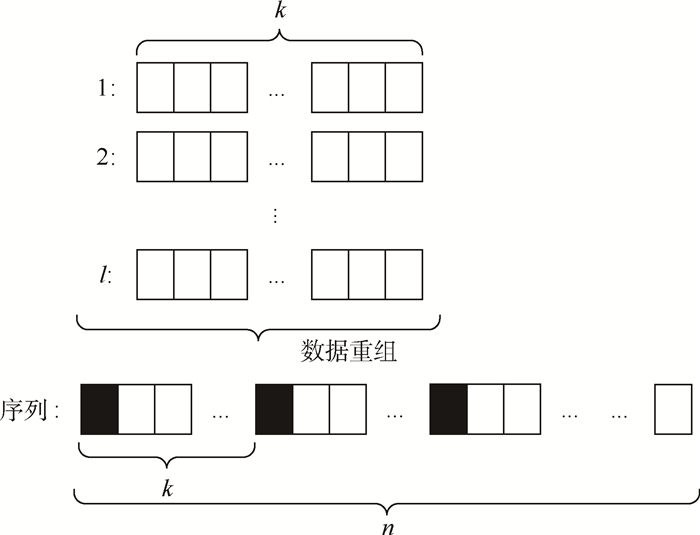
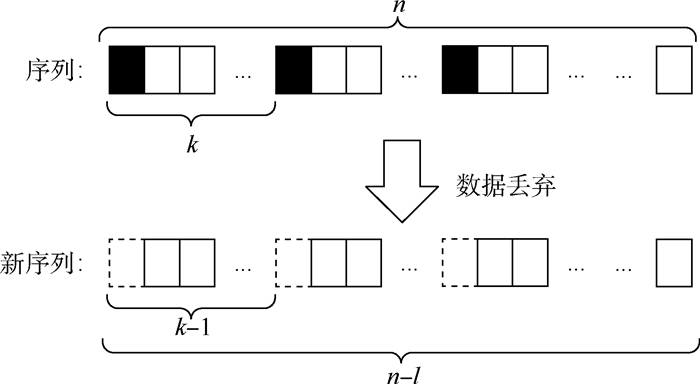
在空地量子密钥分发网络中,空中平台的硬件设备限制使得后处理阶段数据传输速度以及处理能力减弱。针对空中平台的特性,提出了一种适合空地量子密钥分发网络的数据协调方案。首先,采用量子纠错技术减少原始密钥的误码率;其次,设计了一种新方法用来制备低密度奇偶校验(LDPC)译码算法中的随机置换序列;最后,兼顾LDPC译码算法性能和算法硬件实现复杂度,选取了软判决中最小和译码算法。仿真分析表明:量子纠错处理后的原始密钥误码率明显减少,错误率由29.5%减少为4.4%;使用新方法生成随机置换序列,在保证序列随机性的前提下效率提升,生成长度为10 000的随机置换序列所用时间约为0.019 s;LDPC译码算法中最小和译码算法性能适中且硬件实现简单。
-
关键词:
- 空地量子密钥分发网络 /
- 后处理 /
- 数据协调 /
- 纠错算法 /
- 低密度奇偶校验(LDPC)码
Abstract:In the space-ground quantum key distribution network, the hardware device limitation of the air platform makes the data transmission speed and processing capability of the post-processing stage weakened. Aimed at the characteristics of free space and airborne platform, this paper proposes a data reconciliation scheme suitable for the space-ground quantum key distribution network. Firstly, quantum error correction techniques are used to reduce the bit error rate of the original key. Then, a new method is designed to prepare random sequences in Low Density Parity-Check (LDPC) algorithm. Finally, considering the performance of the LDPC decoding algorithm and the hardware implementation complexity of the algorithm, Min-Sum decoding algorithm in the soft decision is selected. The simulation analysis shows that the error rate of the original key after quantum error correction processing is significantly reduced, and the error rate is reduced from 29.5% to 4.4%. Using a new method to generate a random sequence, the efficiency is improved under the premise of ensuring the randomness of the sequence. The time to generate a random replacement sequence with a length of 10 000 is about 0.019 s. The Min-Sum decoding algorithms in the LDPC decoding algorithm are moderate in performance and simple in hardware implementation.
-
[1] 李默, 张春梅, 银振强, 等.量子密钥分配后处理概述[J].密码学报, 2015, 2(2):113-121.LI M, ZHANG C M, YIN Z Q, et al.An overview on the post-processing procedure in quantum key distribution[J].Journal of Cryptologic Research, 2015, 2(2):113-121(in Chinese). [2] 朱焕东, 黄春晖.基于量子密钥分配的数据协调方法[J].计算机安全, 2007(5):27-30.ZHU H D, HUANG C H.Data coordination method based on quantum key distribution[J].Network & Computer Security, 2007(5):27-30(in Chinese). [3] BENNETT C H, BRASSARD G.Quantum cryptography: Public key distribution and coin tossing[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer System and Signal Processing.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1984: 175-179. [4] EKERT A.Quantum cryptography based on Bell's theorem[J].Physical Review Letters, 1991, 67(6):661-663. [5] CHIP E, ALEXANDER C, DAVIN P, et al.Current status of the DARPA quantum network[C]//Proceedings of SPIE-The International Society for Optical Engineering.Cambridge: SPIE, 2005: 138-149. [6] 陈非凡, 胡鑫煜, 赵英浩, 等.全球量子保密通信网络发展研究[J].计算机科学与应用, 2018, 8(10):1628-1641.CHEN F F, HU X Y, ZHAO Y H, et al.Development analysis on global quantum secure communication network[J].Computer Science and Application, 2018, 8(10):1628-1641(in Chinese). [7] HEIM B, ELSER D, BARTLEY T J, et al.Atmospheric channel characteristics for quantum communication with continuous polarization variables[J].Applied Physics B, 2009, 98(4):635-640. [8] ELSER D, BARTLEY T, HEIM B, et al.Feasibility of free space quantum key distribution with coherent polarization states[J].New Journal of Physics, 2009, 11(4):1-13. [9] 李晓峰, 胡渝.空-地激光通信链路总体设计思路及重要概念研究[J].应用光学, 2005, 26(6):57-62.LI X F, HU Y.Research of the design method and some important concepts for space-to-ground optical communication[J].Journal of Applied Optics, 2005, 26(6):57-62(in Chinese). [10] NAUERTH S, MOLL F, RAU M, et al.Air-to-ground quantum communication[J].Nature Photonics, 2013, 7(5):382-386. [11] PUGH C J, KAISER S, BOURGOIN J P, et al.Airborne demonstration of a quantum key distribution receiver payload[J].Quantum Science and Technology, 2017, 2(2):1-13. [12] LIU H Y, TIAN X H, GU C S, et al.Drone-based all-weather entanglement distribution[J/OL].Quantum Physics, 2019(2019-05-23)[2019-10-01]. [13] 任继刚, 印娟, 杨彬, 等.星地量子密钥分发中的时间同步研究[J].红外与毫米波学报, 2011, 30(4):381-384.REN J G, YIN J, YANG B, et al.Time synchronization for quantum key distribution from ground to satellite[J].Journal of Infrared and Millimeter Waves, 2011, 30(4):381-384(in Chinese). [14] 李颖, 张鹏明, 魏俊淦.空中的网络-航空自组网[J].科技信息, 2013(11):181.LI Y, ZHANG P M, WEI J G.Aerial network-Aeronautical ad hoc networks[J].Science & Technology Information, 2013(11):181(in Chinese). [15] 杨汝, 李云霞, 石磊, 等.自由空间量子密钥分发关键技术的研究进展[J].激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(2):28-35.YANG R, LI Y X, SHI L, et al.Research progress on key technologies of free-space quantum key distributions[J].Laser & Optoelectronics Progress, 2018, 55(2):28-35(in Chinese). [16] 屠亮亮.基于LDPC码的离散变量量子密钥分发的数据协调[D].南京: 南京邮电大学, 2016: 33-34.TU L L.Information reconciliatioin for discrete-variable quantum key distribution with LDPC codes[D].Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2016: 33-34(in Chinese). [17] 王瑷玲.标准量子纠错与算子量子纠错[D].西安: 陕西师范大学, 2018.WANG A L.Standard quantum error correction and operator quantum error correction[D].Xi'an: Shaanxi Normal University, 2018(in Chinese). [18] GALLAGER R G.Low density parity-check codes[D].Cambridge: Massachusetts Institute of Technology, 1963. [19] 袁建国, 孙雪敏, 汪哲, 等.光通信系统中LDPC码译码算法的研究进展[J].激光杂志, 2018, 39(2):1-7.YUAN J G, SUN X M, WANG Z, et al.Research progress on decoding algorithm of LDPC codes in optical communication systems[J].Laser Journal, 2018, 39(2):1-7(in Chinese). 期刊类型引用(1)
1. 尚涛,孙海正,刘建伟. 基于斐波那契编码的测量设备无关量子密钥分发方案. 航空科学技术. 2021(03): 71-78 .  百度学术
百度学术其他类型引用(2)
-







 下载:
下载:





 百度学术
百度学术

