Experimental investigation on micro milling holes of high-strength elastic alloy
-
摘要:
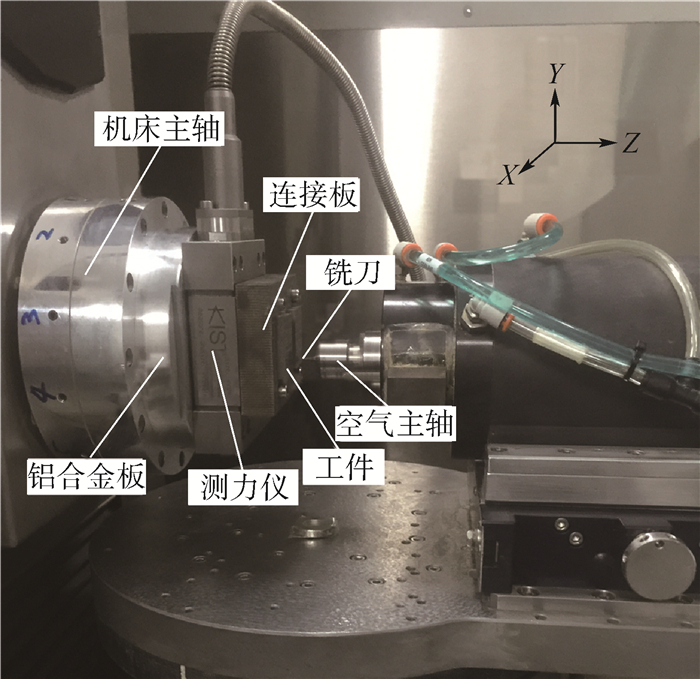
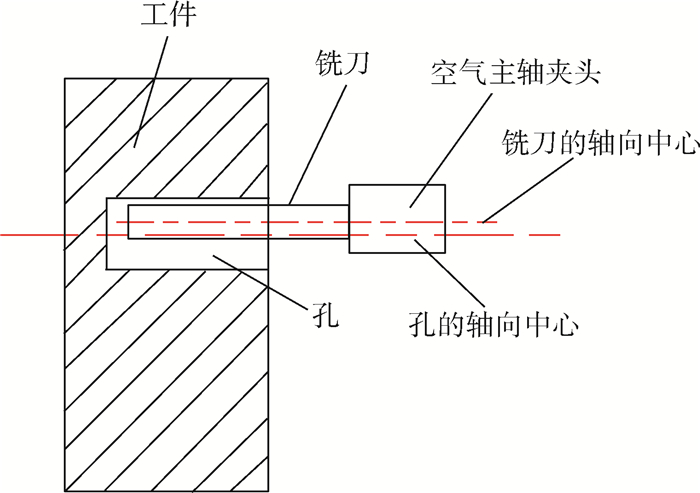
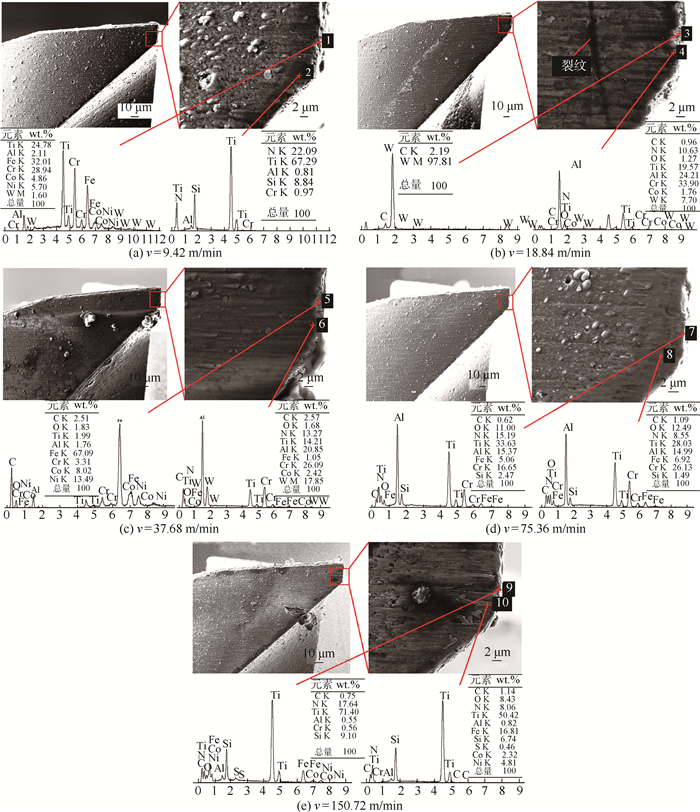
使用超高精度加工中心进行了多组铣削3J33B高强度弹性合金微孔的铣削实验,使用Kistler 9119AA2型高精度测力仪测量铣削力,使用Keyence 3D激光显微镜测量已加工孔的尺寸,使用扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和能谱仪(EDS)测量刀具磨损。实验结果表明,在不同的切削速度条件下,主铣削力的
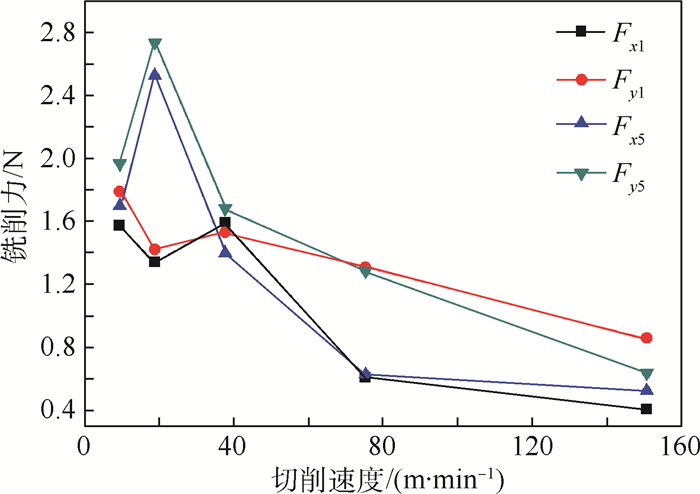
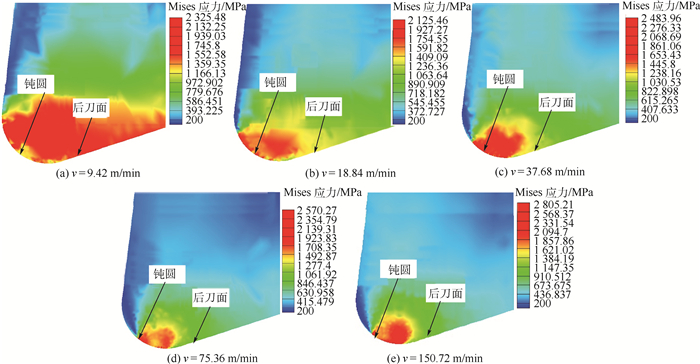
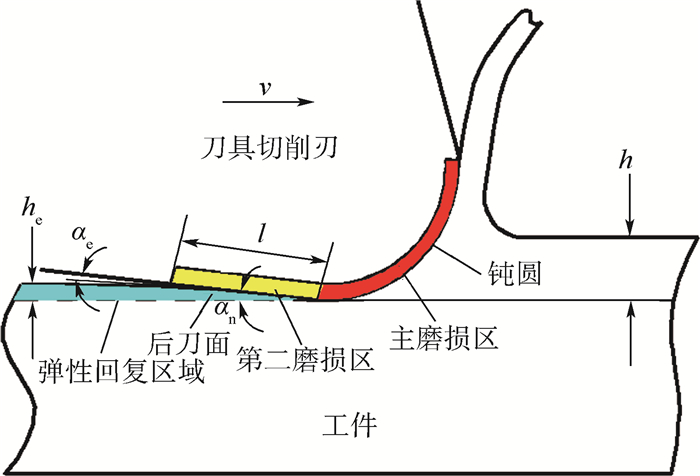
Y 方向分力(Y 方向力)总是大于X 方向分力(X 方向力)。在铣削微孔过程中,使用高切削速度进行微细铣削成孔时,已加工孔的孔口直径尺寸误差会增大,严重影响尺寸精度。刀具磨损最严重的区域在刀尖处,并且发生磨损的区域基本集中在整个切削刃的钝圆和接近钝圆的后刀面处。当在低速切削时,磨粒磨损是刀具的主要磨损形式,然而,随着切削速度的提高,氧化磨损所占比例逐渐增大。已加工表面的弹性回复加剧了后刀面磨损,并影响切削稳定性。Abstract:In this study, several sets of experiments were carried out to evaluate the characteristics of micro milling holes in high-strength elastic alloy 3J33B material using an ultra-precision machine tool. The milling forces were measured using a Kistler 9119AA2 dynamometer, and the sizes and surface burrs on the machined holes were measured using a Keyence 3D laser scanning microscope. Furthermore, tool wear was examined using a Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) and an Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (EDS). Experimental results indicate that the force in
Y direction is always greater than the force inX direction regardless of the cutting speed variation. High cutting speeds or high spindle speeds may affect the machining dimensional accuracy during micro milling holes. The most serious region of tool wear is the tool tip of cutting edge in micro milling holes, and the wear is mainly concentrated on the whole cutting edge roundness and the flank which is near the cutting edge roundness. Abrasive wear is the main form of tool wear at a low cutting speed, and the effect of oxidation wear on tool wear increases with the increase in the cutting speeds. The elastic recovery of the machined surface aggravates the wear of the flank wear and affects the cutting stability.-
Key words:
- micro milling holes /
- high-strength elastic alloy /
- milling forces /
- orifice diameter /
- tool wear
-
表 1 3J33B弹性合金的化学组成
Table 1. Chemical composition of elastic alloy 3J33B
元素 质量分数/% C 0.008 Si 0.10 Mn ≤0.10 P 0.005 S 0.005 Ni 17.50~19.00 Co 1.50~8.50 Mo 4.60~5.20 Ti 0.35~0.50 Al 0.05~0.15 Fe 65 表 2 3J33B弹性合金的基本力学性能
Table 2. Main mechanical properties of elastic alloy 3J33B
参数 数值 抗拉强度/MPa ≥1 800 屈服强度/MPa ≥1 720 弹性模量/GPa 188 延伸率/% ≥8 硬度/HRC 30 表 3 铣削所用加工参数
Table 3. Cutting conditions used in milling
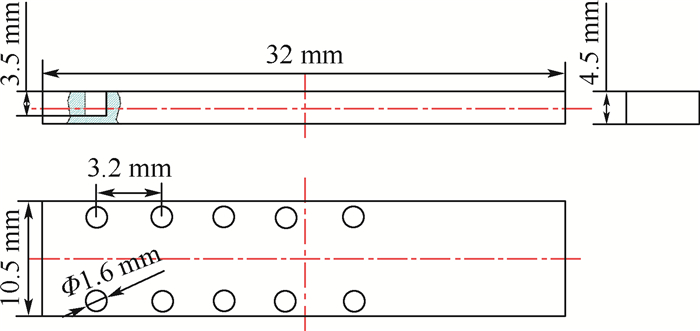
参数 实验号 1 2 3 4 5 n/(r·min-1) 3 000 6 000 12 000 24 000 48 000 v/(m·min-1) 9.42 18.84 37.68 75.36 150.72 vfp/(mm·min-1) 12 vfa/(mm·min-1) 15 lr/mm 0.01 la/mm 0.1 表 4 已加工孔的孔口直径测量值
Table 4. Measured orifice diameters of machined holes
v/(m·min-1) 孔口直径/mm No.1 No.2 No.3 No.4 No.5 9.42 1.613 1.612 1.611 1.610 1.608 18.84 1.610 1.609 1.607 1.606 1.604 37.68 1.612 1.609 1.608 1.607 1.605 75.36 1.611 1.608 1.607 1.605 1.604 150.72 1.630 1.626 1.625 1.623 1.622 -
[1] CHAE J, PAEK S S, FREIHEIT T.Investigation of micro-cutting operations[J].International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2006, 46(3-4):313-332. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2005.05.015 [2] DOENFELD D, MIN S, TAKEUCHI Y.Recent advances in mechanical micromachining[J].CIRP Annals-Manufacturing Technology, 2006, 55(2):745-768. doi: 10.1016/j.cirp.2006.10.006 [3] GRZESIK W.Advanced machining processes of metallic materials[M].Amsterdam:Elsevier, 2008:301-302. [4] ARAMCHAROEN A, MATIVENGA P T.Size effect and tool geometry in micromilling of tool steel[J].Precision Engineering, 2009, 33(4):402-407. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2008.11.002 [5] AFAZOV S M, RATCHEV S M, SEGAL J.Modelling and simulation of micro-milling cutting forces[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2010, 210(15):2154-2162. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.07.033 [6] AFAZOV S M, ZDEBSKI D, RATCHEV S M, et al.Effects of micro-milling conditions on the cutting forces and process stability[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2013, 213(5):671-684. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.12.001 [7] TANSEL I N, ARKAN T T, BAO W Y, et al.Tool wear estimation in micro-machining.Part Ⅰ:Tool usage-cutting force relationship[J].International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2000, 40(4):599-608. doi: 10.1016/S0890-6955(99)00073-5 [8] LIU K, LI X P, RAHMAN M.Characteristics of high speed micro-cutting of tungsten carbide[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2003, 140(1-3):352-357. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(03)00758-1 [9] WANG W, KWEON S H, YANG S H.A study on roughness of the micro-end-milled surface produced by a miniatured machine tool[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2005, 162-163:702-708. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2005.02.141 [10] LEKKALA R, BAJPAI V, SINGH R K, et al.Characterization and modeling of burr formation in micro-end milling[J].Precision Engineering, 2011, 35(4):625-637. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2011.04.007 [11] THEPSONTHI T, OZEL T.Multi-objective process optimization for micro-end milling of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy[J].International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 2012, 63(9-12):903-914. doi: 10.1007/s00170-012-3980-z [12] WU X, LI L, HE N.Investigation on the burr formation mechanism in micro cutting[J].Precision Engineering, 2017, 47:191-196. doi: 10.1016/j.precisioneng.2016.08.004 [13] RAMULU M, BRANSON T, KIM D.A study on the drilling of composite and titanium stacks[J].Composite Structures, 2001, 54(1):67-77. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(01)00071-X [14] BIERMANN D, KAHLEYSS F, KREBS E, et al.A study on micro-machining technology for the machining of NiTi:Five-axis micro-milling and micro deep-hole drilling[J].Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2011, 20(4-5):745-751. doi: 10.1007/s11665-010-9796-9 [15] YAN H B, FENG S S, LU T J, et al.Experimental and numerical study of turbulent flow and enhanced heat transfer by cross-drilled holes in a pin-finned brake disc[J].International Journal of Thermal Science, 2017, 118:355-366. doi: 10.1016/j.ijthermalsci.2017.04.024 [16] ZHAO W S, WANG Z L, DI S C, et al.Ultrasonic and electric discharge machining to deep and small hole on titanium alloy[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2002, 120(1-3):101-106. doi: 10.1016/S0924-0136(01)01149-9 [17] TUNNA L, ONEILL W, KHAN A, et al.Analysis of laser micro drilled holes through aluminium for micro-manufacturing applications[J].Optics and Lasers in Engineering, 2005, 43(9):937-950. doi: 10.1016/j.optlaseng.2004.11.001 [18] KOWSARI K, SOOKHAKLARI M R, NOURAEI H, et al.Hybrid erosive jet micro-milling of sintered ceramic wafers with and without copper-filled through-holes[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2016, 230:198-210. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2015.11.027 [19] ISLAM M M, LI C P, WON S J, et al.A deburring strategy in drilled hole of CFRP composites using EDM process[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017, 703:477-485. doi: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.02.001 [20] IYER R, KOSHY P, NG E.Helical milling:An enabling technology for hard machining precision holes in AISI D2 tool steel[J].International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2007, 47(2):205-210. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2006.04.006 [21] REY P A, LEDREF J, SENATORE J, et al.Modelling of cutting forces in orbital drilling of titanium alloy Ti-6Al-4V[J].International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture, 2016, 106:75-88. doi: 10.1016/j.ijmachtools.2016.04.006 [22] YAN M F, WU Y Q, WANG Y, et al.Nanocrystallization of alloy 3J33 by a complex thermomechanical treatment process[J].Materials Science and Engineering A, 2009, 509(1-2):41-45. doi: 10.1016/j.msea.2009.01.004 [23] RODRIGUEZ P, LABARGA J E.A new model for the prediction of cutting forces in micro-end-milling operations[J].Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2013, 213(2):261-268. doi: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2012.09.009 [24] JARDRET V, ZAHOUANI H, LOUBET J L, et al.Understanding and quantification of elastic and plastic deformation during a scratch test[J].Wear, 1998, 218(1):8-14. doi: 10.1016/S0043-1648(98)00200-2 期刊类型引用(0)
其他类型引用(1)
-








 下载:
下载: