-
摘要:
针对垂直起降固定翼无人机的动力需求特点,提出了一种专用于该类无人机的串联混电系统(S-HES)优化设计方法。首先,建立了旋翼、固定翼及转换模式下的垂直起降固定翼无人机的功率需求模型和基于串联混电系统功率传递路径的混电功率解算方程,给出了计及功率约束、能量约束及电池充电的电池质量解算方法,并在大量统计数据的基础上建立了其他混电部件质量解算方程。其次,使用威兰氏线法建立了考虑发动机工作点变化的燃油消耗模型。使用柯西变异粒子群算法基于各物理数学模型在飞行剖面内的各个飞行阶段展开混电控制参数优化,从而完成垂直起降固定翼无人机的顶层设计要求向串联混电系统最佳供电策略、设计功率及质量分配方案的转化。在城市货运和山区货运2种应用场景下对所提方法进行了验证。最后,分析了优化设计结果对于不同飞行阶段性能要求的敏感性。研究结果表明:所提方法可较好地捕捉垂直起降固定翼无人机任务剖面的调整及各飞行阶段的性能要求变化对串联混电系统优化设计结果的显著影响,对垂直起降固定翼无人机的各类应用场景均具有较好的适应性。
-
关键词:
- 混电系统 /
- 垂直起降固定翼无人机 /
- 垂直起降 /
- 参数优化 /
- 总体设计
Abstract:A new method is proposed, for the optimal design of Series-Hybrid Electric System (S-HES) equipped on the unmanned convertiplane, to cope with the special power demand of this type of new aircraft. The method includes multiple physical and mathematical models to describe the characters of convertiplane's S-HES, such as the power requirement solving model in rotor, fixed-wing, and transition modes, the hybrid power solving model based on S-HES structures, and the battery mass sizing equation considering the power constraint, energy constraint, and battery charging. The mass sizing equations of other S-HES components are also established on large amounts of statistical data, and a fuel consumption analysis model considering the engine operating point variation is built based on the Willans line method. Based on the above physical and mathematical models, the hybrid control parameter optimization is carried out at each flight stage in the flight profile using the Cauchy mutation particle swarm optimization algorithm, and thus the top-level aircraft design demand can be translated into the optimal operating strategies, design power, and mass distribution scheme of S-HES. The proposed method was verified in urban freight and mountain freight application scenarios. The results reveal that the adjustment of the mission profile of the unmanned convertiplane and the performance requirement changes at each flight stage have an important impact on the final optimal S-HES design results, and the proposed method can well capture the impact and has good adaptability to various application scenarios of unmanned convertiplane.
-
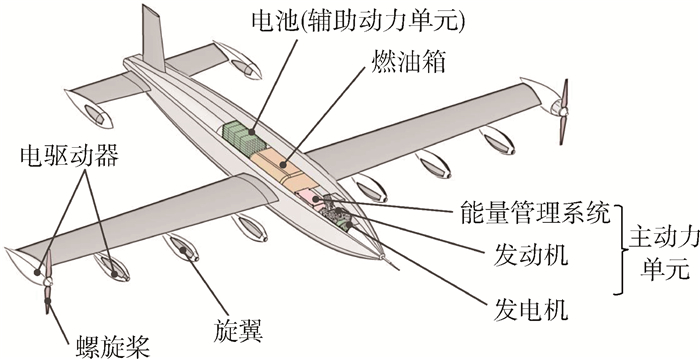
垂直起降固定翼无人机是一种结合了多旋翼无人机和固定翼飞机优势的新型无人飞行器[1]。这类无人机具有较高的巡航效率、较快的飞行速度,以及非常便捷的起降能力,因而可以应付较为复杂的应用场景,是近年来无人机领域的研究热点之一。目前正在开发的垂直起降固定翼无人机有很多,典型的代表有GL-10[2]、Songbird[3]、Panther[4]、Quantix[5]等。其中,大多数垂直起降固定翼无人机以纯电形式提供动力,受当前较低的电池能量密度限制,这类无人机的续航能力往往非常有限[6]。提高其续航能力同时不影响外部动力布置的最有效途径是将纯电动力系统替换为串联混电系统(S-HES)。和纯电动力系统相比,串联混电系统新增加了一个由发动机、发电机、能量管理系统组成的主动力单元,而电池仅作为辅助动力单元在高功率需求状态下进行辅助供电。
受益于燃料较高的储能密度,串联混电系统的引入提供了大幅提升垂直起降固定翼无人机的续航能力,而不引起起飞总重大幅度增加的可能性,但与此同时,其自身所引入的质量和能耗也可能对飞机设计产生较大影响。在串联混电垂直起降固定翼无人机总体设计以及纯电垂直起降固定翼无人机混电改造的初始阶段,开展串联混电系统优化设计是将飞机平台顶层设计要求转化为混电系统最佳运行策略、设计功率、质量分配方案的重要手段,也是充分发挥串联混电系统优势的关键。然而,目前国内外围绕垂直起降固定翼无人机中串联混电系统优化设计的研究还相对较少。现有的混合动力系统在飞机设计领域的应用研究多集中在固定翼无人机领域,其中Finger和Braun[6-7]研究了串联和并联混电系统在传统固定翼无人机设计过程中的应用;Vries等[8]研究了不同的混电系统对于分布式推进固定翼飞机参数选择的影响,而Friedrich和Robertson[9]则在不同指标体系下对混电系统在固定翼无人机上的应用效果进行了综合评价。这些基于传统固定翼无人机飞行剖面和动力需求的混电系统研究工作具有一定的借鉴意义,但均无法直接拓展至垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统设计领域。其核心问题在于:传统固定翼无人机所使用的混合动力系统多为微混动系统,电池功率占比较小且运行工况单一,其优化设计通常为一维优化问题[6-7];而垂直起降固定翼无人机需应对旋翼、转化、固定翼等多种飞行模式,飞行剖面复杂且不同工况下的动力需求差异性更大,其优化设计需考虑全飞行剖面内不同飞行阶段的混电系统运行策略,设计域更广且设计维度更高。除此之外,在固定翼无人机混合动力系统的优化设计中通常所忽略的电池充电、发动机工作点变动等特殊问题,在垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统的优化设计过程中也需特别注意。
为了弥补现有研究的不足,本文在已有研究的基础之上,提出了一种新的垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统优化设计方法。该方法由一系列描述垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统特性的物理数学模型和一个基于柯西变异粒子群算法的全局优化模型组成。利用该方法,可在设计初期快速探索垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统的设计空间,并完成垂直起降固定翼无人机顶层设计要求向串联混电系统最佳供电策略、设计功率及质量分配方案的转化。
1. 物理数学模型
1.1 功率需求模型
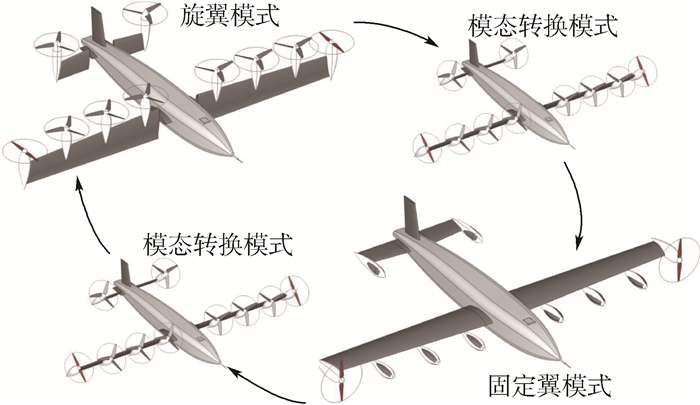
垂直起降固定翼无人机包含倾转机翼无人机、倾转旋翼无人机、尾座式无人机等多种不同类别具备垂直起降和固定翼飞行能力的飞行器,这些飞行器构型差异虽然较大,但应用场景相近,且均包含如图 1所示的固定翼、旋翼、模态转换等主要飞行模式。因此在进行系统设计时,可采用相同方式对不同构型的垂直起降固定翼无人机的功率需求进行描述。
固定翼模式下垂直起降固定翼无人机的典型工况包括巡航/续航飞行、爬升、实用升限、最大飞行速度等。这些工况下螺旋桨/旋翼的吸收功率PPR可统一表示为如下形式[10]:

(1) 式中:W为起飞总重;S为机翼面积;g为重力加速度;β为燃油质量消耗系数;q为飞行动压;CD0为零升阻力系数;K=1/(πe·AR)为升致阻力系数[11],AR为机翼展弦比,e为奥斯瓦尔德因子;h为飞行高度;dh/dt为爬升率;V为飞行速度;ηP为螺旋桨效率。在巡航/续航飞行及最大速度飞行过程中,dh/dt=0。而常值速度爬升时的dh/dt有如下形式[10]:

(2) 式中:CL为升力系数;ρ为空气密度;CD为阻力系数。旋翼模式下垂直起降固定翼无人机的典型工况包括悬停、垂直上升、垂直下降等。各工况下的螺旋桨/旋翼吸收功率计算公式可根据动量理论导出[12]:

(3) 式中:T/W为旋翼模式推重比;FM为旋翼效用因子,FM=0.474 2(T/NR)0.079 3 [13],NR为旋翼数目; vi为静止状态下(dh/dt=0)推力T所对应的旋翼轴向诱导速度,vi=[T/(2ρNRSR)]0.5,SR为单旋翼桨盘面积。推重比T/W使用式(4)计算:

(4) 式中:CD, V为旋翼模式下的全机阻力系数;ζT为飞行状态判定因子, 悬停为0,上升为1,下降为-1。
模态转换过程飞行工况复杂,但是持续时间较短。该模式下的动力系统功率需求与垂直起降固定翼无人机构型、转换策略、飞行姿态等密切相关。在理想运行环境下,经转换策略优化后的尾座类垂直起降固定翼无人机的转换功率需求仅略高于旋翼模式下的最大功率[14],而倾转机翼、倾转旋翼类无人机的转换功率则略低于旋翼模式最大功率[15]。然而,在实际设计过程中为减少转换时间,拓宽转换走廊并为非理想运行工况提供缓冲裕度,转换模式下各类垂直起降固定翼无人机均需具备更大的功率裕度。在初步设计阶段,可使用最大起飞推重比(T/W)max对转换过程中的功率裕度进行等效表征。(T/W)max的值越大,转换过程中的功率裕度越大,则转换过程持续时间越短,同时安全性越好。(T/W)max的典型值在1.15~1.5[14]之间。据此,可将转换模式下的动力系统功率需求表示为如下形式:

(5) 1.2 混电功率解算方程
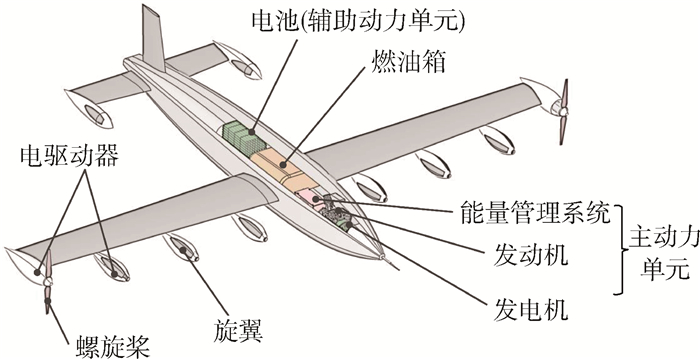
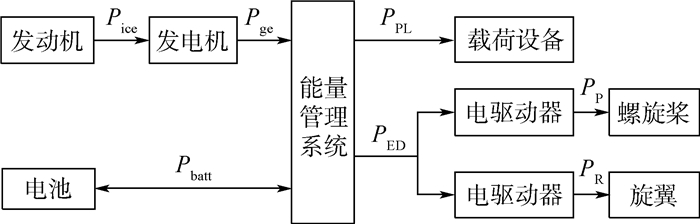
垂直起降固定翼无人机所使用的串联混电系统主要由螺旋桨、旋翼、电驱动器、主动力单元(包括发动机、发电机、能量管理系统)、辅助动力单元(电池)等部件组成(见图 2)。图 3给出了该类串联混电系统的主要结构及其功率传递路径。该路径包含2项需用功率,即载荷设备供电功率PPL和螺旋桨/旋翼总吸收功率PPR,以及4项内部运行功率,包括发动机输出功率Pice、发电机输出功率Pge、电池充/放电功率Pbatt、电驱动器供电功率PED。
基于上述功率传递路径,可建立如式(6)所示的混电功率解算方程组。该混电功率解算方程组由3项功率传递方程和1项混电控制方程构成。功率传递方程用于描述发电机、能量管理系统及电驱动器等部件输入输出功率间的对应关系,其中ηPMS、ηgE和ηED分别为能量管理系统、发电机和电驱动器的功率传递效率。混电控制方程则用于描述每个飞行状态下主动力单元与辅助动力单元(电池)之间的功率配比,Ф=Pbatt/(PED+PPL)为电池混合度,表征当前电池充/放电功率占全部负载功率的比例。

(6) 记Pcmpt=[PED, Pge, Pice, Pbatt]T,Pload=[PPR, PPL]T,可将混电功率解算方程简记为Pcmpt=F(Pload, Ф)。在实际飞行过程中,受飞行状态变化及燃油消耗影响,垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统的功率需求处在不断变化过程中,系统的供电方案(即电池混合度Ф的取值)也可能随之动态调整。为便于解算,可结合功率需求特点将整个飞行过程分为k个阶段,记每个阶段的电池混合度为Фk,则可在每个飞行阶段下对串联混电系统各组件的运行功率分别计算,即Pcmptk=F(Ploadk, Фk)。k的值越大,串联混电系统的设计精度越高,但功率解算的复杂度和优化设计的难度也随之增加。
串联混电系统各组件的设计功率可在各阶段运行功率解算结果的基础上导出。对于独立于高度变化的电驱动器、电池、发电机、能量管理系统等部件来说,其设计功率使用式(7)计算:

(7) 而对于与运行高度密切相关的发动机而言,在求解最大功率之前,需先借助式(8)完成发动机空中运行功率向海平面功率的转换[16]:

(8) 式中:H0和H分别为海平面高度和当前飞行高度;P0和PH分别为海平面高度和当前飞行高度标准大气压力;T0和TH分别为海平面高度和当前飞行高度上的标准大气温度。
1.3 混电质量解算模型
垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统中电池的质量受能量需求和功率需求限制。其中,功率约束下的电池质量可表示为

(9) 式中:Pbattk为电池在第k个飞行阶段的运行功率;ρbatt, P为电池功率密度。能量约束下的电池质量计算则需计及电池充电过程的影响。记第j个飞行阶段为电池充电阶段,则可将能量约束下的电池质量表示为

(10) 式中:ΔTi为第i个阶段的持续时间;ρbatt, E为电池能量密度。除i=j外,ΔTi均由飞行剖面直接确定,而电池充电过程的持续时间ΔTj则由充电前的电池能量消耗、充电过程的电池运行功率Pbattj以及第j个阶段的最大可持续时间ΔTjmax决定,即

(11) 当充电过程发生在固定翼巡航阶段时,最大可持续时间ΔTjmax即为巡航阶段的总持续时间。总电池质量取能量约束和功率约束下电池质量的最大值,即Mbatt=max(Mbatt, P, Mbatt, E)。
除电池组外,串联混电系统其他组件(包括发动机、发电机、能量管理系统、电驱动器、旋翼/螺旋桨)的质量仅由最大设计功率决定,其质量解算方程列在表 1中。其中,发动机、发电机、电驱动器的质量解算方程基于大量已有产品的功率质量统计数据建立(R2分别为0.97,0.98,0.97)[17-20],并使用Jay[21]提出的方法修正了电驱动器最大电压Ued, max与基准电压Ued0, max之间的差异性。能量管理系统的质量由AC/DC转换电路、DC/DC转换电路、电池充电电路、有效载荷供电电路等功能组件的设计功率决定,其质量计算公式根据2款能量管理系统的实测数据得出。螺旋桨/旋翼质量则根据桨叶数Nb、桨叶直径DPR和电驱动器最大输出功率Ped, max,由Roskam[22]提出的方法确定。其中,Pice, max为发动机的最大功率,Pge, max为发电机的最大功率,Pbatt, chg为电池的充电功率。
表 1 其他S-HES组件质量解算方程Table 1. Mass solving equation of other S-HES components组件 质量解算方程 发动机[17] 
发电机[18] MGE=0.385(Pge, max+0.44) 能量管理系统 MPMS=0.1(Pge, max ηPMS- PPL)+0.028 6 Pge, max+0.2 Pbatt, chg+0.21 PPL+0.072(Pge, max+ Pbatt, chg+ Pge, max ηPMS) 电驱动器[19-21] MED=0.158(Ued, max/ Ued0, max)0.158 8 Ped, max+0.024(Ped, max+1.309 6) 螺旋桨/旋翼[22] MPR=0.058 6 Nb0.391(DPR Ped, max)0.782 1.4 燃油消耗模型
垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统在全飞行剖面内的燃油消耗等于各飞行阶段燃油消耗之和,如下:

(12) 式中:




(13) 式中:pme0为平均有效压力损失量;e0和e1为能量转化因子,计算式为

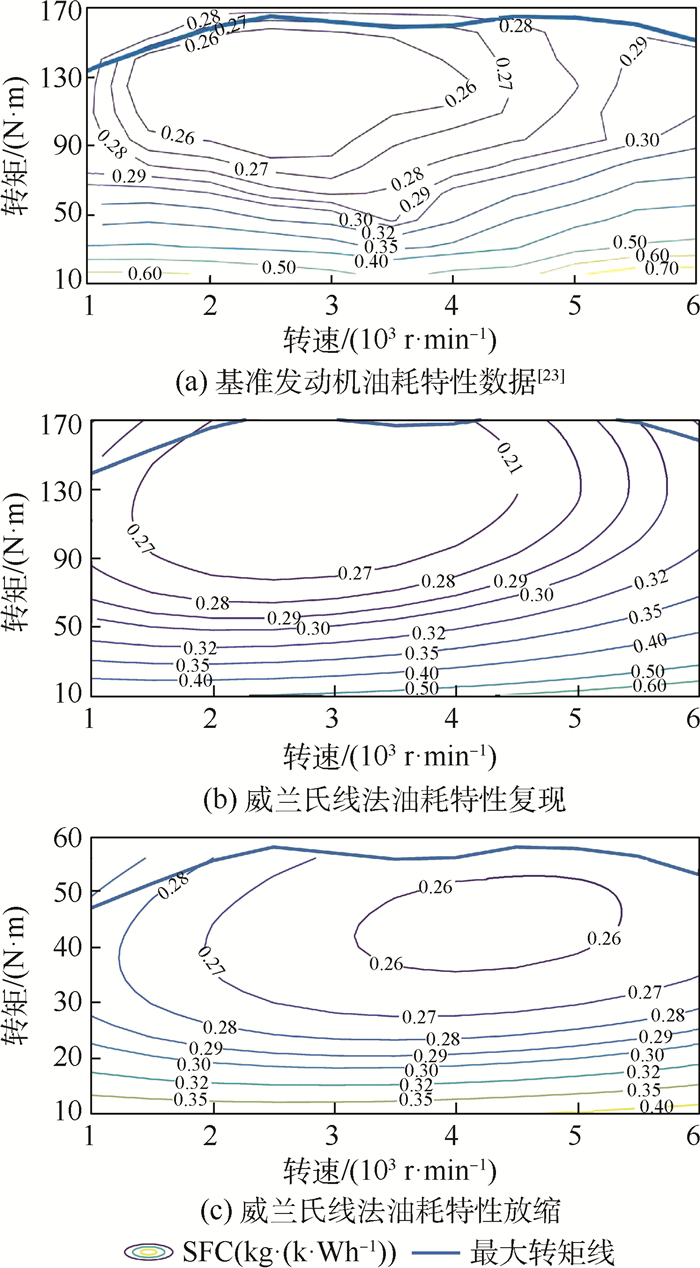
(14) 式中:发动机特征参数e00、e01、e02、e10、e11、pme0, 0、pme0, 2由基准发动机测试数据通过多线性回归确定(对图 4(a)所示的发动机而言,e00、e01、e02、e10、e11、pme0, 0、pme0, 2的值分别为0.412、0.012 7、-3.26×10-4、2.9×10-8、7.15×10-10、1.82×105、662.6)。缩比发动机的排量Vd, s和冲程长度Ss与最大设计功率成正比,而其正则化特性参数pme, s、pmf, s、cm, s的函数关系与基准发动机相同,即

(15) 将基准发动机的特征参数代入式(15),即可根据串联混电垂直起降固定翼无人机中发动机的实际设计功率建立该发动机的正则化参数关系。基于新的正则化发动机性能参数pme, s、pmf, s、cm, s,使用式(16)即可完成所需发动机油耗特性曲线的重建(HLHV为燃油低热值)[24],如图 4(b)和图 4(c)所示。

(16) 式中:Te, s为缩比发动机的转矩;

在串联混电系统中,为了减轻能量管理系统质量,需维持发电机输出电压稳定,这要求发动机在某一额定转速附近运行。该额定转速由发电机额定输出电压及其KV值决定,即NGE=UGE/KVGE。根据由威兰氏线法放缩得到的燃油消耗曲线,在该转速下确定各飞行阶段发动机运行功率所对应的单位时间耗油率,再将其代入式(12),即可完成全飞行剖面内的燃油消耗计算。
2. 设计参数优化
2.1 优化问题描述
垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统优化设计用于在指定任务剖面下,通过优化各飞行阶段的供电策略,找出能够充分发挥系统优势、实现最佳无人机系统效能的混电功率设计及质量分配方案。该优化问题可表示为

(17) 式中:Ψ=(Ф1, Ф2, …, Фk)为k维设计变量,表征全飞行剖面内k个飞行阶段下的串联混电系统供电方案,f(Ψ)为串联混电系统效用评价函数,根据垂直起降固定翼无人机设计用途,可有多种不同表示方式。对货运无人机而言,可使用最大货物质量对串联混电系统效能进行评价,即

(18) 式中:Mcargo为货物质量;MTO、Mempty、MHES分别为起飞总重、空机质量,以及包含主动力单元、电池、燃油、电驱动器、螺旋桨/旋翼在内的串联混电系统总重。对于执行长时侦察监视任务的无人机而言,可使用储备燃油质量Mf, r对串联混电系统效能进行评价,即

(19) 式中:MPL为有效载荷质量。除上述与串联混电系统总质量直接相关的效能评价指标外,还可以使用经济性指标评价串联混电系统效能,如单位载荷里程耗油率、单位时间耗油率等。
约束条件的类别和数量同样根据垂直起降固定翼无人机任务类别和设计需求确定,例如为延长电池寿命,可设定持续充电时间下限,以避免过大的充电功率等。
2.2 优化问题求解
使用柯西变异粒子群算法[25]对式(17)所给出的连续性优化问题进行求解。在k维设计空间中,以拉丁超立方试验设计方法设定s个粒子的初始位置[26]。记第t步迭代时,第i个粒子所处的位置Ψi(t)=(Ф1i(t), Ф2i(t), …, Фki(t)),移动速度vi(t)=(v1i(t), v2i (t), …, vki(t)),粒子自身历史最佳位置pi=(p1i(t), p2i (t), …, pki(t)),所在邻域的历史最佳位置pl=(p1l (t), p2l (t), …, pkl (t)),则下一迭代步该粒子更新速度和位置[25]为

(20) 
(21) 式中:ω1为惯性权值;c1和c2为学习因子;r1和r2为[0, 1]范围内的均匀随机数。在每个迭代步中,使用柯西变异运算对每一代中的具有最佳适应度的全局最优粒子施加扰动以免算法陷入局部最优解[25]。经多步迭代后若所有粒子均聚集到某一位置附近,且该位置不随迭代步的持续增加而继续发生变化,则认为计算收敛。此时具有最佳适应度的粒子的Ψ值即为式(17)所示优化问题的全局最优解。据此可推出串联混电系统在各个飞行阶段的最佳供电策略、运行功率,进而导出各组件的设计功率及质量分配方案,从而完成垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统的优化设计。
3. 结果分析与讨论
3.1 算例分析
在货运场景下对采用图 1中构型的200 kg级垂直起降固定翼无人机开展串联混电系统优化设计,优化设计目标为最大化以货运质量来衡量的单次货运效率。该无人机的通用性设计指标如表 2所示,主要设计输入如表 3所示。
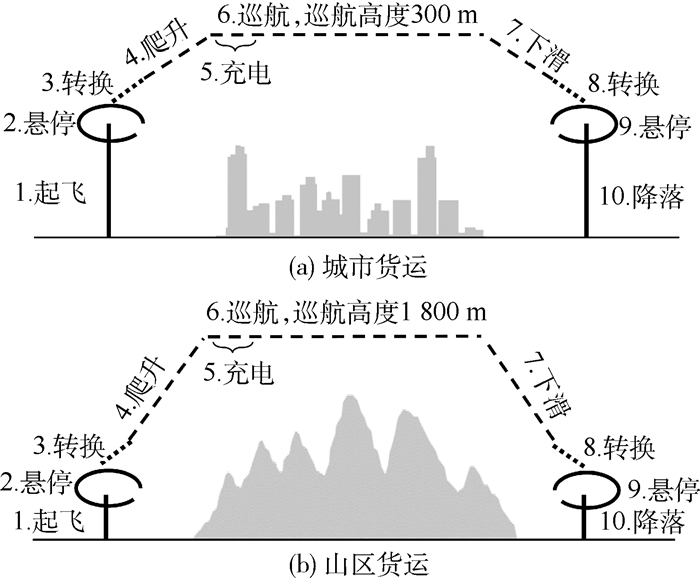
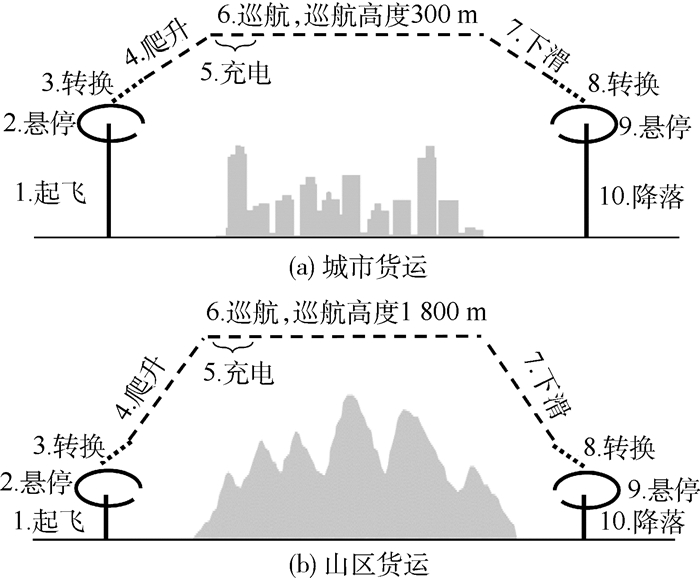
表 2 基本设计要求Table 2. Basic design requirements性能要求 数值 旋翼模式:爬升率/(m·s-1) 3 转换模式: 最大起飞推重比 1.2 转换模式:离地高度/m 150 固定翼模式:爬升率/(m·s-1) 3 固定翼模式:巡航速度/(m·s-1) 35 固定翼模式:巡航距离/km 150 其他:机载设备供电/W 150 表 3 设计输入Table 3. Design input设计输入 数值 动力组件 效率/% 起飞总重/kg 200 发电机 90 空机质量/kg 80 能量管理系统 90 展弦比 18 电驱动器 86 旋翼数目 8 电池(充电) 90 螺旋桨数目 2 螺旋桨 80 单旋翼桨盘面积/m2 0.51 旋翼模式全机阻力系数 3 零升阻力系数 0.03 奥斯瓦尔德因子 0.68 该无人机被设计用于执行如图 5所示的城市货运或山区货运任务。其中,城市货运任务中地形平缓、起降场地较好,故飞机巡航高度低、起降预留悬停时间较短;而山区货运场景中飞机巡航高度高、起降预留悬停时间较长。2种飞行任务下的差异性设计指标如表 4所示,优化设计分别在2种任务剖面下进行。
表 4 城市货运与山区货运剖面差异性设计要求Table 4. Different design indicators in urban freight and mountain freight profiles性能要求 城市货运 山区货运 旋翼模式:单次悬停时长/min 1.5 3 固定翼模式:巡航高度/km 0.3 1.8 固定翼模式:实用升限/m 1 000 2 500 图 5中,城市货运和山区货运2种剖面均被划分为10个不同的飞行阶段(k=10),对应于电池混合度Ф1~Ф10,构成10维设计空间。为降低计算成本,可结合任务剖面特点,合并具有相近功率需求的飞行阶段来压缩设计空间,具体包括:①将旋翼模式下电池混合度(Ф1, Ф2, Ф9, Ф10)均取为ФR; ②将转换模式下电池混合度(Ф3, Ф8)均取为ФT;③将固定翼爬升模式下电池混合度Ф4取为Фclimb,充电模式下电池混合度Ф取为Фchg;④将固定翼巡航状态、下滑状态电池混合度取0。由此,可在4维设计空间下对垂直起降固定翼无人机的串联混电系统进行优化,优化设计变量Ψ=(ФR, ФT, Фclimb, Фchg),优化目标为最大化货物质量。设计约束为持续充电时长大于0.5 h,即ΔTj>0.5 h。
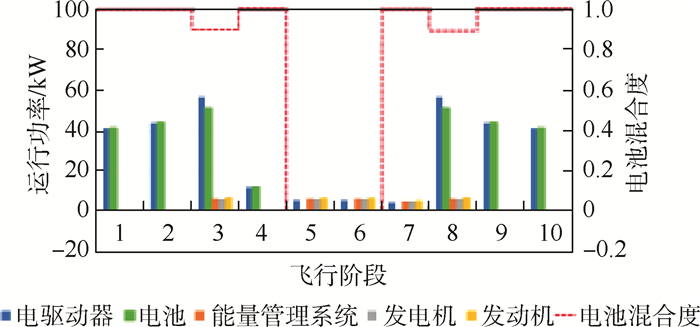
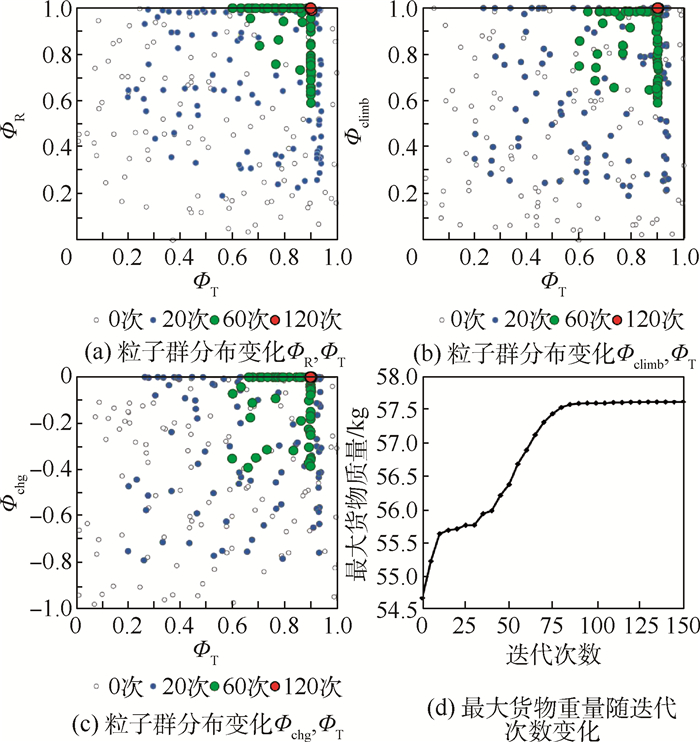
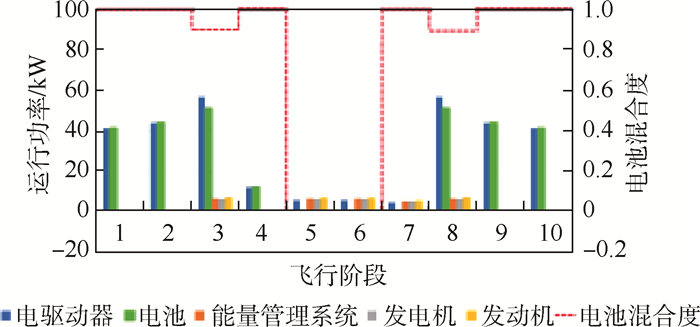
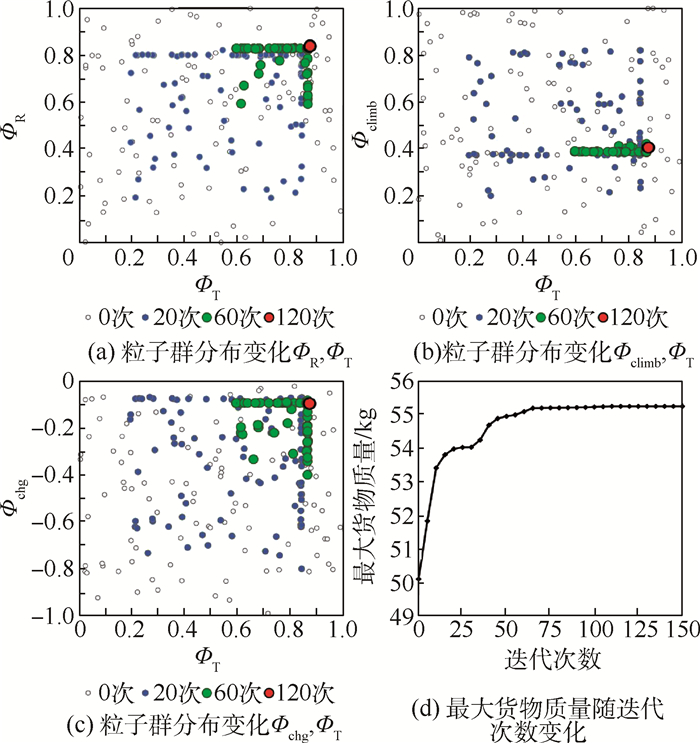
使用拉丁超立方试验设计方法设置100个初始粒子,在城市货运和山区货运2种剖面下分别开展粒子群优化。图 6给出了城市货运剖面下所采用的初始粒子,以及这些粒子在迭代20次、60次、120次后的位置变化。随着迭代次数的增加,粒子位置逐渐向ФR、Фclimb及Фchg的上边界移动。这意味着在该剖面下,旋翼模式固定翼爬升过程中电池功率占比越大、充电功率越小,效用函数的值就越大。最终收敛得到的最大货物质量为57.6 kg,对应最佳优化设计变量Ψ=(1, 0.9, 1, 0),这意味当电池承担100%的旋翼模式供电、90%的转换模式供电、100%的固定翼爬升过程供电,同时不对电池进行充电时,可最大化串联混电系统在该剖面下的应用效益。此时最佳设计点所对应的串联混电系统在全飞行剖面内的供电策略及运行功率变化如图 7所示。相应的串联混电系统各组件设计功率及质量分配方案如表 5所示。
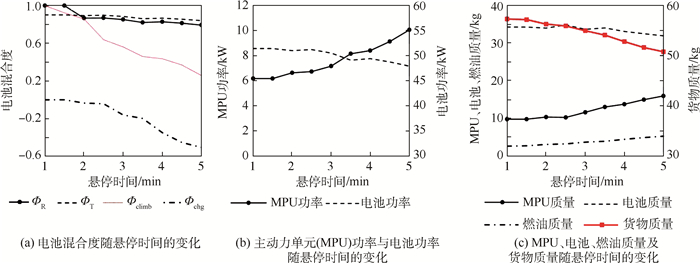
表 5 最佳设计功率及质量分配方案(城市货运)Table 5. Optimal design power and mass distribution scheme (urban freight)组件 设计功率/kW 质量分配/kg 发动机 7.2 5.15 发电机 6.5 2.67 能量管理系统 6.5 1.7 电池 51.1 34.05 电驱动器 56.8 13.48 螺旋桨/旋翼 2.52 燃油 2.8 山区货运剖面下的优化设计结果与城市剖面存在明显差异,如图 8、图 9及表 6所示。该剖面下最大货物质量为55.25 kg,而要达到该最大货物质量,在串联混电系统中,电池需承担旋翼模式总功率需求的83.6%、转换模式总功率需求的87.3%、固定翼爬升过程总功率需求的40.5%,同时在巡航初始阶段需以总功率需求的9.74%为电池充电,即Ψ=(0.836, 0.873, 0.405, -0.097 4)。
表 6 最佳设计功率及质量分配方案(山区货运)Table 6. Optimal design power and mass distribution scheme (mountain freight)组件 设计功率/kW 质量分配/kg 发动机 8.93 6.38 发电机 8.04 3.26 能量管理系统 8.04 2.24 电池 49.7 33.13 电驱动器 56.8 13.48 螺旋桨/旋翼 2.52 燃油 3.73 2种剖面下的串联混电系统优化设计结果差异与其剖面特点密切相关。其中,城市货运剖面悬停时间短、巡航高度低,旋翼模式和固定翼爬升过程能量消耗相对有限,电池质量主要受最大功率限制(即Mbatt, P>Mbatt, E),能量储备较为富余,满足功率需求的电池可独立满足旋翼模式和固定翼爬升过程中的能量需求,故ФR=Фclimb=0,而由于Mbatt, P>Mbatt, E,电池充电不仅无法降低电池质量,反而增加了主动力单元的功率及质量,Фchg=0。相反,山区货运悬停时间较长、巡航高度较大,旋翼模式和固定翼爬升过程中的能量消耗相比于城市货运均大幅提升,电池除受最大功率限制外,还受到能量需求限制,能量储备不再富余。因此,在旋翼模式和爬升过程中,需对主动力单元的既有功率输出能力进行充分利用并对电池进行充电,从而将能量需求上对电池的过多依赖转移至具有更高储能密度的主动力单元,实现串联混电系统总体效用的最大化。
3.2 敏感性分析
以山区货运任务剖面为基准,分析和讨论决定垂直起降固定翼无人机性能要求变化对串联混电系统优化设计结果的影响。
3.2.1 巡航距离对设计结果的影响
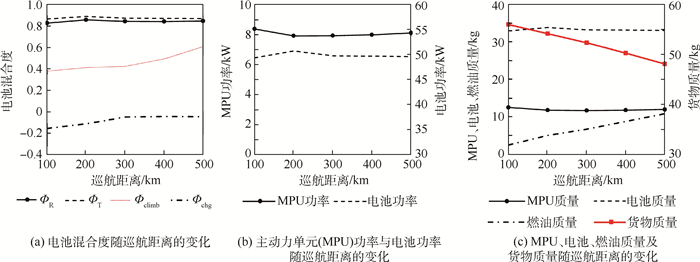
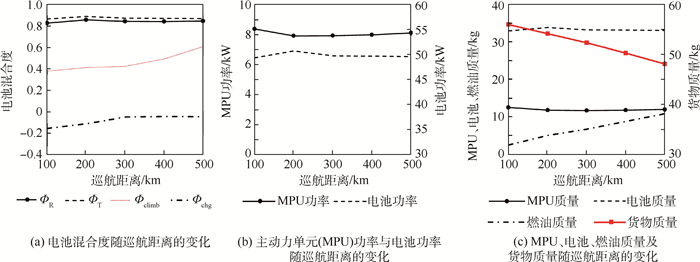
巡航距离对于串联混电系统优化设计结果的影响如图 10所示。在起飞总重限定的情况下,巡航距离的增加显著改变了燃油质量,但对串联混电系统供电策略、设计功率及除燃油质量之外的其他质量分配方案的影响较为有限。仅有的改变在于巡航距离增加提高了电池可充电时长的上限值,因此可使用更小的功率为电池充电(即Фchg减小),从而降低了主动力单元的最大功率负载并减小了主动力单元的质量,但和燃油质量变化相比这些调整均为小量。
3.2.2 巡航高度对设计结果的影响
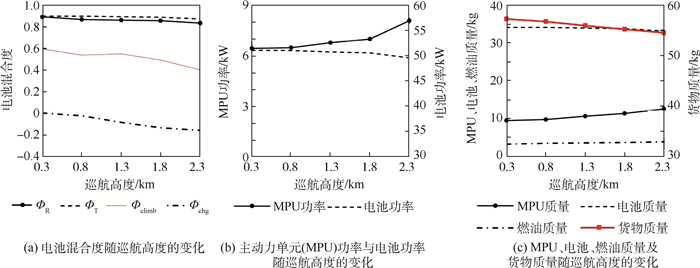
巡航高度对优化设计结果的影响如图 11所示。巡航高度越大,固定翼爬升过程中所需要的能量消耗越大。为充分利用电池的既有储备能量,同时避免引入额外电池质量,随着巡航高度增加,电池输出功率占比逐渐降低(即Фclimb减小),而主动力单元设计功率则不断增加。主动力单元设计功率的增加提高了其在巡航过程中的剩余功率,从而使得电池可以以更大的功率进行充电,从而使得最佳设计点处的Фchg取值不断增加。
3.2.3 悬停时间对设计结果的影响
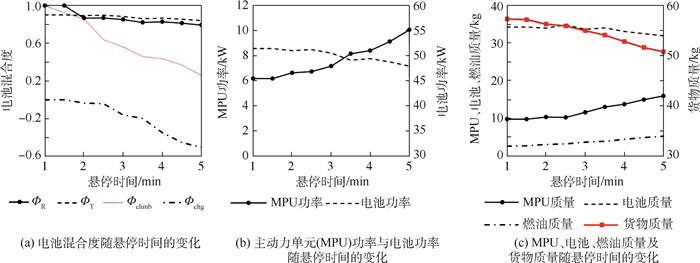
旋翼模式的主要性能指标为悬停时间,其对优化设计结果的影响如图 12所示。悬停时间的增加大幅提升了旋翼模式下的能量消耗,为提供串联混电系统效能,需降低储能密度较低的电池在旋翼模式及固定翼爬升过程等主要能量消耗阶段中的输出功率占比(即减小ФR和Фclimb),而提高主动力单元的设计功率及电池充电功率(即增加Фchg)。
3.2.4 最大起飞推重比对设计结果的影响
转换模式下的主要性能指标(即最大起飞推重比)对优化设计结果的影响如图 13所示。和其他性能指标相比,最大起飞推重比对于最大货物质量有最显著的影响。最大起飞推重比越大,电池设计功率越大,功率约束下的电池质量也就越大。电池质量的增加提高了电池储能,因此在旋翼模式和固定翼模式下的输出功率占比也相应增加(ФR和Фclimb)。同时,由于电池储能的增加,对电池充电的需求逐渐降低,最佳串联混电系统设计方案中Фchg的取值也可减低。另一方面,ФR和Фclimb的提升以及Фchg的降低,又降低了主动力单元的最大负载,因此随着最大起飞推重比的增加,主动力单元的设计功率及质量均可减小。
综合以上分析可知,垂直起降固定翼无人机在不同飞行模式下的设计要求除了直接影响该模式下的串联混电系统最佳供电方案外,也显著改变着其他飞行阶段的串联混电系统供电策略,而这些不同飞行阶段性能变化的耦合影响共同决定了垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统的最终优化设计结果。
3.3 误差分析及修正
本文所提出的垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统优化设计方法是一种从无人机顶层设计要求向系统总体参数及运行策略转化的直接方法。顶层设计要求作为计算输入参与到全部样本点的参数优化过程当中,因此可保证各样本点所对应的无人机总体性能与表 2~表 4中的顶层设计要求之间具备自然一致性。
为提高方法的保真度,在总体参数优化确定过程中所使用的物理模型或基于基本物理规律(如功率需求模型、功率解算模型、电池质量解算模型),或基于测试试验数据并经广泛使用或验证(如发动机威兰氏线模型等)。使用的统计学模型未采用假设或发展预期数据,而是基于当前技术水平下的实际产品(见表 1)。尽管如此,在实际使用过程当中,对每个个体而言,统计预测值与真实值之间的残差不可避免。这一残差是使用本文方法优化设计得到的串联混电系统设计参数与实际制造出的串联混电系统参数之间误差的主要来源。为降低该误差,可根据串联混电系统各部件功率解算的实际范围设置备选设备列表,并根据备选设备列表创建基于准确功率质量数据的二维查找表对表 1中的统计公式进行替换,从而进一步增加串联混电系统优化设计结果的准确性。
4. 结论
1) 基于串联混电垂直起降固定翼无人机数学物理模型及柯西变异粒子群算法,可在垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统的初步设计阶段,完成无人机顶层设计要求向串联混电系统最佳供电策略、设计功率及质量分配方案的快速转换。
2) 垂直起降固定翼无人机串联混电系统的最佳供电策略和最佳设计方案随任务剖面变化。在城市货运场景中,旋翼、转换、爬升等高功率输出状态持续时间较短,电池储能充足,因此电池可承担3种工况下功率负载的100%、90%、100%。而在山区货运场景中,高功率状态持续时间的增加带来了能量需求的大幅提升,因电池储能密度较小,降低其在3种工况下的电池混合度分别至83.6%、87.3%、40.5%才可充分发挥串联混电系统的最佳效能。
3) 巡航高度、悬停时间、最大起飞推重比等单项性能的变化会同时改变多种工况下的最佳电池混合度。其中,巡航高度的增加不仅降低了爬升过程中的电池混合度,还引起了充电功率的提升;悬停时间的增加除影响旋翼模式供电方案外,还会显著影响爬升、充电等过程。这些变化显示,垂直起降固定翼无人机的顶层性能要求对全剖面内最佳串联混电系统供电方案的选择具有耦合影响作用。
4) 所提方法可有效捕捉垂直起降固定翼无人机任务剖面调整、性能要求变化对串联混电系统运行策略、设计参数的影响。该方法既可用于对既有纯电或纯油动垂直起降固定翼无人机平台进行混电改造,也可作为独立的功能模块嵌入到串联混电垂直起降固定翼无人机的完整设计过程当中,两者均具备良好的应用前景。方法的主要误差源于少量组件在统计分析过程中预测值与真实值之间的残差。将统计公式替换为有限数表可消除该误差的影响。
-
表 1 其他S-HES组件质量解算方程
Table 1. Mass solving equation of other S-HES components
组件 质量解算方程 发动机[17] 
发电机[18] MGE=0.385(Pge, max+0.44) 能量管理系统 MPMS=0.1(Pge, max ηPMS- PPL)+0.028 6 Pge, max+0.2 Pbatt, chg+0.21 PPL+0.072(Pge, max+ Pbatt, chg+ Pge, max ηPMS) 电驱动器[19-21] MED=0.158(Ued, max/ Ued0, max)0.158 8 Ped, max+0.024(Ped, max+1.309 6) 螺旋桨/旋翼[22] MPR=0.058 6 Nb0.391(DPR Ped, max)0.782 表 2 基本设计要求
Table 2. Basic design requirements
性能要求 数值 旋翼模式:爬升率/(m·s-1) 3 转换模式: 最大起飞推重比 1.2 转换模式:离地高度/m 150 固定翼模式:爬升率/(m·s-1) 3 固定翼模式:巡航速度/(m·s-1) 35 固定翼模式:巡航距离/km 150 其他:机载设备供电/W 150 表 3 设计输入
Table 3. Design input
设计输入 数值 动力组件 效率/% 起飞总重/kg 200 发电机 90 空机质量/kg 80 能量管理系统 90 展弦比 18 电驱动器 86 旋翼数目 8 电池(充电) 90 螺旋桨数目 2 螺旋桨 80 单旋翼桨盘面积/m2 0.51 旋翼模式全机阻力系数 3 零升阻力系数 0.03 奥斯瓦尔德因子 0.68 表 4 城市货运与山区货运剖面差异性设计要求
Table 4. Different design indicators in urban freight and mountain freight profiles
性能要求 城市货运 山区货运 旋翼模式:单次悬停时长/min 1.5 3 固定翼模式:巡航高度/km 0.3 1.8 固定翼模式:实用升限/m 1 000 2 500 表 5 最佳设计功率及质量分配方案(城市货运)
Table 5. Optimal design power and mass distribution scheme (urban freight)
组件 设计功率/kW 质量分配/kg 发动机 7.2 5.15 发电机 6.5 2.67 能量管理系统 6.5 1.7 电池 51.1 34.05 电驱动器 56.8 13.48 螺旋桨/旋翼 2.52 燃油 2.8 表 6 最佳设计功率及质量分配方案(山区货运)
Table 6. Optimal design power and mass distribution scheme (mountain freight)
组件 设计功率/kW 质量分配/kg 发动机 8.93 6.38 发电机 8.04 3.26 能量管理系统 8.04 2.24 电池 49.7 33.13 电驱动器 56.8 13.48 螺旋桨/旋翼 2.52 燃油 3.73 -
[1] SAEED A S, YOUNES A B, ISLAM S, et al. A review on the platform design, dynamic modeling and control of hybrid UAVs[C]//2015 International Conference on Unmanned Aircraft Systems (ICUAS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 806-815. [2] FREDERICKS W J, MCSWAIN R G, BEATON B F, et al. Greased lightning (GL-10) flight testing campaign: NASA/TM-2017-219643[R]. Washington, D.C. : NASA, 2017: 6-11. [3] THAMM H P, BRIEGER N, NEITZKE K P, et al. Songbird-An innovative UAS combining the advantages of fixed wing and multi rotor UAS[C]//The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences. London: ISPRS Press, 2015: 345-349. [4] KATZ Y. IAI unveils panther tiltrotor UAV[J]. Janes International Defence Review, 2010, 43(12): 26-27. [5] KARKLIN K. AeroVironment quantix tail sitter UAV[EB/OL]. [2019-08-12]. [6] FINGER D F, BRAUN C. Case studies in initial sizing for hybrid-electric general aviation aircraft[C]//2018 AIAA Electric Aircraft Technologies Symposium. Reston: AIAA, 2018: 1-22. [7] FINGER D F, BRAUN C. An initial sizing methodology for hybrid-electric light aircraft[C]//2018 Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2018: 1-10. [8] VRIES R D, BROWN M T, VOS R. A preliminary sizing method for hybrid-electric aircraft including aero-propulsive interaction effects[C]//2018 Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2018: 1-29. [9] FRIEDRICH C, ROBERTSON P A. Design of hybrid-electric propulsion systems for light aircraft[C]//2014 Aviation Technology, Integration, and Operations Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2014: 1-16. [10] HASSANALIAN M, SALAZAR R, ABDELKEFI A. Conceptual design and optimization of a tilt-rotor micro air vehicle[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32(2): 369-381. doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2018.10.006 [11] RAYMER D P. Aircraft design: A conceptual approach[M]. 5th ed. Reston: AIAA, 2012: 93. [12] LEISHMAN J G. Principles of helicopter aerodynamics[M]. London: Cambridge University Press, 2002: 36. [13] TYAN M, NGUYEN N V, KIM S, et al. Comprehensive preliminary sizing/resizing method for a fixed wing-VTOL electric UAV[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2017, 71: 30-41. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2017.09.008 [14] STONE H. The T-wing tail-sitter research UAV[C]//2002 Biennial International Powered Lift Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2002: 1-10. [15] DROANDI G, SYAL M, BOWER G. Tiltwing multi-rotor aerodynamic modeling in hover, transition and cruise flight conditions[C]//Proceeding of the 74th Annual Forum & Technology Display, 2018: 11-17. [16] 张学平, 王小兵, 赵阳旭, 等. 基于无人机汽油发动机高度功率特性研究[J]. 小型内燃机与摩托车, 2010, 39(5): 30-34. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0630.2010.05.008ZHANG X P, WANG X B, ZHAO Y X, et al. Research on static state altitude power characteristics of UAV gasoline engines[J]. Small Internal Combustion Engine and Motorcycle, 2010, 39(5): 30-34(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-0630.2010.05.008 [17] DWYER M. World directory of light aviation[EB/OL]. [2019-08-05]. [18] HALE D. Sullivan alternators[EB/OL]. [2019-08-15]. [19] BAUMANN J. TG series slotless motor kits[EB/OL]. [2019-08-13]. [20] KOEGLER L. UAS multi-rotor brushless motors[EB/OL]. [2019-08-13]. [21] JAY G. Designing unmanned aircraft systems: A comprehensive approach[M]. 2nd ed. Reston: AIAA, 2014: 74-76. [22] ROSKAM J. Airplane aerodynamics and performance[M]. Lawrence: DARcorporation, 2003: 711. [23] MARKEL T, BROOKER A, HENDRICKS T, et al. Advisor: A systems analysis tool for advanced vehicle modeling[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2002, 110(2): 255-266. doi: 10.1016/S0378-7753(02)00189-1 [24] SORRENTINO M, MAURAMATI F, ARSIE I, et al. Application of willans line method for internal combustion engines scalability towards the design and optimization of eco-innovation solutions: 2015-24-2397[R]. Pennsylvania: SAE International, 2015: 1-11. [25] 康岚兰, 董文永, 田降森. 一种自适应柯西变异的反向学习粒子群优化算法[J]. 计算机科学, 2015, 42(10): 226-231.KANG L L, DONG W Y, TIAN J S. Opposition based particle swarm optimization with adaptive Cauchy mutation[J]. Computer Science, 2015, 42(10): 226-231(in Chinese). [26] MICHAEL S. Large sample properties of simulations using Latin hypercube sampling[J]. Technometrics, 1987, 29(2): 143-151. doi: 10.1080/00401706.1987.10488205 -








 下载:
下载:













 下载:
下载: