Numerical analyses of liquid-vapor interface in two-phase thermal-controlled accumulator under microgravity condition
-
摘要:
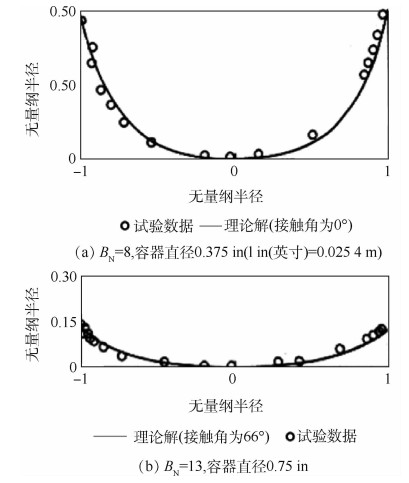
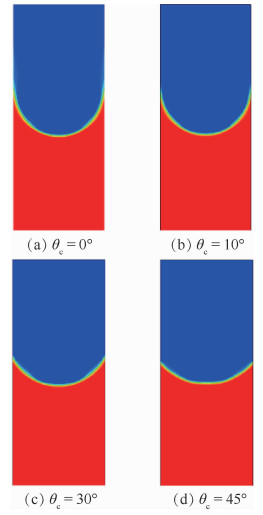
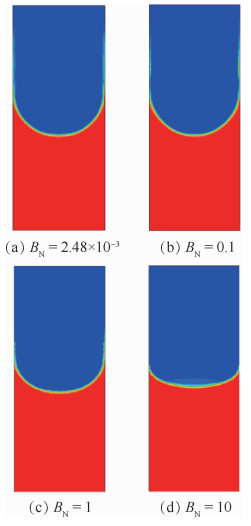
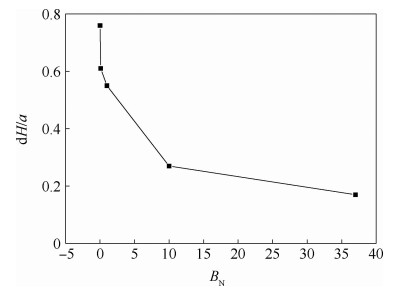
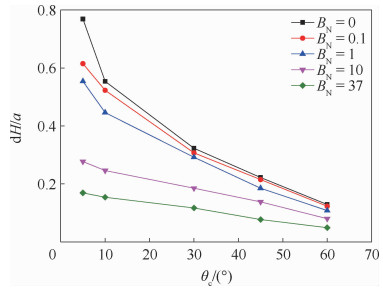
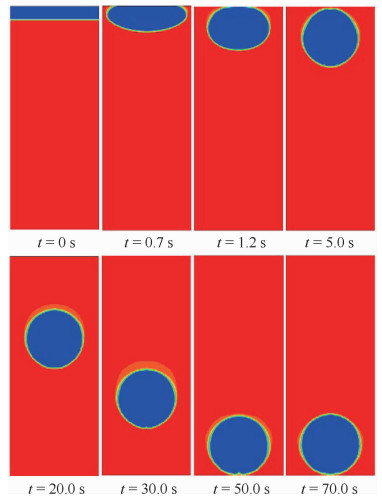
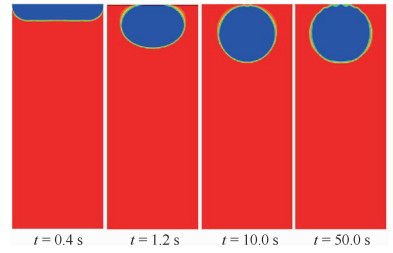
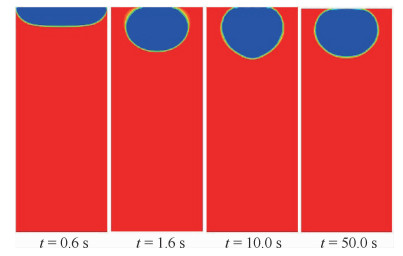
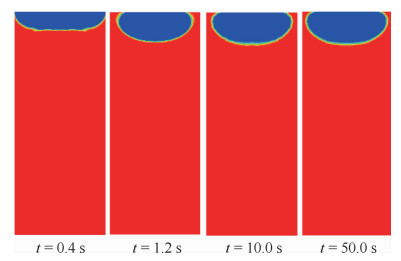
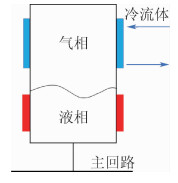
两相控温型储液器对机械泵驱动两相流体回路的稳定运行起到关键作用,而储液器内部气液分布状态是其控温性能的决定性因素之一。在轨微重力条件下,储液器内两相流动特性与地面状态差别巨大,这将给储液器的设计带来较大难度。针对两相控温型储液器在轨微重力下的两相工质分布特性,通过计算流体力学(CFD)方法对其内两相流动行为进行数值模拟。通过使用连续表面张力模型计算表面张力,使用多相流计算的流体体积分数方法对两相控温型储液器内气液界面形态的发展进行了追踪预测,并与理论解进行对比,结果吻合一致。通过对两相控温型储液器在不同Bond数、接触角、工质充灌量等参数下的仿真分析,得到了不同条件下储液器内气液运动及分布情况,结果表明:两相控温型储液器内气液界面状态与储液器尺寸、壁面浸润性、工质充灌量相关。研究结果可以为微重力下两相控温型储液器内气液界面的控制提供理论依据,并能指导储液器研制及在轨应用。
-
关键词:
- 两相控温型储液器 /
- 机械泵驱动两相流体回路 /
- 气液界面 /
- 微重力 /
- 数值模拟
Abstract:Two-phase thermal-controlled accumulator plays a vital role in mechanically pumped two-phase loop system. And the distribution state of liquid and vapor is one of the key factors that decide the temperature control performance of the accumulator. The distribution state of fluid in accumulator under on-orbit microgravity condition is significantly different from that on ground, which brings great difficulties to the accumulator design. In order to study the two-phase medium distribution characteristics of accumulator under on-orbit microgravity condition, Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) method was used to simulate the two-phase flow behavior. The continuum surface force model and volume of fluid method were adopted to calculate the surface tension and track the liquid-vapor interface shape, respectively. By comparison between simulation results and theoretical solution, it shows that the results are consistent. Several influence parameters, including different Bond numbers, contact angles and filing ratios, were studied, the movement and distribution characteristics of the two-phase medium were obtained.The results indicate that the liquid-vapor interface shape is related to the size, wall wettability and medium filling ratio of accumulator. The results presented in this paper can provide theory basis for the control of liquid-vapor interface in accumulator, and can guide the research, development and on-orbit application of accumulator.
-
表 1 氨工质参数
Table 1. Parameters of ammonia as working medium
参数 液相氨 气相氨 密度ρ/(kg·m-3) 610 0.689 黏度μ/(kg·(m·s-1)-1) 1.52×10-4 1.015×10-5 -
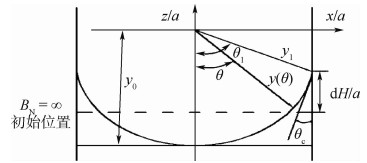
[1] 李春林. 空间光学遥感器热控技术研究[J]. 宇航学报, 2014, 35(8): 863-870. doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2014.08.001LI C L. Research on space optical remote sensor thermal control technique[J]. Journal of Astronautics, 2014, 35(8): 863-870(in Chinese). doi: 10.3873/j.issn.1000-1328.2014.08.001 [2] 赵振明, 孟庆亮, 张焕冬, 等. CCD器件用机械泵驱动两相流体回路仿真与试验[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(5): 893-901. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0519ZHAO Z M, MENG Q L, ZHANG H D, et al. Simulation and experimental study of mechanically pumped two-phase loop for CCD[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(5): 893-901(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0519 [3] ES J V, GERNER H J V, BENTHEM R C V, et al. Component developments in europe for mechanically pumped loop systems (MPLS) for cooling applications in space[C]//46th International Conference on Environmental Systems, 2016: 96-110. [4] STARK J A, BRADSHAW R D, BLATT M H. Low-G fluid behavior technology summaries: NASA CR-134746[R]. Washington, D.C. : NASA STI/Recon Technical Report, 1974: 75-82. [5] AHUJA V, HOSANGADI A, MATTICK S, et al. Computational analyses of pressurization in cryogenic tanks[C]//AIAA/ASME/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference and Exhibit. Reston: AIAA, 2008: 47-52. [6] KASSEMI M, KARTUZOVA O, HYLTON S. Validation of tow-phase CFD models for propellant tank self-pressurization: Crossing fluid types, scales, and gravity levels[J]. Cryogenics, 2017, 89: 1-15. [7] WENDL M C, HOCHSTEIN J I, SASMAL G P, et al. Modeling of jet-induced geyser formation in a reduced gravity environment: AIAA-1991-0803[R]. Reston: AIAA, 1991. [8] BREISACHER K, MODER J. Preliminary simulations of the ullage dynamics in microgravity during the jet mixing portion of tank pressure control experiments: AIAA-2015-3853[R]. Reston: AIAA, 2015. [9] KARTUZOVA O, KASSEMI M. Modeling ullage dynamics of tank pressure control experiment during jet mixing in microgravity[C]//52nd AIAA/SAE/ASEE Joint Propulsion Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2016. [10] DAVID C, KASSEMI M. The zero boil-off tank (ZBOT) experiment role in development of cryogenic fluid storage and transfer technologies: NASA-E-664086[R]. Washington, D.C. : NASA, 2015: 7-12. [11] DAVID C, KASSEMI M. The zero boil-off tank experment contributions to the development of cryogenic fluid management: NASA GRC-E-DAA-TN24539[R]. Washington, D.C. : NASA, 2016: 13-19. [12] KASSEMI M, HYLTON S, KARTUZOVA O. Zero-boil-off tank(ZBOT) experiment-CFD self-pressurization model validation with ground-based & microgravity results[C]//AIAA Propulsion and Energy Forum, Joint Propulsion Conference. Reston: AIAA, 2018: 43-49. [13] 李章国, 刘秋生, 纪岩. 航天器贮箱气液自由界面追踪数值模拟[J]. 空间科学学报, 2008, 28(1): 69-73.LI Z G, LIU Q S, JI Y. Numerical simulation of liquid-vapor interface tracking in tank of spacecraft[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2008, 28(1): 69-73(in Chinese). [14] 胡齐, 李永, 潘海林. 微重力环境下大叶片板式贮箱内流体行为的数值仿真与实验验证[J]. 空间控制技术与应用, 2013, 39(2): 58-62. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2013.02.011HU Q, LI Y, PAN H L. Numerical simulation and experiment verification of fluid behavior in the vane type tank with big vanes in microgravity environment[J]. Aerospace Control and Application, 2013, 39(2): 58-62(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1579.2013.02.011 [15] BRACKBILL U, KOTHE D B, ZEMACH C. A continuum method for modeling surface tension[J]. Journal of Computational Physics, 1992, 100(2): 335-354. [16] 杨旦旦, 岳宝增, 祝乐梅. 用打靶法求解微重力下矩形和旋转对称贮箱内静液面形状[J]. 空间科学学报, 2012, 32(1): 85-91.YANG D D, YUE B Z, ZHU L M. Solving shapes of hydrostatic surface in rectangular and revolving symmetrical tanks under microgravity using shooting method[J]. Chinese Journal of Space Science, 2012, 32(1): 85-91(in Chinese). [17] LEON J, HASTINGS L, RUTHERFORD R. Low gravity liquid-vapor interface shapes in axisymmetric containers and a computer solution: NASA TM X-53790[R]. Washington, D.C. : NASA, 1968: 23-30. -







 下载:
下载: