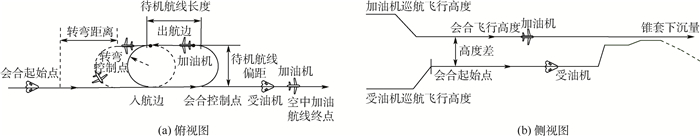
-
摘要:
软式自主空中加油(AAR)技术因其对加油设备的改装需求少且可应用于多种加油场景而受到广泛研究,但对于从起飞到加油结束脱离这一整套飞行控制流程的研究较少。针对软式AAR技术中的会合、编队、对接、加油、脱离5个阶段的控制策略进行研究。首先,分别设计了所对应的飞行指令回路控制律及导引律,通过对国内外空中加油试飞经验和试飞流程的研究,建立了“有人-无人”、“无人-无人”2种不同模式下软式AAR各阶段的控制机制,并分析了2个控制策略的差别。其次,以K8飞机和某飞机为加受油平台,建立完善的多模态控制策略,采用传统的PID控制方法,并通过极点配置法得到各模态的反馈增益和前向增益,使加受油机在多模态综合控制下达到期望的速度、角度等。同时,基于试飞经验数据设计软式AAR各阶段的全过程控制律。最后,对所设计控制律进行仿真验证,结果表明:所设计的控制策略合理可行,控制方法具有较强的抗干扰能力和较高的跟踪精度。
-
关键词:
- 自主空中加油(AAR) /
- 试飞经验 /
- 加油策略 /
- PID控制 /
- 多模态控制
Abstract:The probe-and-drogue Aerial Autonomous Refueling (AAR) technology has been widely studied because it requires little modification of refueling equipment and can be applied to a variety of refueling processes. However, there are few researches on the whole flight control process from take-off to disengagement. In this paper, the corresponding flight command loop control law and guidance law are designed respectively to study the control strategy of rendezvous, formation, docking, refueling and disengagement stages during the probe-and-drogue AAR. Based on the study of domestic and foreign experience and flight procedure of aerial refueling test, the control mechanism of each stage of AAR under two different modes of "manned-unmanned" and "unmanned-unmanned" is established, and the difference between two control strategies is analyzed. Taking K8 aircraft and one aircraft as the tanker and receiver, a complete multi-mode control strategy is established. The traditional PID control method is adopted in the command loop, and the feedback gain and forward gain of each mode are obtained by pole assignment method, so that the aircraft can reach the desired speed and angle under the multi-mode integrated control system. Meanwhile, the whole process control laws for each stage of aerial refueling are designed based on the test flight experience data. Finally, the simulations of the designed control law show that the designed control strategy is reasonable and feasible, and the control method has strong anti-interference ability and high tracking accuracy.
-
表 1 国外无人机自主空中加受油试飞内容和程序
Table 1. Content and procedure of test flight of foreign UAV with aerial autonomous refueling
序号 项目 试飞对象 试飞内容或程序 1 美国国防高级研究计划局AARD研究 B707/F-18B 尾随位置(100ft)试飞、准备对接位置(20ft)试飞,GPS和近距视频引导试飞 2 美国空军研究试验室硬式自主加油试验 KC-135/Learjet 7个空中加油位置试飞:接触,预备接触,到达左翼内侧和右翼内侧观察位置,到达左翼内侧和右翼外侧观察位,解散编队。 3 美国空军AAR试验 KC-135/VISTA 多余度自主编队飞控系统试飞;模拟典型无人机试飞 4 美国海军Learjet变稳飞机演示验证试飞 B707/Learjet “硬式”和“软管”自主加受油演示验证试飞,观察、对接和重新编队位置试飞 5 美国海军KQ-X无人机空中加油能力 “海神”(全球鹰)/全球鹰 13716m高空接近到12 m以内,加油和脱离编队试飞 6 美国海军X-47B自主加受油试飞 KC-707/X-47B X-47B先从1mile的距离外尾随KC-707加油机,开启光学传感器和视频摄像机;接近到距离加油机20ft的过程中进行接近监控 注:1 ft=0.304 8 m,1 mile=1.6 km。 表 2 飞行员目视观测的有人机空中加油故障及应急处置措施
Table 2. Manned vehicle aerial refueling fault by pilot visual observation and contingency measures
序号 故障现象 应急处置措施 1 对接过快, 软管过度弯曲或鞭打 适当减小对接速度,情况严重的退出本次对接 2 空中加油伞套在对接过程中被受油插头戳破 受油机及时脱离,退回至安全距离。如果发现锥套摆动不厉害,则可以继续对接 3 空中加油锥套碰撞受油机,致使受油机机体损伤 如果影响受油机使用,则中止对接,加/受油机返场;如果不影响,则继续对接 4 对接过程中,受油插头折断 受油插头折断,受油机立即与加油机脱离,退出编队至安全位置 5 加油过程中,燃油从加油锥套结合处泄漏 加油机中止加油,受油机脱离并退回至安全区域。加/受油机返场 表 3 主要符号及含义
Table 3. Main symbols and instructions
符号 含义 δt 油门开度量 δa 副翼偏转角 δr 方向舵偏转角 δe 升降舵偏转角 Y 侧向距离 H 飞机高度 θ 俯仰角 ϕ 滚转角 ψ 偏航角 K 比例系数 I 积分系数 -
[1] 钟徳星, 李永强, 李严桵. 无人机自主空中加油技术现状及发展趋势[J]. 航空科学技术, 2014, 25(5): 1-6. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKKX201405002.htmZHONG D X, LI Y Q, LI Y R. State-of-art and tendency of autonomous aerial refueling technologies for unmanned aerial vehicles[J]. Aeronautical Science & Technology, 2014, 25(5): 1-6(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKKX201405002.htm [2] 彭程. 空中加油软管收放过程中动态特性研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2018: 3-8.PENG C.Research on dynamic characteristics of aerial refueling hose in deployment and retrieval process[D].Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018: 3-8(in Chinese). [3] BENNINGTON M A, VISSER K D. Aerial refueling implications for commercial aviation[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2005, 42(2): 366-375. doi: 10.2514/1.4770 [4] 陆宇平, 杨朝星, 刘洋洋. 空中加油系统的建模与控制技术综述[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(9): 2375-2389. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201409001.htmLU Y P, YANG C X, LIU Y Y. A survey modeling and control technologies for aerial refueling system[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(9): 2375-2389(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201409001.htm [5] 全权, 魏子博, 高俊, 等. 软管式自主空中加油对接阶段中的建模与控制综述[J]. 航空学报, 2014, 35(9): 2390-2410. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201409002.htmQUAN Q, WEI Z B, GAO J, et al. A survey on modeling and control problems for probe and drogue autonomous aerial refueling at docking stage[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2014, 35(9): 2390-2410(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-HKXB201409002.htm [6] 董新民, 徐跃鉴, 陈博. 自动空中加油技术研究进展与关键问题[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2008, 9(6): 1-5. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJGC200806002.htmDONG X M, XU Y J, CHEN B. Progress and challenges in automatic aerial refueling[J]. Journal of Air Force Engneering University(Natural Science Edition), 2008, 9(6): 1-5(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KJGC200806002.htm [7] 徐坚, 张晓非. 软式空中加油头波效应建模与仿真[J]. 飞行力学, 2019, 37(5): 40-44. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLX201905008.htmXU J, ZHANG X F. Dynamic modeling and simulation of bow wave effect inhose-drogue aerial refueling system[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2019, 37(5): 40-44(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLX201905008.htm [8] 赵曜, 李璞, 刘娟, 等. 带碰撞角约束的三维有限时间滑模制导律[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2018, 44(2): 273-279. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0087ZHAO Y, LI P, LIU J, et al. Fintte-time sliding mode control based 3D guidance law with impact angle constraints[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018, 44(2): 273-279(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2017.0087 [9] 赵国荣, 李晓宝, 刘帅, 等. 自适应非奇异快速终端滑模固定时间收敛制导律[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(6): 1059-1070. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0621ZHAO G R, LI X B, LIU S, et al. Adaptive nonsingular fast terminal sliding mode guidance law with fixed-time convergence[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(6): 1059-1070(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0621 [10] 刘畅, 杨锁昌, 汪连栋, 等. 基于快速自适应超螺旋算法的制导律[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2019, 45(7): 1388-1397. doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0654LIU C, YANG S C, WANG L D, et al. Guidance law based on fast adaptive super-twisting algorithm[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019, 45(7): 1388-1397(in Chinese). doi: 10.13700/j.bh.1001-5965.2018.0654 [11] VAN'T R R, THOMAS F R.KC-10A refueling boom control system[C]//IEEE Proceedings of the National Aerospace and Electronics Conference.Piscataway: IEEE Press, 1980: 354-361. [12] 刘曌, 周春华, 袁锁中. 软管式自主空中加油飞行控制系统与仿真研究[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2012, 24(10): 20-25. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ201210005.htmLIU Z, ZHOU C H, YUAN S Z. Design and simulation of probe and drogue AAR flight control system[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2012, 24(10): 20-25(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ201210005.htm [13] 王宏伦, 杜熠, 盖文东. 无人机自动空中加油精确对接控制[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2011, 37(7): 822-826. https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2011/V37/I7/822WANG H L, DU Y, GAI W D. Precise docking control in unmanned aircraft vehicle automated aerial refueling[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2011, 37(7): 822-826(in Chinese). https://bhxb.buaa.edu.cn/CN/Y2011/V37/I7/822 [14] 袁锁中, 王新华, 郑峰婴. 空中加油自主会合的制导与控制[J]. 飞行力学, 2014, 32(1): 20-24. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLX201401006.htmYUAN S Z, WANG X H, ZHENG F Y. Guidance and control of autonomous aerial refueling rendezvous[J]. Flight Dynamics, 2014, 32(1): 20-24(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-FHLX201401006.htm [15] 李大伟, 王宏伦. 无人机自动空中加油飞行控制技术[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2010, 22(S1): 126-130. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ2010S1032.htmLI D W, WANG H L. UAV flight control in automa[J]. Flight Control Technology of Automatic aerial Refueling, 2010, 22(S1): 126-130(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-XTFZ2010S1032.htm [16] 王海涛, 董新民. 空中加油动力学与控制[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2016: 56-60.WANG H T, DONG X M. Dynamics and control of aerial refueling[M]. Beijing: National Defence Industry Press, 2016: 56-60(in Chinese). [17] 刘曌, 袁锁中, 周春华. 软管式自主空中加油受油机控制系统研究[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2011, 11(8): 1756-1760. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201108024.htmLIU Z, YUAN S Z, ZHOU C H. Flight control of receiver aircraft in probe and drogue aerial refeuling[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 2011, 11(8): 1756-1760(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-KXJS201108024.htm [18] CAMPA G, NAPOLITANO M R, FRAVOLINI M L. Simulation environment for machine vision based aerial refueling for UAVs[J]. IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45(1): 138-151. doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.4805269 [19] SMITH A L, KUNZ D L. Dynamic coupling of the KC-135 tanker and boom for modeling and simulation[J]. Journal of Aircraft, 2007, 44(3): 1034-1039. doi: 10.2514/1.27241 [20] 周清, 许悦雷, 加尔肯别克. 无人机软管式自主空中加油视觉导航技术[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2020, 7(1): 41-46. https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWSS202001008.htmZHOU Q, XU Y L, JIA E K B K. Visual navigation technology for UAV autonomous hose-drogue aerial refueling[J]. Navigation Positioning & Timing, 2020, 7(1): 41-46(in Chinese). https://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-DWSS202001008.htm -







 下载:
下载: