-
摘要:
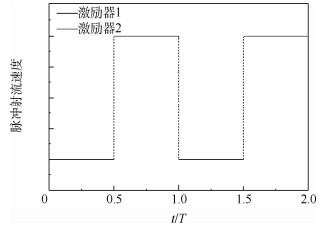
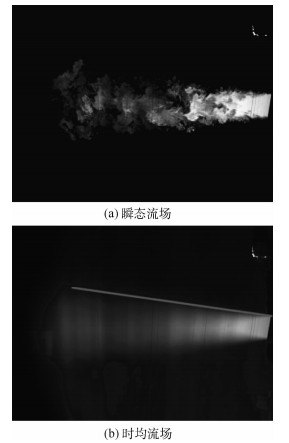
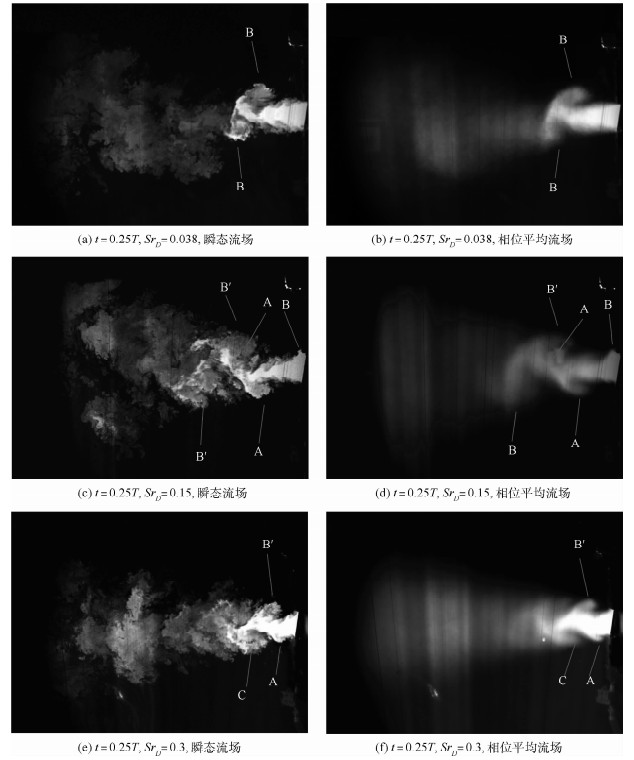
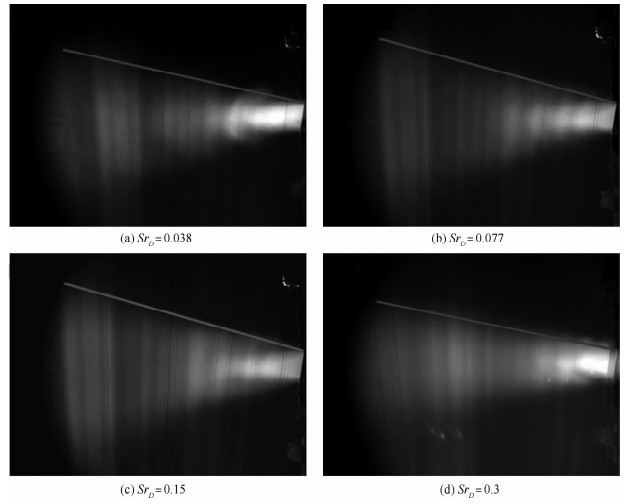
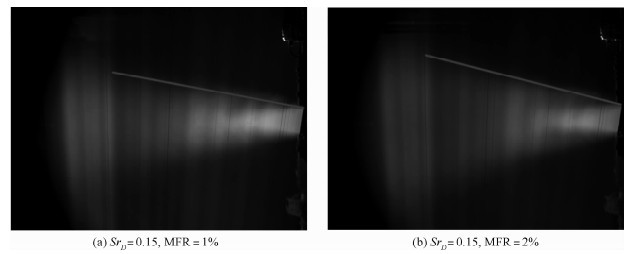
采用激光诱导荧光的流动显示方法研究了在一对反对称模式工作的脉冲射流激励下,雷诺数约为33 000的圆形湍流射流的流场。捕捉了剪切层中大尺度展向涡结构的演化发展过程,研究了激励频率和振幅对涡结构以及强化混合效果的影响。结果表明:受激励后的主喷流剪切层中产生了交错的展向涡结构,引起了喷流的振荡,增强了卷吸能力。激励频率主要影响相邻涡环间的距离。存在最佳激励频率使喷流在受激励平面远场分叉、剪切层扩展最宽。激励振幅对涡结构也存在较大影响,振幅较大时产生的涡结构尺度更大、相干性更强、强化混合效果更好。
Abstract:In this paper, a turbulent jet with Reynolds number 33 000 forced by a pair of pulsed jets working in antisymmetric mode is investigated using laser-induced fluorescence technique. The evolution of large-scale vortex structures in the shear layer is captured and the effect of forcing frequency and amplitude of pulsed jets on vortex structure and mixing enhancement is studied. It is found that inclined and staggered vortex structures are generated in the shear layer, causing the oscillation of primary jet and promoting entrainment. The forcing frequency mainly influences the distance of neighboring vortex rings. There exists optimal excitation frequency that causes the primary jet bifurcating in the far field and spreading most in the shear layer in the forced plane. The forcing amplitude also has effect on the vortex structure. The vortex structures are larger and more coherent at high amplitude, resulting in better mixing enhancement.
-
Key words:
- flow control /
- flow visualization /
- mixing enhancement /
- pulsed jet /
- vortex ring structure
-
-
[1] VALDIS K, JOHN D, DAVID M S, et al. Active flow control technology transition: The boeing ACE program[C]//Proceedings of the 30th AIAA Fluid Dynamics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 1999: 1-12. [2] OBERT F, AHUJA K K, BRIAN C, et al. Jet mixing enhancemen[C]//Proceedings of the 10th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2004: 1-9. [3] CLARENCE F C, JOHN D, DAVID S, et al. Active core exhaust (ACE) control for reduction of thermal loading[C]//AIAA Fluid 2000 Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2000: 1-11. [4] LINDA D K. Active flow control technology[C]//ASME Fluids Engineering Division Technical Brief, 1999. [5] TONG F, JAMES J M. LDA measurements of underexpanded jet flow from an axisymmetric nozzle with solid tabs[C]//Proceedings of the 3rd AIAA Flow Control Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2006: 1-12. [6] CALLENDER B, GUTMARK E. A near-field investigation of chevron nozzle mechanisms[C]//Proceedings of the 9th AIAA/CEAS Aeroacoustics Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2003: 1-16. [7] SUN L Y, TERRENCE W S, SUSAN C, et al. Jet penetration into a scaled microfabricated stirling cycle regenerator[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Energy Conversion Engineering Conference (IECEC). Reston: AIAA, 2008: 1-17. [8] SAMIMY M, KIM J H, KASTNER J, et al. Active control of a mach 0.9 jet for noise mitigation using plasma actuators[J]. AIAA Journal, 2007, 45(4): 890-901. [9] ADNAN E, ROBERT E B. Structure, penetration, and mixing of pulsed jets in cross flow[J]. AIAA Journal, 2001, 39(3): 417-423. doi: 10.2514/2.1351 [10] RITCHIE B D, MUJUMDAR D R, SEITZMAN J M. Mixing in coaxial jets using synthetic jet actuators[C]//Proceedings of the 38th Aerospace Sciences Meeting & Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2000: 1-9. [11] PAREKH D E, KIBENS V, GLEZER A, et al. Innovative jet flow control: Mixing enhancement experiments[C]//Proceedings of the 34th Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 1996. [12] NEW T H, TAY W L. Effects of cross-stream radial injections on a round jet[J]. Journal of Turbulence, 2006, 7(57): 1-20. [13] YANG H, ZHOU Y. Axisymmetric jet manipulated using two unsteady minijets[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2016, 808: 362-396. doi: 10.1017/jfm.2016.634 [14] BEHROUZI P, MCGUIRK J J. Jet mixing enhancement using fluid tabs[C]//Proceedings of the 2nd AIAA Flow Control Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2004: 2401. [15] MUHAMMAD A K, MCGUIRK J J. Unsteady predictions of mixing enhancement with steady and pulsed control jets[J]. AIAA Journal, 2015, 53(5): 1262-1276. doi: 10.2514/1.J053374 [16] DEWEY C. Qualitative and quantitative flow field visualization utilizing laser-induced fluorescence[C]//Proceedings of the AGARD Conference of Non-intrusive Instrumentation in Fluid Flow Research, 1976. [17] XIA Q F, ZHONG S. A PLIF and PIV study of liquid mixing enhanced by a lateral synthetic jet pair[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2012, 37: 64-73. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2012.04.010 [18] YU J Z, VUORINEN V, KAARIO O, et al. Visualization and analysis of the characteristics of transitional underexpanded jets[J]. International Journal of Heat and Fluid Flow, 2013, 44: 140-154. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheatfluidflow.2013.05.015 [19] THONG C X, DALLY B B, BIRZER C H, et al. An experimental study on the near flow field of a round jet affected by upstream multi-lateral side-jet[J]. Experimental Thermal and Fluid Science, 2017, 82: 198-211. doi: 10.1016/j.expthermflusci.2016.11.008 [20] KONG B, LI T, ERI Q. Large-eddy simulation of turbulent jet controlled by two pulsed jets: Effect of forcing frequency[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 89: 356-369. doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.04.010 [21] SUZUKI H, KASAGI N, SUZUKI Y. Active control of an axismmetric jet with distributed electromagnetic flap actuators[J]. Experiments in Fluids, 2004, 36: 498-509. doi: 10.1007/s00348-003-0756-0 -








 下载:
下载: