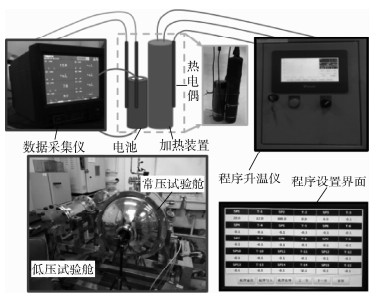
-
摘要:
针对当前锂电池安全性研究侧重于特征参数实验测量及反应机理分析,基于风险评估理论提出锂电池热失控风险指数并应用于锂电池安全定量评价,以点燃参数乘以环境因子表征锂电池热失控风险发生概率,以热释放参数和火势增长参数表征风险造成后果。选取陆空联运的冷链货物温度监测装置中常用的锂锰电池(CR)和锂亚硫酰氯电池(ER),利用自主设计搭建的锂电池热失控实验平台获取上述参数并计算热失控风险指数。实例分析表明:适合于陆空联运的冷链货物ER14250型锂电池热失控风险指数为0.84,其安全性相对最高。所提方法可直接指导陆空联运冷链货物温度监测装置的锂电池选择,保证运输安全。
Abstract:Aimed at the current research on the safety of lithium batteries, focusing on the experimental measurement of characteristic parameters and analysis of reaction mechanisms, this paper proposes the thermal runaway risk index of lithium batteries based on risk assessment theory and applies it to the quantitative evaluation method of lithium battery safety. The ignition parameter is multiplied by the environmental coefficient to characterize the probability of thermal runaway. The consequences of risk are characterized by the heat release parameter and fire growth parameter. Lithium-manganese batteries (CR) and lithium-thionyl chloride batteries (ER) commonly used in temperature monitor devices in cold-chain cargo of air-ground multimodal transport are selected, and the above parameters are obtained by the self-designed lithium battery thermal runaway experimental platform. Thermal runaway risk index is calculated. The example analysis shows that the thermal runaway risk index value of ER14250 lithium battery is 0.84, which demonstrates higher safety than others. This method can directly guide the selection of lithium batteries for temperature detection devices in air-ground multimodal transport for cold-chain cargo to ensure the safety of transportation.
-
表 1 锂电池基本参数
Table 1. Basic parameters of lithium battery
型号 尺寸/(mm×mm) 容量/(mA·h) 电压/V 正极材料 电解质类型 CR2032 2×3.2 240 3 二氧化锰(MnO2) PC(碳酸丙烯酯)+DME(二甲氧基乙烷) CR2 15×27 850 3 CR123A 17×34.5 1 400 3 ER14250 14×25 800 3.6 亚硫酰氯(SOCL2) 非水电解质 ER14335 14×33.5 1 600 3.6 ER14505 14×50.5 2 400 3.6 表 2 低压与常压环境下电池热失控参数对比
Table 2. Comparison of thermal runaway parameters of battery under low and normal pressure
型号 低压 常压 T0/℃ t0/s Tmax/℃ T0/℃ t0/s Tmax/℃ CR2032 172.6 306 319.7 166.5 243 358.8 CR2 172.9 291 527.4 166.7 267 607.3 CR123A 172.9 333 599.8 167.5 303 641.8 ER14250 169.5 321 169.5 166.9 282 253.6 ER14335 174.1 294 185 174.6 240 312.1 ER14505 179.7 276 244.5 170.8 270 545.9 表 3 风险指数量化评价结果
Table 3. Quantitative evaluation result by risk indexes
型号 常压(a=1) 低压(a=0.8) S P V S P V TI THRI FGI TI THRI FGI CR2032 2.83 3.19 2.10 2.37 2.94 2.46 1.86 1.24 CR2 2.87 3.98 2.27 3.15 2.92 3.11 2.13 1.81 CR123A 2.93 4.12 2.32 3.26 2.98 3.26 2.14 1.87 ER14250 2.89 2.90 0.84 0.84 2.96 1.25 0.67 0.22 ER14335 2.84 3.21 1.93 2.18 2.93 1.69 0.61 0.28 ER14505 2.88 3.82 2.39 3.17 2.92 2.44 0.78 0.51 -
[1] WALDMANN T, WOHLFAHRT-MEHRENS M. Effects of rest time after Li plating on safety behaviors-ARC tests with commercial high-energy 18650 Li-ion cells[J]. Electrochimica Acta, 2017, 230: 454-460. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2017.02.036 [2] JHU C Y, WANG Y W, SHU C M, et al. Thermal explosion hazards on 18650 lithium ion batteries with a VSP2 adiabatic calorimeter[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192(1): 99-107. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389411005358 [3] WU T Q, CHEN H D, WANG Q S, et al. Comparison analysis on the thermal runaway of lithium-ion battery under two heating modes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2018, 344: 733-741. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2017.11.022 [4] YE J N, CHEN H D, WANG Q S, et al. Thermal behavior and failure mechanism of lithium ion cells during overcharge under adiabatic conditions[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 182: 464-474. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.124 [5] FEAR C, JUAREZ-ROBLES D, JEEVARAJAN J A, et al. Elucidating copper dissolution phenomenon in Li-ion cells under over discharge extremes[J]. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2018, 165(9): A1639-A1647. doi: 10.1149/2.0671809jes [6] LIU J J, WANG Z R, GONG J H, et al. Experimental study of thermal runaway process of 18650 lithium-ion battery[J]. Materials, 2017, 10(3): 1-12. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28772588 [7] YANG H, SHEN X D. Dynamic TGA-FTIR studies on the thermal stability of lithium/graphite with electrolyte in lithium-ion cell[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2007, 162(2): 515-519. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378775307004296 [8] ROTH E P, DOUGHTY D H. Thermal abuse performance of high-power 18650 Li-ion cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2004, 128(2): 308-318. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2003.09.068 [9] WANG Q S, PING P, SUN J H, et al. Thermal runaway caused fire and explosion of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2012, 208: 210-224. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2012.02.038 [10] 张青松, 曹文杰, 罗星娜, 等. 基于多米诺效应的锂离子电池热释放速率分析方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报. 2017, 43(5): 902-907. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0383ZHANG Q S, CAO W J, LUO X N, et al. Method for analyzing heat release rate of lithium ion battery based on domino effect[J]. Journal of Beihang University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017, 43(5): 902-907(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0383 [11] HUANG P F, PING P, LI K, et al. Experimental and modeling analysis of thermal runaway propagation over the large format energy storage battery module with Li4Ti5O12 anode[J]. Applied Energy, 2016, 183: 659-673. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.08.160 [12] WANG Z, YANG H, LI Y, et al. Thermal runaway and fire behaviors of large-scale lithium ion batteries with different heating methods[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 379: 256-262. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0304389419306739 [13] 汪书苹, 陈伟, 陈国宏, 等. 锂离子电池燃烧性及火灾危险性研究[J]. 电力安全技术, 2019, 21(3): 40-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLAQ201903013.htmWANG S P, CHEN W, CHEN G H, et al. Study on the combustibility and fire hazard of lithium ion batteries[J]. Electric Safety Technology, 2019, 21(3): 40-46(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DLAQ201903013.htm [14] 高飞, 杨凯, 李大贺, 等. 锂离子电池组件燃烧性及危险性评价[J]. 中国安全科学学报, 2015, 25(8): 62-67. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201508010.htmGAO F, YANG K, LI D H, et al. Evaluation of the combustibility and risk of lithium-ion battery components[J]. China Safety Science Journal, 2015, 25(8): 62-67(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-ZAQK201508010.htm [15] 邢志祥, 刘敏, 吴洁, 等. 锂离子电池火灾危险性的研究现状分析[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2019, 38(6): 880-884. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2019.06.038XING Z X, LIU M, WU J, et al. Analysis of research status on fire hazard of lithium ion battery[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2019, 38(6): 880-884(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2019.06.038 [16] IEC.Secondary cells and batteries containing alkaline or other non-acid electrolytes-Safety requirements for portable sealed secondary cells, and for batteries made from them, for use in portable applications: IEC 62133-2012[S].Geneva: IEC, 2012. [17] Underwriters Laboratories Inc.Standard for safety household and commercial batteries(2nd ed): UL 2054[S].Northbrook: Underwriters Laboratories Inc., 2004. [18] 国家发展和改革委员会. 电动汽车用锂离子蓄电池: QC/T 743-2006[S]. 北京: 国家发展和改革委员会, 2006.National Development and Reform Commission.Lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles: QC/T 743-2006[S].Beijing: National Development and Reform Commission, 2006(in Chinese). [19] FENG X N, SUN J, OUYANG M G, et al. Characterization of penetration induced thermal runaway propagation process within a large format lithium ion battery module[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 275: 261-273. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2014.11.017 [20] ZHU J E, WIERZBICKI T, LI W. A review of safety-focused mechanical modeling of commercial lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2018, 378: 153-168. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2017.12.034 [21] LYON R E, WALTERS R N. Energetics of lithium ion batteries failure[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2016, 318: 164-172. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.06.047 [22] ZHANG L L, CHENG X Q, MA Y L, et al. Effect of short-time external circuiting on the capacity feding mechanism during long-term cycling of LiCoO2 mesocarbon microbeads battery[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2016, 318: 154-162. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.03.087 [23] OUYANG M G, REN D S, LU L G, et al. Overcharge induced capacity fading analysis for large format lithium ion batteries with LiyNi1/3Co1/3Mn1/3O2+LiyMn2O4 composite cathode[J]. Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 279: 626-635. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2015.01.051 [24] JHU C Y, WANG Y W, WEN C Y, et al. Self-reactive rating of thermal runaway hazards on 18650 lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2011, 106: 159-163. doi: 10.1007/s10973-011-1452-6 [25] MAO B, HUANG P F, CHEN H D, et al. Self-heating reaction and thermal runaway criticality of the lithium ion battery[J]. International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2020, 149: 119178. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2019.119178 [26] DOH C H, KIM D H, KIM H S, et al. Thermal and electrochemical behaviour of C/LixCoO2 cell during safety test[J]. Journal of Power Source, 2008, 175(2): 881-885. doi: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2007.09.102 [27] FENG X N, HE X M, OUYANG M G, et al. Thermal runaway propagation model for designing a safer battery pack with 25Ah LiNixCoyMnzO2 large format lithium on battery[J]. Applied Energy, 2015, 154: 74-91. doi: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2015.04.118 [28] 张青松, 罗星娜, 程相静, 等. 基于锂电池温降指数的细水雾添加剂筛选方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0362ZHANG Q S, LUO X N, CHENG X J, et al. Method for screening water mist additives based on lithium battery temperature drop index[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(6): 1073-1079(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0362 [29] FENG X N, LU L G, OUYANG M G, et al. A 3D thermal runaway propagation model for a large format lithium ion battery module[J]. Energy, 2016, 115(Part 1): 194-208. [30] WEN C Y, JHU C Y, WANG Y W, et al. Thermal runaway features of 18650 lithium-ion batteries for LiFePO4 cathode material by DSC and VSP2[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2012, 109: 1297-1302. doi: 10.1007/s10973-012-2573-2 [31] UEDA M, OHE M, KIM J H, et al. Effects of surface fluorination on the electrochemical properties and thermal stability of LiFePO4 cathode for lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Fluorine Chemistry, 2013, 149: 88-94. doi: 10.1016/j.jfluchem.2013.01.038 [32] 李平, 尤飞, 秦圣辉, 等. 风机机舱典型液态油品着火特性及潜在火灾危险性评价[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2017, 17(6): 2069-2072. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201706007.htmLI P, YOU F, QIN S H, et al. Ignition characteristics and potential fire hazard evaluation of typical liquid oil in wind turbine engine room[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2017, 17(6): 2069-2072(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201706007.htm [33] 胡毅伟, 马杰, 黄冬梅, 等. 织物-乳胶可燃结构燃烧特性及火灾危险性[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2019, 38(6): 764-767. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2019.06.004HU Y W, MA J, HUANG D M, et al. Combustion characteristics and fire hazard of fabric-latex combustible structure[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2019, 38(6): 764-767(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2019.06.004 [34] 王文和, 何腾飞, 米红甫, 等. 18650型锂离子电池燃烧特性及火灾危险性评估[J]. 安全与环境学报, 2019, 19(3): 729-736. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201903002.htmWANG W H, HE T F, MI H F, et al. Combustion characteristics and fire hazard assessment of 18650 lithium ion battery[J]. Journal of Safety and Environment, 2019, 19(3): 729-736(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-AQHJ201903002.htm [35] 付阳阳. 典型锂离子电池和电解液燃烧特性及航空运输环境对其影响机制研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学, 2017.FU Y Y.Study on the combustion characteristics of typical lithium-ion batteries and electrolytes and the influence mechanism of air transportation environment on them[D].Hefei: University of Science and Technology of China, 2017(in Chinese). [36] CHEN M Y, LIU J H, LIN X, et al. Combustion characteristics of primary lithium battery at two altitudes[J]. Journal of Thermal Analysis and Calorimetry, 2016, 124: 865-870. doi: 10.1007/s10973-015-5219-3 [37] 张青松, 白伟, 程相静. 压力变化对锂金属电池热失控特性的影响研究[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2018, 37(11): 1582-1585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2018.11.041ZHANG Q S, BAI W, CHENG X J. Study on the influence of pressure change on the thermal runaway characteristics of lithium metal batteries[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2018, 37(11): 1582-1585(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2018.11.041 [38] 张青松, 白伟. 冷链航空运输中锂锰电池安全性的影响因素[J]. 消防科学与技术, 2018, 37(6): 813-816. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2018.06.030ZHANG Q S, BAI W. Influencing factors of lithium manganese battery safety in cold chain air transportation[J]. Fire Science and Technology, 2018, 37(6): 813-816(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-0029.2018.06.030 [39] 牛长东, 陈雪梅, 王兴贺, 等. Li/(MnO2+CFX)电池放电发热的研究[J]. 电源技术, 2015, 39(9): 1832-1834. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2015.09.009NIU C D, CHEN X M, WANG X H, et al. Research on discharge heat of Li/(MnO2+CFX) battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2015, 39(9): 1832-1834(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2015.09.009 [40] 王艳峰, 胡欲立, 王家军. ER48660型锂/亚硫酰氯电池热分析[J]. 电源技术, 2010, 34(8): 809-811. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2010.08.017WANG Y F, HU Y L, WANG J J. Thermal analysis of ER48660 lithium/thionyl chloride battery[J]. Chinese Journal of Power Sources, 2010, 34(8): 809-811(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-087X.2010.08.017 -







 下载:
下载: