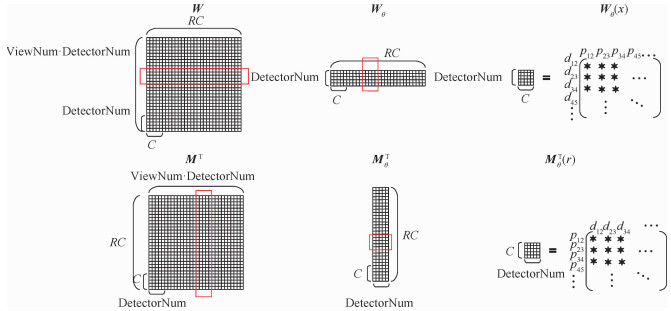
-
摘要:
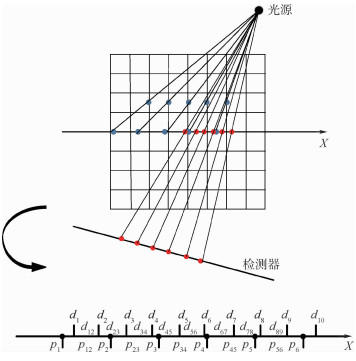
从稀疏投影数据足够精确地重建断层图像,从而能够在显著降低计算机断层成像(CT)检查X-射线辐射剂量的前提下,提供充分适宜影像学临床诊断需求的重建图像。针对圆周扫描扇束投影的二维CT图像重建,提出了投影驱动的系统模型,并将CT迭代图像重建与压缩感知(CS)理论相结合,设计了一种CT迭代图像重建算法,且将算法扩展到圆周扫描锥束投影的三维CT图像重建。仿真实验结果表明:在极稀疏投影数据的条件下([0,2π)范围内扇束/锥束扫描不超过20个投影角度),算法数值精度高,计算复杂度低,内存开销少,有很强的工程实用性。
-
关键词:
- 计算机断层成像(CT) /
- 图像重建 /
- 稀疏投影 /
- 投影驱动 /
- 压缩感知(CS)
Abstract:In order to provide the reconstructed images which are suitable for the clinical imaging diagnosis, this study focuses on reconstructing the tomographic images from sparse projection data with sufficient accuracy under the premise of significantly reducing the X-ray dose of Computerized Tomography (CT) examination. Aimed at 2D image reconstruction of fan-beam projection under circular scanning, this paper proposes the view driven model and designs a CT iterative image reconstruction algorithm by combining the iterative algorithm and the Compressed Sensing (CS) theory. Then the algorithm is extended to 3D image reconstruction of cone-beam projection under circular scanning. The simulation results show that the algorithm has high numerical accuracy, low computational complexity, less memory overhead, and strong engineering practicability under the condition of ultra-sparse projection data (no more than 20 projection angles for fan-beam/cone-beam scanning in the range of[0, 2π)).
-
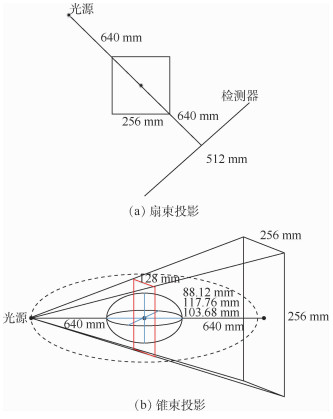
表 1 CT扫描参数和仿真模型信息
Table 1. CT scanning parameters and simulation model information
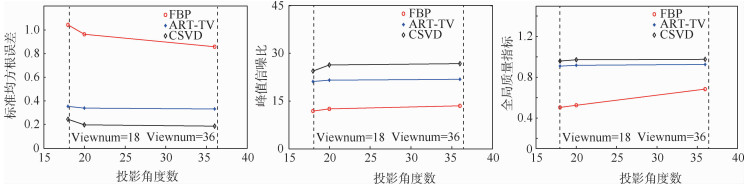
仿真参数 二维扇束 三维锥束 检测器类型 平板检测器 平板检测器 行/列检测器数 512 256 行/列检测器中心 255.5 127.5 行/列检测器间距/mm 1.0 1.0 光源到旋转中心距离/mm 640 640 旋转中心到检测器中心距离/mm 640 640 仿真模型 二维Shepp-Logan 三维Shepp-Logan模型 模型尺寸:512×512 模型尺寸:256×256×256 模型像素尺寸:0.5mm×0.5mm 体素尺寸:0.5mm×0.5mm×0.5mm 表 2 各个投影角度数下不同算法的重建结果
Table 2. Reconstruction results of different algorithms under various projection angles
重建算法 NRMSE PSNR UQI 重建时间/s FBP 0.9641 12.4663 0.5222 4.094 ART-TV 0.3387 21.5526 0.9181 69.585 CSVD 0.1958 26.3113 0.9734 32.997 表 3 CSVD算法重建图像质量评价
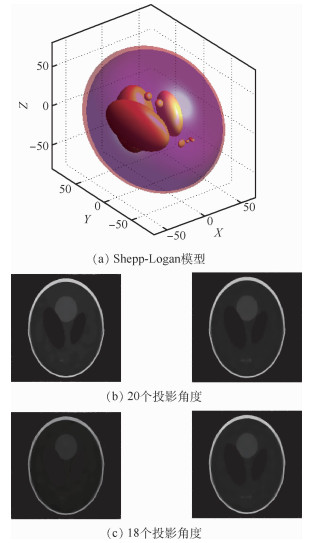
Table 3. Quality evaluation of reconstructed images using CSVD algorithm
质量评价指标 20个投影角度 18个投影角度 NRMSE 0.2887 0.2980 PSNR 22.9883 22.7137 UQI 0.9406 0.9362 -
[1] SABA L, SURI J S.Multi-detector CT imaging principles, head, neck, and vascular systems[M].Boca Raton:CRC Press, 2013:103-122. [2] OHNESORGE B M, FLOHR T G, BECKER C R, et al.Multi-slice CT technology[M].Berlin:Springer, 2007:41-69. [3] NORELLI L J, COATES A D, KOVASZNAY B M.Cancer risk from diagnostic radiology in a deliberate self-harm patient[J].Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 2010, 122(5):427-430. [4] RAMPINELLI C, DE M P, ORIGGI D, et al.Exposure to low dose computed tomography for lung cancer screening and risk of cancer:Secondary analysis of trial data and risk-benefit analysis[J].British Medical Journal, 2017, 356(347):8. [5] PEARCE M S, SALOTTI J A, LITTLE M P, et al.Radiation exposure from CT scans in childhood and subsequent risk of leukaemia and brain tumors:A retrospective cohort study[J]. Lancet, 2012, 380(9840):499-505. [6] MEHYAR L S, ABU-ARJA M H, STANEK J R, et al.The risk of developing secondary central nervous system tumors after diagnostic irradiation from computed tomography in pediatrics:A literature review[J].Pediatric Neurology, 2019, 98:18-24. [7] SIDKY E Y, KAO C M, PAN X.Accurate image reconstruction from few-views and limited-angle data in divergent-beam CT[J].Journal of X-ray Science and Technology, 2006, 14(2):119-139. [8] SIDKY E Y, PAN X.Image reconstruction in circular cone-beam computed tomography by constrained, total-variation minimization[J].Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2008, 53(17):4777-4807. [9] DONOHO D L.Compressed sensing[J].IEEE Transactions on Information Theory, 2006, 52(4):1289-1306. [10] CHEN G H, TANG J, LENG S.Prior image constrained compressed sensing (PICCS):A method to accurately reconstruct dynamic CT images from highly under-sampled projection data sets[J].Medical Physics, 2008, 35(2):660-663. doi: 10.1118/1.2836423 [11] DEBATIN M, ZYGMANSKI P, STSEPANKOU D, et al.CT reconstruction from few-views by anisotropic total variation minimization[C]//2012 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference Record.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 2295-2296. [12] DEBATIN M, HESSER J.Accurate low-dose iterative CT reconstruction from few projections by generalized anisotropic total variation minimization for industrial CT[J].Journal of X-ray Science and Technology, 2015, 23(6):701-726. [13] CANDES E, ROMBERG J, TAO T.Stable signal recovery from incomplete and inaccurate measurements[J].Communications on Pure and Applied Mathematics, 2006, 59(8):1207-1223. doi: 10.1002/cpa.20124/full [14] MAN B D, BASU S.Distance-driven projection and backprojection[C]//2002 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium Conference Record.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2002: 1477-1480. [15] MAN B D, BASU S.Distance-driven projection and backprojection in three dimensions[J].Physics in Medicine and Biology, 2004, 49(11):2463-2475. [16] TUY H K.An inversion formula for cone-beam reconstruction[J].SIAM Journal on Applied Mathematics, 1983, 43(3):546-552. [17] WANG Z, BOVIK A C.A universal image quality index[J].IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2002, 9(3):81-84. -







 下载:
下载: