-
摘要:
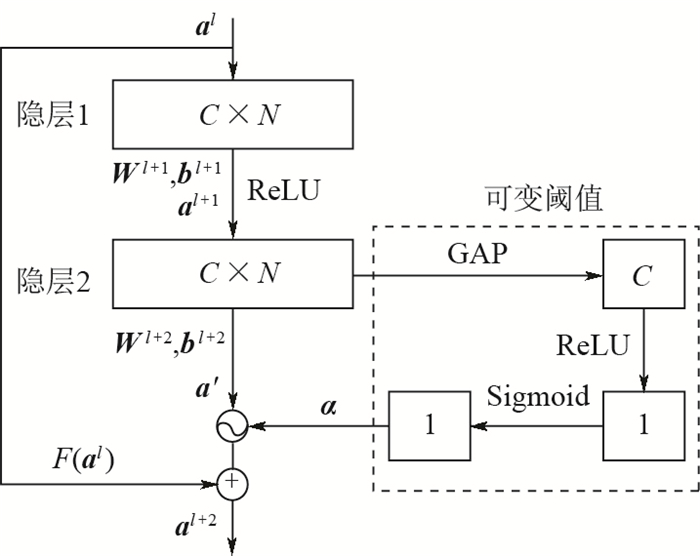
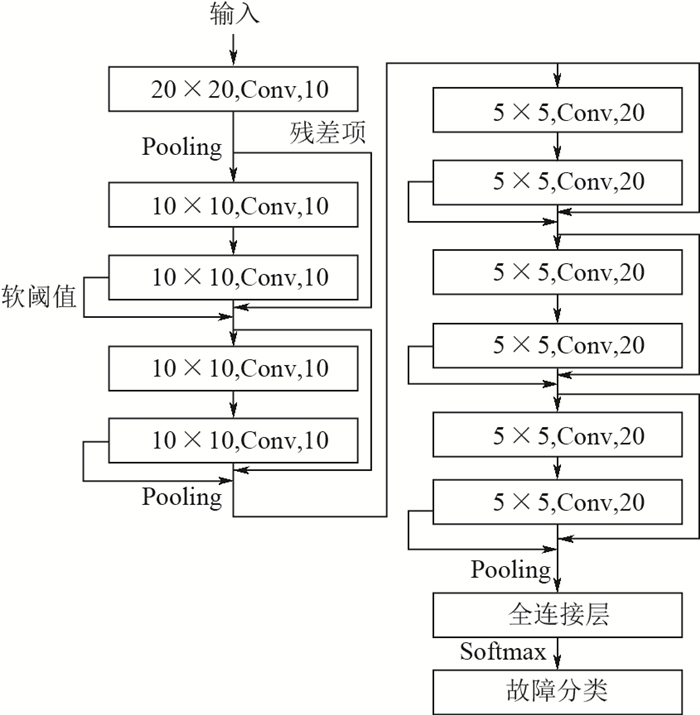
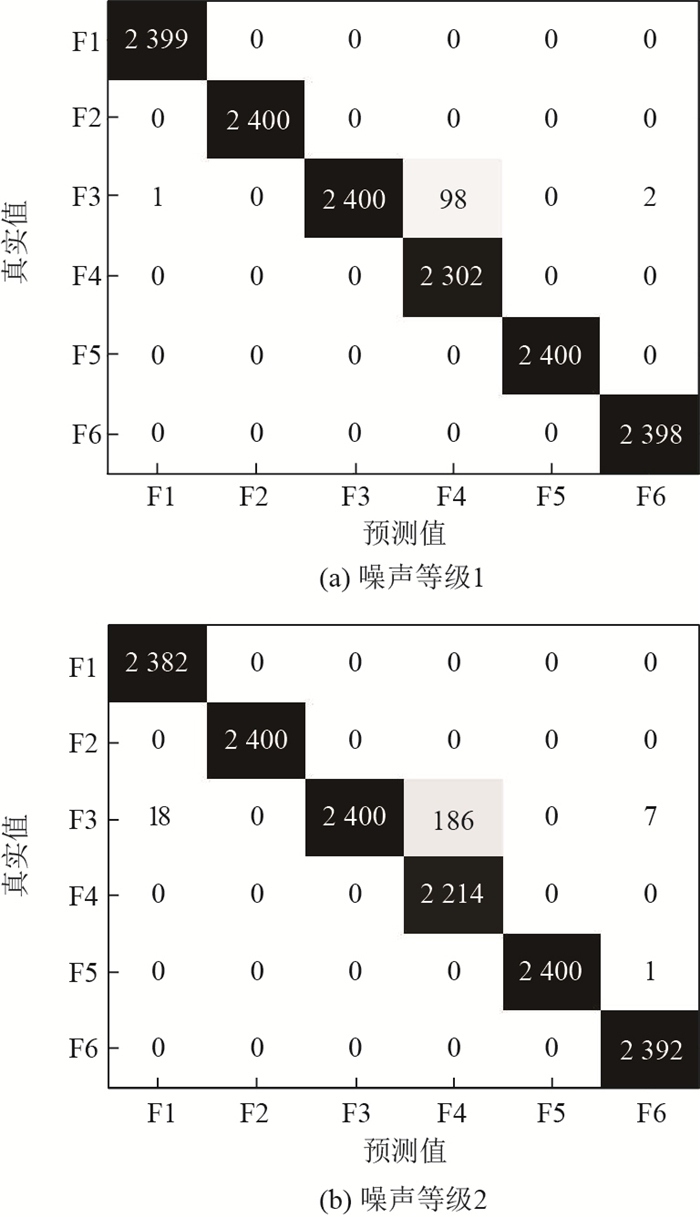
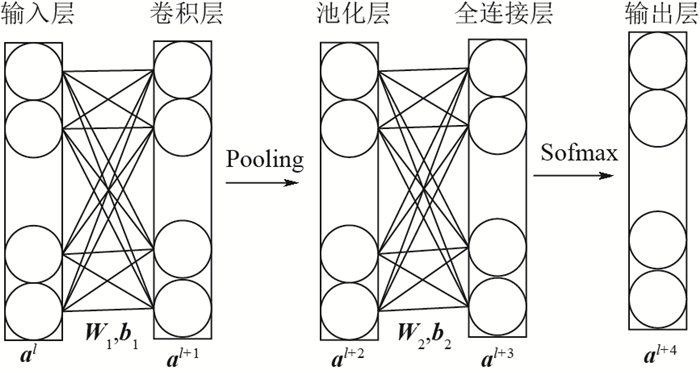
滚动轴承的准确故障诊断是确保机械设备安全可靠运行的必要手段。针对多故障、长时间序列的滚动轴承振动信号,提出了一种基于深度残差收缩网络(DRSN)模型的故障诊断方法。首先,根据采集到的滚动轴承数据构造故障样本,针对多种故障类型下的长时间序列的振动信号,按照一定尺寸将长时间序列矩阵化,构成多故障类型的灰度图故障样本。从正常到故障的滚动轴承性能退化过程,通过多个采样点的随机采样,构造全寿命周期的故障样本用于故障诊断。其次,在多层深度学习模型基础上,将残差收缩网络模块加入到卷积神经网络(CNN)中构建深度残差收缩网络模型用于故障诊断,其中通过将残差项加入到网络中训练解决了多层网络模型的模型退化问题,利用软阈值化实现了样本降噪。最后,为了验证所提方法的有效性,采集了滚动轴承的多故障时间序列样本和全寿命周期故障样本用于故障诊断。实例验证的结果表明:所提深度残差收缩网络模型在处理含噪声样本时仍具有良好的鲁棒性,多层网络模型下没有明显的网络退化,能够保持较高的故障诊断正确率。在处理2种轴承故障数据集时,与其他模型相比,所提方法训练误差更低,平均故障诊断正确率提高1%~6%。
-
关键词:
- 滚动轴承 /
- 故障诊断 /
- 深度残差收缩网络(DRSN) /
- 卷积神经网络(CNN) /
- 软阈值化
Abstract:Accurate fault diagnosis of rolling bearing is a necessary means to ensure the safe and reliable operation of mechanical equipment. In this paper, a fault diagnosis method based on Deep Residual Shrinkage Network (DRSN) is proposed for the vibration signal of rolling bearing with multiple faults and long time series. Firstly, fault samples are constructed according to the collected rolling bearing data. For the vibration signals of long time series under various fault types, the long time series are matrixed according to a certain size, so as to form the gray image fault samples of multiple fault types. Aimed at the performance degradation process of rolling bearings from normal to fault, the whole life cycle fault samples are constructed for fault diagnosis through random sampling of multiple sampling points. Secondly, based on the multi-layer deep learning model, the residual shrinkage network module is added to the Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) to build the deep residual shrinkage network model, in which the model degradation problem of the multi-layer network model is solved by adding the residual term to the network training, and the sample noise reduction is realized by using soft thresholding. Finally, in order to verify the effectiveness of the proposed method, multi-fault time series samples and life cycle fault samples of rolling bearing are collected for fault diagnosis. The result of the example shows that the proposed model has good robustness under the noise interference, there is no obvious network degradation under the multi-layer network model, and it can maintain a high accuracy of fault diagnosis. When dealing with two kinds of bearing fault datasets, compared with other models, this method has lower training error, and the average accuracy of fault classification is increased by 1%-6%.
-
表 1 滚动轴承故障样本集
Table 1. Failure dataset of rolling bearing
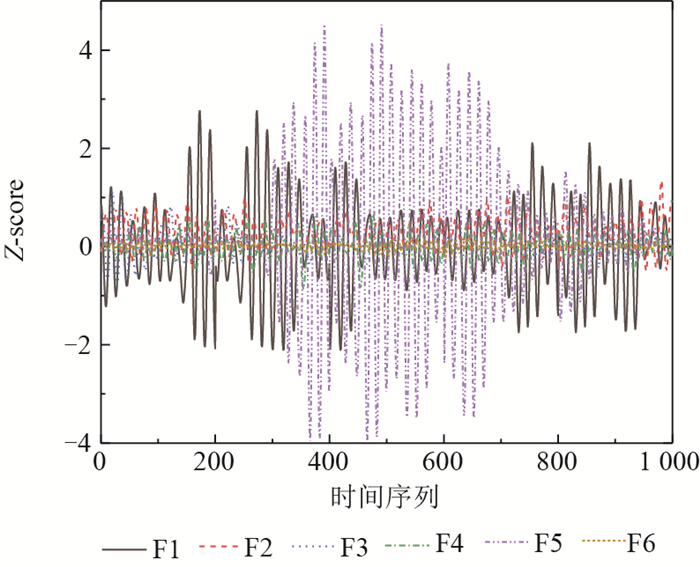
故障代号 故障描述 时间序列数 F1 内圈故障 1×104 F2 滚珠故障 1×104 F3 外圈承压端故障 1×104 F4 外圈侧面故障 1×104 F5 外圈承压端对面故障 1×104 F6 正常状态 1×104 表 2 故障诊断正确率对比
Table 2. Comparison of fault diagnosis accuracy
% 模型 数据集1 数据集2 平均值 原始 N1 N2 原始 N1 N2 DRSN 99.2 98.6 97.1 99.5 99.1 98.7 98.7 DRN 98.2 97.8 96.1 98.8 98.2 97.5 97.8 CNN 97.4 96.2 94.3 98.1 97.7 97.3 96.8 DBN 96.5 94.7 93.8 97.9 96.7 95.8 95.9 SVM 90.8 88.2 85.4 95.6 93.4 91.5 90.8 ANN 91.3 89.4 87.6 96.9 95.1 94.7 92.5 -
[1] LEI Y G, YANG B, JIANG X W, et al. Applications of machine learning to machine fault diagnosis: A review and roadmap[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 138: 106587. [2] 余建波, 吕靖香, 程辉, 等. 基于ITD和改进形态滤波的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(2): 241-249. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0114YU J B, LV J X, CHENG H, et al. Fault diagnosis for rolling bearing based on ITD and improved morphological filter[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(2): 241-249(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0114 [3] 丁显, 徐进, 滕伟, 等. 基于无参数经验小波变换的风电齿轮箱故障特征提取[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(8): 99-105.DING X, XU J, TENG W, et al. Fault feature extraction of a wind turbine gearbox using adaptive parameterless empirical wavelet transform[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(8): 99-105(in Chinese). [4] WANG L M, SHAO Y M. Fault feature extraction of rotating machinery using a reweighted complete ensemble empirical mode decomposition with adaptive noise and demodulation analysis[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2020, 138: 106545. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2019.106545 [5] 李政, 张炜, 明安波, 等. 基于IEWT和MCKD的滚动轴承故障诊断方法[J]. 机械工程学报, 2019, 55(23): 136-146.LI Z, ZHANG W, MING A B, et al. A novel fault diagnosis method based on improved empirical wavelet transform and maximum correlated kurtosis deconvolution for rolling element bearing[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineering, 2019, 55(23): 136-146(in Chinese). [6] 曹惠玲, 高升, 薛鹏. 基于多分类AdaBoost的航空发动机故障诊断[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(9): 1818-1825. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0774CAO H L, GAO S, XUE P. Aeroengine fault diagnosis based on multi-classification AdaBoost[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(9): 1818-1825(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0774 [7] 崔路瑶. 基于机器学习的滚动轴承智能故障诊断方法研究[D]. 南昌: 华东交通大学, 2019: 1-77.CUI L Y. Research on fault diagnosis method of rolling bearing based on machine learning[D]. Nanchang: East China Jiaotong University, 2019: 1-77(in Chinese). [8] 车畅畅, 王华伟, 倪晓梅, 等. 基于深度学习的航空发动机故障融合诊断[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(3): 621-628. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0197CHE C C, WANG H W, NI X M, et al. Fault fusion diagnosis of aero-engine based on deep learning[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(3): 621-628(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0197 [9] 宫文峰, 陈辉, 张泽辉, 等. 基于改进卷积神经网络的滚动轴承智能故障诊断研究[J]. 振动工程学报, 2020, 33(2): 400-413.GONG W F, CHEN H, ZHANG Z H, et al. Intelligent fault diagnosis for rolling bearing based on improved convelutional neural network[J]. Journal of Vibration Engineering, 2020, 33(2): 400-413(in Chinese). [10] 朱丹宸, 张永祥, 潘洋洋, 等. 基于多传感器信号和卷积神经网络的滚动轴承故障诊断[J]. 振动与冲击, 2020, 39(4): 172-178.ZHU D C, ZHANG Y X, PAN Y Y, et al. Fault diagnosis for rolling element bearings based on multi-sensor signals and CNN[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock, 2020, 39(4): 172-178(in Chinese). [11] QIU G Q, GU Y K, CAI Q. A deep convolutional neural networks model for intelligent fault diagnosis of a gearbox under different operational conditions[J]. Measurement, 2019, 145: 94-107. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.05.057 [12] SUN M D, WANG H, LIU P, et al. A sparse stacked denoising autoencoder with optimized transfer learning applied to the fault diagnosis of rolling bearings[J]. Measurement, 2019, 146: 305-314. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.06.029 [13] CHE C C, WANG H W, NI X M, et al. Domain adaptive deep belief network for rolling bearing fault diagnosis[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2020, 143: 106427. [14] ZHANG Y, XING K S, BAI R X, et al. An enhanced convolutional neural network for bearing fault diagnosis based on time-frequency image[J]. Measurement, 2020, 157: 107667. doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2020.107667 [15] LIANG P F, DENG C, WU J, et al. Compound fault diagnosis of gearboxes via multi-label convolutional neural network and wavelet transform[J]. Computers in Industry, 2019, 113: 103132. doi: 10.1016/j.compind.2019.103132 [16] ZHAO M, ZHONG S, FU X, et al. Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis[J]. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, 2020, 16(7): 4681-4690. doi: 10.1109/TII.2019.2943898 [17] QIU W Y, LI D X, JIN X Y, et al. Deep neural network inspired by iterative shrinkage-thresholding algorithm with data consistency (NISTAD) for fast undersampled MRI reconstruction[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2020, 70: 134-144. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2020.04.016 [18] OCAK H, LOPARO K A. HMM-based fault detection and diagnosis scheme for rolling element bearings[J]. Journal of Vibration and Acoustics, 2005, 127: 299-306. doi: 10.1115/1.1924636 [19] SMITH W A, RANDALL R B. Rolling element bearing diagnostics using the Case Western Reserve University data: A benchmark study[J]. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2015, 64-65: 100-131. doi: 10.1016/j.ymssp.2015.04.021 [20] WANG B, LEI Y, LI N, et al. A hybrid prognostics approach for estimating remaining useful life of rolling element bearings[J]. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 2020, 69: 401-412. doi: 10.1109/TR.2018.2882682 -







 下载:
下载: