-
摘要:
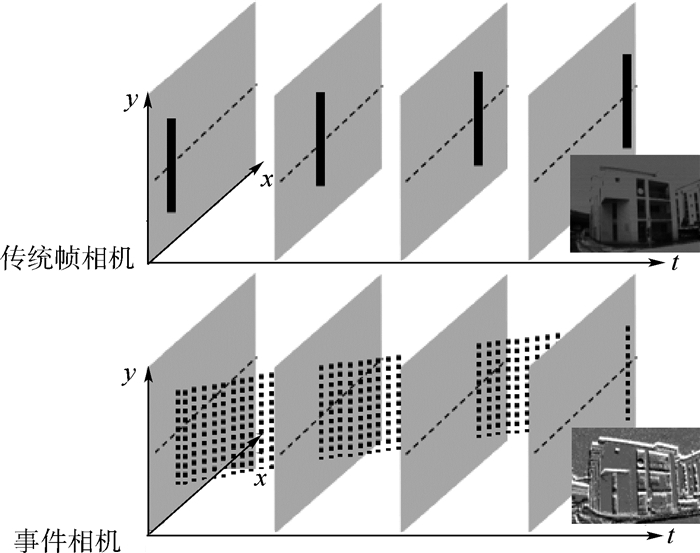
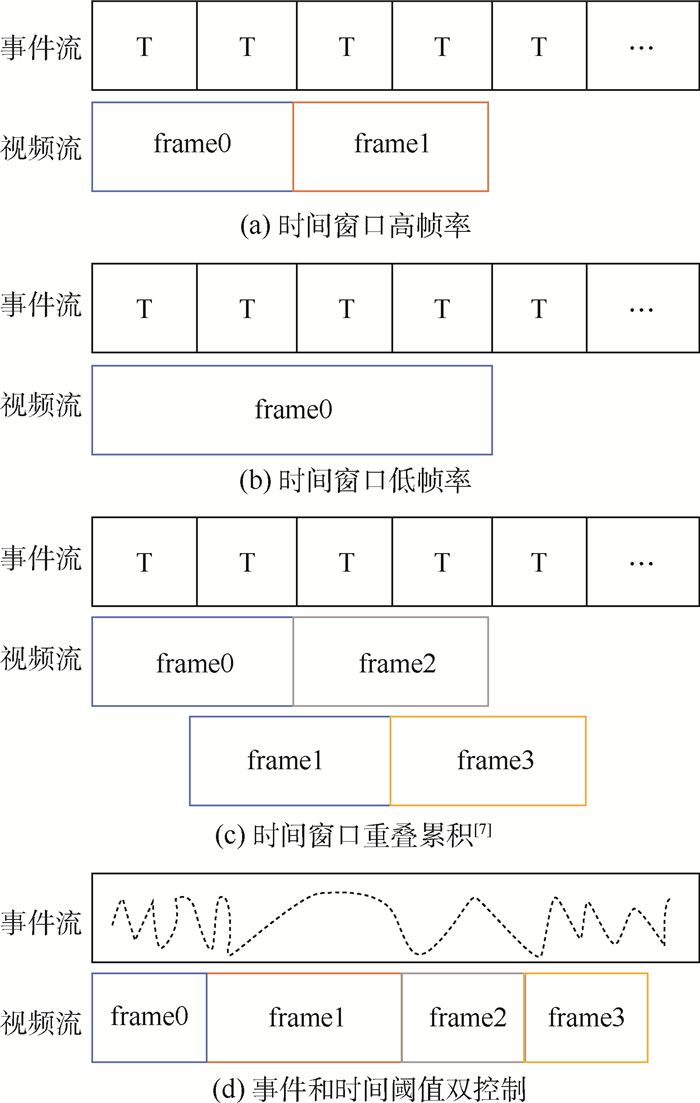
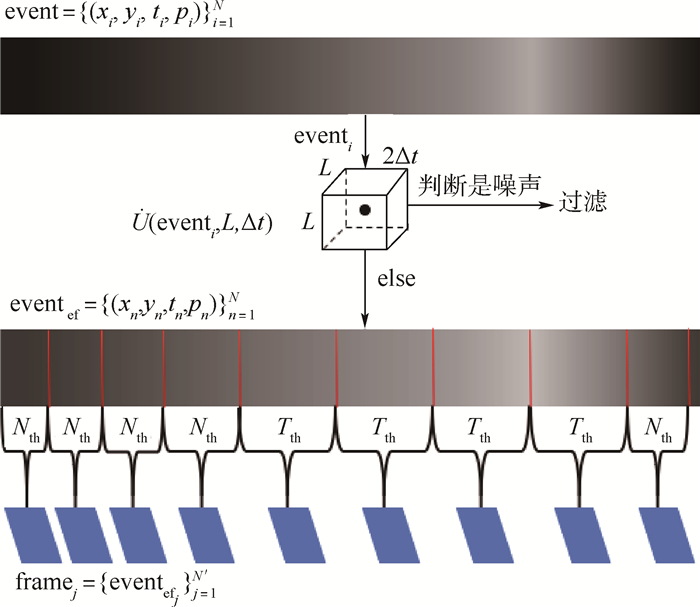
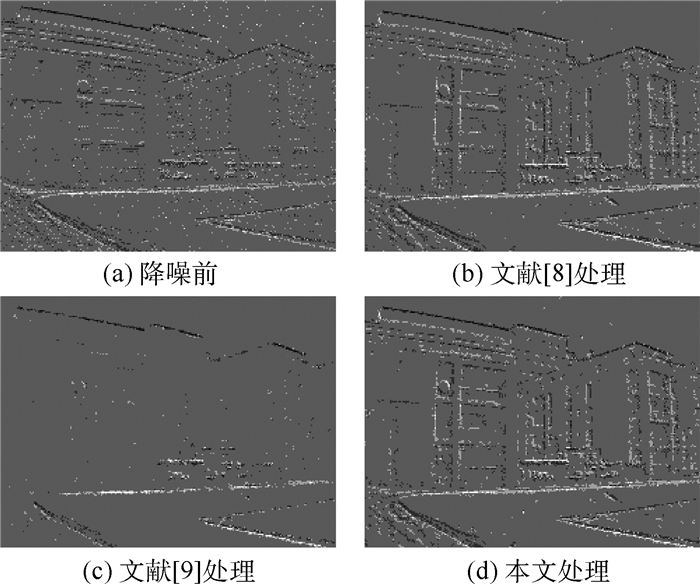
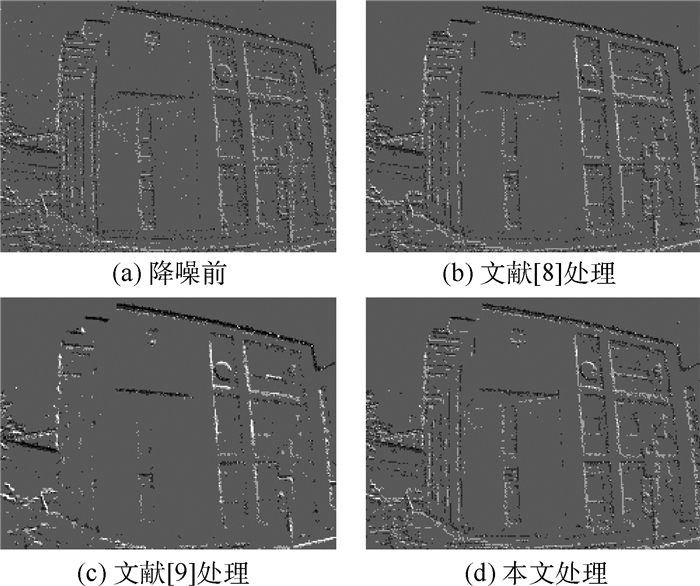
针对事件相机(Event Camera)输出的异步事件流信息不利于人眼观察、难以衔接应用任务且存在大量噪声的问题,介绍一种可视化及降噪算法。结合事件流能够反映场景中物体运动边缘信息的特点,利用物体运动边缘的时间和空间连续性进行降噪处理,进而利用事件数量和时间阈值双限制的方式累积事件得到事件“帧”,达到可视化、便于应用的目的。在真实数据集实验中,降噪算法可以有效处理背景噪声,在运动起始或缓慢时保存更多细节边缘事件信息,提升有效角点检测数量,可视化算法在保证帧率的同时,降低事件数量方差,提高事件“帧”信息的均匀性。实验结果证明了可视化及降噪算法的有效性。
Abstract:To overcome the problem that the asynchronous event stream generated by the event camera is hard to observe, utilize and there is a lot of noise, we introduce an improved visualization and noise reduction algorithm for the event camera. Because the event stream reacts to the object movement, the proposed algorithm gets valid events by filtering the noise with the time and space continuity of moving edge. To easily observe and apply, events are accumulated with a double limitation of the events number and the time threshold. In the real dataset experiment, the noise reduction algorithm can effectively deal with the background activity noise and save the detail edge information when the movement begins or moves slowly, increasing the number of corner detections. The visualization algorithm reduces the variance of events number while ensuring the frame rate, and improves the information uniformity of the "event frame". The experimental results show the effectiveness of the proposed method in terms of noise reduction and visualization.
-
Key words:
- event camera /
- visual navigation /
- noise reduction /
- visualization /
- robustness
-
表 1 噪声处理后事件数量统计(场景1)
Table 1. Counts of the number of events after noise processing (Scene 1)
表 2 噪声处理后事件数量统计(场景2)
Table 2. Counts of the number of events after noise processing (Scene 2)
表 3 事件“帧”帧率及事件方差统计(场景1)
Table 3. Frame rate and variance of events number (Scene 1)
参数 帧率/fps 平均包含事件数 事件数量方差 t=0.005 s 199.61 1 242.46 1 484 647.06 t=0.01 s 99.15 2 493.04 5 904 817.08 重叠t=0.005 s 399.21 1 244.48 1 485 470.66 重叠t=0.01 s 198.95 2 493.03 5 901 746.16 n=5 000 48.92 4 953.70 2 053.29 n=7 500 31.96 7 479.11 396.15 t=0.005 s/n=5 000 198.30 1 250.60 1 488 157.62 t=0.01 s/n=5 000 105.67 2 340.09 3 169 479.88 表 4 事件“帧”帧率及事件方差统计(场景2)
Table 4. Frame rate and variance of events number (Scene 2)
参数 帧率/fps 平均包含事件数 事件数量方差 t=0.005 s 196.38 1 905.05 1 390 079.79 t=0.01 s 96.88 3 810.11 5 418 706.82 重叠t=0.00 s 392.76 1 917.66 1 398 532.31 重叠t=0.01 s 193.76 3 860.91 5 489 364.28 n=5 000 70.69 4 992.55 42.10 n=7 500 47.13 7 239.2 67 523.44 t=0.005 s/n=5 000 196.38 1 905.05 1 389 610.55 t=0.01 s/n=5 000 107.36 3 447.23 2 262 338.62 -
[1] 桑永胜, 李仁昊, 李耀仟, 等. 神经形态视觉传感器及其应用研究[J]. 物联网学报, 2019, 3(4): 63-71.SANG Y S, LI R H, LI Y Q, et al. Research on neuromorphic vision sensor and its applications[J]. Chinese Journal on Internet of Things, 2019, 3(4): 63-71(in Chinese). [2] GALLEGO G, DELBRUCK T, ORCHARD G, et al. Event-based vision: A survey[J]. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2020, 99: 1-1. [3] 王亭亭, 蔡志浩, 王英勋. 无人机室内视觉/惯导组合导航方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(1): 176-186. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0965WANG T T, CAI Z H, WANG Y X. Integrated vision/inertial navigation method of UAVs in indoor environment[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(1): 176-186(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2016.0965 [4] VIDAL A R, REBECQ H, HORSTSCHAEFER T, et al. Ultimate SLAM Combining events, images, and IMU for robust visual SLAM in HDR and high-speed scenarios[J]. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, 2018, 3(2): 994-1001. doi: 10.1109/LRA.2018.2793357 [5] MUEGGLER E, GALLEGO G, REBECQ H, et al. Continuous-time visual-inertial odometry for event cameras[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics, 2018, 34(6): 1425-1440. doi: 10.1109/TRO.2018.2858287 [6] 马艳阳, 叶梓豪, 刘坤华, 等. 基于事件相机的定位与建图算法: 综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2020, 46: 1-11.MA Y Y, YE Z H, LIU K H, et al. Event-based visual localization and mapping algorithms: A survey[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2020, 46: 1-11(in Chinese). [7] XIE X M, DU J, SHI G M, et al.An improved approach for visualizing dynamic vision sensor and its video denoising[C]//Proceedings of the International Conference on Video and Image Processing.New York: ACM, 2017: 176-180. [8] DELBRUCK T.Frame-free dynamic digital vision[C]//Proceedings of International Symposium on Secure-Life Electronics, Advanced Electronics for Quality Life and Society.2008: 21-26. [9] FENG Y, LV H Y, LIU H L, et al. Event density based denoising method for dynamic vision sensor[J]. Applied Sciences, 2020, 10(6): 2024. doi: 10.3390/app10062024 [10] HUANG J, GUO M H, CHEN S S.A dynamic vision sensor with direct logarithmic output and full-frame picture-on-demand[C]//Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems (ISCAS).Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2017: 1-4. [11] MUNDA G, REINBACHER C, POCK T. Real-time intensity-image reconstruction for event cameras using manifold regularization[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2018, 126(12): 1381-1393. doi: 10.1007/s11263-018-1106-2 [12] BARDOW P, DAVISON A J, LEUTENEGGER S.Simultaneous optical flow and intensity estimation from an event camera[C]//Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 2016: 884-892. [13] SCHEERLINCK C, BARNES N, MAHONY R.Continuous-time intensity estimation using event cameras[C]//Lecture Notes in Computer Science.Berlin: Springer, 2018: 308-324. [14] LICHTSTEINER P, POSCH C, DELBRUCK T. A 128×128120 dB 15μs latency asynchronous temporal contrast vision sensor[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2008, 43(2): 556-576. [15] POSCH C, MATOLIN D, WOHLGENANNT R. A QVGA 143 dB dynamic range frame-free PWM image sensor with lossless pixel-level video compression and time-domain CDS[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2010, 46(1): 259-275. [16] BRANDLI C, BERNER R, YANG M, et al. A 240×180130 dB 3μs latency global shutter spatiotemporal vision sensor[J]. IEEE Journal of Solid-State Circuits, 2014, 49(10): 2333-2341. doi: 10.1109/JSSC.2014.2342715 [17] MUEGGLER E, REBECQ H, GALLEGO G, et al. The event-camera dataset and simulator: Event-based data for pose estimation, visual odometry, and SLAM[J]. International Journal of Robotics Research, 2017, 36(2): 142-149. doi: 10.1177/0278364917691115 [18] SHI J B, TOMASI C.Good features to track[C]//Proceedings of IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1994: 593-600. -








 下载:
下载: