Comparative study on immunoreactions of small intestinal submucosa by irradiation and ethylene oxide sterilization treatments
-
摘要:
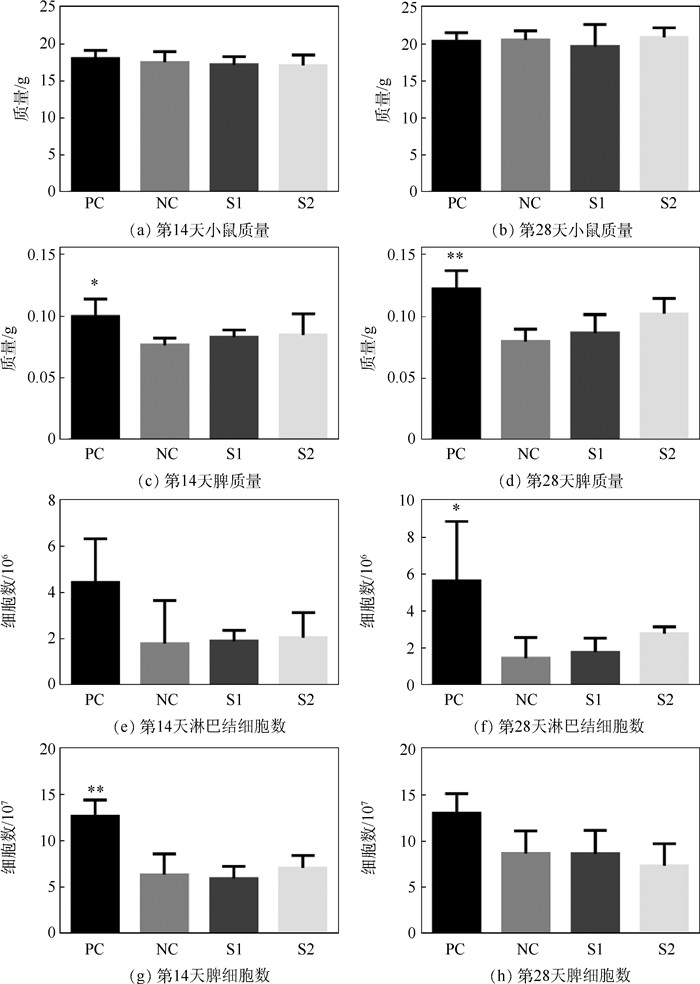
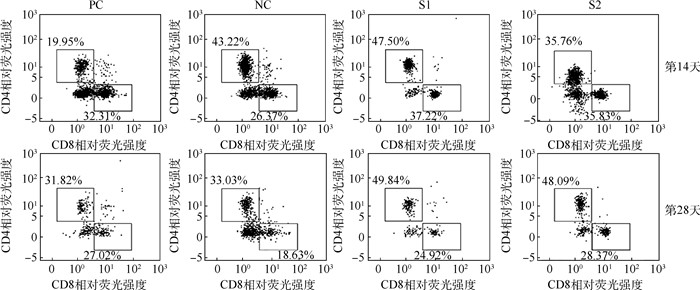
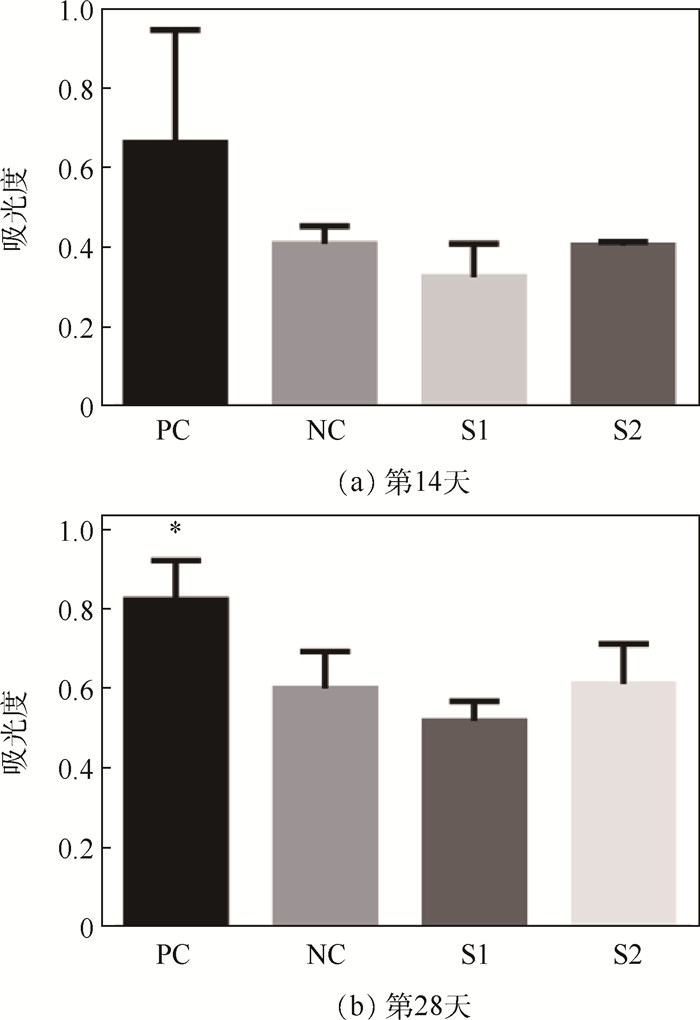
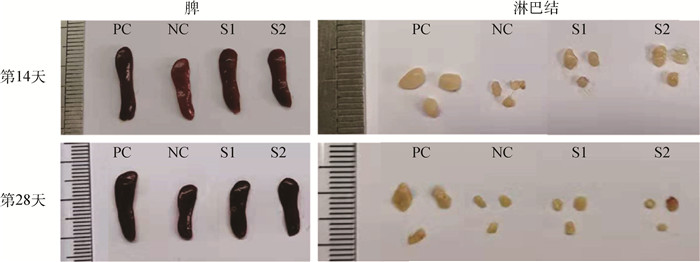
免疫反应大小是决定可植入生物材料能否开展临床应用的关键因素之一。研究评估了辐照和环氧乙烷(EO)两种灭菌方式处理后的小肠黏膜下层(SIS)脱细胞外基质材料在体内的免疫反应,旨在为其临床试验的开展提供可行依据。将两种灭菌方式处理的SIS脱细胞外基质材料皮下植入到BALB/c小鼠,第14和28天取样后,系统性地评估了其免疫反应。与仅手术不植入材料的阴性对照组相比,免疫器官(脾和淋巴结)的形态、质量、细胞数、淋巴细胞的体外增殖及酶联免疫吸附检测结果均无显著性差异,证明两种灭菌方式处理后的SIS脱细胞外基质材料都不会对小鼠引起明显的免疫排斥反应。流式细胞术分析及局部H&E染色结果表明,经EO灭菌处理的SIS脱细胞外基质材料对小鼠的免疫刺激更小,是更适用于此材料的灭菌方法。研究结果为SIS脱细胞外基质材料的灭菌程序及其临床应用提供了支持。
-
关键词:
- 小肠黏膜下层(SIS) /
- 免疫反应 /
- 炎症 /
- 环氧乙烷(EO)灭菌 /
- 辐照灭菌
Abstract:Foreign body reaction is one of the key factors limiting the application of implantable biomaterials. This study evaluates the in vivo immune response of acellular Small Intestinal Submucosa (SIS) materials treated with irradiation and Ethylene Oxide (EO) sterilization technology for providing a basis for clinical trials. The sterilized materials are subcutaneously implanted into BALB/c mice for 14 or 28 days. Compared with negative controlgroup, there is no difference in the size, weight, cell numbers, lymphocytes proliferation and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay of the immune organs for two sterilized materials on mice. These results prove that the SIS materials treated by two sterilization methods do not cause obvious inflammatory reaction. Flow cytometry analysis and H&E staining results show that the materials sterilized by EO have less immune stimulation to mice. It means that EO treatment is a safer and more reliable sterilization method for SIS material, providing a prospect for sterilization procedure and clinical application of acellular SIS materials.
-
-
[1] WANG W, ZHANG L, SUN L, et al.Biocompatibility and immunotoxicology of the preclinical implantation of a collagen-based artificial dermal regeneration matrix[J].Biomedical and Environmental Sciences, 2018, 31(11):829-842. [2] ZHANG L, NIU X, SUN L, et al.Immune response of bovine sourced cross-linked collagen sponge for hemostasis[J].Journal of Biomaterials Applications, 2017, 32(7):920-931. [3] BRYERS J D, GIACHELLI C M, RATNER B D.Engineering biomaterials to integrate and heal:The biocompatibility paradigm shifts[J].Biotechnology and Bioengineering, 2012, 109(8):1898-1911. [4] FRANZ S, RAMMELT S, SCHARNWEBER D, et al.Immune responses to implants-A review of the implications for the design of immunomodulatory biomaterials[J].Biomaterials, 2011, 32(28):6692-6709. [5] PEREZ R A, KIM H W.Core-shell designed scaffolds for drug delivery and tissue engineering[J].Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 21:2-19. [6] 张炜炜, 刘瑾, 陈伟.犬肾脏脱细胞基质凝胶的制备及生物相容性实验研究[J].第三军医大学学报, 2015, 37(19):1942-1945. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DSDX201519007.htmZHANG W W, LIU J, CHEN W.Preparation and biocompatibility of canine kidney acellular matrix gel[J].Journal of Third Military Medical University, 2015, 37(19):1942-1945(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-DSDX201519007.htm [7] ZHAI Y, GHOBRIAL R M, BUSUTTIL R W, et al.Th1 and Th2 cytokines in organ transplantation:Paradigm lost [J].Critical Reviews in Immunology, 1999, 19(2):155-172. [8] SANDRIN M S, MCKENZIE I F.Gal alpha (1, 3)Gal, the major xenoantigen(s) recognised in pigs by human natural antibodies[J].Immunological Reviews, 1994, 141:169-190. [9] DALY K A, STEWART-AKERS A M, HARA H, et al.Effect of the alphaGal epitope on the response to small intestinal submucosa extracellular matrix in a nonhuman primate model[J].Tissue Engineering Part A, 2009, 15(12):3877-3888. doi: 10.1089/ten.tea.2009.0089 [10] ANSALONI L, CAMBRINI P, CATENA F, et al.Immune response to small intestinal submucosa (Surgisis) implant in humans:Preliminary observations[J].Journal of Investigative Surgery, 2009, 20(4):237-241. doi: 10.1080/08941930701481296 [11] BADYLAK S F.The extracellular matrix as a biologic scaffold material[J].Biomaterials, 2007, 28(25):3587-3593. [12] 粟香, 葛良鹏, 李前勇.猪小肠黏膜下层作为组织修复材料的研究进展[J].中国比较医学杂志, 2019, 29(8):122-128. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGDX201908018.htmSU X, GE L P, LI Q Y.Research advances in the preparation and application of porcine small intestinal submucosa as a tissue-repair material[J].Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine, 2019, 29(8):122-128(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGDX201908018.htm [13] 杨凯, 张育敏, 张乃丽, 等.小肠黏膜下层在组织修复重建中的应用研究进展[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2013, 27(9):1138-1143.YANG K, ZHANG Y M, ZHANG N L, et al.Recent progress of small intestinal submucosa in application research of tissue repair and reconstruction[J].Chinese Journal of Reparative and Reconstructive Surgery, 2013, 27(9):1138-1143(in Chinese). [14] 董教明, 莫秀梅, 李雨, 等.天然组织去细胞技术的研究进展[J].生物医学工程学杂志, 2012, 29(5):1007-1013. http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SWGC201205041.htmDONG J M, MO X M, LI Y, et al.Recent research progress of decellularization of native tissues[J].Journal of Biomedical Engineering, 2012, 29(5):1007-1013(in Chinese). http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-SWGC201205041.htm [15] POPE S, TOMARELLI R M, GYÖRGY P.Bifidus factor.Isolation of ethyl N-acetyl-B-d-glucosaminide from Aspergillus fermentations[J].Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 1957, 68(2):362-366. [16] 冯少俊, 伍振峰, 王雅琪, 等.中药灭菌工艺研究现状及问题分析[J].中草药, 2015, 46(18):2667-2673.FENG S J, WU Z F, WANG Y Q, et al.Current situation and problem analysis on sterilization process for Chinese materia medica[J].Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2015, 46(18):2667-2673(in Chinese). [17] 张林, 孙磊, 徐梦浛, 等.可吸收胶原膜的体内免疫反应评价[J].北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(4):879-886. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0230ZHANG L, SUN L, XU M H, et al.Immunological response evaluation of absorbable collagen membrane in vivo[J].Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(4):879-886(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0230 [18] 李计萍.γ射线辐照灭菌法在中药及其制剂中应用现状和相关问题讨论[J].中国中药杂志, 2007, 32(19):2078-2081.LI J P.Application status and related discussions of γ-ray irradiation sterilization method in Chinese medicine and its preparations[J].China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2007, 32(19):2078-2081(in Chinese). [19] 王广芬, 朱梦捷, 廖丹, 等.十二指肠镜清洗消毒及监测研究新进展[J].中华医院感染学杂志, 2017, 27(24):5751-5755.WANG G F, ZHU M J, LIAO D, et al.New development of the study about cleaning, disinfection and monitoring of duodenoscope[J].Chinese Journal of Nosocomiology, 2017, 27(24):5751-5755(in Chinese). [20] 尹广桂, 刘白云.环氧乙烷低温灭菌技术的进展及使用安全管理[J].世界最新医学信息文摘, 2016, 16(32):43-44.YIN G G, LIU B Y.Recent advances and safety management of ethylene oxide low-temperature sterlization technology[J].World Latest Medicine Information, 2016, 16(32):43-44(in Chinese). [21] 赵香玉, 李晓霞.环氧乙烷低温灭菌器使用中存在的问题及对策[J].中国消毒学杂志, 2013, 30(6):574-575.ZHAO X Y, LI X X.Problems and solutions in the use of ethylene oxide low-temperature sterilizer[J].Chinese Journal of Disinfection, 2013, 30(6):574-575(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: