Improved adaptive artificial immune algorithm for solving function optimization problems
-
摘要:
为克服经典人工免疫算法(AIA)在函数优化过程中存在的计算量大、收敛精度不高和收敛速度较慢等不足,引入多个自适应免疫算子,提出了一种改进自适应人工免疫算法(IAAIA)。在经典人工免疫算法中,引入迭代次数对抗体激励度计算算子进行自适应设计,引入种群抗体平均激励度与抗体激励度对免疫选择算子、克隆算子、变异算子与克隆抑制算子进行自适应设计,提升人工免疫算法的收敛速度、收敛精度和稳定性。选择9个典型测试函数作为实验对象,同时选择4种典型人工免疫算法作为对比算法优化实验函数,对比实验结果表明了改进的自适应人工免疫算法在求解函数优化问题的有效性和优越性。
-
关键词:
- 人工免疫算法(AIA) /
- 免疫系统 /
- 自适应 /
- 免疫算子 /
- 函数优化
Abstract:In order to overcome the shortcomings of Artificial Immune Algorithm (AIA) used in the function optimization process, such as huge calculation amount, low convergence accuracy and slow convergence speed, multiple adaptive immune operators are introduced, and an Improved Adaptive Artificial Immune Algorithm (IAAIA) is proposed. In the classic AIA, antibody excitation calculation operator is adaptively designed by introducing the number of iterations, and immune selection operator, clone operator, mutation operator and clonal inhibitory operator are adaptively designed by introducing antibody population average excitation and antibody excitation, which can improve the convergence accuracy, convergence speed and stability of AIA. Nine kinds of typical and widely used functions are chosen as experiment function, and four kinds of typical AIAs are selected as comparative algorithms to optimize the experiment functions. The comparative experiment results indicate the effectiveness and superiority of the IAAIA for solving function optimization problems.
-
Key words:
- Artificial Immune Algorithm (AIA) /
- immune system /
- adaptive /
- immune operator /
- function optimization
-
表 1 人工免疫算法与生物免疫系统中生物概念间对应关系
Table 1. Biology concept corresponding relationship between AIA and biology immune system
生物免疫系统中生物概念 AIA 抗原 待优化问题 抗体 可行解 亲和度 可行解的质量 细胞活化 免疫选择 细胞分化 克隆 亲和度成熟 变异 克隆抑制 克隆抑制 维持动态平衡 种群刷新 表 2 九个典型测试函数的基本特性
Table 2. Basic characteristics of 9 typical test functions
函数 函数维数D 搜索空间 最大迭代次数Gmax 最优解 f1(x) 10 [-20, 20] 1 000 最小值为0 f2(x) 1 [1, 20] 1 000 最小值为-1.293 7 f3(x) 10 [-100, 100] 1 000 最小值为0 f4(x) 2 [-20, 20] 1 000 最小值为0 f5(x) 10 [-5.12, 5.12] 1 000 最小值为0 f6(x) 10 [-600, 600] 1 000 最小值为0 f7(x) 2 [-100, 100] 1 000 最小值为0 f8(x) 10 [-500, 500] 1 500 最小值为-4.189 8×103 f9(x) 10 [-5, 5] 1 500 最小值为-78.332 3 表 3 9个测试函数在5种人工免疫算法下的优化结果分析
Table 3. Optimization results analysis of 9 test functions with 5 kinds of AIAs
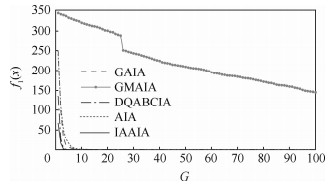
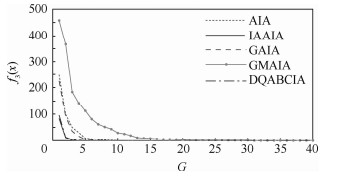
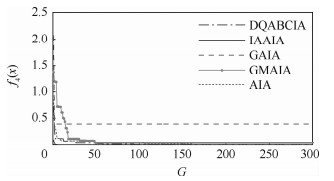
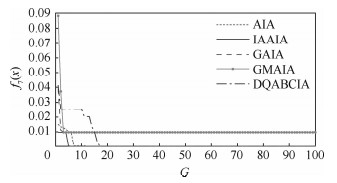
函数 对比项目 AIA GMAIA GAIA DQABCIA IAAIA f1(x) 最优解 1.540 5×10-6 0.027 2 0.029 8 0 0 最差解 8.287 9×10-6 0.221 4 0.960 1 0 0 平均最优解 5.447 4×10-6 0.069 6 0.237 7 0 0 最优解方差 8.672 2×10-6 0.247 2 1.101 6 0 0 平均迭代次数 919.7 341.857 1 11.871 0 915.9 715.2 迭代次数方差 354.756 7 900.238 1 19.169 9 210.662 5 179.846 6 平均优化时间/s 43.456 8 26.525 7 0.637 7 37.647 2 29.609 3 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 0 0 0 100 100 f2(x) 最优解 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 最差解 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 平均最优解 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 -1.293 7 最优解方差 0 0 0 0 0 平均迭代次数 749.575 8 390.700 0 548.500 0 573.200 0 176 迭代次数方差 3.756 8×104 3.152 3×104 4.501 1×104 8.782 6×104 2.064 9×104 平均优化时间/s 3.486 9 5.828 8 5.861 1 3.760 5 0.578 1 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 100 100 100 100 100 f3(x) 最优解 0 0 0 0 0 最差解 0 0 0 0 0 平均最优解 0 0 0 0 0 最优解方差 0 0 0 0 0 平均迭代次数 11.562 5 32.857 1 8.529 4 5.564 1 4.625 0 迭代次数方差 6.623 8 41.452 2 3.804 0 5.439 6 3.391 2 平均优化时间/s 0.551 4 2.262 4 0.492 0 0.228 6 0.192 8 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 100 100 100 100 100 f4(x) 最优解 4.266 1×10-4 0.031 7 0.179 3 0 0 最差解 0.001 2 1.999 5 2.062 7 0 0 平均最优解 8.449 9×10-4 0.238 2 0.989 7 0 0 最优解方差 8.312 5×10-4 2.477 4 2.913 2 0 0 平均迭代次数 785.303 0 22.030 3 2.135 1 342 214.393 9 迭代次数方差 917.073 0 96.555 5 28.431 0 116.944 4 66.857 2 平均优化时间/s 20.035 4 1.307 2 0.075 4 7.880 7 6.363 4 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 0 0 0 100 100 f5(x) 最优解 2.985 1 9.220 9 4.482 5 0 0 最差解 16.914 4 25.479 4 20.679 9 0 0 平均最优解 9.628 7 17.891 4 13.115 9 0 0 最优解方差 15.756 6 23.313 1 23.370 3 0 0 平均迭代次数 932.787 9 44.888 9 6.062 5 62.055 6 48.289 5 迭代次数方差 414.525 7 138.483 1 8.824 7 94.445 2 28.457 3 平均优化时间/s 44.309 3 3.124 4 0.255 4 2.647 4 1.689 5 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 0 0 0 100 100 f6(x) 最优解 0.019 2 0.605 6 0.257 6 0 0 最差解 0.095 5 3.160 1 2.169 4 0 0 平均最优解 0.057 7 1.635 9 0.968 1 0 0 最优解方差 0.109 7 3.121 7 2.371 4 0 0 平均迭代次数 933.969 7 132.727 3 9.925 0 212.789 5 44.500 0 迭代次数方差 330.649 3 145.425 4 15.125 3 183.222 0 19.912 3 平均优化时间/s 46.585 5 9.960 1 0.522 0 8.799 5 2.152 7 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 0 0 0 100 100 f7(x) 最优解 0.009 7 0.009 7 0.009 7 0 0 最差解 0.078 2 0.498 9 0.154 4 0 0 平均最优解 0.067 8 0.074 4 0.043 9 0 0 最优解方差 0.213 5 0.336 6 0.232 2 0 0 平均迭代次数 661.647 1 2.657 9 1.382 4 22.947 4 9.542 9 迭代次数方差 1.548 4×103 13.287 3 3.745 6 22.757 3 11.344 0 平均优化时间/s 16.399 6 0.166 4 0.053 1 0.496 3 0.351 8 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 0 0 0 100 100 f8(x) 最优解 -3.953 0×103 -4.071 4×103 -4.189 8×103 -4.189 8×103 -4.189 8×103 最差解 -3.299 6×103 -3.558 0×103 -4.189 8×103 -4.189 8×103 -4.189 8×103 平均最优解 -3.607 2×103 -3.755 5×103 -4.189 8×103 -4.189 8×103 -4.189 8×103 最优解方差 0.026 3 0.021 2 0 0 0 平均迭代次数 1 416.8 868.363 6 855 904.300 0 404.500 0 迭代次数方差 5.960×103 1.170 0×104 3.403 7×104 1.313 4×105 6.685 4×104 平均优化时间/s 44.445 8 47.129 6 34.009 0 32.291 4 16.743 5 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 0 0 100 100 100 f9(x) 最优解 -78.332 3 -78.329 2 -78.332 0 -78.332 3 -78.332 3 最差解 -72.677 6 -75.500 8 -78.305 4 -78.332 3 -78.332 3 平均最优解 -76.752 9 -76.208 9 -78.317 7 -78.332 3 -78.332 3 最优解方差 2.453 2 1.498 3 1.022 2×10-4 0 0 平均迭代次数 1 375.4 752.875 0 294.900 0 558 421.400 0 迭代次数方差 1.273 5×104 5.940 7×104 5.090 3×104 7.992 3×104 9.140 5×104 平均优化时间/s 42.202 8 71.875 4 12.189 1 15.948 5 7.028 1 收敛到全局最优解成功率/% 43.33 0 0 100 100 -
[1] KALINLI A, KARABOGA N. Artificial immune algorithm for IIR filters design[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2005, 18(8): 919-929. doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2005.03.009 [2] AYDIN I, KARAKOSE M, AKIN E. A multi-objective artificial immune algorithm for parameter optimization in support vector machine[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2011, 11(1): 120-129. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2009.11.003 [3] CASTRO D, ZUBEN V. Learning and optimization using the clonal selection principle[J]. IEEE Transaction on Evolutionary Computation, 2002, 6(3): 239-251. doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2002.1011539 [4] 焦李成, 杜海峰. 人工免疫系统进展与展望[J]. 电子学报, 2003, 31(10): 1540-1548. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2003.10.024JIAO L C, DU H F. Development and prospect of the artificial immune system[J]. Acta Electronic Sinica, 2003, 31(10): 1540-1548(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2003.10.024 [5] 张著洪, 陶娟. 求解非线性区间数规划的微免疫优化算法研究[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2014, 51(12): 2633-2643. doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2014.20131091ZHANG Z H, TAO J. Micro-immune optimization approach solving nonlinear interval number programming[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2014, 51(12): 2633-2643(in Chinese). doi: 10.7544/issn1000-1239.2014.20131091 [6] LI L J, LIN Q Z, LIU S B, et al. A novel multi-objective immune algorithm with a decomposition-based clonal selection[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 81: 105490. doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2019.105490 [7] FORTEST S, HOFMEYR S A. Immunology as information processing, design principles for the immune system and other distributed autonomous systems[M]. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2000: 865-869. [8] GONG M G, ZHANG L J, MA J J, et al. Community detection in dynamic social networks based on multiobjective immune algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer Science and Technology, 2012, 27(3): 455-467. doi: 10.1007/s11390-012-1235-y [9] 彭坤, 果琳丽, 向开恒, 等. 基于混合法的月球软着陆轨迹优化[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(9): 910-915. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2013.0710PENG K, GUO L L, XIANG K H, et al. Optimization of lunar soft landing trajectory based on hybrid method[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014, 40(9): 910-915(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2013.0710 [10] 曹愈远, 张博文, 李艳军. AP聚类改进免疫算法用于航空发动机故障诊断[J]. 航空动力学报, 2019, 34(8): 375-378.CAO Y Y, ZHANG B W, LI Y J. AP clustering improved immune algorithm for aeroengine fault diagnosis[J]. Journal of Aerospace Power, 2019, 34(8): 375-378(in Chinese). [11] 薄华, 马缚龙, 焦李成. 基于免疫算法的SAR图像分割方法研究[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2007, 29(2): 375-378.BO H, MA F L, JIAO L C. Research on immune algorithm based method for SAR image segmentation[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2007, 29(2): 375-378(in Chinese). [12] PARPINELLI R S, BENITEZ C M V, LOPES H S. Parallel approaches for the artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Handbook of Swarm Intelligence, 2011, 8(1): 329-345. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-17390-5_14 [13] 戚玉涛, 刘芳, 焦李成. 基于分布式人工免疫算法的数值优化[J]. 电子学报, 2009, 37(7): 1554-1561. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.07.029QI Y T, LIU F, JIAO L C. A distributed artificial immune algorithm for numerical optimization[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2009, 37(7): 1554-1561(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0372-2112.2009.07.029 [14] 孙学刚, 贠超, 崔一辉. 改进免疫算法在函数优化中的应用[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2010, 36(10): 1180-1188. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2010/V36/I10/1180SUN X G, YUN C, CUI Y H. Improved immune algorithm and applications on function optimization[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2010, 36(10): 1180-1188(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2010/V36/I10/1180 [15] ZHU G P, KWONG S. Gbest-guided artificial bee colony algorithm for numerical function optimization[J]. Applied Mathematics and Computation, 2010, 217(7): 3166-3173. doi: 10.1016/j.amc.2010.08.049 [16] GAO W F, LIU S Y. A modified artificial bee colony algorithm[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2012, 39(3): 687-697. [17] 赵辉, 李牧东, 翁兴伟. 分布式人工蜂群免疫算法求解函数优化问题[J]. 控制与决策, 2015, 30(7): 1181-1188.ZHAO H, LI M D, WENG X W. Distributed artificial bee colony immune algorithm for the problems of function optimization[J]. Control and Decision, 2015, 30(7): 1181-1188(in Chinese). [18] 高阳阳, 陈双艳, 余敏建, 等. 改进人工免疫算法的多机协同空战目标分配方法[J]. 西北工业大学学报, 2019, 37(2): 354-360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2019.02.019GAO Y Y, CHEN S Y, YU M J, et al. Target allocation method of multi-aircraft cooperative air combat based on improved artificial immune algorithm[J]. Journal of Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2019, 37(2): 354-360(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-2758.2019.02.019 [19] 骆清国, 赵耀, 桂勇, 等. 基于多种群协同进化免疫多目标优化算法的百叶窗优化研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2019, 40(4): 689-696. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.04.003LUO Q G, ZHAO Y, GUI Y, et al. Research on optimization of louvered fin with hybrid multi-objective optimizations based on EDA and AIS[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2019, 40(4): 689-696(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1093.2019.04.003 [20] 赵静, 李建勇. 人工免疫智能控制算法的研究与应用[J]. 计算机技术与发展, 2019, 29(11): 128-132. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2019.11.026ZHAO J, LI J Y. Research and application of artificial immune intelligent control algorithm[J]. Computer Technology and Development, 2019, 29(11): 128-132(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-629X.2019.11.026 [21] 孙宁. 人工免疫优化算法及其应用研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2006: 19-44.SUN N.Artificial immune optimization algorithm and applications[D].Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2006: 19-44(in Chinese). [22] 吴建辉, 杨永舒, 陈华, 等. 免疫双向蛙跳算法及其在多峰函数优化中的应用[J]. 计算机工程, 2018, 44(9): 184-191.WU J H, YANG Y S, CHEN H, et al. Immune bidirectional frog leaping algorithm and its application in multi-modal function optimization[J]. Computer Engineering, 2018, 44(9): 184-191(in Chinese). [23] 张著洪, 张仁崇. 求解概率优化问题的微种群免疫优化算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42(9): 1785-1794. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0563ZHANG Z H, ZHANG R C. Micro-immune optimization algorithm for solving probabilistic optimization problems[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42(9): 1785-1794(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2015.0563 [24] 张弛, 贾丽媛, 王加阳. 改进的混合免疫算法在约束函数优化中的应用[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 47(6): 1940-1946.ZHANG C, JIA L Y, WANG J Y. An improved hybrid immune algorithm for multimodal optimization[J]. Journal of Central South University (Science and Technology), 2016, 47(6): 1940-1946(in Chinese). [25] 程呈, 高敏, 刘晓光, 等. 解空间定向优化的快速免疫算法研究及其应用[J]. 控制与决策, 2017, 32(7): 1241-1246.CHENG C, GAO M, LIU X G, et al. Research and application of fast immune algorithm for solution space directional optimization[J]. Control and Decision, 2017, 32(7): 1241-1246(in Chinese). [26] CHELLAPILLA K. Combining mutation operators in evolutionary programming[J]. IEEE Transaction on Evolutionary Computation, 1998, 2(3): 91-96. doi: 10.1109/4235.735431 [27] 包子阳, 余继周, 杨彬. 智能优化算法及其MATLAB实例[M]. 2版. 北京: 电子工业出版社, 2018.BAO Z Y, YU J Z, YANG B. Intelligent optimization algorithms and MATLAB examples[M]. 2nd ed. Beijing: Publishing House of Electronics Industry, 2018(in Chinese). [28] 吴建辉, 章兢, 张小刚, 等. 分层协同进化免疫算法及其在TSP问题中的应用[J]. 电子学报, 2011, 39(2): 336-344.WU J H, ZHANG J, ZHANG X G, et al. Hierarchical co-evolution immune algorithm and its application on TSP[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2011, 39(2): 336-344(in Chinese). [29] 谷远利, 张源, 芮小平, 等. 基于免疫算法优化LSSVM的短时交通流预测[J]. 吉林大学学报(工学版), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857.GU Y L, ZHANG Y, RUI X P, et al. Short-term traffic flow prediction based on LSSVM optimized by immune algorithm[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2019, 49(6): 1852-1857(in Chinese). [30] 张建, 李艳军, 曹愈远, 等. 免疫支持向量机用于航空发动机磨损故障诊断[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2017, 43(7): 1419-1425. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0553ZHANG J, LI Y J, CAO Y Y, et al. Immune SVM used in wear fault diagnosis of aircraft engine[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(7): 1419-1425(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0553 -








 下载:
下载: