-
摘要:
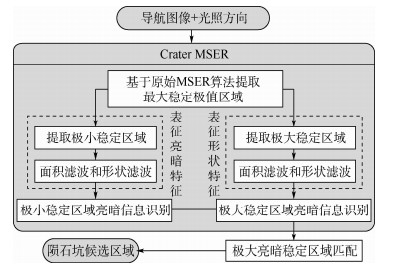
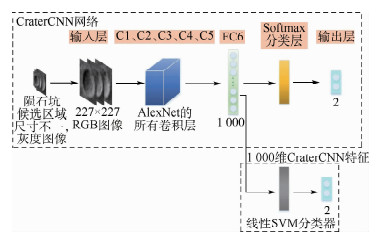
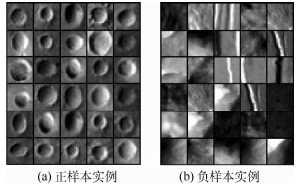
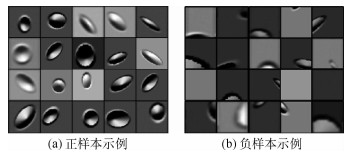
基于陨石坑的视觉导航技术成为一种新颖的高精度空间探测自主导航方式,如何从导航图像中精确地提取陨石坑区域是实现基于陨石坑视觉导航的首要条件。针对这一问题,根据陨石坑导航图像特点,提出了一种基于自动特征学习的陨石坑区域检测算法。首先,基于最大稳定极值区域检测算法提取陨石坑候选区域;其次,利用卷积神经网络(CNN)自动学习提取候选区域的特征;最后,通过支持向量机(SVM)实现候选区域的精确分类,得到真实的陨石坑区域。大量的仿真实验表明:与传统的基于人工特征的陨石坑区域检测算法相比,提出的基于自动特征学习的陨石坑区域检测算法具有更高的检测精度和更好的鲁棒性,在通用火星表面陨石坑数据集上,所提算法的
F 1度量指标较于传统算法高出8%,可以广泛地应用于基于陨石坑的视觉导航算法中的陨石坑区域提取,为基于陨石坑视觉导航算法提供精确的导航路标输入。Abstract:The crater-based navigation technology has been become a novel and precise autonomous navigation method in space exploration, and how to extract the crater regions from the crater navigation image is the essential condition of the crater-based navigation method. Accordingly, in this paper, we propose an algorithm for extracting crater regions via automatic feature learning. First, the candidate crater regions were obtained by the maximal stable external region method. Then, the features of these regions were automatically extracted by Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). Finally, the true crater regions were identified from all the candidate regions through Support Vector Machine (SVM) classifier. The experimental results demonstrate that the proposed algorithm can extract crater regions from the navigation image with higher accuracy and robustness than the traditional crater region detection algorithms based on the handcrafted features. The proposed algorithm obtains an
F 1 score which is 8% higher than that of the traditional method on the standard Mars surface crater database, and can be applied in the crater detection of the crater-based visual navigation method to provide the precise navigation landmarks.-
Key words:
- crater region /
- object detection /
- automatic feature learning /
- deep learning /
- artificial intelligence
-
表 1 h0905_0000陨石坑数据集分组
Table 1. Groups of h0905_0000 crater dataset
区域 正样本数量 负样本数量 西部区域 1 121 1 385 中部区域 443 738 东部区域 458 765 表 2 基于交叉校验数据集的软间隔线性SVM分类器惩罚因子选择实验结果
Table 2. Experimental results for choosing the penalty factor of linear SVM classifier with soft interval based on cross check dataset
序号 惩罚因子pe 平均F1度量值 1 0.000 01 0.832 6 2 0.000 1 0.893 7 3 0.001 0.884 3 4 0.01 0.851 7 5 0.1 0.832 6 6 1 0.832 6 7 10 0.832 6 8 50 0.832 6 表 3 CraterCNN+SVM与其他陨石坑候选区域分类算法对比实验结果
Table 3. Contrast experimental results of Crater CNN+SVM algorithm and other crater candidate regions classification algorithms
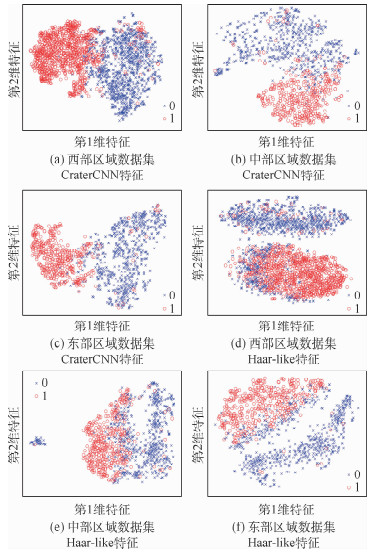
度量指标 特征类型和分类器类型 西部区域 中部区域 东部区域 平均值 查全率P Haar-like+AdaBoost 0.903 0 0.903 0 0.903 0 0.903 0 Haar-like+SVM 0.839 8 0.839 8 0.839 8 0.839 8 CraterCNN+Softmax 0.929 5 0.871 2 0.929 5 0.910 1 CraterCNN+SVM 0.929 5 0.898 9 0.929 5 0.919 3 CraterCNN+AdaBoost 0.898 8 0.905 5 0.898 8 0.901 0 查准率R Haar-like+AdaBoost 0.863 7 0.863 7 0.863 7 0.863 7 Haar-like+SVM 0.829 1 0.829 1 0.829 1 0.829 1 CraterCNN+Softmax 0.916 3 0.880 5 0.916 3 0.904 4 CraterCNN+SVM 0.916 5 0.910 5 0.916 5 0.914 5 CraterCNN+AdaBoost 0.904 2 0.871 1 0.904 2 0.893 2 F1 Haar-like+AdaBoost 0.880 9 0.880 9 0.880 9 0.880 9 Haar-like+SVM 0.832 6 0.832 6 0.832 6 0.832 6 CraterCNN+Softmax 0.922 0 0.874 5 0.922 0 0.906 2 CraterCNN+SVM 0.922 6 0.903 9 0.922 6 0.916 4 CraterCNN+AdaBoost 0.900 4 0.886 7 0.900 4 0.895 8 表 4 不同特征提取及不同分类算法的训练和测试在10-Fold数据集上的平均时间
Table 4. Mean time of different feature extraction algorithms and different classification algorithms on 10-Fold training dataset and testing dataset
测试对象 平均时间值/s 平均值/s 西部区域 中部区域 东部区域 CraterCNN特征提取 1.54 0.74 0.70 0.99 Haar-like特征提取 4.13 2.08 2.33 2.85 CraterCNN+SVM训练 0.34 0.10 0.08 0.17 CraterCNN+Adaboost训练 796.1 191.08 195.83 394.34 CraterCNN+SVM测试 0.01 0.01 0.01 0.01 CraterCNN+Adaboost测试 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 表 5 基于解析数据的陨石坑仿真图像陨石坑候选区域检测结果统计
Table 5. Candidate crater region detection experimental results of crater simulation image based on analytical data
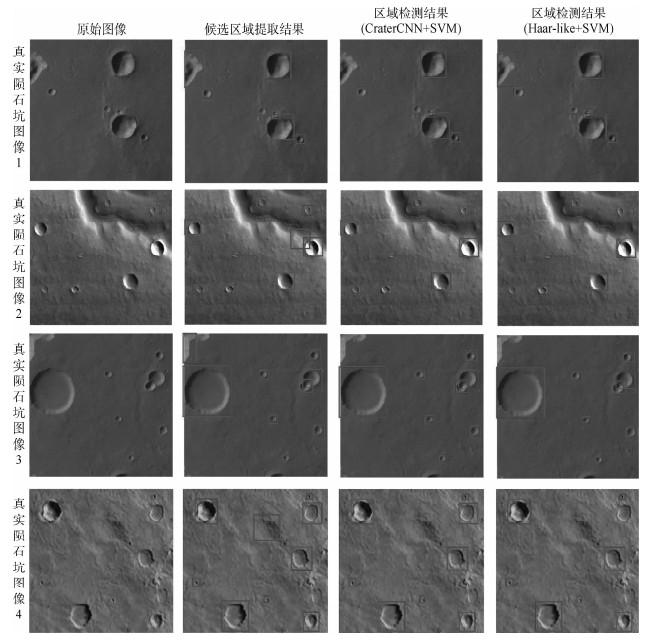
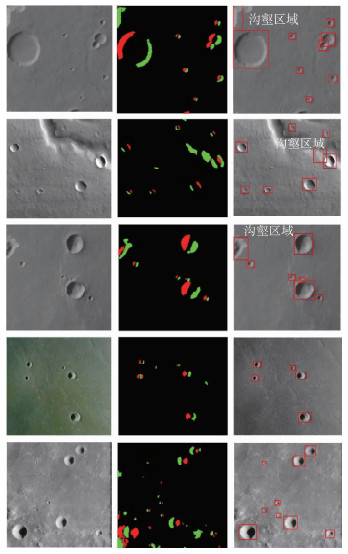
算法 度量指标 仿真图像1(含9个候选区域) 仿真图像2(含11个候选区域) 仿真图像3(含9个候选区域) 仿真图像4(含11个候选区域) CraterCNN+SV 检测个数 9 11 9 11 MHaar-like+SVM 7 10 8 9 本文算法 运行时间/s 35.26 29.17 31.18 33.76 CraterCNN+SV 0.185 3 0.198 6 0.172 8 0.198 5 MHaar-like+SVM 0.240 7 0.264 9 0.231 8 0.253 9 表 6 基于真实陨石坑图像的陨石坑候选区域检测结果统计
Table 6. Candidate crater region detection experimental results based on real crater image
算法 检测个数 真实陨石坑图像1(含6个候选区域) 真实陨石坑图像2(含7个候选区域) 真实陨石坑图像3(含8个候选区域) 真实陨石坑图像4(含9个候选区域) CraterCNN+SVM 6 7 8 9 Haar-like+SVM 7 6 7 8 -
[1] LU T, HU W, LIU C, et al. Relative pose estimation of a lander using crater detection and matching[J]. Optical Engineering, 2016, 55(2): 1-24. [2] YU M, CUI H, TIAN Y. A new approach based on crater detection and matching for visual navigation in planetary landing[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2014, 53(12): 1810-1821. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2013.04.011 [3] TIAN Y, YU M, YAO M B, et al. Crater edge-based flexible autonomous navigation for planetary landing[J]. The Journal of Navigation, 2019, 72(3): 649-668. doi: 10.1017/S0373463318000966 [4] YU M, LI S, WANG S, et al. Single crater-aided inertial navigation for autonomous asteroid landing[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2019, 63(2): 1085-1099. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2018.09.035 [5] MAASS B, WOICKE S, OLIVEIRA W M, et al. Crater navigation system for autonomous precision landing on the moon[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2020, 43(11): 1-18. [6] VIJAYAN S, VANI K, SANJEEVI S. Crater detection, classification and contextual information extraction in lunar images using a novel algorithm[J]. Icarus, 2013, 226(1): 798-815. doi: 10.1016/j.icarus.2013.06.028 [7] JAIN A, SURESH K, THAKORE D, et al. Automatic crater detection on lunar surface[J]. International Journal of Innovative Research in Science Engineering & Technology, 2013, 2(5): 1448-1453. [8] BANDEIRA L, SARAIVA J, PINA P. Impact crater recognition on mars based on a probability volume created by template matching[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2007, 45(12): 4008-4015. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2007.904948 [9] LI K, MU L, LIU J, et al.Impact crater detection based on regional segmentation using Chang'E-1 CCD data[C]//Proceedings of International Congress on Image and Signal Processing.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1911-1915. [10] SAWABE Y, MATSUNAGA T, ROKUGAWA S. Automated detection and classification of lunar craters using multiple approaches[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2006, 37(1): 21-27. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2005.08.022 [11] WEISMULLER T, CABALLERO D, LEINZ M.Technology for autonomous optical planetary navigation and precision landing[C]//Proceedings of AIAA SPACE 2007 Conference & Exposition.Reston: AIAA, 2007: 1-26. [12] SADHUKHAN P, PALIT S.Fast autonomous crater detection by image analysis-for unmanned landing on unknown terrain[C]//Proceedings of Image and Signal Processing.Berlin: Springer, 2016: 293-303. [13] LEROY B, MEDINONI G, JOHNSON E, et al. Crater detection for autonomous landing on asteroids[J]. Image & Vision Computing, 2001, 19(11): 787-792. [14] CHENG Y, MILLER J K. Autonomous landmark based spacecraft navigation system[J]. Advances in the Astronautical Sciences, 2003, 114(3): 1769-1783. [15] CHENG Y, JOHNSON A E, MATTHIES L H, et al.Optical landmark detection for spacecraft navigation[C]//Proceedings of AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting.Reston: AIAA, 2003: 1-19. [16] MAMMARELLA M, RODRIGALVAREZ M A, PIZZICHINI A, et al. Advances in aerospace guidance, navigation and control[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2011: 419-430. [17] HE J, CUI H, FENG J.Edge information based crater detection and matching for lunar exploration[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Intelligent Control and Information Processing.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 302-307. [18] FENG J, CUI P, CUI H.Autonomous hazard detection and landing point selecting for planetary landing[C]//Proceedings of International Symposium on Systems and Control in Aeronautics and Astronautics.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2010: 1292-1296. [19] DING M, CAO Y, WU Q. Method of passive image based crater autonomous detection[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2009, 22(3): 301-306. doi: 10.1016/S1000-9361(08)60103-X [20] DING M, CAO Y F, WU Q X.Autonomous craters detection from planetary image[C]//Proceedings of International Conference on Innovative Computing Information and Control.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2008: 443-448. [21] DING W, STEPINSKI T F, BANDEIRA L, et al.Automatic detection of craters in planetary images: An embedded framework using feature selection and boosting[C]//Proceedings of ACM Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.New York: ACM Press, 2010: 749-758. [22] DING W, STEPINSKI T F, MU Y, et al. Subkilometer crater discovery with boosting and transfer learning[J]. ACM Transactions on Intelligent Systems & Technology, 2011, 2(4): 1-22. [23] MARTINS R, PINA P, MARQUES J S, et al. Crater detection by a boosting approach[J]. IEEE Geoscience & Remote Sensing Letters, 2009, 6(1): 127-131. [24] BANDIEIRA L, DING W, STEPINSKI T F. Detection of sub-kilometer craters in high resolution planetary images using shape and texture features[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2012, 49(1): 64-74. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2011.08.021 [25] JIN S, ZHANG T. Automatic detection of impact craters on Mars using a modified adaboosting method[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2014, 99(1): 112-117. [26] COHEN J P, DING W. Crater detection via genetic search methods to reduce image features[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2014, 53(12): 1768-1782. doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2013.05.010 [27] TAKEDA Y, AOYAMA N, TANAAMI T, et al. Study on crater detection using FLDA[J]. World Academy of Science Engineering & Technology, 2012, 6(11): 1373-1377. [28] LENA D, TED J S, JONATHAN P H.Deep learning crater detection for lunar terrain relative navigation[C]//Proceedings of AIAA Scitech 2020 Forum.Reston: AIAA, 2020: 1-12. [29] EMAMI E, AHMAD T, BEBIS G, et al. Crater detection using unsupervised algorithms and convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2019, 57(8): 5373-5383. doi: 10.1109/TGRS.2019.2899122 [30] LEE C. Automated crater detection on Mars using deep learning[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2019, 170: 16-28. doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2019.03.008 [31] NISTER D, STEWENIUS H.Linear time maximally stable extremal regions[C]//Proceeding of 10th European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin: Springer, 2008: 183-196. [32] ROERDINK J B T M, MEIJSTER A. The watershed transform: Definitions, algorithms and parallelization strategies[J]. Fundamenta Informaticae, 2000, 41(1): 187-228. [33] SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A.Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//Procceeding of ICLR, 2015: 1-14. [34] CHERON G, LAPTEV I, SCHMID C.P-CNN: Pose-based CNN features for action recognition[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 3218-3226. [35] KOBCHAISAWAT T, CHALIDABHONGSE T H.Thai text localization in natural scene images using convolutional neural network[C]//Proceedings of Signal and Information Processing Association Annual Summit and Conference (APSIPA).Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-7. [36] RANJAN R, PATEL V M, CHELLAPPA R.A deep pyramid deformable part model for face detection[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Biometrics Theory, Applications and Systems.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-8. [37] SHARIF R A, AZIZPOUR H, SULLIVAN J, et al.CNN features off-the-shelf: An astounding baseline for recognition[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2014: 806-813. [38] VIOLA P A, JONES M J.Detecting pedestrians using patterns of motion and appearance in videos: US7212651B2[P].2007-05-01. [39] DALAL N, TRIGGS B.Histograms of oriented gradients for human detection[C]//Proceedings of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 886-893. [40] PIETIKINEN M, HADID A, ZHAO G, et al. Computer vision using local binary patterns[M]. Berlin: Springer, 2011: 3-10. [41] SZARVAS M, YOSHIZAWA A, YAMAMOTO M, et al.Pedestrian detection with convolutional neural networks[C]//Proceedings of Intelligent Vehicles Symposium.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2005: 224-229. [42] NIU X X, SUEN C Y. A novel hybrid CNN-SVM classifier for recognizing handwritten digits[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2012, 45(4): 1318-1325. doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2011.09.021 [43] ZHANGL L, SHI Z, WU J. A hierarchical oil tank detector with deep surrounding features for high-resolution optical satellite imagery[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2015, 8(10): 1-15. doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2016.2514638 [44] Math Works.Pretrained convolutional neural networks[EB/OL].[2020-02-24]. [45] Knowledge Discovery Lab.Crater datbase[EB/OL].[2020-02-15]. [46] LU T, HU W, JIANG Z.An effective algorithm for generation of crater gray image[C]//Proceedings of IEEE International Conference on Computational Intelligence and Virtual Environments for Measurement Systems and Applications.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2015: 1-6. [47] 陆婷婷, 李潇, 张尧, 等. 基于三维点云模型的空间目标光学图像生成技术[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46(2): 274-286. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0189LU T T, LI X, ZHANG Y, et al. A technology for generation of space object optical image based on 3D point cloud model[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46(2): 274-286(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2019.0189 -








 下载:
下载: