Weapon-target assignment in UAV cluster based on pheromone heuristic wolf pack algorithm
-
摘要:
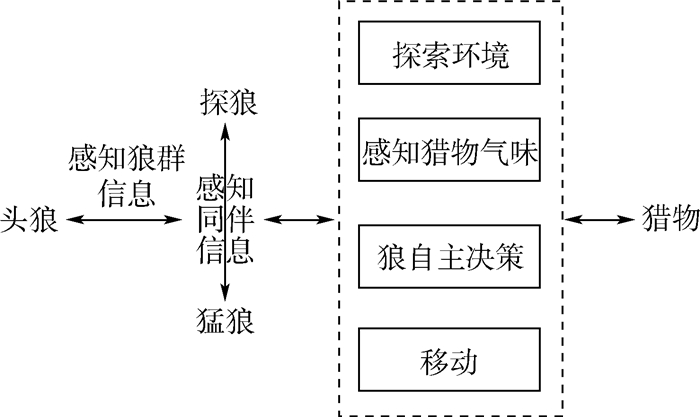
无人机(UAV)集群作战是未来智能化战争的重要作战样式。为充分发挥UAV集群整体作战优势,得到最优武器-目标分配(WTA)方案,使得UAV集群在火力分配中既能够满足任务要求,又能够较少作战单元消耗,建立了包含任务完成、有效杀伤、攻击消耗约束的UAV集群火力分配数学模型,采用带有游走、召唤算子的改进狼群算法(WPA)对模型进行求解。为提高算法全局寻优效率,避免陷入局部最优,引入蚁群优化(ACO)算法中信息素启发规则,对游走行为及狼群更新机制进一步改进,提出了基于信息素启发狼群算法(PHWPA)的UAV集群进攻的火力分配方法。仿真结果表明:所提方法是有效的,相比较于其他算法,PHWPA具有更高效的寻优能力,能够为UAV集群作战火力规划提供支持。
-
关键词:
- 无人机(UAV) /
- 武器-目标分配(WTA) /
- 狼群算法(WPA) /
- 蚁群优化(ACO)算法 /
- 信息素启发规则
Abstract:Unmanned Aerial Vehicle (UAV) cluster operation is an important mode of intelligent warfare in the future. In order to give full play of the overall operational advantages of UAV cluster, a mathematical model is constructed to solve the Weapon-Target Assignment (WTA) problem in UAV cluster attacks and obtain the optimal scheme. The constraints of mission completion, effective killing and attack consumption are established in the model, which can meet the requirements of the mission, and also save the consumption of UAV combat units to maintain the power of UAV cluster. The improved Wolf Pack Algorithm (WPA) with scouting and summoning operators is used to solve the model. To obtain the higher global optimization efficiency and avoid trapping in local optimum, the weapon-target assignment in UAV cluster attack based on Pheromone Heuristic Wolf Pack Algorithm (PHWPA) is proposed to improve WPA's scouting behavior and renewable mechanism by using pheromone heuristic rules from Ant Colony Optimization (ACO). The simulation results show that the proposed method is effective. Compared with several algorithms, PHWPA has more efficient search ability. The proposed method can provide support for firepower planning of UAV cluster.
-
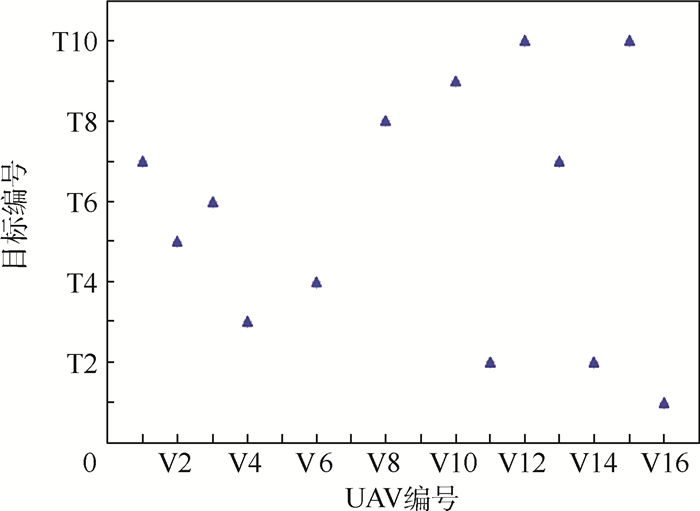
表 1 无人机编号与目标编号
Table 1. UAV number and target number
UAV型号 UAV编号 目标编号 Ⅰ型 V1~V4 T1~T10 Ⅱ型 V5~V8 T1~T10 Ⅲ型 V9~V12 T1~T10 Ⅳ型 V13~V16 T1~T10 表 2 最优攻击分配方案
Table 2. Optimal UAV-target assignment
UAV型号 UAV编号 对应分配目标编号 Ⅰ型 V1 V2 V3 V4 T8 T5 T6 T3 Ⅱ型 V5 V6 V7 V8 - T4 - T8 Ⅲ型 V9 V10 V11 V12 - T9 T2 T10 Ⅳ型 V13 V14 V15 V16 T7 T2 T10 T1 表 3 各目标杀伤概率
Table 3. Kill probability of each target
目标编号 杀伤概率 T1 0.9 T2 0.985 T3 0.91 T4 0.91 T5 0.9 T6 0.9 T7 0.979 T8 0.91 T9 0.92 T10 0.979 -
[1] 罗德林, 徐阳, 张金鹏. 无人机集群对抗技术新进展[J]. 科技导报, 2017, 35(7): 26-31.LUO D L, XU Y, ZHANG J P. New progresses on UAV swarm confrontation[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2017, 35(7): 26-31(in Chinese). [2] 牛轶峰, 肖湘江, 柯冠岩. 无人机集群作战概念及关键技术分析[J]. 国防科技, 2013, 34(5): 37-43.NIU Y F, XIAO X J, KE G Y. Operation concept and key techniques of unmanned aerial vehicle swarms[J]. National Defense Science & Technology, 2013, 34(5): 37-43(in Chinese). [3] 段海滨, 申燕凯, 王寅, 等. 2018年无人机领域热点评述[J]. 科技导报, 2019, 37(3): 82-90.DUAN H B, SHEN Y K, WANG Y, et al. Review of technological hot spots of unmanned aerial vehicle in 2018[J]. Science & Technology Review, 2019, 37(3): 82-90(in Chinese). [4] LLOYD S P, WITSENHAUSEN H S.Weapon allocations is NP-complete[C]//IEEE Summer Conference on Simulation.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1986: 88-95. [5] 张永利, 计文平, 宋本钦. 舰空导弹对空中目标打击辅助决策研究[J]. 指挥控制与仿真, 2019, 41(3): 19-23.ZHANG Y L, JI W P, SONG B Q. Research on auxiliary decision of surface-to-air missiles strike to air targets[J]. Command Control & Simulation, 2019, 41(3): 19-23(in Chinese). [6] 董朝阳, 路遥, 王青. 改进的遗传算法求解火力分配优化问题[J]. 兵工学报, 2016, 37(1): 97-102.DONG C Y, LU Y, WANG Q. Improved genetic algorithm for solving firepower distribution[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2016, 37(1): 97-102(in Chinese). [7] 吴凯, 徐利, 孙海涛. 防空作战火力资源优化分配研究[J]. 空天防御, 2019, 2(2): 5-8.WU K, XU L, SUN H T. Research on optimal assignment of fire resources in air-defense operations[J]. Air & Space Defense, 2019, 2(2): 5-8(in Chinese). [8] 罗德林, 段海滨, 吴顺详, 等. 基于启发式蚁群算法的协同多目标攻击空战决策研究[J]. 航空学报, 2006, 27(6): 1166-1170.LUO D L, DUAN H B, WU S X, et al. Research on air combat decision-making for cooperative multiple target attack using heuristic ant colony algorithm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2006, 27(6): 1166-1170(in Chinese). [9] 段海滨, 丁全心, 常俊杰, 等. 基于并行蚁群优化的多UCAV任务分配仿真平台[J]. 航空学报, 2008, 29(S): S192-S197.DUAN H B, DING Q X, CHANG J J, et al. Multi-UCAVs task assignment simulation platform based on parallel ant colony optimization[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2008, 29(S): S192-S197(in Chinese). [10] 魏政磊, 赵辉, 黄汉桥, 等. 基于SAGWO算法的UCAVs动态协同任务分配[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(8): 1651-1664. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0589WEI Z L, ZHAO H, HUANG H Q, et al. Dynamic UCAVs cooperative task allocation based on SAGWO algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(8): 1651-1664(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0589 [11] 李俨, 董玉娜. 基于SA-DPSO混合优化算法的协同空战火力分配[J]. 航空学报, 2010, 31(3): 626-631.LI Y, DONG Y N. Weapon-target assignment based on simulated annealing and discrete particle swarm optimization in cooperative air combat[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2010, 31(3): 626-631(in Chinese). [12] 顾佼佼, 赵建军, 颜骥, 等. 基于MODPSO-GSA的协同空战武器目标分配[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2015, 41(2): 252-258. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2014.0119GU J J, ZHAO J J, YAN J, et al. Cooperative weapon-target assignment based on multi-objective discrete particle swarm optimization-gravational search algorithm in air combat[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2015, 41(2): 252-258(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2014.0119 [13] 李天龙, 张军超. 基于融合算法的空-地多目标攻击火力分配[J]. 电光与控制, 2019, 26(11): 56-59.LI T L, ZHANG J C. Air-to-ground multi-target attack firepower assignment based on fusion algorithm[J]. Electronics Optics & Control, 2019, 26(11): 56-59(in Chinese). [14] 邱少明, 胡宏章, 杜秀丽, 等. 基于DDE改进蝙蝠算法的动态火力分配方法[J]. 现代防御技术, 2019, 47(6): 61-67.QIU S M, HU H Z, DU X L, et al. Dynamic fire distribution method using improved bat algorithm based on DDE[J]. Modern Defence Technology, 2019, 47(6): 61-67(in Chinese). [15] 吴虎胜, 张凤鸣, 吴庐山. 一种新的群体智能算法——狼群算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2013, 35(11): 2430-2438.WU H S, ZHANG F M, WU L S. New swarm intelligence algorithm-Wolf pack algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(11): 2430-2438(in Chinese). [16] 吴虎胜, 张凤鸣, 战仁军, 等. 求解0-1背包问题的二进制狼群算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2014, 36(8): 1660-1667.WU H S, ZHANG F M, ZHAN R J, et al. A binary wolf pack algorithm for solving 0-1 knapsack problem[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(8): 1660-1667(in Chinese). [17] 吴虎胜, 张凤鸣, 战仁军, 等. 利用改进的二进制狼群算法求解多维背包问题[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2015, 37(5): 1084-1091.WU H S, ZHANG F M, ZHAN R J, et al. Improved binary wolf pack algorithm for solving multidimentional knapsack problem[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(5): 1084-1091(in Chinese). [18] 刘永兰, 李为民, 吴虎胜, 等. 基于狼群算法的无人机航迹规划[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2015, 27(8): 1838-1843.LIU Y L, LI W M, WU H S, et al. Track planning for unmanned aerial vehicles based on wolf pack algorithm[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2015, 27(8): 1838-1843(in Chinese). [19] 惠晓滨, 郭庆, 吴娉娉, 等. 一种改进的狼群算法[J]. 控制与决策, 2017, 32(7): 1164-1172.HUI X B, GUO Q, WU P P, et al. An improved wolf pack algorithm[J]. Control and Decision, 2017, 32(7): 1164-1172(in Chinese). [20] 钱荣鑫. 一种基于文化机制的狼群算法[J]. 信息技术, 2015, 39(12): 98-102.QIAN R X. A wolf pack algorithm based on cultural mechanism[J]. Information Technology, 2015, 39(12): 98-102(in Chinese). [21] DORIGO M, MANIEZZO V, COLORNI A. The ant system optimization by a colony of cooperating agents[J]. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics-Part B, 1996, 26(1): 1-13. [22] 段海滨. 蚁群算法原理及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2005: 24-29.DUAN H B. Principle and application of ant colony algorithm[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2005: 24-29(in Chinese). -







 下载:
下载: