-
摘要:
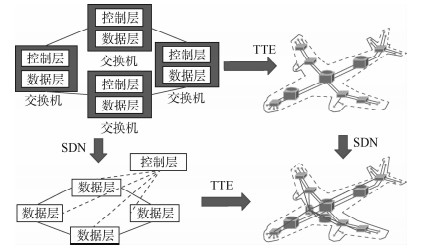
软件定义时间触发以太网(TTE)作为优化航空电子系统中消息调度的一种新模式,其动态在线调度算法必须尽力保证任何情况下所有消息的传输确定性。针对时间触发(TT)消息调度间隔小于消息帧长(小时隙)时,速率约束RC消息延迟增大、传输确定性降低的问题,对TT消息调度算法进行改进。首先,构建了TTE的系统模型,阐明了最小延迟(MID)调度算法和背靠背(B2B)调度算法的机制;然后在其基础上提出了大孔隙(MAV)调度算法,以减少(RC)消息的等待延迟;最后,利用OMNeT++实验分析这3种调度算法的性能。实验结果表明:当无小时隙TT消息时,B2B算法的消息延迟最大、MAV调度算法和MID调度算法的消息延迟接近。当有小时隙TT消息时,MAV调度算法的消息传输确定性更好,相比于MID调度算法,MAV调度算法下RC消息的传输确定性提高了87.3%。
-
关键词:
- 调度算法 /
- 时间触发以太网(TTE) /
- 软件定义网络(SDN) /
- 消息延迟 /
- 传输确定性
Abstract:Software defined Time-Triggered Ethernet (TTE) optimizes message scheduling in avionics systems, and its dynamic online scheduling algorithm must ensure the transmission determinacy of all the messages in any case. When time interval of Time-Triggered (TT) message is less than the frame length, the Rate-Constrained (RC) message delay increases, and transmission determinacy goes down. This paper improves the TT message scheduling algorithm. First, a system model of software defined time-triggered Ethernet was established. And the mechanisms of Minimum Delay (MID) scheduling algorithm and Back to Back (B2B) scheduling algorithm were introduced. Then, on this basis, a Macrovoid (MAV) scheduling algorithm was proposed to reduce the waiting delay for RC messages in special cases. Finally, OMNeT++ experiment was conducted to analyze the performance of these three algorithms. Experimental results show when there is no small time interval TT messages, the message delay in the back to back scheduling algorithm is the largest, and the macrovoid scheduling algorithm has similar message delay as the minimum delay scheduling algorithm. However, when there are small time interval TT messages, the macrovoid scheduling algorithm has better transmission determinacy than the minimum delay scheduling algorithm, and the transmission determinacy of RC message by macrovoid scheduling algorithm is improved by 87.3%, compared with minimum delay scheduling algorithm.
-
表 1 实验消息配置
Table 1. Message configuration in experiment
终端系统 类型 参数 配置 ES 1~ES 4 TT 数量 32条 帧长 1 250 B 周期 32 ms 间隔时间 150 μs/240 μs RC 数量 32条 帧长 1 250 B BAG 32 ms 表 2 无小时隙TT消息下不同调度算法的消息延迟统计
Table 2. Statistics of message delays by different scheduling algorithms without small time interval TT messages
算法 TT/ms RC/ms 最大 平均 标准差 最大 平均 标准差 MID 0.401 0.355 0.069 32.396 31.298 0.789 B2B 1.610 0.960 0.371 37.595 32.259 1.708 MAV 0.401 0.355 0.069 32.396 31.298 0.789 表 3 有小时隙TT消息下不同调度算法的消息延迟统计
Table 3. Statistics of message delays by different scheduling algorithms with small time interval TT messages
算法 TT/ms RC/ms 最大 平均 标准差 最大 平均 标准差 MID 0.401 0.355 0.069 36.792 31.992 1.511 B2B 4.400 2.355 1.201 35.567 31.653 1.197 MAV 0.479 0.395 0.072 32.830 31.364 0.756 -
[1] KOPETZ H, ADEMAJ A, GRILLINGER P, et al. The Time-Triggered Ethernet (TTE) design[C]//Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Symposium on Object-Oriented Real-Time Distributed Computing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 22-33. [2] STEINER W, BAUER G, HALL B, et al. TTEthernet dataflow concept[C]//Proceedings of the 8th IEEE International Symposium on Network Computing & Applications. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2009: 319-322. [3] KOPETZ H. Event-triggered versus time-triggered real-time systems[M]. Berlin: Springer, 1991: 86-101. [4] GOPALAKRISHNAN S, CACCAMO M, SHA L. Switch scheduling and network design for real-time systems[C]//Proceedings of the 12th IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2006: 289-300. [5] SUETHANUWONG E. Scheduling time-triggered traffic in TTEthernet systems[C]//Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 17th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2012: 1-4. [6] CRACIUNAS S S, OLIVER R S, ECKER V. Optimal static scheduling of real-time tasks on distributed time-triggered networked systems[C]//Proceedings of the 2012 IEEE 17th Conference on Emerging Technology & Factory Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 1-8. [7] BARRETT C, TINELLI C. Satisfiability modulo theories[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2018: 305-343. [8] SEBASTIANI R. Lazy satisfiability modulo theories[J]. Journal on Satisfiability, Boolean Modeling and Computation, 2007, 3: 141-224. doi: 10.3233/SAT190034 [9] CRACIUNAS S S, OLIVER R S. Combined task-and network-level scheduling for distributed time-triggered systems[J]. Real-time Systems, 2016, 52(2): 161-200. doi: 10.1007/s11241-015-9244-x [10] SCHOLER C, KRENZ-BAATH R, MURSHED A, et al. Computing optimal communication schedules for time-triggered networks using an SMT solver[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Industrial Embedded Systems. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 1-9. [11] STEINER W. An evaluation of SMT-based schedule synthesis for time-triggered multi-hop networks[C]//Proceedings of the 31st IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 375-384. [12] POZO F, STEINER W, RODRIGUEZ-NAVAS G, et al. A decomposition approach for SMT-based schedule synthesis for time-triggered networks[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 20th Conference on Emerging Technologies & Factory Automation. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-8. [13] TAMAS-SELICEAN D, POP P, STEINER W. Timing analysis of rate constrained traffic for the ttethernet communication protocol[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE 18th International Symposium on Real-Time Distributed Computing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 119-126. [14] YAO J, XU X, LIU X. MixCPS: Mixed time/event-triggered architecture of cyber-physical systems[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 2016, 104(5): 923-937. doi: 10.1109/JPROC.2016.2519381 [15] ZHAO L X, POP P, LI Q, et al. Timing analysis of rate-constrained traffic in TTEthernet using network calculus[J]. Real-time Systems, 2017, 53(2): 254-287. doi: 10.1007/s11241-016-9265-0 [16] BOYER M, DAIGMORTE H, NAVET N, et al. Performance impact of the interactions between time-triggered and rate-constrained transmissions in TTEthernet[J]. Embedded Real time Systems, 2016, 14(2): 217-225. http://hal.archives-ouvertes.fr/hal-01255939 [17] STEINER W. Synthesis of static communication schedules for mixed-criticality systems[C]//IEEE International Symposium on Object/Component/Service-Oriented Real-time Distributed Computing Workshops. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 11-18. [18] TAMAS-SELICEAN D, POP P, STEINER W. Synthesis of communication schedules for TTEthernet-based mixed-criticality systems[C]//Proceedings of the 8th ACM International Conference on Hardware/Software Codesign & System Synthesis. New York: ACM, 2012: 473-482. [19] ZHANG L, GOSWAMI D, SCHNEIDER R, et al. Task-and network-level schedule co-synthesis of Ethernet-based time-triggered systems[C]//Proceedings of the 19th Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference (ASP-DAC). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 119-124. [20] FORGET J, BONIOL F, GROLLEAU E, et al. Scheduling dependent periodic tasks without synchronization mechanisms[C]//Proceedings of the 16th IEEE Real-Time and Embedded Technology and Applications Symposium. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 301-310 [21] MCKEOWN N, ANDERSON T, BALAKRISHNAN H, et al. OpenFlow: Enabling innovation in campus networks[J]. ACM Sigcomm Computer Communication Review, 2008, 38(2): 69-74. doi: 10.1145/1355734.1355746 [22] TIAN Z, LI S, WANG Y, et al. Priority scheduling of networked control system based on fuzzy controller with self-tuning scale factor[J]. IAENG International Journal of Computer Science, 2017, 44(3): 308-315. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/319458469_Priority_scheduling_of_networked_control_system_based_on_fuzzy_controller_with_self-tuning_scale_factor [23] SAMPIGETHAYA K. Software-defined networking in aviation: Opportunities and challenges[C]//Proceedings of the 8th Integrated Communication, Navigation, and Surveillance Conference (ICNS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-21. [24] HEISE P, GEYER F, OBERMAISSER R. Deterministic OpenFlow: Performance evaluation of SDN hardware for avionic networks[C]//Proceedings of the 8th 11th International Conference on Network and Service Management (CNSM). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 372-377. [25] KUMAR R, HASAN M, PADHY S, et al. End-to-end network delay guarantees for real-time systems using SDN[C]//Proceedings of the 8th IEEE Real-Time Systems Symposium (RTSS). Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 231-242. [26] LU J, XIONG H G, HE F, et al. Enhancing real-time and determinacy for network-level schedule in distributed mixed-critical system[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8: 23720-23731. doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2970266 [27] CRACIUNAS S, OLIVER R. SMT-based task-and network-level static schedule generation for time-triggered networked systems[C]//International Conference on Real-time Networks & Systems. New York: ACM, 2014: 45-54. [28] 何锋, 周璇, 赵长啸, 等. 航空电子系统机载网络实时性能评价技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(4): 651-665. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0297HE F, ZHOU X, ZHAO C X, et al. Real-time performance evaluation technology of airborne network for avionics system[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(4): 651-665(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0297 [29] 王荣巍, 何锋, 周璇, 等. 面向无人机蜂群的航电云多层任务调度模型[J]. 航空学报, 2019, 40(11): 1-12. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201911019.htmWANG R W, HE F, ZHOU X, et al. Avionics cloud multi-layer task scheduling model for UAV swarm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2019, 40(11): 1-12(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201911019.htm [30] 鲁俊, 何锋, 熊华钢. 航空电子云系统架构与网络[J]. 航空电子技术, 2017, 28(3): 1-9. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKDZ201703001.htmLU J, HE F, XIONG H G. System and network architecture of avionics cloud[J]. Avionics Technology, 2017, 28(3): 1-9(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKDZ201703001.htm [31] TIAN Z, LI S, WANG Y, et al. Scheduling method for networked control system with resource constraints based on fuzzy feedback priority and variable sampling period[J]. Transactions of the Institute of Measurement & Control, 2018, 40(4): 1136-1149. http://smartsearch.nstl.gov.cn/paper_detail.html?id=74806279b8fe25ee41ac9b1a8cee93e9 [32] FRANCES F, FRABOUL C, GRIEU J. Using network calculus to optimize the AFDX network[J]. Medical Imaging IEEE Transactions on Embedded Real Time Systems, 2006, 25(10): 1319-1328. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/27813294_Using_network_calculus_to_optimize_the_AFDX_network/download [33] BOYER M, MIGGE J, FUMEY M. PEGASE-A robust and efficient tool for worst-case network traversal time evaluation on AFDX[J]. Physiology and Behavior, 2011, 25(4): 589-593. http://www.researchgate.net/publication/289860018_PEGASE_-_A_robust_and_efficient_tool_for_worst-case_network_traversal_time_evaluation_on_AFDX?ev=auth_pub [34] KLEIN D, JARSCHEL M. An OpenFlow extension for the OMNeT++ INET framework[C]//Proceedings of the 6th International Institute for Computer Sciences, Social-Informatics and Telecommunications (ICST) Conference on Simulation Tools and Techniques. Reston: ACM, 2013: 322-329. [35] SALIH M A, COSMAS J, ZHANG Y. OpenFlow 1.3 extension for OMNeT++[C]//2015 IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology Ubiquitous Computing and Communications Dependable, Autonomic and Secure Computing; Pervasive Intelligence and Computing. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1632-1637. -







 下载:
下载: