Infrared and visible image fusion based on latent low-rank representation decomposition and VGG Net
-
摘要:
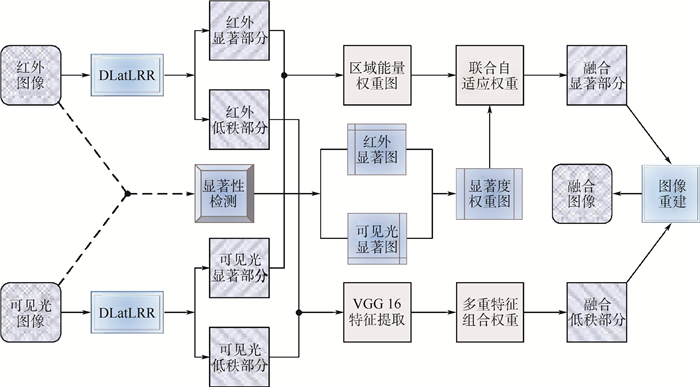
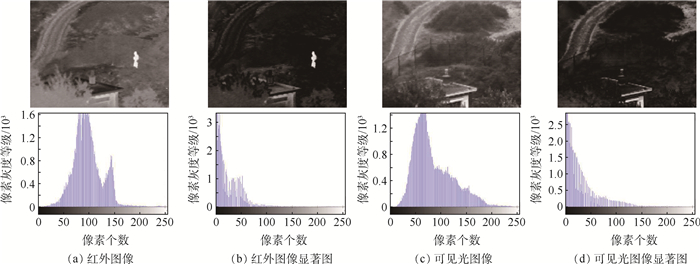
针对红外与可见光图像融合中特征损失严重、显著目标不突出的问题,提出了一种低秩表示分解与深度神经网络相结合的图像融合算法。首先,对源图像进行潜在低秩表示分解(DLatLRR),得到相应的低秩部分、显著部分及稀疏噪声。然后,分别采用16层的VGG Net模型和联合特征加权算法对低秩部分与显著部分进行融合,舍弃二者的稀疏噪声。最后,对融合得到的低秩部分和显著部分进行图像重建,得到最终的融合图像。实验结果表明:与其他算法进行比较,所提算法能够对图像的深层次细节特征进行融合,突出场景中的感兴趣区域,且融合图像的相关差异和、结构相似性、线性相关度等多种客观指标均有所提升,提升最大值分别为0.73、0.15、0.11,噪声产生率的最大缩减值为0.041 2。
-
关键词:
- 图像处理 /
- 图像融合 /
- 潜在低秩表示分解(DLatLRR) /
- VGG Net /
- 联合特征加权
Abstract:An image fusion algorithm combining low-rank representation decomposition and deep neural network is proposed to solve the problem of serious feature loss and non-prominent target in infrared and visible image fusion. First, Latent Low-Rank Representation Decomposition (DLatLRR) was performed on the source image to obtain the corresponding low-rank part, saliency part and sparse noise. Then, the VGG Net model and the joint feature weighting algorithm were used to fuse the low-rank part and the saliency part respectively, and the sparse noise of two parts were discarded. Finally, image reconstruction was carried out on the low-rank part and saliency part of the fusion to obtain the final fusion image. Compared with other methods, the experimental results show that the algorithm can fuse the deep details of the image and highlight the "interested" area in the scene. The objective indexes of the fused image including the sum of the correlations of differences, structure similarity index measure, correlation coefficient all improve, with the maximum values of 0.73, 0.15 and 0.11 respectively, and the maximum reduction value of noise generation rate is 0.041 2.
-
表 1 VGG 16结构参数
Table 1. VGG 16 structure parameters
卷积组 卷积 通道数 池化 输出 1(1_1, 1_2) 3×3, 1 64 Max, 2×2 N×N 2(2_1, 2_2) 3×3, 1 128 Max, 2×2 N/2×N/2 3(3_1, 3_2) 3×3, 1 256 Max, 2×2 N/4×N/4 4(4_1, 4_2, 4_3) 3×3, 1 512 Max, 2×2 N/8×N/8 5(5_1, 5_2, 5_3) 3×3, 1 512 Max, 2×2 N/16×N/16 -
[1] JIN X, JIANG Q, YAO S W, et al. A survey of infrared and visual image fusion methods[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 85: 478-501. [2] MA J Y, MA Y, LI C. Infrared and visible image fusion methods and applications: A survey[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 45: 153-178. [3] LI S T, KANG X D, FANG L Y, et al. Pixel-level image fusion: A survey of the state of the art[J]. Information Fusion, 2016, 33: 100-112. [4] KUMAR B K S. Image fusion based on pixel significance using cross bilateral filter[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2015, 9(5): 1193-1204. doi: 10.1007/s11760-013-0556-9 [5] LI S T, KANG X D, HU J W. Image fusion with guided filtering[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2013, 22(7): 2864-2875. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2013.2244222 [6] 蔡怀宇, 卓励然, 朱攀, 等. 基于非下采样轮廓波变换和直觉模糊集的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 光子学报, 2018, 47(6): 0610002.CAI H Y, ZHUO L R, ZHU P, et al. Fusion of infrared and visible images based on non-subsampled contourlet transform and intuitionistic fuzzy set[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2018, 47(6): 0610002(in Chinese). [7] 江泽涛, 吴辉, 周哓玲. 基于改进引导滤波和双通道脉冲发放皮层模型的红外与可见光图像融合算法[J]. 光学学报, 2018, 38(2): 0210002.JIANG Z T, WU H, ZHOU X L. Infrared and visible image fusion algorithm based on improved guided filtering and dual-channel spiking cortical model[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2018, 38(2): 0210002(in Chinese). [8] 邓辉, 王长龙, 胡永江, 等. 基于非下采样双树复轮廓波与自适应分块的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 光子学报, 2019, 48(7): 0710006.DENG H, WANG C L, HU Y J, et al. Fusion of infrared and visible images based on non-subsampled duak tree complex contourlet and adaptive block[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2019, 48(7): 0710006(in Chinese). [9] 吴冬鹏, 毕笃彦, 何林远, 等. 基于NSSCT的红外与可见光图像融合[J]. 光学学报, 2017, 37(7): 0710003.WU D P, BI D Y, HE L Y, et al. A fusion algorithm of infrared and visible image based on NSSCT[J]. Acta Optica Sinica, 2017, 37(7): 0710003(in Chinese). [10] LIU Y, CHEN X, WARD R K, et al. Image fusion with convolutional sparse representation[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2016, 23(12): 1882-1886. doi: 10.1109/LSP.2016.2618776 [11] ZHANG Q, FU Y, LI H, et al. Dictionary learning method for joint sparse representation-based image fusion[J]. Optical Engineering, 2013, 52(5): 057006. doi: 10.1117/1.OE.52.5.057006 [12] LIU C H, QI Y, DING W R. Infrared and visible image fusion method based on saliency detection in sparse domain[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 83: 94-102. [13] LIU Y, CHEN X, WANG Z F, et al. Deep learning for pixel-level image fusion: Recent advances and future prospects[J]. Information Fusion, 2018, 42: 158-173. doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2017.10.007 [14] LIU Y, CHEN X, CHENG J, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion with convolutional neural networks[J]. International Journal of Wavelets, Multiresolution and Information Processing, 2018, 16(3): 1850018. doi: 10.1142/S0219691318500182 [15] LI H, WU X J. DenseFuse: A fusion approach to infrared and visible images[J]. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, 2019, 28(5): 2614-2623. doi: 10.1109/TIP.2018.2887342 [16] LIU G C, LIN Z C, YU Y. Robust subspace segmentation by low-rank representation[C]//Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2010: 663-670. [17] LIU G C, YAN S C. Latent low-rank representation for subspace segmentation and feature extraction[C]//IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2011: 1615-1622. [18] KAREN S, ANDREW Z. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition[C]//International Conference on Learning Representations, 2015, 5(3): 345-358. [19] MA J L, ZHOU Z Q, WANG B, et al. Infrared and visible image fusion based on visual saliency map and weighted least square optimization[J]. Infrared Physics & Technology, 2017, 82: 8-17. [20] SRIVASTAVA R, PRAKASH O, KHARE A. Local energy-based multimodal medical image fusion in curvelet domain[J]. IET Computer Vision, 2016, 10(6): 513-527. doi: 10.1049/iet-cvi.2015.0251 [21] WANG Z, BOVIK A C. A universal image quality index[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2002, 9(3): 81-84. doi: 10.1109/97.995823 [22] ASLANTAS V, BENDES E. A new image quality metric for image fusion: The sum of the correlations of differences[J]. International Journal of Electronics and Communications, 2015, 69(12): 1890-1896. doi: 10.1016/j.aeue.2015.09.004 [23] KUMAR B K S. Multifocus and multispectral image fusion based on pixel significance using discrete cosine harmonic wavelet transform[J]. Signal, Image and Video Processing, 2013, 7(6): 1125-1143. doi: 10.1007/s11760-012-0361-x -








 下载:
下载: